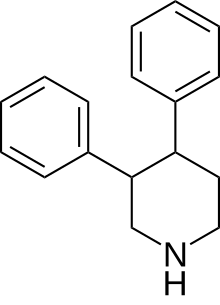
3,4-Diphenylpiperidine
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H19N |
| Molar mass | 237.346 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
The 3,4-Diphenylpiperidine class of antidepressants was invented by Serge Petit and Jacques Dreux of French Hoechst in the 1980’s-1990’s.[1][2][3][4][5]
It is a positional isomer of the gem-substituted 4,4-diphenylpiperidine [34273-01-3], which is the secondary amine of budipine, prodipine & medipine.
SAR analogy
[edit]Structure activity relationship can be drawn to 2,3-Diphenyltropanes were reported at RTI.[6]
Further SAR analogy can be drawn to nocaine, which is a piperidine homolog of RTI-31.
3,4-Diphenylpyrrolidine[7] & 3,4-diphenylazepane are both positional isomers that have been reported in separate studies. The lactam precursor, 3,4-diphenylpyrrolidin-2-one was already fully active as an antidepressant/anxiolytic.[8] Details of its synthesis are also discussed in separate patents.[9][10]
The similarity to 3,4-Diphenylquinuclidine is clearly noticeable.
A somewhat related agent is (cis)-1,6-Diphenyl-3-aza-bicyclo(3.1.0)hexane. However, it is the geminally substituted positional isomer, 6,6-Diphenyl-3-azabicyclo(3.1.0)hexane, that is discussed in a 1962 patent.[11]
SAR similarity occurs to another Hoechst compound, PC13469647.[12] The precursor compound is made by the same pathway as other compounds from Hoechst (this compound has been tentatively been called Piprozac).[13]
The unreduced lactam is very similar to a similar Hoechst compound called Lomevactone.
Note: the trans-3’,4’-dichloro lactam analog (Ex 19) was tabulated to be the most powerful psychostimulant out of those that were tested. The starting cinnamonitrile for this was synthesized in the LR-5182 patent and therefore has dual use.
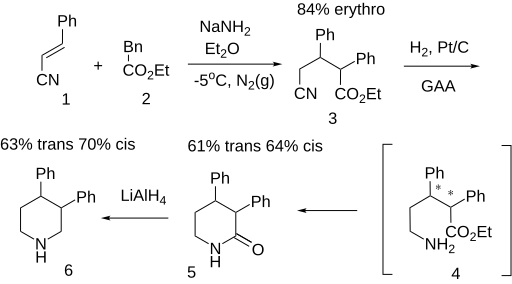
Synthesis
[edit]Note: The intermediate nitrile-esters have use for the treatment of acute and chronic renal insufficiency.
References
[edit]- ^ Serge Petit, et al. EP0273199 (1988 to Sanofi Aventis France).
- ^ Jacques Dreux & Serge Petit, US4785007 (1988 to Sanofi Aventis France).
- ^ Jacques Prof. Dreux & Serge Petit, EP0203308 (1986 to Sanofi Aventis France).
- ^ Petit, S., Nallet, J., Guillard, M., Dreux, J., Chermat, R., Poncelet, M., Bulach, C., Simon, P. (October 1990). "Synthèses et activités psychotropes de 3,4-diarylpiperidin-2-ones: corrélation structure-activité". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 25 (8): 641–652. doi:10.1016/0223-5234(90)90129-Q.
- ^ Petit, S., Nallet, J., Guillard, M., Dreux, J., Chermat, R., Poncelet, M., Bulach, C., Simon, P., Fontaine, C., Barthelmebs, M., Imbs, J. (January 1991). "Synthèses et activités psychotropes de 3,4-diarylpipéridines. Corrélation structure-activité et recherche d'une activité antihypertensive". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 26 (1): 19–32. doi:10.1016/0223-5234(91)90209-6.
- ^ Chang, A.-C., Burgess, J. P., Mascarella, S. W., Abraham, P., Kuhar, M. J., Carroll, F. I. (1 April 1997). "Synthesis and Transporter Binding Properties of 2,3-Diphenyltropane Stereoisomers. Comparison to 3β-Phenyltropane-2β-carboxylic Acid Esters". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 40 (8): 1247–1251. doi:10.1021/jm960703k.
- ^ Villani Frank John, Grove Cedar, & Sperber Nathan, US2852526 (1958 to Merck Sharp and Dohme LLC).
- ^ Joseph Honore Strubbe & Raymond Armand Linz, U.S. patent 3,956,314 (1976 to UCB SA).
- ^ Peter Liestal Ch Hofer, GB2028307 (1983 to Mundipharma AG).
- ^ Peter Hofer, U.S. patent 4,443,616 (1984 to Purdue Frederick Co).
- ^ Mehta Nariman Bomanshaw, Russell Peter Byrom, Baltzly Richard, US3065230 (1962 to Bur-roughs Wellcome Co).
- ^ Solomon S. Klioze, US4544745 (1985 to Aventis Pharmaceuticals Inc).
- ^ EP0014997 idem Solomon Samuel Klioze & Frederick Jacob Ehrgott, US4216218, US4302590, US4312876, US4382141, US4424357 (1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984 all to Hoechst AG).
