Portal:World
Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
The World Portal

The world is the totality of entities, the whole of reality, or everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique, while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object, while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world or universe is commonly defined as "the totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon, or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind.
Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God, or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world, while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole, or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole, and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1
 Least developed countries (designated by the UN as of 2023)Former least developed countries
Least developed countries (designated by the UN as of 2023)Former least developed countries
The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) on 18 November 1971.
A country is classified among the Least Developed Countries if it meets three criteria:- Poverty – adjustable criterion based on Gross national income (GNI) per capita averaged over three years. As of 2018[update], a country must have GNI per capita less than US$1,025 to be included on the list, and over $1,230 to graduate from it.
- Human resource weakness (based on indicators of nutrition, health, education and adult literacy).
- Economic vulnerability (based on instability of agricultural production, instability of exports of goods and services, economic importance of non-traditional activities, merchandise export concentration, handicap of economic smallness, and the percentage of population displaced by natural disasters).
-
Image 2

Map of global water stress (a symptom of water scarcity) in 2019. Water stress is the ratio of water use relative to water availability and is therefore a demand-driven scarcity.
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity. One is physical. The other is economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands. This includes water needed for ecosystems to function. Regions with a desert climate often face physical water scarcity. Central Asia, West Asia, and North Africa are examples of arid areas. Economic water scarcity results from a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources. It also results from weak human capacity to meet water demand. Many people in Sub-Saharan Africa are living with economic water scarcity.
There is enough freshwater available globally and averaged over the year to meet demand. As such, water scarcity is caused by a mismatch between when and where people need water, and when and where it is available. This can happen due to an increase in the number of people in a region, changing living conditions and diets, and expansion of irrigated agriculture. Climate change (including droughts or floods), deforestation, water pollution and wasteful use of water can also mean there is not enough water. These variations in scarcity may also be a function of prevailing economic policy and planning approaches. (Full article...) -
Image 3NATO and Warsaw Pact states during the Cold War era
The Cold War was a period of global geopolitical tension and struggle for ideological dominance and economic influence between the United States and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. It started in 1947 and lasted until the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991. The term cold war is used because there was no direct fighting between the two superpowers, though each supported opposing sides in major regional conflicts known as proxy wars. Aside from the nuclear arms race and conventional military deployment, the struggle for supremacy was expressed indirectly via psychological warfare, propaganda campaigns, espionage, far-reaching embargoes, sports diplomacy, and technological competitions such as the Space Race.
After World War II, the USSR installed satellite governments in the territories of Eastern and Central Europe it had occupied, promoted the spread of communism to North Korea in 1948, and created an alliance with the People's Republic of China in 1949. The US declared the Truman Doctrine of "containment" in 1947, launched the Marshall Plan in 1948 to assist in Western Europe's economic recovery, and founded the NATO military alliance in 1949 (which was matched by the Soviet-led Warsaw Pact in 1955). A major proxy war was the Korean War of 1950 to 1953, which ended in stalemate. (Full article...) -
Image 4Global change in broad sense refers to planetary-scale changes in the Earth system. It is most commonly used to encompass the variety of changes connected to the rapid increase in human activities which started around mid-20th century, i.e., the Great Acceleration. While the concept stems from research on the climate change, it is used to adopt a more holistic view of the observed changes. Global change refers to the changes of the Earth system, treated in its entirety with interacting physicochemical and biological components as well as the impact human societies have on the components and vice versa. Therefore, the changes are studied through means of Earth system science. (Full article...)
-
Image 5Superpower describes a sovereign state or supranational union that holds a dominant position characterized by the ability to exert influence and project power on a global scale. This is done through the combined means of economic, military, technological, political, and cultural strength as well as diplomatic and soft power influence. Traditionally, superpowers are preeminent among the great powers. While a great power state is capable of exerting its influence globally, superpowers are states so influential that no significant action can be taken by the global community without first considering the positions of the superpowers on the issue.
In 1944, during World War II, the term was first applied to the British Empire, the Soviet Union, and the United States. During the Cold War, the British Empire dissolved, leaving the United States and the Soviet Union to dominate world affairs. At the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991, the United States became the world's sole superpower, a position sometimes referred to as that of a "hyperpower". Since the late 2010s and into the 2020s, China has increasingly been described as an emerging superpower or even an established one, as China represents the "biggest geopolitical test of the 21st century" to the United States, as it is "the only country with enough power to jeopardize the current global order". (Full article...) -
Image 6

Great powers are recognized in several international structures, including the United Nations Security Council.
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power influence, which may cause middle or small powers to consider the great powers' opinions before taking actions of their own. International relations theorists have posited that great power status can be characterized into power capabilities, spatial aspects, and status dimensions.
While some nations are widely considered to be great powers, there is considerable debate on the exact criteria of great power status. Historically, the status of great powers has been formally recognized in organizations such as the Congress of Vienna of 1814–1815 or the United Nations Security Council, of which permanent members are: China, France, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The United Nations Security Council, NATO Quint, the G7, the BRICS, and the Contact Group have all been described as great power concerts. (Full article...) -
Image 7
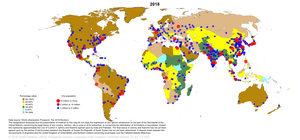
Global urbanization map showing the percentage of urbanization and the biggest global population centres per country in 2018, based on UN estimates.
Urbanization (or urbanisation in British English) is the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It can also mean population growth in urban areas instead of rural ones. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas.
Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth. Urbanization refers to the proportion of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the absolute number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050 about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. This is predicted to generate artificial scarcities of land, lack of drinking water, playgrounds and so on for most urban dwellers. The predicted urban population growth is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all global population growth from 2017 to 2030 will be by cities, with about 1.1 billion new urbanites over the next 10 years. In the long term, urbanization is expected to significantly impact the quality of life in negative ways. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 1Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 213th-century French historiated initial with the three classes of medieval society: those who prayed (the clergy), those who fought (the knights), and those who worked (the peasantry)
-
Image 3Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 6Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 7Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 8Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 9A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 10Cuneiform inscription, eastern Turkey
-
Image 11Earth's history with time-spans of the eons to scale. Ma means "million years ago". (from History of Earth)
-
Image 12Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 13Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 14Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 16A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 17Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 18Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
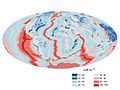
Image 19A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 21Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 22The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 23Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 24Model of a Australopithecus afarensis at the Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History. This reconstruction depicts the facultative bipedalism hypothesis, indicated by the use of the tree for stabilization. (from Human history)
-
Image 30A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 31Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
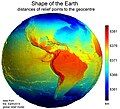
Image 32Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 33Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 34Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 35Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 36Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 37A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 39Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 41Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 42The first airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 45Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 47The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 48Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack, a result of globalizing maritime trade
-
Image 49An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 50Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 51Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 52Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 54Portrait of Alfraganus in the Compilatio astronomica, 1493. Islamic astronomers began just before the 9th century to collect and translate Indian, Persian and Greek astronomical texts, adding their own astronomy and enabling later, particularly European astronomy to build on. Symbolic for the post-classical period, a period of an increasing trans-regional literary culture, particularly in the sciences, spreading and building on methods of science. (from Human history)
-
Image 55A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 57A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 59A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
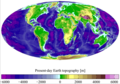
Image 62Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 63Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
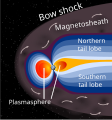
Image 64A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 66Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 67A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 68A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69One of the eleven Rock-hewn Churches of Lalibela constructed during the Zagwe dynasty in Ethiopia (from Human history)
-
Image 71Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 72Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 73An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 75Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 76Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 77An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 79Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 81Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 82Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 84Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 87Successive dispersals of Homo erectus (yellow), Homo neanderthalensis (ochre) during Out of Africa I and Homo sapiens (red, Out of Africa II), with the numbers of years since they appeared before present. (from Human history)
-
Image 88A pillar at Neolithic Göbekli Tepe
Megacities of the world - show another
Xiamen, historically romanized as Amoy, is a sub-provincial city in southeastern Fujian, People's Republic of China, beside the Taiwan Strait. It is divided into six districts: Huli, Siming, Jimei, Tong'an, Haicang, and Xiang'an. All together, these cover an area of 1,700.61 square kilometers (656.61 sq mi) with a population of 5,163,970 as of 2020 and estimated at 5.308 million as of 31 December 2022. The urbanized area of the city has spread from its original island to include most parts of all six of its districts, as well as 4 Zhangzhou districts (Xiangcheng, Longwen, Longhai and Changtai), which form a built-up area of 7,284,148 inhabitants. This area also connects with Quanzhou in the north, making up a metropolis of nearly ten million people. The Kinmen Islands (Quemoy) administered by the Republic of China (Taiwan) lie less than 6 kilometers (4 mi) away separated by Xiamen Bay. As part of the Opening Up Policy under Deng Xiaoping, Xiamen became one of China's original four special economic zones opened to foreign investment and trade in the early 1980s.
Xiamen Island possessed a major international seaport. The port of Xiamen is a well-developed first-class trunk line port in the Asia-Pacific region. It is ranked the 7th-largest container port in China and ranks 14th in the world. It is the 4th port in China with the capacity to handle 6th-generation large container ships. On 31 August 2010, Xiamen Port incorporated the neighboring port of Zhangzhou to form the largest port of China's Southeast. Ever since the 12th century, Xiamen was also an important origin for many migrants to Singapore, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines. The overseas Chinese used to support Xiamen's educational and cultural institutions. Xiamen is classified as a Large-Port Metropolis. (Full article...)
Did you know - load new batch

- ... that the satellite TRUTHS is planned to enable the precise calibration of Earth observation data from other satellites?
- ... that English missionary Reverend Thomas Sparshott co-wrote a book in Swahili, and his daughter Margaret Elwyn Sparshott was responsible as matron for 22 hospitals in World War I?
- ... that James B. Tapp was the first United States Army Air Forces pilot to be recognized as a flying ace for flying very-long-range missions over Japan in P-51s during World War II?
- ... that there was an organism from which all current life on Earth is descended?
- ... that two Wisconsin radio stations purchased and reassembled the Wisconsin Pavilion from the 1964 New York World's Fair for use as their studios?
- ... that in 2022, Briton Charlotte Payne broke the world record for a hammer throw by a deaf woman by almost 5 metres (16 ft)?
- ... that Swiss archaeologist Marguerite Gautier-van Berchem created a service for the International Committee of the Red Cross to help prisoners of war from the French colonies during World War II?
- ... that an Elvin man sang Poems and Songs of Middle Earth?
Countries of the world - show another

Kiribati (/ˈkɪrɪbæs/ ⓘ KIRR-i-bass, Gilbertese: [kiɾibas]), officially the Republic of Kiribati (Gilbertese: Ribaberiki Kiribati), is an island country in the Micronesia subregion of Oceania in the central Pacific Ocean. Its permanent population is over 119,000 as of the 2020 census, and more than half live on Tarawa atoll. The state comprises 32 atolls and one remote raised coral island, Banaba. Its total land area is 811 km2 (313 sq mi) dispersed over 3,441,810 km2 (1,328,890 sq mi) of ocean.
The islands' spread straddles the equator and the 180th meridian, making Kiribati the only country in the world located simultaneously in all four hemispheres: the Northern, Southern, Western, and Eastern hemispheres. The International Date Line goes around Kiribati and swings far to the east, almost reaching 150°W. This brings Kiribati's easternmost islands, the southern Line Islands south of Hawaii, into the same day as the Gilbert Islands and places them in the most advanced time zone on Earth: UTC+14. (Full article...)
The Seven Wonders of Russia as determined by a project organized by the newspaper Izvestia, Radio Mayak, and the television channel Russia. The competition took place in three stages from 1 October 2007 through 1 June 2008, with the final results declared in Moscow's Red Square on 12 June 2008. (Full article...)
Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
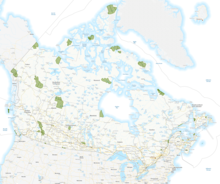
Image 1This is a list of protected areas of Afghanistan.
- Ab-i-Estada Nature Reserve, Ghazni Province
- Ajar Valley Nature Reserve, Bamyan Province
- Bamiyan National Heritage Park, Bamyan Province
- Bamiyan Plateau Protected Landscape, Bamyan Province
- Band-e Amir National Park, Bamyan Province
- Darqad (Takhar) Wildlife Reserve, Takhar Province
- Dasht-i-Nawar Waterfowl Sanctuary, Ghazni Province
- Hamun-i-Puzak Waterfowl Sanctuary, Farah and Nimroz provinces
- Imam Sahib (Kunduz) Wildlife Reserve, Kunduz Province
- Khulm Landmark Protected Area, Balkh Province
- Koh-e Baba (Shah Foladi) Protected Landscape, Bamyan province
- Kol-i-Hashmat Khan Waterfowl Sanctuary, Kabul Province
- Northwest Afghanistan Game Managed Reserve, Herat Province
- Nuristan National Park and Wildlife Reserve, Nuristan Province
- Pamir-i-Buzurg Wildlife Reserve, Badakhshan Province
- Registan Desert Wildlife Managed Reserve, Kandahar Province
- Wakhan National Park, Badakhshan Province
- Zadran National Reserve, Paktia Province
-
Image 2

Wales, a country that is part of the United Kingdom, contains protected areas under various designations. The largest designation by land area is Wales' three national parks, followed by the five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (sometimes collectively the "Designated Landscapes of Wales").
Among these protected areas is Snowdonia (Eryri), Wales' first and the UK's third designated national park, and the Gower AONB covering parts of the Gower Peninsula being both Wales' and the UK's first Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB), as well as smaller designations. (Full article...) -
Image 3

The protected areas of Bhutan are its national parks, nature preserves, and wildlife sanctuaries. Most of these protected areas were first set aside in the 1960s, originally covering most of the northern and southern regions of Bhutan. Today, protected areas cover more than 42% of the kingdom, mostly in the northern regions. Protected areas also line most of Bhutan's international borders with China and India. (Full article...) -
Image 4The country of Burundi in Africa has the following national parks and other protected areas. (Full article...)
-
Image 5

There are numerous parks throughout the sovereign island country of Singapore. This is a list of parks in Singapore that currently exist and have articles on Wikipedia. Most parks in Singapore are managed by the National Parks Board, although smaller, neighbourhood parks are managed by the Housing Development Board. Most of these parks are connected via the Park Connector Network (PCN) walking/running/cycling paths. (Full article...) -
Image 6The National Parks of Argentina make up a network of 35 national parks in Argentina. The parks cover a very varied set of terrains and biotopes, from Baritú National Park on the northern border with Bolivia to Tierra del Fuego National Park in the far south of the continent. The Administración de Parques Nacionales (National Parks Administration) is the agency that preserves and manages these national parks along with Natural monuments and National Reserves within the country.
The headquarters of the National Parks Service are in downtown Buenos Aires, on Santa Fe Avenue. A library and information centre are open to the public. The administration also covers the national monuments, such as the Jaramillo Petrified Forest, and natural and educational reserves. (Full article...) -
Image 7
This is a list of protected areas of Yukon. The Yukon, formerly called Yukon Territory and sometimes referred to as just Yukon is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 35,874 people as of the 2016 Census. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Centre for Nature Education at the Białowieża National Park, Poland
Protected areas of Poland include the following categories, as defined by the Act on Protection of Nature (Polish: Ustawa o ochronie przyrody) of 16 April 2004, by the Polish Parliament: (Full article...) -
Image 10
Mombacho Volcano Natural Reserve
The protected areas of Nicaragua are areas that have natural beauty or significance and are protected by Nicaragua. Nicaragua has 78 protected areas that cover 22,422 km2, about 17.3% of the nations landmass. The National System of Protected Areas (SINAP) is administered by the Ministry of the Environment and Natural Resources (MARENA). (Full article...) -
Image 11Kentucky's system of 44 state parks has been referred to as "the nation's finest" and experiences more repeat business annually than those of any other U.S. state. The state's diverse geography provides a variety of environments to experience. From mountain lakes to expansive caves to forests teeming with wildlife, park-goers have their choice of attractions, and they are all within a day's drive of each other.
Unless otherwise specified, data in the following lists are taken from Kentucky State Parks by Bill Bailey. (Full article...) -
Image 12Protected areas of West Bengal cover 4% of the state area. Forests make up 14% of the geographical area of West Bengal, which is lower than the national average of 33%. West Bengal has a wide variety of fauna, including Bengal tigers, Indian leopards, sloth and Himalayan black bears, chital and sambar (deer), Indian boars, pygmy hogs, Indian elephants, Indian peafowl, great Indian hornbills, Eurasian spoonbills, brahminy ducks, king and Indian cobras, white-lipped pit viper, Indian and reticulated pythons, mugger crocodiles, saltwater crocodiles, gharials, and many more. A huge montane forest, Dooars, is situated in the Northern West Bengal districts of Alipur Duar, Darjeeling, and Kalimpong. Part of the world's largest mangrove forest, Sundarbans, is located in southern West Bengal.
There are 6 national parks and 15 wildlife sanctuaries in West Bengal. (Full article...) -
Image 13This is a list of protected areas of Romania.
About 5.18% of the area of Romania has a protected status (12,360 km2), including the Danube Delta, which makes half of these areas (2.43% of Romania's area). (Full article...) -
Image 14This is a list of protected areas of Cambodia.
A total of 8 forms of protected areas are recognized under the Cambodian Protected Area Law of 2008. These are: (Full article...) -
Image 15
Selected world maps
-
Image 1United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 2Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
-
Image 3Mollweide projection of the world
-
Image 4The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 5Time zones of the world
-
Image 6The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 7Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
Image 81516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
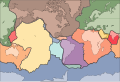
Image 9A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
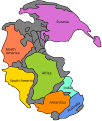
Continents of Earth | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Cenozoic Era (present–66.0 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mesozoic Era (66.0–252 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Paleozoic Era (252–539 Ma) |
| ||||||||||||
| Proterozoic Eon (539 Ma–2.5 Ga) |
| ||||||||||||
| Archean Eon (2.5–4 Ga) | |||||||||||||
| Hadean Eon (4–4.6 Ga) | |||||||||||||
ka = kiloannum (thousand years ago); Ma = megaannum (million years ago); Ga = gigaannum (billion years ago). See also: Geologic time scale • | |||||||||||||
| City proper | |
|---|---|
| Metropolitan area | |
| Urban area/agglomeration | |
| Historical | |
| Related articles | |
| Locations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Related | ||
| Retrospectively recognized expositions | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BIE-recognized Universal expositions | |||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized specialized expositions |
| ||||||||||||
| BIE-recognized horticultural exhibitions (AIPH) | |||||||||||||
| Not BIE- recognized |
| ||||||||||||
†Postponed to 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic | |||||||||||||
| Confederations | |
|---|---|
| World Championships | |
| World Cup | |
| Special events | |
| Presidents |
|
| Awards | |
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||
Economic classification of countries | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three-World Model | |||||
| Gross domestic product (GDP) |
| ||||
| Gross national income (GNI) | |||||
| Wages | |||||
| Wealth | |||||
| Other national accounts | |||||
| Human development | |||||
| Digital divide | |||||
| Net international investment position (NIIP) | |||||
| Technological |
| ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociological | |||||
| Ecological |
| ||||
| Biological |
| ||||
| Astronomical | |||||
| Eschatological |
| ||||
| Others |
| ||||
| Fictional | |||||
| Organizations | |||||
| Theatres |
| ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Principal participants |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspects |
| ||||||||||||||||||
| General |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Participants |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Timeline |
| ||||||||||||||||
Categories
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
- Pages using the Phonos extension
- Portals with undated maintenance templates
- Manually maintained portal pages with no date
- All manually maintained portal pages
- Portals with triaged subpages
- All portals with triaged subpages
- Portals with named maintainer
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 201–500 articles in article list
- Pages including recorded pronunciations
- Pages with Gilbertese IPA
- Automated article-slideshow portals with 101–200 articles in article list
- Portals needing placement of incoming links

![Image 1 Least developed countries (designated by the UN as of 2023) Former least developed countries The least developed countries (LDCs) are developing countries listed by the United Nations that exhibit the lowest indicators of socioeconomic development. The concept of LDCs originated in the late 1960s and the first group of LDCs was listed by the UN in its resolution 2768 (XXVI) on 18 November 1971. A country is classified among the Least Developed Countries if it meets three criteria: Poverty – adjustable criterion based on Gross national income (GNI) per capita averaged over three years. As of 2018[update], a country must have GNI per capita less than US$1,025 to be included on the list, and over $1,230 to graduate from it. Human resource weakness (based on indicators of nutrition, health, education and adult literacy). Economic vulnerability (based on instability of agricultural production, instability of exports of goods and services, economic importance of non-traditional activities, merchandise export concentration, handicap of economic smallness, and the percentage of population displaced by natural disasters). (Full article...)](/uploads/wikipedia/en/d/d2/Blank.png?auto=webp)