ZNF816
| ZNF816 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | ZNF816, ZNF816A, zinc finger protein 816 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | HomoloGene: 134445; GeneCards: ZNF816; OMA:ZNF816 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Zinc Finger Protein 816 (ZNF816) is a protein encoded by the ZNF816 gene, located on chromosome 19 in humans.
Gene
[edit]The ZNF816 gene is located on the minus-strand of chromosome 19, cytogenetic band 19q13.41[3]. It spans 35,746 base pairs, from 52,927,135 to 52,962,881, containing 5 exons[3].
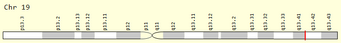
Transcripts
[edit]ZNF816 has three transcript variants, the longest is 2,711 base pairs, with 5 exons[5]. The other two have 4 exons, while all three isoforms encode 651 amino acids. The molecular weight and isoelectric point of is consistent across all three isoforms.
| Isoform number | AC# | mRNA length (base pairs) | Exons | AC# | Protein Length (Amino Acids) |
| 1 | NM_001031665 | 2711 | 5 | NP_001026835 | 651 |
| 2 | NM_001202456.3 | 2570 | 4 | NP_001189385 | 651 |
| 3 | NM_001202457.3 | 2560 | 4 | NP_001189386.1 | 651 |
Proteins
[edit]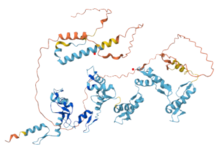

The product protein of the ZNF816 gene is 651 amino acids in length, with a predicted molecular weight of 75.7 kDa and an isoelectric point of 9.44[6].
Domains
[edit]ZNF816 has a Krüppel-associated box[7], which is characterized by a KRAB domain and an array of fifteen C2H2 Zinc fingers. This domain suppresses transcription by recruiting co-repressor proteins, which create heterochromatin, blocking RNA polymerase from accessing the gene. The amino acid sequence includes six disordered regions[8], and eight protein binding sites[8].
Structure
[edit]The predicted secondary structure of ZNF816 from AlphaFold[9] consists of mainly alpha helices, from the C2H2 zinc finger motifs. The tertiary structure of ZNF816 was predicted by iTasser[10] and annotated (Icn3D[11]) according to the characteristics of other zinc finger proteins and prominent domains.
Gene Level Regulation
[edit]ZNF816 shows a moderately variable expression pattern, with detectable levels in most tissues. While some tissues, like the adrenal gland, testes, thyroid, and salivary gland, exhibit relatively higher expression[12], ZNF816 is generally expressed across a wide range of tissues.
RNA-Seq Data
[edit]RNA-seq data[13] confirm that ZNF816 is broadly expressed at varying levels across tissues. In normal tissues, it shows moderate to high mRNA levels, suggesting consistent transcriptional activity. Data from 20 human tissues further support the gene's widespread expression, with some variability in transcription levels.
In Situ Hybridization
[edit]In situ hybridization results from the Allen Brain Atlas[14] confirm widespread expression across human brain regions, including the hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum.
Protein Localization and Abundance
[edit]Immunohistochemistry data show ZNF816 protein is localized in the nucleus (95.7%)[15] across various human tissues. It is seen to be expressed at high levels relative to other proteins[16].
Homology/Evolution
[edit]Paralogs
[edit]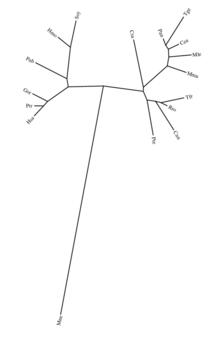
ZNF816 has several paralogs within the zinc finger protein family. Its closest paralog is ZNF813, which shares 69.74% sequence identity. A more distant paralog is ZNF836, with 52.03% identity[18]. These paralogs likely maintain similar roles in transcriptional regulation, reflecting the conserved functions characteristic of zinc finger proteins.
Orthologs
[edit]Orthologs of human ZNF816 are highly conserved in mammals, specifically primates. The closest ortholog is found in the Bonobo (Pan paniscus), with 88.8% identity[18], indicating strong conservation within the Hominidae family. The most divergent ortholog is found in the Olive Baboon (Papio anubis), with 78.2% identity[18], reflecting moderate divergence within primates. Orthologs are absent in non-mammalian species.
| Species name | Genus | Common name | Family | Date of div. (MYA)[17] | % Identity[18] | % similarity[18] | Protein length (Amino Acids) | Accession Number |
| Homo sapiens | Homo | Human | Hominidae | 0 | 100.00% | 100.00% | 651 | NP_001189386 |
| Pan paniscus | Pan | Bonobo | Hominidae | 6.4 | 88.80% | 90.00% | 598 | XP_024782426.3 |
| Pan troglodytes | Pan | Common chimpanzee | Hominidae | 6.4 | 80.50% | 81.30% | 730 | XP_054528711.1 |
| Gorilla gorilla gorilla | Gorilla | Western lowland gorilla | Hominidae | 8.6 | 51.70% | 52.60% | 681 | XP_030860498.2 |
| Pongo pygmaeus | Pongo | Bornean orangutan | Hominidae | 15.2 | 86.60% | 88.30% | 642 | XP_054321989.1 |
| Pongo abelii | Pongo | Sumatran orangutan | Hominidae | 15.2 | 80.40% | 81.80% | 698 | XP_024093826.3 |
| Symphalangus syndactylus | Symphalangus | Siamang | Hylobatidae | 19.5 | 79.30% | 81.8% | 749 | XP_063471613.1 |
| Hylobates moloch | Hylobates | Silvery gibbon | Hylobatidae | 19.5 | 83.00% | 85.90% | 721 | XP_058281887.1 |
| Cercocebus atys | Cercocebus | Sooty mangabey | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 80.50% | 85.10% | 697 | XP_011936585.1 |
| Macaca fascicularis | Macaca | Long-tailed macaque (Crab-eating macaque) | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 80.80% | 85.10% | 697 | XP_005590270.3 |
| Rhinopithecus bieti | Rhinopithecus | Black snub-nosed monkey | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 82.00% | 86.20% | 694 | XP_017714826.1 |
| Colobus angolensis palliatus | Colobus | Angolan black-and-white colobus | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 82.10% | 85.80% | 641 | XP_011801561.1 |
| Papio anubis | Papio | Olive baboon | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 78.20% | 83.00% | 717 | XP_009193448.2 |
| Rhinopithecus roxellana | Rhinopithecus | Golden snub-nosed monkey | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 74.20% | 77.70% | 776 | XP_010374801.2 |
| Theropithecus gelada | Theropithecus | Gelada | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 77.60% | 82.10% | 695 | XP_025222771.1 |
| Macaca mulatta | Macaca | Rhesus macaque | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 80.80% | 85.10% | 697 | XP_014980263.2 |
| Chlorocebus sabaeus | Chlorocebus | Green monkey (Savanna monkey) | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 78.30% | 83.30% | 647 | XP_037847362.1 |
| Trachypithecus francoisi | Trachypithecus | François' langur | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 75.70% | 80.20% | 726 | XP_033084859.1 |
| Macaca nemestrina | Macaca | Southern pig-tailed macaque | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 65.90% | 71.00% | 721 | XP_011766059.1 |
| Mandrillus leucophaeus | Mandrillus | Drill | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 76.30% | 81.10% | 669 | XP_011835608.1 |
| Piliocolobus tephrosceles | Piliocolobus | Ugandan red colobus | Cercopithecidae | 28.8 | 70.20% | 73.80% | 812 | XP_023051555.1 |
Evolutionary Rate
[edit]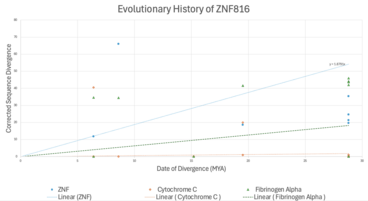
ZNF816 is evolving relatively slowly, as its rate of divergence is not significantly higher than that of Cytochrome C, a highly conserved protein, and is notably slower than proteins like Fibrinogen Alpha, indicating its functional conservation across species.
Distant Homologs
[edit]While ZNF816 is not present in non-mammalian species, distant homologs containing its zinc finger domains can be found in other vertebrates, including birds and fish[19].
Interacting Proteins
[edit]ZNF816 interacts with several proteins involved in similar cellular processes. It binds with TRIM28, ZNF813, ZNF845, and ZNF468, all of which are linked to transcriptional regulation, indicating that ZNF816 likely plays a role in controlling gene expression. Additionally, CUL3, DCAF1, TRIM39, TRIM37, and RNF219 are involved in ubiquitination and protein degradation, suggesting that ZNF816 may help regulate protein turnover through the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. TRIM28, TRIM39, and VPRBP are also associated with DNA repair, further supporting the idea that ZNF816 contributes to maintaining genomic stability. These interactions emphasize ZNF816's involvement in transcriptional regulation, protein degradation, and DNA repair.
Clinical Significance
[edit]Disease Association
[edit]Although direct disease associations are still being explored, ZNF816 is considered a potential candidate for diseases such as emphysema[20], MRKH syndrome[21], and early-onset psoriasis[22] due to the relationship of the diseases to variants in the gene.
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000180257 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "ZNF816 zinc finger protein 816 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "GeneCards - Human Genes | Gene Database | Gene Search". www.genecards.org. Archived from the original on 2024-05-14. Retrieved 2024-12-14.
- ^ "ZNF816 zinc finger protein 816 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-12-14.
- ^ www.ebi.ac.uk https://www.ebi.ac.uk/jdispatcher/seqstats. Retrieved 2024-12-14.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ Yang, Peng; Wang, Yixuan; Macfarlan, Todd S. (2017-11-01). "The Role of KRAB-ZFPs in Transposable Element Repression and Mammalian Evolution". Trends in Genetics. Transposable Elements. 33 (11): 871–881. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2017.08.006. ISSN 0168-9525. PMC 5659910. PMID 28935117.
- ^ a b "PredictProtein - Protein Sequence Analysis, Prediction of Structural and Functional Features". predictprotein.org. Retrieved 2024-12-14.
- ^ "AlphaFold Protein Structure Database". alphafold.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "I-TASSER server for protein structure and function prediction". zhanggroup.org. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "iCn3D: Web-based 3D Structure Viewer". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "National Center for Biotechnology Information". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-12-14.
- ^ "ZNF816 zinc finger protein 816 [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "Microarray Data :: Allen Brain Atlas: Human Brain". human.brain-map.org. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "PSORT WWW Server". psort.hgc.jp. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ "PaxDb: Protein Abundance Database". pax-db.org. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ a b "TimeTree :: The Timescale of Life". timetree.org. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ a b c d e www.ebi.ac.uk https://www.ebi.ac.uk/jdispatcher/psa. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ "Motif Scan". myhits.sib.swiss. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ Radder, Josiah E.; Zhang, Yingze; Gregory, Alyssa D.; Yu, Shibing; Kelly, Neil J.; Leader, Joseph K.; Kaminski, Naftali; Sciurba, Frank C.; Shapiro, Steven D. (2017-07-15). "Extreme Trait Whole-Genome Sequencing Identifies PTPRO as a Novel Candidate Gene in Emphysema with Severe Airflow Obstruction". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 196 (2): 159–171. doi:10.1164/rccm.201606-1147oc. ISSN 1073-449X. PMC 5519967. PMID 28199135.
- ^ Chen, M.-J.; Wei, S.-Y.; Yang, W.-S.; Wu, T.-T.; Li, H.-Y.; Ho, H.-N.; Yang, Y.-S.; Chen, P.-L. (2015-04-29). "Concurrent exome-targeted next-generation sequencing and single nucleotide polymorphism array to identify the causative genetic aberrations of isolated Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome". Human Reproduction. 30 (7): 1732–1742. doi:10.1093/humrep/dev095. ISSN 0268-1161. PMID 25924657.
- ^ Sun, Liang-Dan; Cheng, Hui; Wang, Zai-Xing; Zhang, An-Ping; Wang, Pei-Guang; Xu, Jin-Hua; Zhu, Qi-Xing; Zhou, Hai-Sheng; Ellinghaus, Eva; Zhang, Fu-Ren; Pu, Xiong-Ming; Yang, Xue-Qin; Zhang, Jian-Zhong; Xu, Ai-E; Wu, Ri-Na (2010-10-17). "Association analyses identify six new psoriasis susceptibility loci in the Chinese population". Nature Genetics. 42 (11): 1005–1009. doi:10.1038/ng.690. ISSN 1061-4036. PMC 3140436. PMID 20953187.


