Talk:Maxwell's equations/Archive 5
| This is an archive of past discussions about Maxwell's equations. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. |
| Archive 1 | ← | Archive 3 | Archive 4 | Archive 5 | Archive 6 |
Delete monopoles section and move the statements + links + refs to the lead?
This article should concentrate on the non-monopole equations. The same section is in the monopoles article, everything is covered there. There would be no loss of continuity if:
these statements were moved to the end of the lead (or after introducing them first time in diff/int form)
|
|---|
|
"Maxwell's equations posit electric charge, but not magnetic charge, which has never been observed[1] and may not exist. Nevertheless, Maxwell's equations can be generalized to include non-zero magnetic charges densities and currents, which become fully symmetric under interchange of electric and magnetic fields;[2][3] see magnetic monopoles for detail. If every particle has the same ratio of electric to magnetic charge, then an E and B field can be defined that obeys the normal Maxwell equations (having only electric charges and currents - not magnetic).[4]" |
keeping the refs and linking to the main article. It doesn't add anything to just state the monopole equations as a "preview table" then link to the article where the same table is found. Also it cuts back on extra details which are elsewhere. Opposition? Maschen (talk) 22:55, 22 September 2012 (UTC)
- I support the principle of trimming excess "preview" detail and cross-article duplication, and that this article should not directly address this topic. I don't really agree with it going into the lead; it is too tangential to be introduced there. Thus, some section (akin to the "Generalizations" section of many articles) is probably still appropriate. As such, trimming the section to what is in the box here makes sense to me. — Quondum 06:32, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- What about the end of section conceptual description, since after describing the equations in words, we extend to their modifications to monopoles? I thought to just do it so we can actually see, feel free to revert or move the paragraph somewhere else. Maschen (talk) 07:29, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- That works very nicely, IMO. — Quondum 07:38, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- I like it too. I just edited it a bit, hope that's OK. One thing was, I deleted about duality transformations. Not wrong, but I think it was too brief to be understandable. People are accustomed (for good reason) to believing that electrons have electric charge and the earth has a magnetic field, not the other way around. If I said "I believe that the electrons have both electric and magnetic charge", you could correctly respond to me, "No, you're wrong!". Therefore when you propose that people are free to redefine what is electric and what is magnetic, it could cause confusion ... anyway I think it's too subtle for one sentence. (In the magnetic monopole article OTOH a discussion of duality transformations is sorely missed!) --Steve (talk) 13:07, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- The statement about an arbitrary linear transformation provided, to me, a major epiphany. Perhaps it should be included in Magnetic monopole. It was saying that it was not simply a duality, but rather a U(1) symmetry, broken only by a constraint on the charge type. (I'm not disagreeing with the deletion.) — Quondum 13:25, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- Yes, "duality transformation" is the technical term for the continuous U(1) symmetry that you're referring to. I think you are assuming that the word "duality" can only refer to discrete things, but that's not the case here. (Sorry in advance if I'm not remembering this correctly ... it's discussed in Jackson's textbook, the section was cited by Maschen. But I don't have the book on hand right now.) Yes, this should be discussed in the magnetic monopole article. --Steve (talk) 18:23, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- ...I didn't add any reference to the shortened paragraph, someone else did, and do not have Jackson's book, all refs are intended to be preserved. The sentence before Jackson's citation was:
- "Further, if every particle has the same ratio of electric to magnetic charge, then an E and a B field can be defined that obeys the normal Maxwell's equation (having no magnetic charges or currents) with its own charge and current densities<ref>This is known as a duality transformation. See {{cite book|author=J.D. Jackson|title=Classical Electrodynamics|edition=3rd|chapter=6.12|isbn=0-471-43132-X}}.</ref>"
- and I only trimmed that slightly... anyway thanks for your edits. Maschen (talk) 19:02, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- ...I didn't add any reference to the shortened paragraph, someone else did, and do not have Jackson's book, all refs are intended to be preserved. The sentence before Jackson's citation was:
- Oh, I didn't realize that it was already there. I guess I haven't read that section in a while. :-) --Steve (talk) 20:00, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- Okay, I've learned something now. You were right, I had "duality" pegged as a discrete exchange of some sort. — Quondum 20:59, 23 September 2012 (UTC)
- Update: I added it as a new section in Magnetic monopole. --Steve (talk) 19:36, 24 September 2012 (UTC)
Magnetic fields do not induce Electric fields
This is a widespread errorneous interpretation of the Maxwells equations, the EM field is one object, the faraday tensor, its components are frame dependant. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 123.118.116.112 (talk) 12:50, 18 October 2012 (UTC)
- Which part of the article are you unhappy about? I guess it's the part that says, "Faraday's law describes how a time varying magnetic field creates ("induces") an electric field." ... is that correct? --Steve (talk) 20:31, 18 October 2012 (UTC)
Faraday did not discover electromagnetic induction. http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x29j.htm . He discovered Crosstalk http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x0305.htm . Ivor Catt, 1 March 2014 — Preceding unsigned comment added by 86.164.171.64 (talk) 21:50, 1 March 2014 (UTC)
intro paragraph on space and time
This paragraph was just added to the intro by User:RogierBrussee
Underlying the Maxwell equations is the concept of space and time. The "classical" Maxwell equations can be considered as a special form of more symmetric equations defined on four dimensional space-time adapted to a split in space and time. These four dimensional equations are also called Maxwell equations. They are widely used in high energy and gravitational physics because they are manifestly invariant under Lorentz and even, when properly formulated, general coordinate transformations. In this formulation, the Maxwell equations restrict the Faraday tensor that combines the electric and magnetic field and relate it with the four-current that combines charge and current. The four dimensional invariance properties and four dimensional space-time formulation of the Maxwell equations were very important for the development of special and general relativity.
The "more symmetric equations defined on four dimensional space-time" is, I presume, and . Right? It seems to me that these are exactly equivalent to "the "classical" Maxwell's equations" ... they are not a generalization, just a restatement using different variables and notation. Do you agree, RogierBrussee?
Moreover, the covariant formulation of the equations were not particularly important in the development of special relativity. The original formulation of the equations were the important ones for the historical development. How do I know? Because the covariant ones could not have possibly been written down until special relativity was already pretty well understood!!
Overall, I don't see how anything in this paragraph improves on the previous version ("It is often useful to write Maxwell's equations in other forms; these representations are still formally termed "Maxwell's equations". A relativistic formulation in terms of covariant field tensors is used in special relativity, while in quantum mechanics, a version based on the electric and magnetic potentials is preferred."). Except the mention that Maxwell's equations were important for the development of special relativity ... That is worth saying, but only requires one sentence. Other than that, it seems to me to add too much length and jargon and detail to the intro. I propose to restore the previous version --Steve (talk) 13:49, 20 October 2012 (UTC)
- Agreed. SR (1905) came before the Faraday tensor (~1908) didn't it? [1] Anyway the intro needs to only say there are other convenient forms without any detail. This added paragraph may be good for Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field or suchlike, not so much here. Maschen (talk) 15:18, 20 October 2012 (UTC)
- Indeed I mean the equations and . I personally prefer the differential form formuation over the index notation but my personal taste is irrelevant. The heart of the matter is that the 4 dimensional equations are simpler, express the physical content of the theory more concisely, and do not incorporate a choice (the split in space and time) thereby revealing their 4 dimensional symmetry. From a conceptual point of view, the conventional 3D Maxwell equations have the same status as an expression in spherical coordinates, that is a convenient form to use when the physics has special symmetry. Thus, the 3d Maxwell equations are better though of a reformulation of the 4d equations rather than vice versa, in exactly the same sense that an equation in spherical coordinates is a reformulation of a vector equation rather than vice versa. This was the point I made. Of course, being earth bound creatures, rather than zipping through the universe at relativisic speeds, are used to treating space time differently and use plenty of non relativistic physics, but that is just our own restriction. For the same reason, historically, Maxwell historically obviously wrote down the 3d equations first. However, wherever relativistic formulations of the physics are used (high energy physics, quantum field theory, graviational physics) physicsts routinely call the 4D equations the Maxwell equations. RogierBrussee (talk) 09:24, 26 October 2012 (UTC)
- Of course I agree that people doing relativistic physics are probably well-advised to use the formulation of Maxwell's equations that is written in an obviously-4D-symmetric way. And people doing non-relativistic quantum mechanics are probably well-advised to use the formulation written in terms of A and φ in the Coulomb gauge. And electrical engineers are probably well-advised to use the version with E, B, D, H as taught to undergrads.
- I don't think you've justified your belief that the 4D formulation is so important that it warrants a large paragraph of discussion, as the third paragraph of the article. The intro, by the way, spends just two words mentioning the relation of Maxwell's equations to optics, two words about circuit theory, zero mention of "radios", "electromagnetic waves", "gauge invariance", Gauss or Hertz or Heaviside, "CGS units", etc. So I think it is far out of proportion to devote this large paragraph to the fact that Maxwell's equations can be formulated in an obviously-4D-symmetric way. (Since we live in a Lorentz-invariant universe, every correct law of physics can be formulated in an obviously-4D-symmetric way, including Newton's laws, conservation of energy, etc. So I don't think this fact is quite so remarkable!)
- I think the relativistic formulation warrants one and only one sentence in the introduction. That was the status quo before your edit. I am unlikely to object if you edit that one sentence to your liking, as long as you don't significantly increase the length. More details are already in the body of the article and a lot more detail is in dedicated articles like Covariant formulation of classical electromagnetism. :-) --Steve (talk) 14:21, 26 October 2012 (UTC)
Look I really don't want to start an edit war, but you miss the point: the question is not why the 4D equations of a 4D Lorentz invariant phenomenon like EM warrant mention in the introduction but why the 3D equations do (and of course they do for historic and practical reasons). And no, you cannot formulate Newtons law in any sort of reasonable Lorentz invariant way because it implies action at a distance. And yes, electromagnetic waves should be mentioned in the introduction. And come to mention it, why does the intro even mention things like quantum entanglement, which is an important subject but clearly outside the scope of the Maxwell equations. So I guess the main reason I care is that I think it is a bad idea that after pages and pages of differences between CGS and SI units and microscopic and macroscopic formulations, integral and PDE formulations the main body of the article relegates the fundamental 4 dimensional formulation to "alternative" formulation and mathematical curiosity, mixing it with alternative 3D formulations, and the coupling of (classical) Dirac electrons with an external EM field that satisfies Maxwell equations i.e. not a formulation of the Maxwell equations at all).
What one can argue about, of course, is whether one has to mention the Faraday tensor in the introduction. RogierBrussee (talk) 19:27, 26 October 2012 (UTC)
- Removing quantum entanglement from the intro is an excellent idea, I just did it. :-)
- I will try to dramatically shorten your paragraph without taking away any important points. Here goes:
- "Maxwell's equations are Lorentz-invariant, i.e. consistent with special relativity. In fact, investigation of the symmetry properties of Maxwell's equations helped Einstein formulate special relativity."
- How did I do? I'm sure you think I ruined it. But the parts I left out, it seems to me, are so brief and jargony as to be incomprehensible to someone who isn't already familiar with those things. For example, even a long paragraph is insufficient to teach someone what is special relativity and why is it exciting. :-)
- You answered the question of why the 3D equations are important: Very few people do covariant tensor calculations compared to how many people want to know how a transformer works or an EM wave or a transmission line. Also, all measurements, not to mention people's intuitions, are set in a particular inertial reference frame. It seems sensible to me to ensure that people understand the physics of a single reference frame first, and only later try to understand the relation between different reference frames. In other words, first learn the traditional Maxwell's equations, and second explore the relation to special relativity and four-dimensional spacetime. Usually special relativity is taught in that kind of way in my experience. :-)
- In the Maxwell's equations and relativity section, there is certainly room (IMHO) for a few sentences like
- "After special relativity was developed, it became clear that Maxwell's equations can be written in a way that is far more concise and convenient, by taking advantage of their Lorentz symmetry, i.e. writing everything in terms of four-dimensional tensors in four-dimensional spacetime, etc. etc."
- In fact, in previous years, this article has been organized differently to group together (1) the historical discussion of Maxwell's equations helping in the discovery of SR, (2) the covariant formulation of Maxwell's equations, and also (3) a brief conceptual discussion of how an electric force in one frame can be a magnetic force in another frame. Without going all the way back to that previous organization, it might be possible to expand the Maxwell's equations and relativity section a bit with another paragraph or two along those lines. :-) --Steve (talk) 13:51, 27 October 2012 (UTC)
- Rogier -- I like your newer round of intro edits :-) --Steve (talk) 23:44, 2 November 2012 (UTC)
Constitutive relations already has its own article
No objections to the additions to the constitutive relations (this article) section, but recently it was trimmed and transferred to Constitutive relations (main article). Why not just add the context there? Let's not allow this article to pile up with information again which could be in the main articles... (and eventually become unreadably long, not that I'm saying this is currently happening, the additions are in good faith, correct, etc.) M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 11:33, 23 December 2012 (UTC)
- Rogier, apart from the obvious 'spac-time' typo, I can't understand what you are trying to say in your newest contribution to this section. It seems to me that nonlinear optics items like Kerr cells and Pockels cells, Hall effect devices, or the highly modulated magnetic devices, might also be subjects of this section. Or perhaps this discussion should be in the constitutive relations article. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 12:07, 24 December 2012 (UTC)
- I radically cut the constitutive relations section down. And did a bit of editing on the main article. Does that satisfy people's concern?
- RogierBrussee (talk) 20:10, 1 January 2013 (UTC)
- Looks better now, thanks. You could have transferred the non-linear materials subsection you extended to the constitutive relations article directly and just linked from here to there, but it's not essential right now... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 09:43, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
About the sectioning...
I moved [2] the "potential formulations" material back into the main section "alternative formulations"; why have an entire section on potential forms then a compact section which says "alternative formulations" but only discusses the tensor/differential form equations... and fields, and with the potential equations there anyway? The potential equations were duplicated... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 11:06, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
- Well I was going to remove them from the alternative formulation section (which I don't like, allhough I do like having an overview table), but went to make a cup of coffee first.... The reason is I want to expand on gauge equivalence and gauge fixing, because they are somewhat subtle and quite essential even in an overview article, in my opinion. I can live with the current situation though.
- RogierBrussee (talk) 12:25, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
It seems the section on alternative formulations is there so summarize them, linking to the main articles, achieved by a table of formulae with explanations following it...
Sadly the geometric algebra formulae have been removed [3][4] as "obscure", but I won't reinstate those, to prevent an edit war... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 11:06, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
- I really don't think that the geometric algebra formulation is important enough to warrant inclusion. The geometric algebra community is good at marketing, but is just a really confusing way to write (as a 1 form). Also using a Clifford algebra (which is what a geometric algebra is) mixes in the metric everywhere, and is bad if you want to understand invariance properties of the equations. More to the point, I am unaware of important applications and use of this Clifford algebra point of view by people outside of the geometric algebra community that would make this an important point of view to know. I did add a see also though.
- This raises the legitimate question why do we have to keep forms (you probably all know the below, but I think it is good to have on the table). Mathematicians have been using forms, the exterior derivative and Hodge duality, as THE right formulation of higher dimensional generalisation of vector calculus since the forties (younger physicists are following since the 90's) because they behaves well with respect to curvilinear coordinate change, and therefore live on manifolds (with a metric if you need Hodge duality). The Faraday tensor is an alternating rank 2 tensor which is a two form by definition. The Maxwell equations are written completely naturally in terms of exterior derivative and Hodge duality, and this cleanly isolates the dependence of the Maxwell equations on the metric and gives you a generally covariant formulation for free. Finally, if you think of EM as a U(1) gauge theory and the Faraday tensor as the curvature of a connection, it comes out as a 2-form. In fact the form version of the 3 dimensionsional vector calculus formulation is increasingly used by engineers and numerical analysists and I would argue that it does warrant inclusion.
- RogierBrussee (talk) 12:25, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
- The reason is that some time ago the article did have separate sections, on each formalism, and over time people would keep piling material up which should be in the other main articles, recently this article was trimmed way back from 120kB to around 84kB. I'm not saying you're overflowing the article again, it seems only to fluctuate around 84kB while the text is generally improved when you're editing which is fine. The section was moved back for a uniform format in summary style, and although inessential the GA formulations deserve even the slightest mention by WP:NPOV (as they were in the table)...
- I would propose that this article just concentrate fully on the microscopic/macroscopic formulations in terms of E, D, P, B, H, M, if you're going to write more about the potential formulation (or any), by all means do so, although it would be better expand all other articles
- and mention motivations and reasons for doing so in this article, which the original section "alternative formulations" did some way or another, and provide links in plenty... Maxwell's equations are throughout WP, not just this article.
- Just my veiws, which everyone is welcome to disagree... I don't want to interrupt your good work so I'll stay out from now on... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 13:18, 2 January 2013 (UTC)
Hi RogierBrussee, nice new table, a lot clearer in terminology. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 16:00, 3 January 2013 (UTC)
Matrix rep and GA formulation in Alternative formulations
These edits have reinstated the GA formalism, and this edit has introduced a link to a recent article Matrix representation of Maxwell's equations, with an excessive number of 6 refs.
I'm sorry, but yet again... the Alternative formulations section has become too long (mainly due to the new GA formulation) when there are plenty of specialized articles and after this article has been trimmed.
What should we do about this trend? Probably nothing... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 08:06, 3 March 2013 (UTC)
- I agree that this is a problem. I've had to revert insertion of unpublished Matrix rep articles before. For the Matrix rep, this is likely a conflict of interest as the author of some of the refs is inserting those refs into the article; it seems promotional and POV pushing to me. The same author created Matrix representation of Maxwell's equations. --Mark viking (talk) 15:06, 3 March 2013 (UTC)
- The article 'Matrix representation of Maxwell's equations' currently has markup errors, as well. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 15:43, 3 March 2013 (UTC)
- Most likley to be mine but where? Can't find any... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 15:59, 3 March 2013 (UTC)
- After Resistance function, etc. In terms of these functions: Failed to parse (lexing error): ε= \frac{1}{v h}\,,\quad \mu = \frac{h}{v}
- That didn't show up using mathjax... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 17:44, 3 March 2013 (UTC)
- You're right, it looked fine under IE & Firefox, but not Puffin.
I'll ask at village pumpLooks good. Thank you; I was worried that my everyday browser was XXX… __Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 00:51, 4 March 2013 (UTC)
- You're right, it looked fine under IE & Firefox, but not Puffin.
- No problem! Best, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 01:09, 4 March 2013 (UTC)
- I removed the geometric algebra formulation but am guilty of extending the table with the tensor formulation on curved space time. Unlike the geometric algebra formulation, I think they are sufficiently mainstream and give enough physical insight to be included. Best RogierBrussee (talk) 10:20, 6 January 2014 (UTC)
- Nothing to be guilty about. I like the table! ^_^ M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 17:36, 6 January 2014 (UTC)
Scope
The scope of this article is way too big.
EM is tricky, and if presented in the order of historical development (Gauss law, this law, that law, ...), it becomes even trickier. It all becomes a huge cookbook recipe with too many ingredients for anybody to have available at home. It's of course an utopia, but if EM is presented at the outset as one theory, and the immensely complicated macroscopic approximations are left out, then I believe it could be easier to grasp. This is unfortunately not the approach of most modern textbooks or this article, but the approach exists. See L&L for a masterful exposition of microscopic EM as compared to a merely very good one (like Jackson's). It is decidedly easier, cleaner, and much better, to go for the full set of equations right away, provided that one has a little of the the math background. Gauss law, this law, that law, ..., will follow. Lets face it, two screens full of equations and tables of terms is a mouthful. This reasoning of mine is only hypothetical, because it would be too much of a job to attempt anything, most people (incorrectly!) disagree, and the article is still pretty good as it is. YohanN7 (talk) 16:15, 7 March 2013 (UTC)
B t w, what is reference #36 (Myron Evans) doing here? He is not reliable, especially not when it comes to naming equations. YohanN7 (talk) 17:14, 7 March 2013 (UTC)
- Above, I have been saying over and over that this is too long as people continuously add content which belongs to the main articles, explicitly listed in detail... Although microscopic/macroscopic formulations should be kept in. An overview table with links to the details is nice, but still the article drowns in advanced explanations of formalisms...
- You know, maths of the EM field is basically about Maxwell's equations in various formalisms, so maybe we could move that page to a new name, and keep all formalisms there (from therein linking to advanced articles which is more or less the current case), restricting this article to just the E, B, D, H, P, M fields and no potentials, no differential forms, tensor fields, no geometric calculus? Nah - that wouldn't last long!... Someone will add! add! add!... (Don't get me wrong they are in good faith) M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 17:42, 7 March 2013 (UTC)
- YohanN7, By L&L I assume you mean 'gasp' Landau & Lifshitz vol 2, Classical theory of fields. But there is an undergrad text, Corson & Lorrain 1962, Electromagnetic fields & waves, with the same program: start with Special relativity, and derive Maxwell's equations. Or take James Franck's suggestion to start with the constant of proportionality between electric & magnetic fields to derive SR, or start with moving electric field and shift frame to see magnetic field instead, etc., etc. Or start with continuity equation for electric charge.
- But then there probably is an article about the interrelationships already. __Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 18:31, 7 March 2013 (UTC)
- Thank you for the book reference Ancheta. When I took an EM course for the first time, the approach was the common one. When we finally hit the full set of equations (page 400 or something in Roald Wangsness, forgot the name of the book) we all said pretty much that the whole course should have been taught backwards. But I guess it is much a matter of taste and emphasis. All of the physics lie in the microscopic equations, preferably presented in covariant form with rationalized Lorentz-Heaviside units. Most of he engineering lies in the macroscopic equations using SI units. (In my view, even the ε0 and μ0 are mainly complicating factors.) The macroscopic equations are a huge subject in their own right, and they present an additional layer of concepts. They really logically belong higher up in the food chain. But, I am not insisting on anything. YohanN7 (talk) 10:31, 8 March 2013 (UTC)
Fundamental natural quantities which are constant and observable are regarded as independent. Examples of these are the speed of light and the electronic charge.
In the often presented equation c = 1/sqrt(mu * epsilon) the result is an error about which quantity is the natural constant, and which are derived constants.
C, the speed of light, is the natural constant. The correct order is either that either mu = mu( c, epsilon ) or epsilon = epsilon ( c, mu ) or of course both. The problem is that mu and epsilon are arbitrary, if it is allowed they are represented by glass, diamond, plastic, or other noticeable dielectrics, or iron, cobalt, manganese, aluminum if they are ferromagnetic or diamagnetic, etc.
It appears the first definitions of permittivity were made assuming that glass, crystal or diamond, etc, were the substances of choice. This resulted in a value for permittivity being selected which was very far from the square root of c. The socio-economic causes of the selection cannot be discussed here except that permittivity was defined in the British Isles under the Royal Society.
With permittivity based on crystal and diamond, etc., the definition of the magnetic characteristics of the speed of light were left to Maxwell in Washington D.C., some seventy degrees of longitude to the West. Maxwell had no choice but to assume that the permittivity defined in Britain would have to be used, and the result was that the exponent for permeability was far smaller - and permeability itself was a much coarser quantity which was closely coordinated with iron such as is found in many constructions, tools and weapons.
Since Maxwell's work in the United States, the differences of opinion regarding optimum fundamental measures of permittivity and permeability have been lost in the longitudinal variation, that is, the 70 degree difference in time zones between London and Washington.
The particular example of the speed of light, presented as if it is a constant derived from two derived constants, is frequent. The correct order is that the speed of light is the observed natural constant. This fundamental natural constant is now operationally observed with high accuracy through communications between Earth and other planets such as Mars and Saturn and, of course with the GPS systems.
It is time to reconcile the wide disparity in magnitude of the permittivity and permeability, so that both have relatively close magnitudes. A ratio of 2*pi, or the Golden Mean, or some such constant would be useful as it would free users from confusion on the basis of absolute value alone.
The present, extreme difference appears makeshift, and it is quite possible they would naturally be close to equal, and different only in the topology of their existence - the one in linear fields, the other in curl-dominated fields.SyntheticET (talk) 00:37, 24 March 2013 (UTC)
Recent edits (26/03/2013) to Alternative formulations
Couldn't fit in summary [5], so...
- Deleted "clarification needed" tag in the classical electromagnetism and special relativity section - none was even needed anyway but still trimmed the end of that sentence which didn't add much.
- Applied the {{main}} template for main links to the articles, used as headings to make clear these are the main articles to read.
- Deleted the excessive number of references (discussed above) for the matrix representation of Maxwell's equations, move that link to a {{see also}} at the top.
- Removed the now-redundant {{main}} link to classical electromagnetism and special relativity at the top of the section.
M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 16:38, 26 March 2013 (UTC)
Removal of history section
I took the liberty of splitting off the history section to the article History of Maxwell's equations, to see how it would turn out. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 07:56, 5 May 2013 (UTC)
Similarly to the above, c.f. this and here. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 08:52, 7 May 2013 (UTC)
Table removed, restructured the lead of the article
Considering YohanN7's comments above, I tried to remove the tables (contrary to how much I really like tables) and rewrite in continuous prose.
- The links to the articles for each quantity should describe the units and alternative names. (The table of terms was in fact what motivated me to create the articles of equation tabulations, complete with units and quantities in physics equations).
- For this article, it was odd to bunch all the conceptual descriptions, micro/macro-scopic equations, then all the definitions, etc, in their own places, rather then in a (at least slightly more) continuously flowing prose. The article should just get to the equations as soon as possible, then describe their meaning.
- I split the micro/macro equations also, it makes sense since the macroscopic equations have the auxiliary fields defined and discussed later.
- Also removed the clumsy and pointless notation "Qenc(V)" for "charge Q enclosed in volume V": since equations and quantities are supposed to be explained in words - the context should make the meaning clear. All that needs to be said is "Q is the charge enclosed in a volume" then the volume integral of ρ follows.
Apologies to suddenly "dominate" the article. Anyone is more than welcome to complain if I screwed up. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 08:31, 12 May 2013 (UTC)
- I also rewrote the integral equations in terms of the volume integrals of charge and surface integral of current,
- since it's much easier to see the connection between the differential and integral equations this way (all that needs to be done is to change surface integrals into volume integrals, and line integrals into surface integrals, then equating integrands automatically, with no prior substitutions of definitions).
- Also equations are tidier when factorized and it's much easier to see the dimensions this way, for example we can immediately see ε0∂E/∂t has dimensions of current density J.
- With the physical interpretations, there are "hints" on the connection between flux/divergence and circulation/curl without explicitly writing down the div/curl theorems in terms of E and B, complete with a fluid dynamics analogy to circulation/vorticity.
- Hopefully section 1 is now a bit more stimulating for the reader to appreciate the physical nature of vector calculus inevitable in electromagnetism and contained within Maxwell's equations, and maybe even decide to pick up some vector calculus for him/her-self... M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 13:33, 12 May 2013 (UTC)
- The restructuring looks reasonable to me, thanks for doing this. There remains the pedagogic problem of the table integral and differential formulations given without any explanation of the notation. It looks like much of the explanation is in the next section. Should we make a forward reference to the next section, or rearrange sections? --Mark viking (talk) 16:38, 12 May 2013 (UTC)
- Thanks for feedback. I tried right now to resection, but since the integral notation fits in so well with the "relations between the integral and diff equations" I left them there for now, maybe a forward reference would be best? M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 16:51, 12 May 2013 (UTC)
- I agree that a forward reference is a reasonable option--looking forward to the next section won't interrupt the flow of reading too much and anyone interested in the table will likely want to read the next section in any case. Thanks, --Mark viking (talk) 20:57, 13 May 2013 (UTC)
- The forward reference was rather difficult, so I tried to smooth out the prose at the cost of introducing some repetition of stating the quantities and notations...
- The "Relation between int/diff forms" is independent of units and should not be made a subsection or merged with the SI units, so it should stay it's own section, yet as close as possible to the first mention of the equations.
- At this point it's better for someone else to continue further rewriting. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 21:16, 14 May 2013 (UTC)
- I agree that a forward reference is a reasonable option--looking forward to the next section won't interrupt the flow of reading too much and anyone interested in the table will likely want to read the next section in any case. Thanks, --Mark viking (talk) 20:57, 13 May 2013 (UTC)
- Maschen, The article now renders a ?mathjax? error in the Vacuum equations, electromagnetic waves and speed of light section
"which identify
Failed to parse (lexing error): c = \frac{1}{\sqrt{ \mu_0 \varepsilon_0}} = 2.99792458 × 10^8 \, \mathrm{ms}^{-1}
with the speed of light in free space." I am using Firefox 21.0 --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 17:43, 15 May 2013 (UTC)
wave propagation picture/comment
I have a vage impression, that electromagnetic wave propagates as E=sin(), B=cos(); instead of E=sin(), B=sin(), as stated in the article, and depicted on the rdawing. Pls somebody comment. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 87.205.149.171 (talk) 06:38, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- That is correct, the one is sine, the other is cosine. See Landau & Lifshitz 1962 Classical Theory of Fields "Monochromatic plane waves" equation 48.9, p131. It would appropriate to alter the picture, or delete it. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 11:39, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Uhh... The E and B fields in a sinusoidal plane wave are in phase in time and space, though oriented at right angles in space (both perpendicular to the direction of propagation). Therefore E=sin(), B=sin() as in this diagram is correct. — Quondum 13:39, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Then where does the energy go when both B & E are zero, and in phase? It's not as if the fields are in a box ... Anyway, take an infinite waveguide of rectangular cross-section in x & y, with z the infinite direction; Jackson 1962 Classical Electrodynamics p.247 equations 8.46 shows that B & E are indeed sines in x and y, but that is 90 degrees out of phase with a sine, and with a cosine down the infinite waveguide, in the mode. More precisely, if you take away the box, and let a circularly polarized wave propagate in the z direction, the peak transverse E & B will rotate as they propagate, in an eternal braid. (I am not asking that the animation take this into account.) --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 15:41, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Uhh... The E and B fields in a sinusoidal plane wave are in phase in time and space, though oriented at right angles in space (both perpendicular to the direction of propagation). Therefore E=sin(), B=sin() as in this diagram is correct. — Quondum 13:39, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Quondum is correct; they are in-phase when the wave is propagating in a vacuum. Taking turns is a inappropriate generalization from L-C circuits. As to where the energy goes, it travels with the wave in those parts where E and B are non-zero. JRSpriggs (talk) 16:21, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Ancheta, the waveguide example is a bad place to start. Though I have not checked on the specific mode you are referring to, one tell-tale point will be that the propagation of the phase down the waveguide is at less than the speed of light. Every mode of propagation down a rectangular waveguide should be expressible as a superposition of several plane waves each travelling at an angle to the axis of the waveguide, none of which travel directly along the waveguide. In some (most?) waveguide modes, there are longitudinal components of E and/or H. In short: the waveguide example is far more complicated than one would think, and confuses the simple free-space plane wave example. — Quondum 18:54, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Quondum, I apologize for misreading Landau & Lifshitz, p 131: the text mentioned x & y (x the direction of propagation, y and z transverse to x). The equation 48.9 was for y (sin) and z (cos), not x. The y & z are used for describing the components of the transverse fields. So my question is answered: the energy flux is in the direction of propagation (the Poynting vector, p. 126). --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 12:19, 19 May 2013 (UTC)
Missing factor in Gaussian equation?
To Maschen: Could you check again macroscopic version of Ampère's law (with Maxwell's extension) at Maxwell's equations#Equations in Gaussian units. I think you may be missing a factor of 4π. Or perhaps the error is in Gauss's law (an extra factor of 4π). JRSpriggs (talk) 10:56, 19 May 2013 (UTC)
- Yes, there should be a factor of 4π multiplying the free current density Jf. Thanks, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 11:01, 19 May 2013 (UTC)
Minus sign missing in alternative formulation, tensor calculus.
In alternative formulation, in the row "tensor calculus", "potentials, Lorentz gauge, flat spacetime" I think there should be a minus sign. Currently is says:
now if I take the last one:
For now I will modify the table, if you find a mistake in my derivarion please correct the table and provide explanation here. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 89.65.5.6 (talk) 12:08, 16 June 2013 (UTC)
- I reverted the edit. The sign was correct before:
- Seems there was a sign error at the end of your working, which should be because of the prior . M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 12:24, 16 June 2013 (UTC)
- Thank you for your reply. Please have a look two rows above in the same table, "Tensor calculus, Fields, Flat spacetime", there it is written that , it is in a contradiction with the first equation that you have written in your answer above. 89.65.5.6 (talk) 13:31, 16 June 2013 (UTC)
- Sorry, yes, the equation is the correct one, so you're sign was correct. Before checking in textbooks (MTW and Griffiths), I recalled the contraction with the first index on F, not the second. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 13:50, 16 June 2013 (UTC)
- Thank you. And sorry that I did not login before. Janek Kozicki (talk) 14:04, 16 June 2013 (UTC)
Memristors, the 4th 'solution' to the Equations is missing....why is this?
Work has been progressing on the real and theoretical nature of memristors since then.
Memristors have the potential to up-end all of electronics and especially computer design....all of whose circuits are currently based on Von Neumann architecture which separates memory from operations. That separation may no longer be necessary.
An explanation of this development is a serious omission from this page.
Sadly, I do not feel technically able to start this work.
Artied (talk) 13:02, 21 September 2013 (UTC)
- In the same way that Kirchhoff's circuit laws are a consequence of Maxwell's equations, so too are memristors. They do not represent new physics, but rather new engineering and materials science. What I mean is, memristors are worthy objects of study by electrical engineers, students, and applied researchers, for their own sake. There are in fact many such kinds of electrical, optical, electro-optical, magneto-optical, etc., objects out there, all of which can be understood from consequences of the basic equations of this article. However, these objects each have their own series of articles, even if their theory stems from this article. __Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 15:36, 21 September 2013 (UTC)
- This article is about physics, not engineering. So discussion of electronic components is inappropriate in this article. JRSpriggs (talk) 00:54, 22 September 2013 (UTC)
Roadmap to the thermodynamic web
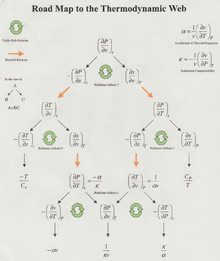
I just uploaded a "map" I created of thermodynamic equations. I wanted to convert it to SVD (e.g., using Inkscape), however, I am not really good at graphic design. If anyone has the time and know-how, please feel free to convert it to SVG. Also, I am not sure if this article is the best place for it. I am only including this comment on this article, as this "map" helped me a lot as an undergrad whilst learning thermodynamics, etc. --Thorwald (talk) 00:51, 7 December 2013 (UTC)
- There is a tremendous difference between Maxwell's equations for electromagnetism (fundamental field equations) and Maxwell relations for thermodynamics (partial derivatives which follow from the definitions of thermodynamic potentials and symmetry in 2nd order partial derivatives). So these should be at Maxwell relations and not here. Nice picture though, will try and convert to SVG later but I'm tied up right now. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:22, 7 December 2013 (UTC)
- Oh. Wow. I meant to post this on the Maxwell relations. Note to self: Never post whilst up way past bedtime. Adding this thread to that article now. --Thorwald (talk) 22:11, 7 December 2013 (UTC)
Maxwell's correction?
Is this the normal English terminology? 'Correction' suggest that it is a minor tweak, whilst it is essential to the wave equation. It also suggests to me that Ampere got it wrong, which is not really fair.
What about Maxwell's 'addition' or 'modification' ? Martin Hogbin (talk) 19:52, 10 February 2014 (UTC)Harmuth (talk) 21:23, 28 March 2014 (UTC) Reference the book "Modified Maxwell Equations in Quantum Electrodynamics" H.F.Harmuth. T.W.Barrett, B.Meffert, World Scientific Publishers, Singapore. It modifies Maxwell's equations by adding the magnetic dipole current density left out by Maxwell and produces equations that have transient solutions (Maxwell's equations have only steady state solutions).
- I agree with "Maxwell's addition" as quantitatively and qualitatively more reflective of what Maxwell actually did, and will implement the changes. Good point, thanks, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 18:26, 4 March 2014 (UTC)
I may be a hypocrite or curmudgeon (actually I'm 22)... while I understand the good faith motivations to add a list of variables after a set of equations, in rewriting parts of this article (including the section Maxwell's equations#Conventional formulation in SI units), I attempted to explain the symbols in the equations in words, directly under the table (and some even before the table, directly above). Also, are we not supposed to explain formulae in words rather than lists (Wikipedia:Manual of Style/Mathematics#Explanation of symbols in formulae)? So why do we have a list of all the variables which duplicates what is already explained?
We used to have a gigantic table of all the constants, variables, terminology, and units, which was converted into prose as it probably should for an encyclopedia (see the history in pre-2013). Editors (by all means in good faith) may add the units, alternative names and symbols, etc. to the list and make it longer and denser, then eventually there would be a good reason to resurrect the big table format again...
I will not delete the list, but there doesn't seem to be much benefit in keeping it there.
Finally, yes, admittedly I used to add bulleted lists to equations in articles, but that was years ago and as and when they have been or will be converted to prose. Best, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 18:26, 4 March 2014 (UTC)
- I agree that variables and mathematical notation are best explained in prose. It may be a font problem. For those of us not using MathJax, e.g., B and look completely different, so it may not have been obvious that the prose variables corresponded to the table variables. For this reason I don't like the hack of using LaTex for display math and HTML/wiki markup for inline math. But converting the inline math to LaTeX runs afoul of WP:RETAIN. As a compromise, I'll convert the lists to prose and remove the unneeded bigmath modifiers. There will still be redundancy to deal with. --Mark viking (talk) 19:14, 4 March 2014 (UTC)
- Hi Mark, I'm not sure if you misunderstood: all I meant was the list is redundant and could be deleted. The paragraphs below explain all the symbols in the default font (the only symbols which could be potentially bad are the curly partial d and nabla, but the math template has nothing to do with this, and fonts do not seem to be the motivation for the lists). Your efforts are appreciated, but converting the list into prose has only duplicated the explanations. Thanks, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 20:10, 4 March 2014 (UTC)
- Hi Maschen, sorry for not explaining my motivation better. When I saw the lists, I asked myself, why did the editor create these redundant lists? Is it a love of bulleted lists? Is it because they jumped straight to the equations and seeing no definition of variables next to the table, decided to add them? Or is it because, for instance, the prose B in the previous section and display in the table look so different that they did not realize that these represented the same variable? I guessed that the last explanation was the possible one. Actually in my browser wiki bold B, math template B, and LaTeX mathbf are all rendered in different fonts; the wiki bold is in a bold sans-serif font, the template is in a bold serif font and the Latex is in a much larger and not particularly bold serif font. I kept the math templated symbols as a compromise between the wiki bold and LaTeX mathbf versions. All the different fonts might have confused me if I was learning this stuff for the first time. It is a typographic train wreck.
- Feel free to delete the now prose paragraph--I agree it is redundant in content, if not in form. But it would be good to figure out why the lists were added in the first place. --Mark viking (talk) 20:41, 4 March 2014 (UTC)
- I disagree. I like having the variables explained in a list immediately after the equations. When someone is reading the equations and trying to understand them, he will most easily find the explanation that way, just a quick glance downward to the bulleted definition and then back to the equation. JRSpriggs (talk) 06:34, 5 March 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, I realize that, but keeping the list still amounts to duplication and in all this time editors have been trying cut repetition from the article. The paragraphs explaining the symbols are as compressed as they need to be, it's not like they go on forever.
- As a compromise: we could reinstate the list with a hidden note telling people not to make it too big, those inclined can do this. Thanks, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 07:26, 5 March 2014 (UTC)
Hope people are happy with this change. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 22:31, 8 March 2014 (UTC)
- Those changes look good to me, thanks. --Mark viking (talk) 21:40, 28 March 2014 (UTC)
- To update: I removed the pure list of symbols at the bottom of the table of equations (only to be followed by a more detailed sequence of symbols) and broke the prose into a list. Now we have a list of symbols with the neccersary explanations. Hope the change is not too controversial. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:39, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
Three notes
"Paraphernalia, such as sweatshirts or T-shirts with "And God Said", followed by the Maxwell's equations, are extremely popular among physicists, and geek-types, because of the elegance of these equations that provide a bridge between classical physics and religion. The phrase refers to Genesis 1:3: and God Said "let there be light" and there was light, whereas the equations represent the essence of light, which is a form of electromagnetism." Three notes:
First, I don't understand what the word "extremely" means. How many of them? How much they feel about such T-shirts? There is a strong need to be concrete, otherwise it's not an encyclopaedia. For that matter, I don't understand what the word "geek" means, either.
Second, what is "the essence of light" depends on how you interpret the Bible, what this light is important for and how we are supposed to make judgements of it (is it the physical logic behind light? is it a sensation of light? is it an idea of light-like goodness? is it something else? all three are very different objects that have very little to do with one another). Also, it depends on how you interpret the ability of a human to know; after all, the equations are nothing more than a human understanding of light, a representation of some of our ways of reasoning of it, but they are not light itself. So this statement must have been discussed at length and with different outcomes. I don't see any links that lead to extra-Wikipedia discussions of what this section says, anyway.
Third, I don't see what this section has to do with the essence of Maxwell equations. Lots of things can be said à propos, does one need to have them all in an encyclopaedic article? Just imagine someone addresses the first point of mine and adds some links to statistical figures and quotes of famous physicists or "geeks", where they explain what they feel about such T-shirts… Without such links and discussions, it is not encyclopaedical. With such links, it is evidently out of place here. - 91.122.10.59 (talk) 19:00, 3 April 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, good find. I have boldly removed the section. It is entirely unsourced. If someone insists that it really belongs in the article, I'm sure they will find a solid source. - DVdm (talk) 19:08, 3 April 2014 (UTC)
- (ec – thanks, DVdm) You make some cogent points. The section and its content is IMO is extremely non-encyclopaedic, and really does not belong here. Besides, the interpretive phrasing "because ... provide a bridge between classical physics and religion" is potentially simply wrong: I see it as an in-joke poking fun at the wording of the Book of Genesis, in a sense via a pun. I'd hardly call this "providing a bridge". —Quondum 19:20, 3 April 2014 (UTC)
- These kind of popular culture "mentions" abound in other wiki articles and I find them pretty enlightening. But for me Maxwell's equations are all business or should be. Good call to remove the T-shirt exegesis.
- But do leave the actual image in. I've never found it disrespectful to religion; it well expresses a clockmaker paradigm that became popular during the Enlightenment and no doubt informs many people's thinking today. 84.227.250.178 (talk) 16:55, 8 April 2014 (UTC)
- I had left the image in there because it doesn't do much harm—and it's a bit funny
 . I have now moved it next to the introduction of the section on alternative formulations, which looks like a better place. - DVdm (talk) 17:27, 8 April 2014 (UTC)
. I have now moved it next to the introduction of the section on alternative formulations, which looks like a better place. - DVdm (talk) 17:27, 8 April 2014 (UTC)
- I had left the image in there because it doesn't do much harm—and it's a bit funny
- I'm fine with removing the religous OR, but these shirts have been around for at least 50 years. Check out the 1963 ad on page 3 of the MIT newspaper. It is reasonable to mention these shirts. --Mark viking (talk) 17:31, 8 April 2014 (UTC)
- I've reworded the caption of the picture slightly, so that it makes only reference to the fact of the equations on the T-shirt. Highlighting the allusion to the passage in Genesis is unnecessary, and makes it specific to this example of the "bumper sticker"-like popularity of Maxwell's equations – for example, the advert in the MIT newspaper referred to above shows a sweat-shirt with only the equations on it. I think the picture serves as a light point (heh-heh) in the article, without making unreferenced claims or allusions. Most who have dealt with Maxwell's equations will need no more than the picture itself to appreciate the humour. I think too that it probably falls easily within the WP guidelines in that it is a related illustration, which typically does not carry such a burden of notability or relevance. —Quondum 17:35, 15 June 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, I agree with this tweak. - DVdm (talk) 18:25, 15 June 2014 (UTC)
Italic vs. roman 'd' for derivative; distinguishing notation for distinct operations
This reverts an edit that was to make italic/roman font use consistent ; the revert does not take into account all the other equivalent uses of the same symbol and thus introduces inconsistency.
Two distinct concepts are used in the article: the derivative using Leibniz's notation, and the exterior derivative. For the former, we have had much discussion, and I would be in favour of using an italic d throughout for the Leibniz notation. The same discussion does not seem to have been as conclusive about the notation for the exterior derivative. However, I would like the two to be distinguished in this article to minimize confusion, so I propose explicitly mentioning the choice of notation and the distinguishing role of the font, and changing one to italic and keeping the other roman throughout. I nominate the italic d for the Leibniz notation, and roman d for the exterior derivative in this article. —Quondum 13:51, 29 August 2014 (UTC)
Why was my edit on Maxwell's equations undone?
Please read my edit on Maxwell's equations:
From a historical perspective, the equations that Maxwell arrived at are fairly distant and cumberous from the present form of four elegant equations. These set of four equations owe their present elegance to Oliver Heaviside, who reformulated Maxwell's field equations in terms of electric and magnetic forces and energy flux. Hence, for a time the equations were rightly called as Maxwell-Heaviside Equations.
This is historically correct. Maxwell's paper was scrutinised and the elegance of the modern form of the equations wasn't there. It is unfortunate that Oliver Heaviside's name has been removed. The common public may not have done justice to the man, but wikipedia, an encyclopedia, must not be swayed by Google's page ranks or the absence of it in attributing the credit to the man who deserves it. The article on Oliver Heaviside may please be referred to. YohanN7 has referred to one "Myron Evans". It's not clear how the present edit is related to the person. Discussion is welcome. Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 17:38, 15 September 2014 (UTC)
- Your edit was reverted by user YohanN7, most likely because it lacked a reliable source. The revert should have specified the reason and you probably should have been given a little message on your talk page explaining the problem. Anyway, see wp:RS and wp:NOR. Cheers - DVdm (talk) 18:04, 15 September 2014 (UTC)
- Here is what I replied on my talk page when you asked me there:
- It might be worth a footnote in the history section (if you can source it), not a large (and POV, it didn't read well) chunk in the lead.
- And, as a matter of my POV, reorganizing equations is not really the same as discovering them. An undergraduate student can do the former. YohanN7 (talk) 19:46, 15 September 2014 (UTC)
- It is clear on my talk page why I refer to Myron Evans. He is the reference for the term "Heaviside-Maxwell equations" usage today in History of Maxwell's equations. And, yes, I believe it is the Myron Evans, the most inappropriate man alive to name equations, see Einstein-Cartan-Evans theory, named so after Myron Evans, by himself. YohanN7 (talk) 19:57, 15 September 2014 (UTC)
- I've read Maxwell's papers on E.M. As an undergraduate physics student I'd read the elegant Heaviside equations and wrongly attributed them to Maxwell. Much later, when I read Maxwell's papers I found the two papers were long, difficult and convoluted. The only thing that comes through clearly enough is the speed of light from an algebraic manipulation of permittivity and permeability.
- And no, it is beyond the capability of even a talented undergraduate to reinterpret Maxwell's papers to the elegant vectorial form we now know them wrongly as Maxwell's equations. What you say here is very cruel to a man who did so much, including developing the vector calculus notations. Please do read the page on Heaviside along with external references in the wikipedia itself. So either delete that page, or accept my edit in the present wiki page to make the information commensurate with each other.
- Bkpsusmitaa 12:02, 1 October 2014 (UTC)
- I'll just repeat what I wrote:
- It might be worth a footnote in the history section (if you can source it), not a large (and POV, it didn't read well) chunk in the lead.
- There are several formulations of the Maxwell equations in use. For this, see the article. I personally think you give Heaviside undue credit. The equations of electromagnetism (whether ugly or pretty) were inconsistent when Maxwell introduced his contributions, and after that they were consistent (whether ugly or pretty). Therein lies the physics. With Maxwell, the classical theory of electromagnetism reached its present form.
- Scientific literature older than, say, 50 years is unbearable to read. But just because scientists today are better at presenting science, and better notation is available, it doesn't mean that credit is moved from the original discoverers.
- Nobody stops you from making a new attempt, and I certainly will not say in advance that I will revert you. I have nothing against Heaviside, and it appears as the vector calculus formulation is due to him. (I personally think it is messy compared to the tensor and differential form versions.) Just don't give it undue weight.
- How about this:
- The most common modern formulation, the vector calculus formulation, is due to Oliver Heaviside + citation. YohanN7 (talk) 13:09, 1 October 2014 (UTC)
- ----------------------------------------
- Actually, Heaviside's reformulation revolutionised the development of E.M., as the equations, and with it the theory, became easily comprehensible. And this comprehensibility encouraged further development. A cursory glance at the history of development of E.M. before and after Heaviside's contribution will support this hypothesis.
- And no, I won't repost. I would reason with you. If you are convinced, you would revert the earlier page. It is still there.
- The POV is that Maxwell's equations, that we use today, are not Maxwell's. It is Heaviside's ;) !
- Your logic, "Scientific lit ... older than ... 50 years ... unbearable to read ... better ... presenting...better notation ...doesn't mean ... credit ... moved from the original discoverers" does not apply in this case. Maxwell didn't even frame the simplest one-dimensional E.M. wave equation, or the Poynting Vector. John Henry Poynting, Oliver Heaviside and Nikolay Umov independently co-invented the Poynting vector. So Heaviside is not some fanciful page designer. He is a real scientist who did real work, and so deserves his due credit.
- Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 04:53, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- This qualifies as a perennial topic. You are not the first editor to note Heaviside's role in the article. The archives reveal this and the current article still has traces of previous attempts to rename, revise, or otherwise rework the equations' history. Please bear with us, for having seen this before, both in the article, and the talk page. You are seeing the consensus. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 06:18, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- @Bkpsusmitaa: I don't think it is giving Heaviside credit for having reformulated Maxwell's equations that is the problem. It is your POV (per above) that is the problem. It — and more — shines through in your edit.
- Please let's not get personal, or begin a flame war. I am naturally sympathetic to scientists who are ignored by the highly deterministic, rigid, government-controlled education system and school syllabi. Like Rosalind Franklin, Tycho Brahe, Jagadish Chandra Bose, ... . If these selfless men vanish from our memories science would lose its true history and become a domain of a clan of university-educated scholars, a very distorted view. I maintain that despite many brilliant scientists at the time, the aeroplane owes its invention to bicycle-repairers.
- Why forget that science is not about degrees, it is about original queries. I hope I have explained myself. Let's focus on the topic instead.
- I'll just repeat what I wrote:
I'd personally be happy to see a mention, like the one I suggested (+ suitable citation), perhaps in Formulation in terms of electric and magnetic fields, that anyway begins with hailing of the formulation as "powerful". It is after all Maxwell's equations in Heaviside's formulation that is used in this article. Credit goes where credit is due. History is also not undone, yet history does not impinge on this article. (It has its own, as does Heaviside.) Yes, I'd like that. YohanN7 (talk) 09:38, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- I can sympathize with Bkpsusmitaa that this article neglects the modern vector calculus form is due to Heaviside, not Maxwell. Yes Maxwell published the original complete set, but it is important not to neglect Heaviside as this article does. History of Maxwell's equations does not (because I wrote the lead, not the rest of the content). The term "Heaviside-Maxwell equations" is definitely non-standard and should not be used. I'll tweak the article. Along these lines. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 09:56, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- If you've read Maxwell's two papers you'd find a remote connection between his equations and the present, elegant formulation. Maxwell included every possible equations available to E.M. till that time. It is our hindsight that allows us to identify Maxwell's set of equations. Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 15:41, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- Hope this change is not too controversial, a source can be added any time. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:41, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- TBH, I think you overdid it big time, but that is my POV. For me, Maxwell's equations isn't a collection of any particular (unwieldy) collection of mathematical symbols. It is the a synonym for the classical theory of electromagnetism. I oppose to the change. A parenthetical remark (and not in the lead) would suffice IMO. YohanN7 (talk) 11:31, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- Fine, but it read before that Maxwell is responsible for the vector calculus formulation. I'll remove Heaviside out of the lead and not the first vector calculus section. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 11:40, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- As a compromise, could we not have something in the lead like, 'the current form of the equations is due to Oliver Heaviside'? Martin Hogbin (talk) 14:11, 2 October 2014 (UTC) I see something like that has already been suggested, I would support that. Anything stronger takes away the credit that is rightly due to Maxwell. Martin Hogbin (talk) 14:15, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- My edit is already on the top of this section. So why not use that instead? :) Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 15:45, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- Why not? (EC: Not referring to the crackpot's of above contribution) Please also remove Heaviside from other mentions (like my last edit) unless there are other reasons to keep him in (like Heaviside-Lorentz units). Keep the article clean, about EM only and not about who did what to develop practical knowledge about EM. We have plenty of articles about such things, and 1000 years from now, there may be millions. This article is about the foundations of it all, and there Coulomb, ..., Ampére, ..., Gauss, ..., and finally Maxwell belong. Not Heaviside, sorry. YohanN7 (talk) 16:01, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- I have seen the edit you have incorporated. It satisfies my first objective. I forgot to say 'thank you'.
- But Maxwell's equations are not Maxwell's! That is the moot point. Only one, with the addition of the J vector (original one), is his contribution. And why are you instructing me to keep the article clean? It looks like an allegation. Did I tamper it? And Heaviside did contribute to the foundation, via the Poynting Vector as well. Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 16:34, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
- Why not? (EC: Not referring to the crackpot's of above contribution) Please also remove Heaviside from other mentions (like my last edit) unless there are other reasons to keep him in (like Heaviside-Lorentz units). Keep the article clean, about EM only and not about who did what to develop practical knowledge about EM. We have plenty of articles about such things, and 1000 years from now, there may be millions. This article is about the foundations of it all, and there Coulomb, ..., Ampére, ..., Gauss, ..., and finally Maxwell belong. Not Heaviside, sorry. YohanN7 (talk) 16:01, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
Personally, I think that this would be moot with a short history section just after the lead. Heaviside's name does not need to appear anywhere else IMO. In any case, I strongly object to resurrecting the name Maxwell-Heaviside equations. The purpose of naming equations is to make it easier for scientists to communicate and not to honor the person (people) who developed the equation. There are very few equations, if they are any at all, whose name reflects the people who made the most significant contributions to that law. One note of irony is that one of the main motivations of Heaviside was to purge Maxwell's equations of A and V. Yet, the most valid form of E&M (QED) is not based on E and B but the potentials. TStein (talk) 16:53, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
@Bkpsusmitaa: Yes of course it is unfair to not mention Heaviside at all, but it was a simple tweak to make and it is now made. There is an entire article on the history of the equations, so his work is not neglected in the EM section of wikipedia. Is your concern is solved by now? M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 18:34, 2 October 2014 (UTC)
All except one: Maxwell's equations are not Maxwell's! So it is better to rename the topic as 'Maxwell's Equation', rather than 'Equations'. People, clans, cults, ghettos, etc., alter history little by little, using apparently innocuous methods. Renaming is one of them. Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 04:05, 3 October 2014 (UTC)
- The EM articles here and elsewhere make it clear Maxwell's equations are Guass' laws, Faraday's law, and Ampere's law with modification, and that Maxwell modified Ampere's law like this:
- for time-dependent E fields, and pulled all the equations together to form classical EM as a unified theory, and predict EM waves. The physics literature and community is well aware of this, so no - there is no unfair renaming or loss of knowledge. Which equation is "Maxwell's equation"? The time-dependent generalization of Ampere's law isn't "Maxwell's" equation if that's what you mean. It is absolutely standard to call the complete set of equations "Maxwell's equations" and should stay that way.
- In short - no renaming since it is non-standard and wrong. This was a very simple matter that has been resolved, it has dragged on for too long. Can we end it here now? Thanks, M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 08:11, 3 October 2014 (UTC)
- I know! You could stop the discussion whenever you choose, needn't drag the discussion. Please don't get me wrong. I am aware of Maxwell's equations. But I would still say my observations remain valid :). I wrote the following at various times :
- (1) The equations that Maxwell arrived at are fairly distant and cumberous from the present form of four elegant equations. These set of four equations owe their present elegance to Oliver Heaviside, who reformulated E.M. field equations in terms of electric and magnetic forces and energy flux.
- (2) The common public may not have done justice to the man, but wikipedia, an encyclopedia, must not be swayed by Google's page ranks or the absence of it in attributing the credit to the man who deserves it.
- (3) The ... elegant Heaviside equations and wrongly attributed them to Maxwell. Much later, when I read Maxwell's papers I found the two papers were long, difficult and convoluted. The only thing that comes through clearly enough is the speed of light from an algebraic manipulation of permittivity and permeability.
- (4) Maxwell didn't even frame the simplest one-dimensional E.M. wave equation, or the Poynting Vector. Only one, with the addition of the J vector (original one), is his contribution.
- (5) Some scientists are ignored by the highly deterministic, rigid, government-controlled education system and school syllabi. Like Rosalind Franklin, Tycho Brahe, Jagadish Chandra Bose, ... . If these selfless men vanish from our memories science would lose its true history and become a domain of a clan of university-educated scholars, a very distorted view.
- Why forget that science is not about degrees, it is about original queries. I hope I have explained myself. Let's focus on the topic instead.
- I add this: (6) The purpose of naming equations is to _is_ to honour the inventor/discoverer, not to make it easier for scientists to communicate. Otherwise, Maxwell's Equations could be better recalled as The Four E.M.Field Equations :) . And scientists are those who work for truth. A man who chooses an easy life of remembering things and not stick to truth is no scientist at all. I maintain that despite many brilliant scientists at the time, the aeroplane owes its invention to bicycle-repairers.
- Still, unfortunately, an editor unnecessarily took the time to painstakingly write and post the equation involving the J vector, despite my writing on the matter. Sometime, I find I can't just reach people by writing plainly. To really reach the reader it's also required of the readers' choice to whether read what is written or just ignore it. It makes me believe people are forever imprisoned within their own minds and constructs.
- I rest my case, and end this discussion.
- Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 04:05, 4 October 2014 (UTC)
- I know! You could stop the discussion whenever you choose, needn't drag the discussion. Please don't get me wrong. I am aware of Maxwell's equations. But I would still say my observations remain valid :). I wrote the following at various times :
- Yes many of us oppose the revisionism of attributing credit to discovery. In general it's better to just name equations (laws, theorems, whatever) by their content rather than after people (although people who misplace patriotism will always disagree with that), and attribute credit to people separately, but since the name "Maxwell's equations" have stuck for such a long time, for the purposes of Wikipedia they should be called that, and their history clarified separately. For what it's worth: I have Maxwell's treatise on EM vol 1 and vol 2, so I know what his formulation is like.
- In any case you have raised yet again the same points over and over even after they have been fixed - it seems you do not read what others write (YohanN7, DVdm, Ancheta Wis, Martin Hogbin, TStein, possibly others elsewhere, and myself).
- I will not post further. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:42, 4 October 2014 (UTC)
- Counter-allegations, false aspersions, Eh!? Good! Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 06:34, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
- I will not post further. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:42, 4 October 2014 (UTC)
- You have also screwed up this thread by sticking in your cranky comments by intersecting other posts or blocks of posts. Do you mess up on purpose? YohanN7 (talk) 14:29, 4 October 2014 (UTC)
- Personal attack? Groupism? Good! Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 06:34, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
- You have also screwed up this thread by sticking in your cranky comments by intersecting other posts or blocks of posts. Do you mess up on purpose? YohanN7 (talk) 14:29, 4 October 2014 (UTC)
I am compelled to post my last comments: No decision is so final in a Human Society that it can't be altered at some time in future. When Maxwell didn't discover the three field equations by himself, why not call this Page "The Four E.M. Field Equations" and redirect search on "Maxwell's Equations" to the renamed page, rather than perpetuate a lie? Wikipedia is a public-edited encyclopedia. Why should it promote a lie popularised by textbooks and vested interests, if any? It should speak the truth. — Preceding unsigned comment added by Bkpsusmitaa (talk • contribs) 06:53, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
- Wikipedia speaks the common textbook literature—see also WP:Verifiability, not truth. - DVdm (talk) 09:10, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
Earlier comment, "wikipedia ... should speak the truth", amended: in place of truth in the end, Verifiable truth... LOL
I quote from Wikipedia, "..."Verifiability" was used in this context to mean that material added to Wikipedia must have been published previously by a reliable source...Sources must also be appropriate, and must be used carefully, and must be balanced relative to other sources per Wikipedia's policy on due and undue weight...does not mean Wikipedians have no respect for truth and accuracy...We empower our readers. We don't ask for their blind trust..."
In the light of the above consider these:
(a) It is proven here that Maxwell's equations are not Maxwell's, except the equation involving the J term.
(b) The elegant form that we use today is owing to Oliver Heaviside.
The above facts have been verified in Wikipedia itself.
Why then it negates the proof and calls the said equations Maxwell's equations? Just because the Text Books do?
What is wikipedia doing? In effect, furthering a lie! Call this the Wikipedia Paradox :) LOL
Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 11:43, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
Please see History_of_Maxwell's_equations, particularly, "...But it wasn't until 1884 that Oliver Heaviside, concurrently with similar work by Josiah Willard Gibbs and Heinrich Hertz, grouped the twenty equations together into a set of only four, via vector notation. This group of four equations was known variously as the Hertz–Heaviside equations and the Maxwell–Hertz equations,but are now universally known as Maxwell's equations..."
In short, a perpetuation of an incorrect assumption. One could have written, The four Electromagnetic Field Equations, and redirect searches on Maxwell's Equation to this topic to maintain neutrality and accuracy and not perpetuate an incorrect assumption.Bkpsusmitaa (talk) 12:11, 5 October 2014 (UTC)
Relationship between differential and integral formulations?
The article has the following quote:
"The differential and integral formulations of the equations are mathematically equivalent"
I do not believe this is correct because the integral formulation carries boundary conditions while the differential formulation doesn't. Any thoughts? --Frozenport (talk) 10:27, 19 February 2015 (UTC)
- Whenever you solve partial differential equations involving space and/or time, you need corresponding boundary and/or initial conditions. And yes, the set of equations are mathematically equivalent, you get from the differential forms to the integral forms by the relevant vector calculus identities. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 10:46, 19 February 2015 (UTC)
- Yes, equivalent in their shared domains of applicability. One can pick mathematical nits and say that there are cases where the integral formulation is defined and the differential formulation is not, where the fields are integrable but not differentiable (e.g. in the classical context when the charge and current is confined to a surface). But this does not relate to the original question with regard to boundary conditions, only to a strict interpretation of general mathematical equivalence. I am not advocating a change, though. —Quondum 16:54, 19 February 2015 (UTC)
Accepting that they are equivalent, then the first sentence: "Maxwell's equations are a set of coupled partial differential equations " is, well, not so much wrong, as misleading. I first learnt (and tried to understand) them in line integral form. I am proposing that this sentence be altered to include the line integral form. Let's face it, T-shirts seem to offer both forms in roughly equal amounts :D — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2001:8003:E48C:E601:A408:ED0C:B596:882 (talk) 11:49, 24 June 2022 (UTC)
"Microscopic" versus "macroscopic"
In the section ""Microscopic" versus "macroscopic"" E and B look like they are both "microscopic" and "macroscopic" fields. There is an averaging and therefore I think the last statement in "Auxiliary fields, polarization and magnetization" is not pertinent, or is misleading, or need an explanation on what it shows.Ludo987 (talk) 09:50, 28 April 2015 (UTC)
- D and H are the macroscopic fields, which include permittivity and permeability of macroscopic objects. Fundamentally, it is the electrons in atoms that cause these effects. Gah4 (talk) 18:19, 13 August 2015 (UTC)
- It seems way more pertinent to emphasize first that this is vacuum vs matter then say matter formulation does not hold at microscopic level in matter while E B formulation does (which yeilds name macroscopic fields). The statement that formulation are equivalent should be removed either way. (basing purposed changes off of Zhangwill Modern Electrodynamics). Someone should let me know what they think. Ehaarer (talk) 21:18, 2 May 2023 (UTC)
Classical
Since the mid-20th century, it has been understood that Maxwell's equations are not exact but are a classical approximation to the more accurate and fundamental theory of quantum electrodynamics.
As well as I know it, Maxwell's equations satisfy special relativity. Classical is often used in descriptions that satisfy Newton but not Einstein. Should this say "relativistic approximation" or "non-quantum approximation"? Gah4 (talk) 18:22, 13 August 2015 (UTC)
- Not necessarily. "Classical" more generally sometimes means "not quantum": Newtonian mechanics or Einstein's special/general relativity. Maxwell's equations are not "relativistic approximation"s because special relativity by design is already consistent with (you even pointed this out). "Non-quantum approximation" is better, feel free to go ahead and change. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 19:15, 13 August 2015 (UTC)
- In mechanics "classical" means pre-relativity. In field theory, classical means non-quantum, i.e. it includes general relativity (and of course EM). (I'm not sure about topics like statistical mechanics tbh.) We actually have an article, Classical field theory, that could be linked under "clasical". YohanN7 (talk) 19:40, 13 August 2015 (UTC)
- I was thinking about this not so long ago. In the early days of quantum mechanics, around the time that Einstein explained the photoelectric effect, and even though Plank showed that his constant was needed to explain black body radiation, Einstein was one of the few believing in quantization of the electromagnetic field and photons. Partly that was because Maxwell's equations worked so well. Many believed that it was only a mathematical trick to generate the black body spectrum. Others that electron energy levels changed in quantum jumps, but that the EM field was still not quantized. Gah4 (talk) 02:40, 12 February 2020 (UTC)
- In mechanics "classical" means pre-relativity. In field theory, classical means non-quantum, i.e. it includes general relativity (and of course EM). (I'm not sure about topics like statistical mechanics tbh.) We actually have an article, Classical field theory, that could be linked under "clasical". YohanN7 (talk) 19:40, 13 August 2015 (UTC)
Phase
In addition, E and B are mutually perpendicular to each other and the direction of wave propagation, and are in phase with each other. A sinusoidal plane wave is one special solution of these equations.
In the sinusoidal case, special solution as it says, E and B are in phase. That is, they are both sinusoids with a constant ratio. But for other waveforms, it isn't so easy to define phase. Should the in phase comment apply only to sinusoids? Gah4 (talk) 23:24, 19 August 2015 (UTC)

- For propagation in vacuum, phase is a useful concept in general, since we can analyze waves into sums of sinusoids. Another solution is for the circularly polarized wave which is the animated sinusoid, a spiral, shifting from E only and gradually transferring to B only, and back to E only, again in the picture. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 02:24, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
- The circular polarized case needs an Ex, Ey, Bx, By, which that diagram doesn't show. Gah4 (talk) 18:09, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
- Meaning the range of the blue and red projections on the x & y axes are but half the story, I presume. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 18:49, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
- Even more, I don't know which half. First I thought it was Ex and By, but maybe Ex and Ey. I don't know how to make these diagrams, and maybe one with Ex, Ey, Bx, By would be too hard to understand when looking at it. Gah4 (talk) 20:23, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
- Meaning the range of the blue and red projections on the x & y axes are but half the story, I presume. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 18:49, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
- Um, actually in circularly polarized light the spiral in the animation is just a single field, either E or B but not both. If it's E, then the animation shows it shifting from purely Ex to purely Ey and so on, so that the magnitude of E is constant. The magnitude of B is also constant and B is always at a right angle to E. If you only look at the field components along a single axis, then it looks E and B are out of phase. For example, looking along x we will see that when Ex is at a maximum (or minimum), Bx is zero, and visa versa. --FyzixFighter (talk) 13:14, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Yes. But notice that the article animation has a red E and blue B, and that the caption here mentions E and B. Would it be too much to have a circularly polarized version, with rotating E and B? (That is, not components of E and B, but the actual vector E and B in perspective?) But I don't know how to make one. Gah4 (talk) 17:40, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Ancheta's caption of the animation is incorrect. The red and blue are not different field but are orthogonal components (red=y and blue=x) of the single field, either E or B. See also circular polarization and polarization (waves)#Polarization state (which has a correct caption for the animation). An equivalent animation with both E and B would look similar but would have a double-helix like structure rotating around the axis of propagation. --FyzixFighter (talk) 18:08, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Conveniently, the caption doesn't actually say that one is E and the other B, but does seem to suggest it. Yes, the double-helix is what I was thinking about. Gah4 (talk) 19:51, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- I apologize if the caption is incorrect. But what does the rotating arrow alternately red and blue signify to you? It seems that the blue and red projections alternately apply to the arrow... --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 21:31, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- I'm holding my fingers in the poynting vector S=ExH mnemonic we learned in school: right hand, forefinger poynting in the direction of propagation forward S, thumb sticking upward E, middle finger projecting to the left H. I rotate my thumb to the right 90 deg , poynting finger still points forward, and now the middle finger sticks upward, replacing the direction formerly held by my thumb. Now I compare to the animation. The arrow seems to change color 4 times in one cycle at the corresponding changes of orientation of E and H. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 22:54, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- You asked what the rotating arrow alternately red and blue signify to me - if this is describing the electric field for circular polarization, then how red the arrow is corresponds to the magnitude its y-axis projection at that instant, and how blue to its x-axis projection. Another way to describe this is that circular polarization is the superposition of horizontal and vertical polarizations with equal amplitude and a 90° phase delay between the two. The colors then correspond to the contribution of each polarization to the total E (red=vertical, blue=horizontal) at that instant in time. The result is that the E vector has a constant magnitude but changes direction in a rotary manner. H would show up as a second vector orthogonal to E and also of constant magnitude, which would also trace out a second helix so that each instance ExH would give you the correct Poynting vector and direction of propagation. --FyzixFighter (talk) 23:31, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- And the reason why E and B have to be in phase ... otherwise the Poynting vector averages to zero. We could have one with red E field, x and y components, blue B field, x and y components. That would match the article diagram for circular polarization. Gah4 (talk) 00:23, 22 August 2015 (UTC)
- Fixed caption. Danke gut, as we say in
SpanishGerman. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 09:22, 22 August 2015 (UTC)
- Fixed caption. Danke gut, as we say in
- And the reason why E and B have to be in phase ... otherwise the Poynting vector averages to zero. We could have one with red E field, x and y components, blue B field, x and y components. That would match the article diagram for circular polarization. Gah4 (talk) 00:23, 22 August 2015 (UTC)
- You asked what the rotating arrow alternately red and blue signify to me - if this is describing the electric field for circular polarization, then how red the arrow is corresponds to the magnitude its y-axis projection at that instant, and how blue to its x-axis projection. Another way to describe this is that circular polarization is the superposition of horizontal and vertical polarizations with equal amplitude and a 90° phase delay between the two. The colors then correspond to the contribution of each polarization to the total E (red=vertical, blue=horizontal) at that instant in time. The result is that the E vector has a constant magnitude but changes direction in a rotary manner. H would show up as a second vector orthogonal to E and also of constant magnitude, which would also trace out a second helix so that each instance ExH would give you the correct Poynting vector and direction of propagation. --FyzixFighter (talk) 23:31, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Conveniently, the caption doesn't actually say that one is E and the other B, but does seem to suggest it. Yes, the double-helix is what I was thinking about. Gah4 (talk) 19:51, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Ancheta's caption of the animation is incorrect. The red and blue are not different field but are orthogonal components (red=y and blue=x) of the single field, either E or B. See also circular polarization and polarization (waves)#Polarization state (which has a correct caption for the animation). An equivalent animation with both E and B would look similar but would have a double-helix like structure rotating around the axis of propagation. --FyzixFighter (talk) 18:08, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- Yes. But notice that the article animation has a red E and blue B, and that the caption here mentions E and B. Would it be too much to have a circularly polarized version, with rotating E and B? (That is, not components of E and B, but the actual vector E and B in perspective?) But I don't know how to make one. Gah4 (talk) 17:40, 21 August 2015 (UTC)
- The circular polarized case needs an Ex, Ey, Bx, By, which that diagram doesn't show. Gah4 (talk) 18:09, 20 August 2015 (UTC)
B is the magnetic field?
That honor belongs to the H field according to (at least some of) my books. The field B is there the called the magnetic induction or the magnetic flow density. I thought that that order of business was the most common. YohanN7 (talk) 13:52, 24 November 2015 (UTC)
- There have been extensive discussions on terminology, see talk:Magnetic field#Definition. The definition of H is given in this and other articles (e.g. Maxwell's equations #Constitutive relations), so if readers want to convert B to H, they can. M∧Ŝc2ħεИτlk 14:07, 24 November 2015 (UTC)
- See A Treatise on Electricity and Magnetism for the ultimate reference. — Rgdboer (talk) 01:58, 25 November 2015 (UTC)
Agree with YohanN7. In Jackson, over his 3 editions, that H field is to be used in Amperes law instead of total magnetic induction B. Otherwise materials with high inductance mu are underestimated.
Alternative formulation section
What is A ? You use it, but you don't define it anywhere on the page. Non-expert readers (that is to say, most people reading the page) won't have a clue what this is on about, so that's bad writing. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 94.196.243.2 (talk) 12:07, 13 March 2016 (UTC)
- A is defined below the table, in the first item; look below the last line of the wikitable at Maxwell's equations #Alternative formulations
Formalism Formulation Homogeneous equations Non-homogeneous equations
- "where ... A is the vector potential "
- --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 12:43, 13 March 2016 (UTC)
Student query I could not answer
This text comes from the article.
"Maxwell's addition to Ampère's law is particularly important: it shows that not only does a changing magnetic field induce an electric field, but also a changing electric field induces a magnetic field."
I could not answer this question from a school age student.
If each field is induced by a change in the other, why do all the text book diagrams show the magnetic and electric fields in phase? When the E field is changing fastest (passing the zero line) the B field should be maximum. Are all the text books wrong? --Neil (talk) 11:36, 20 June 2016 (UTC) http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x18j184.pdf - Ivor Catt, 1.5.2022 — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2.24.141.28 (talk) 00:28, 1 May 2022 (UTC)
- This is something for our WP:Reference desk/Science, not for article talk pages, where we should discuss the article, not the content—see wp:Talk page guidelines. Good luck at the ref desk! - DVdm (talk) 11:39, 20 June 2016 (UTC)
- OK, but if the article isn't clear about something, then we can discuss it here to see if it can be fixed. Gah4 (talk) 20:33, 27 July 2016 (UTC)
- If all the text books are wrong, this article will need correcting too. If the text books are correct, a simple explanation in this article would be nice to have. --Neil (talk) 11:48, 20 June 2016 (UTC)
- If all the text books are wrong, then—by design—Wikipedia will (and must) be wrong too. DVdm (talk) 12:10, 20 June 2016 (UTC)
- This common confusion is caused by the ambiguity of the English language. You should use mathematical equations rather than words to examine this question. A slightly better translation of the equations into words would be "a (shear) change in the magnetic field over space causes a change in the electric field over time, just as a (shear) change in the electric field over space causes a change in the magnetic field over time". JRSpriggs (talk) 18:59, 20 June 2016 (UTC)
- If all the text books are wrong, then—by design—Wikipedia will (and must) be wrong too. DVdm (talk) 12:10, 20 June 2016 (UTC)
- For running waves E and B acquire a common phase factor of π/2. For standing waves E acquires a temporal and B a spatial phase factor of π/2. Aoosten (talk) 16:07, 19 January 2024 (UTC)
The easy answer is to say "special relativity" and leave it at that. If you want to ask where the E and B are, where the energy is, you have to specify the reference frame. If you consider a wave on a spring, it is not so hard to derive the wave equation, which has energy moving between kinetic (motion of the spring), and potential (stretched spring). In the case of mechanical waves in pretty much any system (springs, strings, sound through air) at any point, energy moves between kinetic and potential. In the EM case, it is usual to equate one of E and B with kinetic, and the other with potential, though it doesn't matter which. (Equate E with moving electrons, or with the field that causes them to move.) In any case, energy does move between E and B, but where is that energy? Consider 1/4 cycle, when a changing E is creating B, and also that, at the speed of light, the wave has moved on 1/4 of the wavelength. This means you can't ignore special relativity, which we already knew, but now you can see why. In the spring case, the spring has a fixed reference frame. In EM case, there is no fixed frame to look at it in. E and B are in phase in any frame. Gah4 (talk) 20:33, 27 July 2016 (UTC)
http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x0102em.htm Einstein and Feynman wrongly say changing E causes H and changing H causes E. These ideas are derived from Oersted and Faraday’s experiments, which are misinterpreted (by them and everyone else.). http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x267.pdf . I expect the Wikipedia Thought Police to rapidly remove this (dirty secret) paragraph. Ivor Catt 13.30 GMT, 27 Feb 2018 — Preceding unsigned comment added by 86.169.30.218 (talk) 13:30, 27 February 2018 (UTC)
Answer by Ivor Catt; Maxwell's Treatise, volume 2, page 439, article 790, Fig. 67, correctly has E and H in phase. E and H do not cause each other. If they did, we could only have monochromatic light. Einstein and Feynman (and all text books and Wikipedia entries) are wrong when they say the one causes the other. http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x18j51.pdf ; http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/x0102em.htm - Ivor Catt, 9.8.2021
- I think a better explanation is that the term Maxwell added allowed him to derive a wave equation that had a propagating solution. If you chase the math, it looks like this:

Depiction showing how the fields in a propagating plane wave "cause" each other. - From E you can derive D. From D you can derive ∂D/∂t ( the electric displacement current). From that, you derive H. From H you derive B. From B you derive dB/dt (the magnetic displacement current). Notice that the arrows mean "is derived from" and do not mean "causes". However, when speaking casually, it is common to interchange the notion of "is derived from" with "causes". As an aside, the two displacement current terms are legitimate fields that can be drawn and plotted just like any other field. So, if you want to intuitively understand how E causes H and H causes E, it is easier if you use four fields. Notice that the two displacement current terms involve differentiation. In a monochromatic wave, that causes 90 degrees of phase shift. The Maxwell–Faraday equation includes a minus sign that provides another 180 degrees of phase shift. If you chase your way around the loop then, you get 360 degrees of phase shift. The gain is "unity". It is exactly the condition for self-sustaining oscillation. Constant314 (talk) 21:09, 9 August 2021 (UTC)
- From the horse's mouth. http://www.ivorcatt.co.uk/maxwell8.pdf Maxwell's Figure 67 shows E and H in phase. I hope the Wikipedia Thought Police don't remove this. That would be defending peer revued error against the truth. Does Wales want this; peer revued material or correct material? - Ivor Catt — Preceding unsigned comment added by 2.24.141.17 (talk • contribs) 15:47, 10 August 2021 (UTC)
- Please put new comments at the bottom, and sign all your talk page messages with four tildes (~~~~) — See Help:Using talk pages. Thanks. DVdm (talk) 10:08, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- I am not trying to derive the whole thing on the talk page. If I add a few more steps, dD/dt causes curl{H}. The curl operator adds 90 degrees of spacial phase shift that accounts for E and H aligning in a propagating plane wave. Constant314 (talk) 14:47, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- It is interesting to remember that Maxwell's equations were the original inspiration for special relativity. Lorentz transformation was needed to make it work. One reason to expect different phase for E and B is that in other wave systems, such as vibrations on a string, the displacement and velocity are, for a sine moving one direction on a string, 90 degrees out of phase. Note that it gets more complicated with other shapes. On the other hand, consider a standing wave on a string, such as a violin mode. In that case, the displacement nodes match the velocity nodes. Next, the same nodes for E and B is only true for an unmodulated sine going one direction. (I didn't do the math, though.) Modulation will shift the nodes. And finally, consider EM standing waves. In that case, the E nodes are 90 degrees from the B nodes. Gah4 (talk) 21:03, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- Funny story. In my undergrad E&M class, we had a lecture demonstration showing the similarity between sound waves (in an air column) and EM waves (in a coaxial cable). It was meant to show the connection between nodes and boundary conditions (close/open tube end, short/open end of the coaxial cable). But then it came out wrong. There is a voltage node at the end of a shorted cable, but a pressure antinode, as measured by a microphone. That should have been fine, but in the next lecture the same setup returned, but with a current probe on the oscilloscope. Now antinodes agree! Gah4 (talk) 21:03, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- Another thought, though, is to look at in in terms of Φ and A. That is, scalar and vector potential, which are components of a four-vector in special relativity. Gah4 (talk) 21:03, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- E relates to electric displacement current (dD/dt) like pressure relates to velocity (or maybe the other way). Constant314 (talk) 21:29, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
- I am not trying to derive the whole thing on the talk page. If I add a few more steps, dD/dt causes curl{H}. The curl operator adds 90 degrees of spacial phase shift that accounts for E and H aligning in a propagating plane wave. Constant314 (talk) 14:47, 11 August 2021 (UTC)
Derivation from Quantum Mechanics
It may be useful to discuss the derivation of Maxwell's equations from quantum mechanics. Some material on this topic is being gathered at: https://www.quora.com/Can-Maxwell%E2%80%99s-equations-be-derived-from-quantum-mechanics Including a paper at: http://www.cft.edu.pl/~birula/publ/PhotonAPP.pdf Thanks! --Lbeaumont (talk) 12:00, 27 July 2016 (UTC)
- Rather than describing the photon with a complex combination of E and B, it is more usual to describe the photon with the electromagnetic four-potential. JRSpriggs (talk) 18:05, 27 July 2016 (UTC)
Light-by-light scattering
Is it worth referring to an article suggesting an exception to the equations?
- Yes, but not here. There. YohanN7 (talk) 09:52, 6 September 2017 (UTC)
- The fourth paragraph in the lead covers the "exceptions" (as you put it) decently. YohanN7 (talk) 09:54, 6 September 2017 (UTC)
Maxwell's field equations can be formulated in the form of Dirac equation
Besides those formulations given in this article, Maxwell's field equations can also be formulated in the same form as Dirac equation. Please refer to an article entitled FORMULATION OF MAXWELL FIELD EQUATIONS FROM A SYSTEM OF LINEAR FIRST ORDER PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS posted on ResearchGate by Vu B Ho for more details.101.189.62.166 (talk) 09:01, 15 February 2018 (UTC)
- But see ResearchGate, which is criticized as a social networking site for those with institutional affiliations, and which lists predatory journals. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 09:18, 15 February 2018 (UTC)
- Might this paper be found on arXiv.org? 09:21, 15 February 2018 (UTC)
Table format
In the Formulation in SI units section, the table as of a few days ago was too big. It didn't fit in the standard Wikipedia page width, and the text was awkwardly shoehorned into narrow columns.
The current format fits into the standard width, which is a big help for readers using mobile devices. The headings are simple and obvious, and the whole table fits in one or two pages.
The meanings should absolutely NOT be deleted, because they do a great job of explaining the equations to readers.
—Coder Dan (talk) 05:13, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
User:JohnBlackburne has reverted my changes to the table format twice, even after I simplified the format. I understand that not everyone is interested in editing tables, but the original table was too big. The compact format makes the table more accessible to readers who use mobile devices or large font sizes, and the formula meanings in the table are a valuable aid in helping readers understand the formulas.
—Coder Dan (talk) 16:18, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
- The problem with your preferred format is it is largely incoprehensible. In particular the central column contains both the names and the meanings, jumbled up so it is unclear which goes with which; e.g. ""The electric flux through a closed surface is proportional to the charge inside the enclosed volume." is right next to "Gauss's law for magnetism", but they do not go together. The formulae are similarly broken up and disconnected from their headings. It’s only possible to interpret it if you already know the formulae and meanings, so know which go with which.
- Looking to address the width problem I removed the meanings from the second table as there is no point repeating them. This then looked so much better with them removed that I did the same to the first table. Again the table is vastly improved, and readers can find fuller descriptions of the meanings at #Conceptual descriptions as well as in the individual articles by clicking on the links. I think this is much better that including the meanings in the table where they don’t easily fit.--JohnBlackburnewordsdeeds 16:20, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
- > your preferred format ... is largely incoprehensible.
- I don't believe that for a second. The two-row format is simple and obvious.
- > the central column contains both the names and the meanings
- There is no "central column".
- > "The electric flux ..." is right next to "Gauss's law for magnetism", but they do not go together.
- There was a blank line between them in the original version, but you reverted that. I would be delighted to discuss minor variations in the format.
- > The formulae are similarly broken up and disconnected from their headings.
- "broken up and disconnected" is exaggeration. The added complexity is minimal.
- > It’s only possible to interpret it if you already know the formulae and meanings.
- This is pure gibberish. It sounds bad, but there's no truth to it at all.
- > I removed the meanings from the second table as there is no point repeating them.
- That's fine.
- > This then looked so much better with them removed that I did the same to the first table.
- The purpose of Wikipedia is to provide useful information, not pretty pictures.
- > readers can find fuller descriptions of the meanings at #Conceptual descriptions
- Readers also like to have convenient summaries. The meanings in the table are very helpful to readers.
- > I think this is much better that including the meanings in the table where they don’t easily fit.
- The meanings fit in the compact format just fine.
- —Coder Dan (talk) 17:13, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
- I agree with John Blackburne that this table is confusing/badly designed. Headbomb {t · c · p · b} 18:06, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
- On the other hand, I have found the meaning in words, when placed directly below the mathematical notation by Coder Dan, restate and reinforce the notation. This is especially meaningful to me when I mentally compare the equations, in their various formulations, to other other articles, such as Stokes' theorem. That said, the verbal descriptions which are currently elided in the John Blackburne version actually correspond to the integrals column. The two columns side by side really say the same thing to those of us who studied this subject in school. That suggests we might replace the partial differential column with the verbal restatement for the readers who need it (which is most readers).
- I notice that the columns currently have a minimum width at which we can no longer see both columns.--Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 19:00, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
Now that Ancheta Wis mentions it, the original table didn't really make sense, since the meanings are specific to one column.
I understand the logic behind the table format, and many technical workers display large amounts of data with large screens and small fonts, so it might not seem like a big deal. But other people use large fonts or mobile devices, so it's a huge problem for some of us.
The problem is that text is primarily horizontal in extent, whereas web pages are mostly vertical. There's a fundamental mismatch between those two shapes, and tables just makes it worse (and the meanings are too good to delete).
—Coder Dan (talk) 19:50, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
- Thank you for your rapid response to the comments. Lest we swing to a text-only format, I have to say that the tables for the relativistic and gauge formulations have their place in the article, as they serve to compress a ton of information that can be ignored at the verbal level. But the article is very suggestive when we 'read between the lines' but cannot write about here because we are editors only. I hope others get this same impression about the encyclopedia article, and are inspired to write these original thoughts elsewhere. --Ancheta Wis (talk | contribs) 20:22, 24 June 2018 (UTC)
For comparison, there's a version of the page with compact tables here.
—Coder Dan (talk) 16:07, 25 June 2018 (UTC)
Hi Andy. Other editors have been reverting tables with more than one row per entry, so I'm not sure how your most recent version will be received. Also, as Ancheta Wis pointed out, the meaning only applies to the integral form of the equations. There's a cleaned up version of the table here if you're interested.
—Coder Dan (talk) 16:15, 25 June 2018 (UTC)
- ^ Recently, scientists have described behavior in a crystalline state of matter known as spin-ice which have macroscopic behavior like magnetic monopoles. (See http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/1178868 and http://www.nature.com/nature/journal/v461/n7266/full/nature08500.html .) The divergence of B is still zero for this system, though.
- ^ J.D. Jackson. "6.11". Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). ISBN 0-471-43132-X.
- ^ "IEEEGHN: Maxwell's Equations". Ieeeghn.org. Retrieved 2008-10-19.
- ^ This is known as a duality transformation. See J.D. Jackson. "6.12". Classical Electrodynamics (3rd ed.). ISBN 0-471-43132-X..












![{\displaystyle F_{\alpha \beta }=\partial _{[\alpha }A_{\beta ]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c40c63bc2d0f08495216298514da4127a178e525)











