Portal:World
Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1White Chuck Glacier in the United States in 1973
The retreat of glaciers since 1850 is a well-documented effect of climate change. The retreat of mountain glaciers provide evidence for the rise in global temperatures since the late 19th century. Examples include mountain glaciers in western North America, Asia, the Alps in central Europe, and tropical and subtropical regions of South America and Africa. Since glacial mass is affected by long-term climatic changes, e.g. precipitation, mean temperature, and cloud cover, glacial mass changes are one of the most sensitive indicators of climate change. The retreat of glaciers is also a major reason for sea level rise. Excluding peripheral glaciers of ice sheets, the total cumulated global glacial losses over the 26 years from 1993 to 2018 were likely 5500 gigatons, or 210 gigatons per year.
On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions. Glaciers also exist in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Glacial bodies larger than 50,000 km2 (19,000 sq mi) are called ice sheets. They are several kilometers deep and obscure the underlying topography. (Full article...) -
Image 2

The FIFA World Cup, often called the World Cup, is an international association football competition among the senior men's national teams of the members of the Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA), the sport's global governing body. The tournament has been held every four years since the inaugural tournament in 1930, with the exception of 1942 and 1946 due to the Second World War. The reigning champions are Argentina, who won their third title at the 2022 tournament by defeating France.
The contest starts with the qualification phase, which takes place over the preceding three years to determine which teams qualify for the tournament phase. In the tournament phase, 32 teams compete for the title at venues within the host nation(s) over the course of about a month. The host nation(s) automatically qualify for the group stage of the tournament. The competition is scheduled to expand to 48 teams, starting with the 2026 tournament. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The largest Antarctic ozone hole recorded (September 2006)
The Montreal Protocol on Substances That Deplete the Ozone Layer is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force on 1 January 1989. Since then, it has undergone several amendments and adjustments, with revisions agreed to in 1990 (London), 1992 (Copenhagen), 1995 (Vienna), 1997 (Montreal), 1999 (Beijing), 2007 (Montreal), 2016 (Kigali) and 2018 (Quito). As a result of the international agreement, the ozone hole in Antarctica is slowly recovering. Climate projections indicate that the ozone layer will return to 1980 levels between 2040 (across much of the world) and 2066 (over Antarctica). Due to its widespread adoption and implementation, it has been hailed as an example of successful international co-operation. Former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan stated that "perhaps the single most successful international agreement to date has been the Montreal Protocol". In comparison, effective burden-sharing and solution proposals mitigating regional conflicts of interest have been among the success factors for the ozone depletion challenge, where global regulation based on the Kyoto Protocol has failed to do so. In this case of the ozone depletion challenge, there was global regulation already being installed before a scientific consensus was established. Also, overall public opinion was convinced of possible imminent risks.
The ozone treaty has been ratified by 198 parties (197 states and the European Union), making it the first universally ratified treaty in United Nations history. (Full article...) -
Image 4
The Global Positioning System (GPS), originally Navstar GPS, is a satellite-based radio navigation system owned by the United States Space Force and operated by Mission Delta 31. It is one of the global navigation satellite systems (GNSS) that provide geolocation and time information to a GPS receiver anywhere on or near the Earth where there is an unobstructed line of sight to four or more GPS satellites. It does not require the user to transmit any data, and operates independently of any telephone or Internet reception, though these technologies can enhance the usefulness of the GPS positioning information. It provides critical positioning capabilities to military, civil, and commercial users around the world. Although the United States government created, controls, and maintains the GPS system, it is freely accessible to anyone with a GPS receiver. (Full article...) -
Image 5Climate change mitigation (or decarbonisation) is action to limit the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere that cause climate change. Climate change mitigation actions include conserving energy and replacing fossil fuels with clean energy sources. Secondary mitigation strategies include changes to land use and removing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Current climate change mitigation policies are insufficient as they would still result in global warming of about 2.7 °C by 2100, significantly above the 2015 Paris Agreement's goal of limiting global warming to below 2 °C.
Solar energy and wind power can replace fossil fuels at the lowest cost compared to other renewable energy options. The availability of sunshine and wind is variable and can require electrical grid upgrades, such as using long-distance electricity transmission to group a range of power sources. Energy storage can also be used to even out power output, and demand management can limit power use when power generation is low. Cleanly generated electricity can usually replace fossil fuels for powering transportation, heating buildings, and running industrial processes. Certain processes are more difficult to decarbonise, such as air travel and cement production. Carbon capture and storage (CCS) can be an option to reduce net emissions in these circumstances, although fossil fuel power plants with CCS technology is currently a high cost climate change mitigation strategy. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The dodo became extinct during the mid-to-late 17th century due to habitat destruction, overhunting, and predation by introduced mammals. It is an often-cited example of a human-driven extinction.
The Holocene extinction, also referred to as the Anthropocene extinction, is an ongoing extinction event caused by human activities during the Holocene epoch. This extinction event spans numerous families of plants and animals, including mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and invertebrates, impacting both terrestrial and marine species. Widespread degradation of biodiversity hotspots such as coral reefs and rainforests has exacerbated the crisis. Many of these extinctions are undocumented, as the species are often undiscovered before their extinctions.
Current extinction rates are estimated at 100 to 1,000 times higher than natural background extinction rates and are accelerating. Over the past 100–200 years, biodiversity loss has reached such alarming levels that some conservation biologists now believe human activities have triggered a mass extinction, or are on the cusp of doing so. As such, after the "Big Five" mass extinctions, the Holocene extinction event has been referred to as the sixth mass extinction. However, given the recent recognition of the Capitanian mass extinction, the term seventh mass extinction has also been proposed. (Full article...) -
Image 7The history of the Internet originated in the efforts of scientists and engineers to build and interconnect computer networks. The Internet Protocol Suite, the set of rules used to communicate between networks and devices on the Internet, arose from research and development in the United States and involved international collaboration, particularly with researchers in the United Kingdom and France.
Computer science was an emerging discipline in the late 1950s that began to consider time-sharing between computer users, and later, the possibility of achieving this over wide area networks. J. C. R. Licklider developed the idea of a universal network at the Information Processing Techniques Office (IPTO) of the United States Department of Defense (DoD) Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA). Independently, Paul Baran at the RAND Corporation proposed a distributed network based on data in message blocks in the early 1960s, and Donald Davies conceived of packet switching in 1965 at the National Physical Laboratory (NPL), proposing a national commercial data network in the United Kingdom. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 2Portrait of Alfraganus in the Compilatio astronomica, 1493. Islamic astronomers began just before the 9th century to collect and translate Indian, Persian and Greek astronomical texts, adding their own astronomy and enabling later, particularly European astronomy to build on. Symbolic for the post-classical period, a period of an increasing trans-regional literary culture, particularly in the sciences, spreading and building on methods of science. (from Human history)
-
Image 4A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 5One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
-
Image 6Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 8Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 9Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 10Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago". (from History of Earth)
-
Image 11Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack, a result of globalizing maritime trade
-
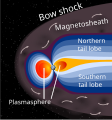
Image 12A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 13Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 14Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 15Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 17Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
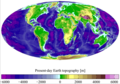
Image 18Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 19Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 20Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 21Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
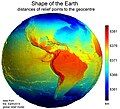
Image 22Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 23An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 25Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 27Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 28Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 29Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 31Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
-
Image 32Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 33A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 34Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
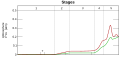
Image 35Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 36Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 37Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
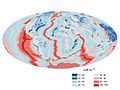
Image 39Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 40Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 42A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 44Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 45A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 46Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 48Successive dispersals of Homo erectus (yellow), Homo neanderthalensis (ochre) during Out of Africa I and Homo sapiens (red, Out of Africa II), with the numbers of years since they appeared before present. (from Human history)
-
Image 49The first airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 50Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 51Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 54Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 5513th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry)
-
Image 58Model of a Australopithecus afarensis at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. This reconstruction depicts the facultative bipedalism hypothesis, indicated by the use of the tree for stabilization. (from Human history)
-
Image 61Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 62A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 63A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
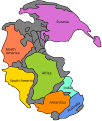
Image 64Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 65An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
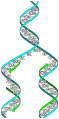
Image 66The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 67Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 69Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 72Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 77A pillar at Neolithic Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 79Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 80An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 83A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 84Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 85The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 87A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 88A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
Megacities of the world - show another
Lahore (/ləˈhɔːr/ lə-HOR; Punjabi: لہور [lɔː˩˥ɾ]; Urdu: لاہور [laːˈɦɔːɾ] ⓘ) is the capital and largest city of the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the second largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and 27th largest in the world, with a population of over 14 million. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial, educational and economic hubs. It has been the historic capital and cultural center of the wider Punjab region, and is one of Pakistan's most socially liberal, progressive, and cosmopolitan cities.
Lahore's origin dates back to antiquity. The city has been inhabited for around two millennia, although it rose to prominence in the late 10th century with the establishment of the Walled City, its fortified interior. Lahore served as the capital of several empires during the medieval era, including the Hindu Shahis, Ghaznavid Empire and Delhi Sultanate. It reached the height of its splendor under the Mughal Empire between the late 16th and early 18th centuries, being its capital city for many years. During this period, it was one of the largest cities in the world. The city was captured by the forces of the Afsharid ruler Nader Shah in 1739. Although the Mughal authority was re-established, it fell into a period of decay while being contested among the Afghans and the Sikhs between 1748 and 1798. Lahore eventually became the capital of the Sikh Empire in the early 19th century, regaining some of its lost grandeur. Lahore was annexed to the British Raj in 1849 and became the capital of British Punjab. Lahore was central to the independence movements of both India and Pakistan, with the city being the site of both the Declaration of Indian Independence and the resolution calling for the establishment of Pakistan. It experienced some of the worst rioting during the Partition period preceding Pakistan's independence. Following the success of the Pakistan Movement and the subsequent partition of British India in 1947, Lahore was declared the capital of Pakistan's Punjab province. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that the Central Powers brought their armies under a supreme headquarters in September 1916, 18 months before the Allies did the same?
- ... that British physician James A. Glover found that "spacing-out" beds prevented epidemics of meningitis in the military during World War I?
- ... that alongside a 7th-century BC Phoenician shipwreck, two additional wrecks from various historical periods were unearthed in Bajo de la Campana, situated off the coast of Cartagena, Spain?
- ... that in 1991, Juan López Mella was the first Spanish rider to achieve a podium place in the Superbike World Championship?
- ... that the New York State Pavilion, one of the most popular attractions at the 1964 World's Fair, later stored hazardous waste?
- ... that the archaeologist Alan Wace worked undercover for British intelligence during both world wars?
- ... that youthful Second World War resistance leader Jean-Pierre Lévy was advised by the Free French intelligence service to dye his hair grey to appear older?
- ... that examples of artificial planets in science fiction include Riverworld, the Well World, and the Death Star?
Countries of the world - show another

Saint Vincent and the Grenadines (/ˌɡrɛn.əˈdiːnz/ ⓘ GREN-ə-DEENZ), sometimes known simply as Saint Vincent or SVG, is an island country in the eastern Caribbean. It is located in the southeast Windward Islands of the Lesser Antilles, which lie in the West Indies, at the southern end of the eastern border between the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean. To the north lies Saint Lucia, to the east is Barbados, and Grenada lies to the south.
Spanning a land area of 369 km2 (142 sq mi), most of its territory consists of the northernmost island of Saint Vincent, which includes the capital and largest city, Kingstown. To the south lie two-thirds of the northern part of the Grenadines, a chain of 32 smaller islands; the remaining southern third make up Grenada. Seven of the islands are inhabited, of which the largest and most populous are Bequia, Mustique, Canouan, and Union Island. (Full article...)
Eighth Wonder of the World is an unofficial title sometimes given to new buildings, structures, projects, designs or even people that are deemed to be comparable to the seven Wonders of the World. (Full article...)
Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1Protected areas of Slovakia are areas that need protection because of their environmental, historical or cultural value to the nation. Protected areas in Slovakia are managed by institutions and organizations governed by the Ministry of the Environment.
Types of protected areas:- National Park (Slovak: Národný park; abbr. NP)
- Protected Landscape Area (Chránená krajinná oblasť; CHKO)
- National Nature Reserve (Národná prírodná rezervácia; NPR)
- Nature Reserve (Prírodná rezervácia; PR)
- National Nature Monument (Národná prírodná pamiatka; NPP)
- Nature Monument (Prírodná pamiatka; PP)
- Protected Site (Chránený areál; CHA)
- Protected Landscape Element (Chránený krajinný prvok; CHKP)
- Protected Bird Area* (Chránené vtáčie územie; CHVÚ) *Technically Special Protection Area (SPA) under the EU Bird's Directive
- Protected Tree (Chránený strom; CHS)
-
Image 2Greece is characterized by an extremely fragmented, rugged landscape hosting a great diversity of ecosystems and an outstanding biodiversity. Almost 5% of its extensive coastline consists of ecologically sensitive wetlands. Two thirds of the total population live no further than 2 km from the coast and most of the important urban centers are coastal, while almost all of the tourist infrastructure is divided among islands and the coastal mainland. (Full article...)
-
Image 3
-
Image 4

The Valley of the Giants skywalk at Walpole-Nornalup National Park
Western Australia is the second largest country subdivision in the world.
As of 2022, based on the latest Collaborative Australian Protected Areas Database report, it contains 1857 separate land-based protected areas with a total area of 76,142,710 hectares (188,152,700 acres), accounting for just over 30 percent of the state's land mass. By area, Indigenous Protected Areas account for the largest part of this, almost 67 percent while, by number, nature reserves hold the majority with two-third of all land-based protected areas being nature reserves. (Full article...) -
Image 5Protected areas of Libya include any geographical area protected for a specific use.
Most protected areas are intended for the conservation of flora and fauna. Libya's national parks and nature reserves are maintained by the "Technical Committee of Wildlife and National Parks" which was created in 1990, as part of the General Secretariat of Agricultural Reclamation and Land Reform. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Viru bog in Lahemaa National Park
Protected areas in Estonia are national parks, nature reserves and landscape protection areas (nature parks).
Estonia has five national parks, 167 nature reserves and 152 landscape conservation areas. In addition, there are 116 (118) protected areas with an old (Soviet-era) protection regulation and 537 parks. In total, 18.1% of Estonia are protected nature areas, with Lääne County having the highest percentage (32%) and Põlva County the lowest percentage of protected areas, about 9%. (Full article...) -
Image 7

Kejimkujik National Park, Little River
This is a list of protected areas of Nova Scotia. (Full article...) -
Image 8The Ulyanovsk Oblast in Russia contains about 118 protected natural areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 9
-
Image 10

Entrance to Tanintharyi Nature Reserve.
This list of protected areas of Myanmar includes national parks, wildlife sanctuaries and botanical gardens that were established since 1927. (Full article...) -
Image 11The state of Johor in Malaysia is noted for its national parks and forest reserves which preserve virgin rainforests known for its biodiversity and endangered species of animals.
Mangrove swamps and coral reefs are also protected within these parks. (Full article...) -
Image 12
-
Image 13The Protected areas of New South Wales include both terrestrial and marine protected areas. As of June 2020[update] there are 225 national parks in New South Wales. A number established since the late 1970s followed campaigns by local residents and environmentalists.
Based on the Collaborative Australian Protected Area Database (CAPAD) 2020 data there are 2136 separate terrestrial protected areas with a total land area of 7,696,641 hectares (19,018,810 acres) (9.61% of the state's area). CAPAD data also shows 18 marine protected areas with a total area of 348,849 hectares (862,020 acres), covering 39.63% of NSW waters. (Full article...) -
Image 14

The sun over the Lake Niassa Reserve
Protected areas in Mozambique are known as conservation areas, and are currently grouped into national parks, national reserves, forest reserves, wildlife utilisation areas (coutadas), community conservation areas, and private game farms (fazendas de bravio). There are also a number of areas that have been declared as protected areas under a variety of different legislation, which for reasons of simplicity are here grouped together as "other protected areas." Under the Conservation Law of 2014 (Law 16/2014 of June 20), protected areas will need to be reclassified into a much more flexible series of new categories which are closer to the international system used by the IUCN. International initiatives such as transfrontier parks are grouped at the end of the page. (Full article...) -
Image 15Papua New Guinea is home to several protected areas, which receive protection because of their environmental, cultural or similar value.
The total area of Papua New Guinea protected territories is 14,330 km2 (5,530 sq mi), which amounts to approximately 3.07% of the country's territory. The total number of protected areas as 2018 is 71. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
Image 1Time zones of the world
-
Image 2The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 3Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 4United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 5Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
-
Image 6Mollweide projection of the world
-
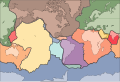
Image 7A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 8The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 91516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Portals with undated maintenance templates
- Manually maintained portal pages with no date
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 201–500 articles in article list
- Pages with Punjabi IPA
- Pages with Urdu IPA
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Portals needing placement of incoming links