User:Phlsph7/Declarative knowledge

Declarative knowledge is an awareness of facts that can be expressed using declarative sentences, like knowing that Princess Diana died in 1997. It is also called theoretical knowledge, descriptive knowledge, propositional knowledge, and knowledge-that. It is not tied to a specific purpose and can be stored in books or on computers.
Epistemology is the main discipline studying declarative knowledge. Among other things, it investigates the essential components of declarative knowledge. According to a traditionally influential view, it has three components: it is a belief that is true and justified. It is usually held that the involved belief is not just a weak presumption but a strong commitment to the accuracy of the believed claim. That the belief is true means that it presents an aspect of reality as it actually is. This is an objective component of knowledge that goes beyond the subjective attitude of belief. To be justified, a belief has to be rational in the sense that it is supported by sufficient evidence or based on good reasons. This component emphasizes that mere guesses do not amount to knowledge even if they are true. The theory that these three components are sufficient for declarative knowledge is often rejected in contemporary epistemology. An influential reason for this rejection is the claim that, in cases of epistemic luck, a justified true belief is not knowledge if the justification is not relevant to the truth. Various additional and alternative components are discussed to avoid this problem. They include conditions like that no defeating evidence is present, that knowledge states should be responsive to what the world is like, that the belief should be a manifestation of reliable cognitive processes or epistemic virtues, and that the belief is infallible.
Different types of declarative knowledge can be distinguished based on the source of knowledge, the type of claim that is known, and how certain the knowledge is. A central distinction is between a posteriori knowledge, which arises from experience, and a priori knowledge, which is grounded in pure rational reflection. The distinction between domain-specific knowledge and general knowledge concerns whether the topic is only relevant to one specific field or applies to many different fields. Other classifications include knowledge of facts, concepts, and principles as well as explicit and implicit knowledge.
Declarative knowledge is often contrasted with practical knowledge and knowledge by acquaintance. Practical knowledge consists of skills, like knowing how to ride a horse. It is a form of non-intellectual knowledge since it does not need to involve true beliefs and usually cannot be proven by deducing it from premises. Knowledge by acquaintance is a familiarity with something based on first-hand experience, like knowing the taste of chocolate. This familiarity can be present even if the person does not possess any factual information about the object. Some theorists also contrast declarative knowledge with conditional knowledge, prescriptive knowledge, structural knowledge, case knowledge, and strategic knowledge.
Declarative knowledge is required for various activities, such as labeling phenomena as well as describing and explaining them. It can guide the processes of problem-solving and decision-making. In many cases, its value is based on its usefulness in achieving one's goals. However, its usefulness is not always obvious and not all instances of declarative knowledge are valuable. A lot of knowledge taught at school is declarative knowledge. It can be learned through rote memorization of individual facts but in many cases, it is advantageous to foster a deeper understanding that integrates the new information into wider structures and connects it to pre-existing knowledge. Sources of declarative knowledge are perception, introspection, memory, reasoning, and testimony.
Definition and semantic field
[edit]Declarative knowledge is an awareness or understanding of facts. It can be expressed through spoken and written language using declarative sentences and can thus be acquired through verbal communication.[1][2][3] Examples of declarative knowledge are knowing "that Princess Diana died in 1997" or "that Goethe was 83 when he finished writing Faust".[1] Declarative knowledge involves mental representations in the form of concepts, ideas, theories, and general rules. Through these representations, the person stands in a relationship to a particular aspect of reality by depicting what it is like. Declarative knowledge tends to be context-independent: it is not tied to any specific use and may be employed for many different tasks.[4][5][6] It includes a wide range of phenomena and encompasses both specific knowledge of individual facts, for example, that the atomic mass of gold is 196.97 u, as well as general laws, for example, that the color of leaves of some trees changes in autumn.[7] Due to its verbal nature, declarative knowledge can be stored in media like books and harddisks. It may also be processed using computers and plays a key role in various forms of artificial intelligence, for example, in the knowledge base of expert systems.[8]
Terms like theoretical knowledge, descriptive knowledge, propositional knowledge, and knowledge-that are used as synonyms of declarative knowledge and express its different aspects. Theoretical knowledge is knowledge of what is the case, in the past, present, or future independent of a practical outlook concerning how to achieve a specific goal. Descriptive knowledge is knowledge that involves descriptions of actual or speculative objects, events, or concepts. Propositional knowledge asserts that a certain proposition or claim about the world is true. This is often expressed using a that-clause, as in "knowing that kangaroos hop" or "knowing that 2 + 2 = 4". For this reason, it is also referred to as knowledge-that.[9] Declarative knowledge contrasts with non-declarative knowledge, which does not concern the explicit comprehension of factual information regarding the world. In this regard, practical knowledge in the form of skills and knowledge by acquaintance as a type of experiential familiarity are not forms of declarative knowledge.[10][11][12] The main discipline investigating declarative knowledge is called epistemology. It tries to determine its nature, how it arises, what value it has, and what its limits are.[13][14][15]
Components
[edit]A central issue in epistemology is to determine the components or essential features of declarative knowledge. This field of inquiry is called the analysis of knowledge. It aims to provide the conditions that are individually necessary and jointly sufficient for a state to amount to declarative knowledge. In this regard, it is similar to how a chemist breaks down a sample by identifying all the chemical elements composing it.[16][17][18]
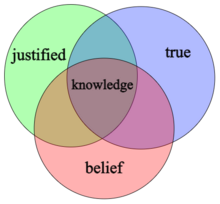
A traditionally influential view states that declarative knowledge has three essential features: it is (1) a belief that is (2) true and (3) justified.[19][20][21] This position is referred to as the justified-true-belief conception of knowledge and is often seen as the standard view.[22][23] This view faced significant criticism following a series of counterexamples given by Edmund Gettier in the latter half of the 20th century. In response, various alternative theories of the components of declarative knowledge have been suggested. Some see justified true belief as a necessary condition that is not sufficient by itself and discuss additional components that are needed. Another response is to deny that justification is needed and seek a different component to replace it.[24][25][26] Some theorists, like Timothy Williamson, reject the idea that declarative knowledge can be deconstructed into various constituent parts. They argue instead that it is a fundamental and unanalyzable epistemological state.[27]
Belief
[edit]One commonly accepted component of knowledge is belief. In this sense, whoever knows that whales are animals automatically also believes that whales are animals. A belief is a mental state that affirms that something is the case. As an attitude toward a proposition, it belongs to the subjective side of knowledge. Some theorists, like Luis Villoro, distinguish between weak and strong beliefs. Having a weak belief implies that the person merely presumes that something is the case. They guess that the claim is probably correct while acknowledging at the same time that they might very well be mistaken about it. This contrasts with strong belief, which implies a substantial commitment to the believed claim. It involves certainty in the form of being sure about it. For declarative knowledge, this stronger sense of belief is relevant.[28][29]
A few epistemologists, like Katalin Farkas, claim that, at least in some cases, knowledge is not a form of belief but a different type of mental state. One argument for this position is based on statements like "I don't believe it, I know it", which may be used to express that the person is very certain and has good reason to affirm this claim. However, this argument is not generally accepted since knowing something does not imply that the person disbelieves the claim. A different explanation is to hold that this statement is a linguistic tool to emphasize that the person is well-informed. In this regard, it only denies that a weak belief exists without rejecting that a stronger form of belief is involved.[30]
Truth
[edit]Beliefs are either true or false depending on whether they accurately represent reality. Truth is usually seen as one of the essential components of knowledge. This means that it is impossible to know a claim that is false. For example, it is possible to believe that Hillary Clinton won the 2016 US Presidential election but nobody can know it because this event did not occur. That a proposition is true does not imply that it is common knowledge, that an irrefutable proof exists, or that someone is thinking about it. Instead, it only means that it presents things as they are. For example, when flipping a coin, it may be true that it will land heads even if it is not possible to predict this with certainty. Truth is an objective factor of knowledge that goes beyond the psychological sphere of belief since it usually depends on what the world outside the person's mind is like.[31][32][33]
Some epistemologists hold that there are at least some forms of knowledge that do not require truth. For example, Joseph Thomas Tolliver argues that certain mental states amount to knowledge only because of the causes and effects they have even though they do not represent anything and are therefore neither true nor false.[33][34] A different outlook is found in the field of the anthropology of knowledge, which studies how knowledge is acquired, stored, retrieved, and communicated. In this discipline, knowledge is often understood in a very wide sense that is roughly equivalent to understanding and culture. In this regard, the main interest is usually about how people ascribe truth values to meaning-contents, like when affirming an assertion, independent of whether this assertion is true or false.[35][36][37] Despite these positions, it is widely accepted in epistemology that truth is an essential component of declarative knowledge.[31]
Justification
[edit]In epistemology, justification means that a proposition is supported by evidence or that a person has good reasons for believing it. This implies some form of appraisal in relation to an evaluative standard of rationality.[38][39] For example, a person who just checked their bank account and saw that their balance is 500 dollars has a good reason to believe that they have 500 dollars in their bank account.[40] However, justification by itself does not imply that a belief is true. For example, if someone reads the time from their clock they may form a justified belief about the current time even if the clock stopped a while ago and shows a false time now.[41] If a person has a justified belief then they are often able to articulate what this belief is and to provide arguments stating the reasons supporting it. However, this ability to articulate one's reasons is not an essential requirement of justification.[39]
Justification is usually included as a component of knowledge to exclude lucky guesses. For example, a compulsive gambler flipping a coin may be certain that it will land heads this time without a good reason for this belief. In this case, the belief does not amount to knowledge even if it turns out that it was true. This observation can be easily explained by including justification as an essential component: the gambler's belief does not amount to knowledge because it lacks justification. In this regard, mere true opinion is not enough to establish knowledge. A central issue in epistemology concerns the standards of justification, i.e., what conditions have to be fulfilled for a belief to be justified. Internalists understand justification as a purely subjective component, akin to belief. They claim that a belief is justified if it stands in the right relation to other mental states of the believer. For example, perceptual experiences can justify beliefs about the perceived object. This contrasts with externalists, who claim that justification involves objective factors that are external to the person's mind. Such factors can include causal relations with the object of the belief or that reliable cognitive processes are responsible for the formation of the belief.[42][43]

A closely related issue concerns the question of how the different mental states have to be related to each other to be justified. For example, one belief may be supported by another belief. However, it is questionable whether this is sufficient for justification if the second belief is itself not justified. For example, a person may believe that Ford cars are cheaper than BMWs because they heard this from a friend. However, this belief may not be justified if there is no good reason to think that the friend is a reliable source of information. This can lead to an infinite regress since whatever reason is provided for the friend's reliability may itself lack justification. Three popular responses to this problem are foundationalism, coherentism, and infinitism. According to foundationalists, some reasons are foundational and do not depend on other reasons for their justification. Coherentists also reject the idea that an infinite chain of reasons is needed and argue that different beliefs can mutually support each other without one being more basic than the others. Infinitists, on the other hand, accept the idea that an infinite chain of reasons is required.[44]
Many debates concerning the nature of declarative knowledge focus on the role of justification, specifically whether it is needed at all and what else might be needed to complement it. Influential in this regard was a series of thought experiments by Edmund Gettier. They present concrete cases of justified true beliefs that fail to amount to knowledge. The reason for their failure is a type of epistemic luck. This means that the justification is not relevant to whether the belief is true. In one thought experiment, Smith and Jones apply for a job and before officially declaring the result, the company president tells Smith that Jones will get the job. Smith saw that Jones has 10 coins in his pocket so he comes to form the justified belief that the successful candidate has 10 coins in his pocket. In the end, it turns out that Smith gets the job after all. By lucky coincidence, Smith also has 10 coins in his pocket. Gettier claims that, because of this coincidence, Smith's belief that the successful candidate has 10 coins in his pocket does not amount to knowledge even though it is justified and true because the justification is not relevant to the truth.[45][46]
Others
[edit]
In response to Gettier's thought experiments, various further components of declarative knowledge have been suggested. Some of them are intended as additional elements besides belief, truth, and justification while others are understood as replacements for justification.[47][48][49]
According to defeasibility theory, an additional condition besides having evidence in favor of the belief is that no defeating evidence is present. Defeating evidence of a belief is evidence that undermines the justification of the belief. For example, if a person looks outside the window and sees a rainbow then this impression justifies their belief that there is a rainbow. However, if the person just ate a psychedelic drug then this is defeating evidence since it undermines the reliability of their experiences. Defeasibility theorists claim that, in this case, the belief does not amount to knowledge because defeating evidence is present. As an additional component of knowledge, they require that the person has no defeating evidence of the belief.[50][51][52] Some theorists demand the stronger requirement that there is no true proposition that would defeat the belief, independent of whether the person is aware of this proposition or not.[53] A closely related theory holds that beliefs can only amount to knowledge if they are not inferred from a falsehood.[54]
A different theory is based on the idea that knowledge states should be responsive to what the world is like. One suggested component in this regard is that the belief is safe or sensitive. This means that the person has the belief because it is true but that they would not hold the belief if it was false. In this regard, the person's belief tracks the state of the world.[55]
Some theories do not try to provide additional requirements but instead propose replacing justification with alternative components. For example, according to some forms of reliabilism, a true belief amounts to knowledge if it was formed through a reliable cognitive process. A cognitive process is reliable if it produces mostly true beliefs in actual situations and would also do so in counterfactual situations. [49][56][57] Examples of reliable processes are perception and reasoning.[58] A consequence of reliabilism is that knowledge is not restricted to humans since reliable belief-formation processes may also be present in other animals, like dogs, apes, or rats, even if they do not possess justification for their beliefs.[49] Virtue epistemology is a closely related approach that understands knowledge as the manifestation of epistemic virtues. It agrees with regular forms of reliabilism that knowledge is not a matter of luck but puts additional emphasis on the evaluative aspect of knowledge and the underlying skills responsible for it.[59][60][61]
According to causal theories of knowledge, a necessary element of knowing a fact is that this fact somehow caused the knowledge of it. This is the case, for example, if a belief about the color of a house is based on a perceptual experience, which causally connects the house to the belief. This causal connection does not have to be direct and can be mediated through different steps like activating memories and drawing inferences.[62][49]
In many cases, the goal of suggesting additional components is to avoid cases of epistemic luck. In this regard, some theorists have argued that the additional component would have to ensure that the belief is true. This approach is reflected in the idea that knowledge implies a form of certainty. But it sets the standards of knowledge very high and may require that a belief has to be infallible to amount to knowledge. This means that the justification ensures that the belief is true. For example, Richard Kirkham argues that the justification required for knowledge must be based on self-evident premises that deductively entail the held belief. Such a position leads to a form of skepticism about knowledge since the great majority of regular beliefs do not live up to these requirements. It would imply that people know very little and that most who claim to know a certain fact are mistaken. However, a more common view among epistemologists is that knowledge does not require infallibility and that many knowledge claims in everyday life are true.[63]
Types
[edit]Declarative knowledge arises in different forms. It is possible to distinguish between them based on the type of content of what is known. For example, empirical knowledge is knowledge of observable facts while conceptual knowledge is an understanding of general categorizations and theories as well as the relations between them.[64][65][66] Other examples are ethical, religious, scientific, mathematical, and logical knowledge as well as self-knowledge. A different distinction focuses on the mode of how something is known. On a causal level, different sources of knowledge correspond to different types of declarative knowledge. Examples are knowledge through perception, introspection, memory, reasoning, and testimony.[64][67][68] On a logical level, forms of knowledge can be distinguished based on how a knowledge claim is supported by its premises. This classification corresponds to the different forms of logical reasoning, such as deductive and inductive reasoning.[64][69][70] A closely related categorization focuses on the strength of the source of the justification and distinguishes between probabilistic and apodictic knowledge while the distinction between a priori and a posteriori knowledge focuses on the type of the source. These different classifications overlap with each other at various points. For example, a priori knowledge is closely connected to apodictic, conceptual, deductive, and logical knowledge. A posteriori knowledge, on the other hand, is associated with probabilistic, empirical, inductive, and scientific knowledge. Self-knowledge may be identified with introspective knowledge.[64][71]
The distinction between a priori and a posteriori knowledge is determined by the role of experience and matches the distinction between empirical and non-empirical knowledge. A posteriori knowledge is knowledge from experience. This means that experience, like regular perception, is responsible for its formation and justification. Knowing that the door of one's house is green is one example of a posteriori knowledge since some form of sensory observation is required. For a priori knowledge, on the other hand, no experience is required. It is based on pure rational reflection and can neither be verified nor falsified through experience. Examples are knowing that 7 + 5 = 12 or that whatever is red everywhere is not blue everywhere.[72] In this context, experience means primarily sensory observation but can also include related processes, like introspection and memory. However, it does not include all conscious phenomena. For example, having a rational insight into the solution of a mathematical problem does not mean that the resulting knowledge is a posteriori. And knowing that 7 + 5 = 12 is a priori knowledge even though some form of consciousness is involved in learning what symbols like "7" and "+" mean and in becoming aware of the associated concepts.[73][74][71]
One classification distinguishes between knowledge of facts, concepts, and principles. Knowledge of facts pertains to the association of concrete information, for example, that the red color on a traffic light means stop or that Christopher Columbus sailed in 1492 from Spain to America. Knowledge of concepts applies to more abstract and general ideas that group together many individual phenomena. For example, knowledge of the concept of jogging implies knowing how it differs from walking and running as well as being able to apply this concept to concrete cases. Knowledge of principles is an awareness of general patterns of cause and effect, including rules of thumb. It is a form of understanding how things work and being aware of the explanation of why something happened the way it did. Examples are that if there is lightning then there will be thunder or if a person robs a bank then they may go to jail.[75][76] Similar classifications distinguish between declarative knowledge of persons, events, principles, maxims, and norms.[77][78][79]
Declarative knowledge is traditionally identified with explicit knowledge and contrasted with tacit or implicit knowledge. Explicit knowledge is knowledge of which the person is aware and which can be articulated. Implicit knowledge, on the other hand, is a form of embodied knowledge that the person cannot articulate. The traditional association of declarative knowledge with explicit knowledge is not always accepted in the contemporary literature and some theorists have argued that there are forms of implicit declarative knowledge. A putative example is a person who has learned a concept and is now able to correctly classify objects according to this concept even though they are not able to provide a verbal rationale for their decision.[80][81][82]
A further distinction is between domain-specific and general knowledge. Domain-specific knowledge applies to a narrow subject or a particular task but is useless outside this focus. General knowledge, on the other hand, concerns wide topics or has general applications. For example, declarative knowledge of the rules of grammar belongs to general knowledge while having memorized the lines of the poem The Raven is domain-specific knowledge. This distinction is based on a continuum of cases that are more or less general without a clear-cut line between the types.[7][83] According to Paul Kurtz, there are six types of descriptive knowledge: knowledge of available means, of consequences, of particular facts, of general causal laws, of established values, and of fundamental needs.[84] Another classification distinguishes between structural knowledge and perceptual knowledge.[85]
Contrast with other forms of knowledge
[edit]
Declarative knowledge is often contrasted with other types of knowledge. A common classification in epistemology distinguishes it from practical knowledge and knowledge by acquaintance. All of them can be expressed with the verb "to know" but their differences are reflected in the grammatical structures used to articulate them. Declarative knowledge is usually expressed with a that-clause, as in "Ann knows that koalas sleep most of the time". For practical knowledge, a how-clause is used instead, for example, "Dave knows how to read the time on a clock". Knowledge by acquaintance can be articulated using a direct object without a preposition, as in "Emily knows Obama personally".[11][12][86]
Practical knowledge consists of skills. Knowing how to ride a horse or how to play the guitar are forms of practical knowledge. The terms "procedural knowledge" and "knowledge-how" are often used as synonyms.[12][87][88] It differs from declarative knowledge in various aspects. It is usually imprecise and cannot be proven by deducing it from premises. It is non-propositional and, for the most part, cannot be taught in abstract without concrete exercise. In this regard, it is a form of non-intellectual knowledge.[12][11] It is tied to a specific goal and its value lies not in being true, but rather in how effective it is to accomplish its goal.[89] Practical knowledge can be present without any beliefs and may even involve false beliefs. For example, a ball player may know how to catch a ball despite falsely believing that their eyes continuously track the ball while, in truth, their eyes perform a series of abrupt movements that anticipate the ball's trajectory rather than following it.[90] Another difference is that declarative knowledge is commonly only ascribed to animals with highly developed minds, like humans. Practical knowledge, on the other hand, is more prevalent in the animal kingdom. For example, ants know how to walk through the kitchen despite presumably lacking the mental capacity for the declarative knowledge that they are walking through the kitchen.[91]
Declarative knowledge is also distinguished from knowledge by acquaintance, which is also known as objectual knowledge, and knowledge-of. Knowledge by acquaintance is a form of familiarity or direct awareness that a person has with another person, a thing, or a place. For example, a person who has tasted the flavor of chocolate knows chocolate in this sense, just like a person who visited Lake Taupō knows Lake Taupō. Knowledge by acquaintance does not imply that the person can provide factual information about the object. It is a form of non-inferential knowledge that depends on first-hand experience. For example, a person who has never left their home country may acquire a lot of declarative knowledge about other countries by reading books without any knowledge by acquaintance.[88][92][93] Knowledge by acquaintance plays a central role in the epistemology of Bertrand Russell. He holds that it is more basic than other forms of knowledge since to understand a proposition, one has to be acquainted with its constituents. According to Russell, knowledge by acquaintance covers a wide range of phenomena, such as thoughts, feelings, desires, memory, introspection, and sense data. It can happen in relation to particular things and universals. Knowledge of physical objects, on the other hand, belongs to declarative knowledge, which he calls knowledge by description. It also has a central role to play since it extends the realm of knowledge to things that lie beyond the personal sphere of experience.[94]
Some theorists, like Anita Woolfolk et. al., distinguish declarative knowledge and procedural knowledge from conditional knowledge. According to this view, conditional knowledge is about knowing when and why to use declarative and procedural knowledge. For many issues, like solving math problems and learning a foreign language, it is not sufficient to know facts and general procedures if the person does not know under which situations to use them. To master a language, for example, it is not enough to acquire declarative knowledge of different verb forms if one lacks conditional knowledge of when it is appropriate to use them. Some theorists understand conditional knowledge as one type of declarative knowledge and not as a distinct category.[95]
A further distinction is between declarative or descriptive knowledge in contrast to prescriptive knowledge. Descriptive knowledge represents what the world is like. It describes and classifies what phenomena are there and in what relations they stand toward each other. It is interested in what is true independently of what people want. Prescriptive knowledge is not about what things actually are like but what they should be like. This concerns specifically the question of what purposes people should follow and how they should act. It guides action by showing what people should do to fulfill their needs and desires. In this regard, it has a more subjective component since it depends on what people want. Some theorists equate prescriptive knowledge with procedural knowledge but others distinguish them based on the claim that prescriptive knowledge is about what should be done while procedural knowledge is about how to do it.[96] Other classifications contrast declarative knowledge with structural knowledge, meta knowledge, heuristic knowledge, control knowledge, case knowledge, and strategic knowledge.[97][78][79]
Some theorists argue that one type of knowledge is more fundamental than others. For example, Robert E. Haskell claims that declarative knowledge is the basic form of knowledge since it constitutes a general framework of understanding and thereby is a precondition for acquiring other forms of knowledge.[98] However, this position is not generally accepted and philosophers like Gilbert Ryle defend the opposing thesis that declarative knowledge presupposes procedural knowledge.[99][100]
Value
[edit]Declarative knowledge plays a central role in human understanding of the world. It underlies activities such as labeling phenomena, describing them, explaining them, and communicating with others about them.[101] The value of declarative knowledge depends in part on its usefulness in helping people achieve their objectives. For example, to treat a disease, knowledge of its symptoms and possible cures is beneficial. Or if a person has applied for a new job then knowing where and when the interview takes place is important.[102][103][104] Due to its context-independence, declarative knowledge can be used for a great variety of tasks and because of its compact nature, it can be easily stored and retrieved.[5][4] Declarative knowledge can be useful for procedural knowledge, for example, by knowing the list of steps needed to execute a skill. It also has a key role in understanding and solving problems and can guide the process of decision-making.[105][106][107] A related issue in the field of epistemology concerns the question of whether declarative knowledge is more valuable than true belief, since, for most purposes, true belief seems to be as useful as knowledge to achieve one's goals.[104][108][109]
Declarative knowledge is primarily desired in cases where it is immediately useful.[98] But not all forms of knowledge are useful. For example, indiscriminately memorizing phone numbers found in a foreign phone book is unlikely to result in useful declarative knowledge.[103] However, it is often difficult to assess the value of knowledge if one does not foresee a situation where it would be useful. In this regard, it can happen that the value of apparently useless knowledge is only discovered much later. For example, Maxwell's equations linking magnetism to electricity were considered useless at the time of discovery until experimental scientists discovered how to detect electromagnetic waves.[98] Occasionally, knowledge may have a negative value, for example, when it hinders someone to do what would be needed because their knowledge of associated dangers paralyzes them.[103]
Learning
[edit]
The value of knowledge is specifically relevant in the field of education to make it possible to decide which of the vast amount of knowledge should become part of the curriculum to be passed on to students.[102] Many types of learning at school involve the acquisition of declarative knowledge.[101] One form of declarative knowledge learning is so-called rote learning. It is a memorization technique in which the claim to be learned is repeated again and again until it is fully memorized. Other forms of declarative knowledge learning focus more on developing an understanding of the subject. This means that the learner should not only be able to repeat the claim but also to explain, describe, and summarize it. For declarative knowledge to be useful, it is often advantageous if it is embedded in a meaningful structure. For example, learning about new concepts and ideas involves developing an understanding of how they are related to each other and to what is already known.[105]
According to Ellen Gagné, learning declarative knowledge happens in four steps. In the first step, the learner comes into contact with the material to be learned and apprehends it. Next, they translate this information into propositions. Following that, the learner's memory triggers and activates related propositions. As the last step, new connections are established and inferences are drawn.[105] A similar process is described by John V. Dempsey, who emphasizes that the new information must be organized, subdivided, and linked to existing knowledge. He distinguishes between learning that involves recalling information in contrast to learning that only requires being able to recognize certain patterns.[110] A related theory is defended by Anthony J. Rhem, who holds that the process of learning declarative knowledge involves organizing new information into groups and drawing relations between these groups as well as connecting the new information to pre-existing knowledge.[111]
Some theorists, like Robert Gagné and Leslie Briggs, distinguish between different types of declarative knowledge learning based on the cognitive processes involved: learning of labels and names, of facts and lists, and of organized discourse. Learning labels and names requires forming a mental connection between two elements. Examples include memorizing foreign vocabulary and learning the capital city of each state. Learning facts involves relationships between concepts, for example, that "Ann Richards was the governor of Texas in 1991". This process is usually easier if the person is not dealing with isolated facts but possesses a network of information into which the new fact is integrated. The case for learning lists is similar since it involves the association of many items. Learning organized discourse encompasses not discrete facts or items but a wider comprehension of the meaning present in an extensive body of information.[105][110][111]
Various sources of declarative knowledge are discussed in epistemology. They include perception, introspection, memory, reasoning, and testimony.[67][68][64] Perception is usually understood as the main source of empirical knowledge. It is based on the senses, like seeing that it is raining when looking out the window.[112][113][114] Introspection is similar to perception but provides knowledge of the internal sphere and not of external objects.[115] An example is directing one's attention to a pain in one's toe to assess whether it has intensified.[116] Memory differs from perception and introspection in that it does not produce new knowledge but merely stores and retrieves pre-existing knowledge. As such, it depends on other sources.[68][117][118] It is similar to reasoning in this regard, which starts from a known fact and arrives at new knowledge by drawing inferences from it. Empiricists hold that this is the only way how reason can arrive at knowledge while rationalists contend that certain claims can be known by pure reason independent of additional sources.[114][119][120] Testimony is different from the other sources since it does not have its own cognitive faculty. Rather, it is grounded in the notion that people can acquire knowledge through communication with others, for example, by speaking to someone or by reading a newspaper.[121][122][123] Some religious philosophers include religious experiences (through the so-called sensus divinitatis) as a source of knowledge of the divine. However, such claims are controversial.[68][124]
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ a b Colman, Andrew M. (1 January 2009). "declarative knowledge". A Dictionary of Psychology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-953406-7.
- ^ Woolfolk, Anita E.; Hughes, Malcolm; Walkup, Vivienne (2008). Psychology in Education. Pearson Longman. p. 307. ISBN 978-1-4058-3541-1.
- ^ Strube, G.; Wender, K. F. (1 October 1993). The Cognitive Psychology of Knowledge. Elsevier. p. 354. ISBN 978-0-08-086755-7.
- ^ a b Morrison, Associate Professor of English Robert (18 April 2005). The Cambridge Handbook of Thinking and Reasoning. Cambridge University Press. p. 371. ISBN 978-0-521-82417-0.
- ^ a b Reif, Frederick (2008). Applying Cognitive Science to Education: Thinking and Learning in Scientific and Other Complex Domains. MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-18263-8.
- ^ Zagzebski 1999, p. 93.
- ^ a b Woolfolk, Anita; Margetts, Kay (25 July 2012). Educational Psychology Australian Edition. Pearson Higher Education AU. p. 251. ISBN 978-1-4425-5145-9.
- ^
- "knowledge". The American Heritage Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 25 October 2022.
- Magee, Bryan; Popper, Karl R. (1971). "Conversation with Karl Popper". In Magee, Bryan (ed.). Modern British philosophy. New York: St. Martin's Press. pp. 74–75. ISBN 978-0-19-283047-0. OCLC 314039.
Popper: Putting our ideas into words, or better, writing them down, makes an important difference. ... It is what I call 'knowledge in the objective sense'. Scientific knowledge belongs to it. It is this knowledge which is stored in our libraries rather than our heads. Magee: And you regard the knowledge stored in our libraries as more important than the knowledge stored in our heads. Popper: Much more important, from every point of view
- Walton, Douglas N. (January 2005). "Pragmatic and idealized models of knowledge and ignorance". American Philosophical Quarterly. 42 (1): 59–69 (59, 64). JSTOR 20010182.
It is a pervasive assumption in recent analytical philosophy that knowledge can be defined as a modality representing a rational agent's true and consistent beliefs. Such views are based on rationality assumptions. One is that knowledge can only consist of true propositions. This way of speaking is sharply at odds with the way we speak about knowledge, for example, in computing, where a so-called knowledge base can be a database, that is, a set of data that has been collected and is thought to consist of true propositions, even though, realistically speaking, many of them might later be shown to be false or untenable. ... The pragmatic account of knowledge starts with a knowledge system, meaning a working system with an agent having a database. ... The notion of a search can be a social one, in many instances. A group of agents can be engaged in the search, and some of them can know things that others do not know.
- Leondes, Cornelius T. (26 September 2001). Expert Systems: The Technology of Knowledge Management and Decision Making for the 21st Century. Elsevier. p. 804. ISBN 978-0-08-053145-8.
- Kent, Allen; Williams, James G. (18 November 1993). Encyclopedia of Microcomputers: Volume 13 - Optical Disks to Production Scheduling. CRC Press. p. 295. ISBN 978-0-8247-2711-6.
- ^
- Sadegh-Zadeh, Kazem (28 September 2011). Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 450–1. ISBN 978-94-007-2260-6.
- Burstein, Frada; Holsapple, Clyde W. (22 January 2008). Handbook on Decision Support Systems 1: Basic Themes. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 44–5. ISBN 978-3-540-48713-5.
- Hetherington, Stephen. "Knowledge". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1b. Knowledge-That. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Sadegh-Zadeh, Kazem (6 April 2015). Handbook of Analytic Philosophy of Medicine. Springer. p. 470. ISBN 978-94-017-9579-1.
- ^ Colman, Andrew M. (1 January 2009). "non-declarative knowledge". A Dictionary of Psychology. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-953406-7.
- ^ a b c Pavese, Carlotta (2022). "Knowledge How". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ a b c d Klauer, Bernd; Manstetten, Reiner; Petersen, Thomas; Schiller, Johannes (1 September 2016). Sustainability and the Art of Long-Term Thinking. Taylor & Francis. pp. 105–6. ISBN 978-1-134-98618-7.
- ^ Truncellito, David A. "Epistemology". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 8 March 2023.
- ^ Moser, Paul K. (27 October 2005). The Oxford Handbook of Epistemology. Oxford University Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-19-020818-9.
- ^ Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 2.3 Knowing Facts: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 8 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^ Zagzebski 1999, p. 96.
- ^ Gupta, Anil (2021). "Definitions: 1.1 Real and nominal definitions". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ^ Klein, Peter D. (1998). "Knowledge, concept of". In Craig, Edward (ed.). Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London; New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780415249126-P031-1. ISBN 978-0-415-25069-6. OCLC 38096851. Archived from the original on 13 June 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- ^ Zagzebski 1999, p. 99–100.
- ^ Seel, Norbert M. (5 October 2011). Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 1001. ISBN 978-1-4419-1427-9.
- ^ Hetherington, Stephen (1 September 2016). Knowledge and the Gettier Problem. Cambridge University Press. p. 219. ISBN 978-1-316-75729-1.
- ^ Carter, J. Adam; Gordon, Emma C.; Jarvis, Benjamin W. (2017). Knowledge First: Approaches in Epistemology and Mind. Oxford University Press. p. 114. ISBN 978-0-19-871631-0.
- ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 3. The Gettier Problem: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Kornblith, Hilary (2008). "1 Knowledge Needs No Justification". In Smith, Quentin (ed.). Epistemology: New Essays. Oxford University Press. pp. 5–6. ISBN 9780191718472.
- ^ Hetherington, Stephen. "Gettier Problems". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction. Archived from the original on 19 February 2009. Retrieved 28 May 2022.
- ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 11. Knowledge First: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^
- Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1.2 The Belief Condition: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Villoro 1998, p. 144, 148-9
- Zagzebski 1999, p. 93
- Black, C. (1 April 1971). "Knowledge without belief". Analysis. 31 (5): 152–158. doi:10.1093/analys/31.5.152.
- ^ Farkas, Katalin (February 2015). "Belief May Not Be a Necessary Condition for Knowledge". Erkenntnis. 80 (1): 185–200. doi:10.1007/s10670-014-9620-2.
- Kleinman, Paul (18 September 2013). Philosophy 101: From Plato and Socrates to Ethics and Metaphysics, an Essential Primer on the History of Thought. Simon and Schuster. p. 258. ISBN 978-1-4405-6768-1.
- Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1.2 The Belief Condition: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
- ^
- Hacker, P. M. S. (1 July 2013). The Intellectual Powers: A Study of Human Nature. John Wiley & Sons. p. 211. ISBN 978-1-118-60906-4.
- Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1.2 The Belief Condition: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 29 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Black, C. (1 April 1971). "Knowledge without belief". Analysis. 31 (5): 152–158. doi:10.1093/analys/31.5.152.
- Farkas, Katalin (February 2015). "Belief May Not Be a Necessary Condition for Knowledge". Erkenntnis. 80 (1): 185–200. doi:10.1007/s10670-014-9620-2.
- ^ a b Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1.1 The Truth Condition: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Villoro 1998, p. 199-200.
- ^ a b Tolliver, Joseph Thomas (May 1989). "Knowledge without truth". Philosophical Studies. 56 (1): 29–51. doi:10.1007/bf00646208.
- ^ Villoro 1998, p. 206-10.
- ^ Cohen, Emma (2010). "Anthropology of knowledge". The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute. 16: S193–S202. doi:10.1111/j.1467-9655.2010.01617.x. hdl:11858/00-001M-0000-0012-9B72-7. JSTOR 40606072.
- ^ Barth, Fredrik (February 2002). "An Anthropology of Knowledge". Current Anthropology. 43 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1086/324131. hdl:1956/4191. ISSN 0011-3204.
- ^ Allwood, Carl Martin (17 October 2013). "Anthropology of Knowledge". The Encyclopedia of Cross-Cultural Psychology. John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 69–72. doi:10.1002/9781118339893.wbeccp025. ISBN 978-1-118-33989-3.
- ^ Watson, Jamie Carlin. "Justification, Epistemic". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Introduction. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^ a b Goldman, Alvin I. (1992). Liaisons: Philosophy Meets the Cognitive and Social Sciences. MIT Press. pp. 105–6. ISBN 978-0-262-07135-2.
- ^ Evans, Ian; Smith, Nicholas D. (25 April 2013). Knowledge. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 32–3. ISBN 978-0-7456-6141-4.
- ^ Pritchard, Duncan (18 May 2023). What is this thing called Knowledge?. Taylor & Francis. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-000-87480-8.
- ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1.3 The Justification Condition: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Poston, Ted. "Internalism and Externalism in Epistemology". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
- ^
- Klein, Peter D. (1998). "Knowledge, concept of". In Craig, Edward (ed.). Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. London; New York: Routledge. doi:10.4324/9780415249126-P031-1. ISBN 978-0-415-25069-6. OCLC 38096851. Archived from the original on 13 June 2022. Retrieved 13 June 2022.
- Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 21 July 2020. Retrieved 22 May 2022.
- Lehrer, Keith (15 October 2015). "1. The Analysis of Knowledge". Theory of Knowledge. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-19609-7. Archived from the original on 2 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- Cameron, Ross (2018). "Infinite Regress Arguments". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 2 January 2020. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ Hetherington, Stephen. "Gettier Problems". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 3. Gettier’s Original Challenge. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 3. The Gettier Problem: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Borges, Rodrigo; Almeida, Claudio de; Klein, Peter D. (1 December 2017). Explaining Knowledge: New Essays on the Gettier Problem. Oxford University Press. p. 180. ISBN 978-0-19-103682-8.
- ^ Broadbent, Alex (5 February 2016). Philosophy for Graduate Students: Metaphysics and Epistemology. Routledge. p. 128. ISBN 978-1-317-39714-4.
- ^ a b c d Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 6. Doing Without Justification?: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Craig, Edward, ed. (1996). "Knowledge, defeasibility theory of". Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Routledge. ISBN 9780415073103.
- ^ Lee, James (25 August 2017). A Metaphysician's User Guide: The Epistemology of Metaphysics. Syracuse University. pp. 6–9.
- ^ Sudduth, Michael. "Defeaters in Epistemology". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Introduction; 1. The Concept of Defeasibility. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Sudduth, Michael. "Defeaters in Epistemology". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 2b. Defeasibility Analyses and Propositional Defeaters. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 4. No False Lemmas: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 30 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Ichikawa, Jonathan Jenkins; Steup, Matthias (2018). "The Analysis of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5. Modal Conditions: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Bernecker, Sven; Pritchard, Duncan (19 January 2011). The Routledge Companion to Epistemology. Routledge. p. 266. ISBN 978-1-136-88200-5.
- ^ Becker, Kelly (13 May 2013). Epistemology Modalized. Routledge. p. 12. ISBN 978-1-136-78632-7.
- ^ Crumley, Jack S. (30 July 2009). An Introduction to Epistemology - Second Edition. Broadview Press. p. 117. ISBN 978-1-4604-0116-3.
- ^ Turri, John; Alfano, Mark; Greco, John (2021). "Virtue Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5. Knowledge: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Baehr, Jason S. "Virtue Epistemology". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction; 2. Virtue Reliabilism. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Battaly, Heather (4 September 2018). The Routledge Handbook of Virtue Epistemology. Routledge. p. 772. ISBN 978-1-317-49528-4.
- ^ Schelling, Birte (2 May 2013). Knowledge - Genetic Foundations and Epistemic Coherence. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 55–6. ISBN 978-3-11-032266-8.
- ^
- Kirkham, Richard L. (1984). "Does the Gettier Problem Rest on a Mistake?". Mind. XCIII (372): 503, 512–3. doi:10.1093/mind/XCIII.372.501.
- Hetherington, Stephen. "Knowledge". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 6. Standards for Knowing. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - Zagzebski 1999, p. 97-8
- Christensen, Peter Holdt (2003). Knowledge Management: Perspectives and Pitfalls. Copenhagen Business School Press DK. p. 29. ISBN 978-87-630-0119-9.
- ^ a b c d e Campbell, Joseph Keim; O'Rourke, Michael; Silverstein, Harry S. (21 May 2010). Knowledge and Skepticism. MIT Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-262-01408-3.
- ^ Cassirer, H. W. (11 March 2021). A Commentary of Kant's Critique of Judgment. Routledge. p. 208. ISBN 978-1-317-20272-1.
- ^ Freitas, Sara de; Jameson, Jill (5 April 2012). The e-Learning Reader. Bloomsbury Publishing. p. 189. ISBN 978-1-4411-7679-0.
- ^ a b Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5. Sources of Knowledge and Justification: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ a b c d Blaauw, Martijn (31 March 2020). Epistemology A-Z. Edinburgh University Press. p. 49. ISBN 978-0-7486-8082-5.
- ^ Flick, Uwe (10 December 2013). The SAGE Handbook of Qualitative Data Analysis. SAGE. p. 123. ISBN 9781446296691.
- ^ Bronkhorst, Hugo; Roorda, Gerrit; Suhre, Cor; Goedhart, Martin (December 2020). "Logical Reasoning in Formal and Everyday Reasoning Tasks". International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education. 18 (8): 1673–6. Bibcode:2020IJSME..18.1673B. doi:10.1007/s10763-019-10039-8. S2CID 254541202.
- ^ a b Moser, Paul K. "A posteriori". Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Routledge. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^
- Moser, Paul K. "A posteriori". Routledge Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Routledge. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- Hamilton, Christopher (2003). Understanding Philosophy for AS Level. Nelson Thornes. p. 23. ISBN 978-0-7487-6560-7.
- Barber, Alex; Stainton, Robert J. (6 April 2010). Concise Encyclopedia of Philosophy of Language and Linguistics. Elsevier. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-08-096501-7.
- Baehr, Jason S. "A Priori and A Posteriori". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1. An Initial Characterization. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link)
- ^ Baehr, Jason S. "A Priori and A Posteriori". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1. An Initial Characterization. Retrieved 17 September 2022.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Russell, Bruce (2020). "A Priori Justification and Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 18 September 2022.
- ^ Price, Kay M.; Nelson, Karna L. (1 January 2013). Planning Effective Instruction: Diversity Responsive Methods and Management. Cengage Learning. p. 4. ISBN 978-1-285-49991-8.
- ^ Foshay, Wellesley R.; Silber, Kenneth H. (19 November 2009). Handbook of Improving Performance in the Workplace, Instructional Design and Training Delivery. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 14–5. ISBN 978-0-470-52506-7.
- ^ Chiu, Chi-Yue; Hong, Ying-yi (16 December 2013). Social Psychology of Culture. Psychology Press. p. 102. ISBN 978-1-317-71018-9.
- ^ a b Jankowski, Natasha A.; Marshall, David W. (11 January 2016). Partners in Advancing Student Learning: Degree Qualifications Profile and Tuning: New Directions for Institutional Research, Number 165. John Wiley & Sons. p. 70. ISBN 978-1-119-24064-8.
- ^ a b Scott, Peter; Gallacher, Jim; Parry, Gareth (2017). New Languages and Landscapes of Higher Education. Oxford University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-19-878708-2.
- ^ Bengson, John; Moffett, Marc A. (6 January 2012). Knowing How: Essays on Knowledge, Mind, and Action. Oxford University Press. p. 328. ISBN 978-0-19-045283-4.
- ^ Kikoski, Catherine Kano; Kikoski, John F. (2004). The Inquiring Organization: Tacit Knowledge, Conversation, and Knowledge Creation : Skills for 21st-century Organizations. Greenwood Publishing Group. pp. 62, 65–6. ISBN 978-1-56720-490-2.
- ^ Reber, Arthur S.; Allen, Rhianon (2022). The Cognitive Unconscious: The First Half Century. Oxford University Press. p. 281. ISBN 978-0-19-750157-3.
- ^ Finlay, Janet (29 October 2020). An Introduction To Artificial Intelligence. CRC Press. p. 13. ISBN 978-1-000-15403-0.
- ^ Fischer, Frank (4 June 2019). Politics, Values, And Public Policy: The Problem Of Methodology. Routledge. p. 66. ISBN 978-1-000-30762-7.
- ^ Yamamoto, Sakae (4 July 2016). Human Interface and the Management of Information: Information, Design and Interaction: 18th International Conference, HCI International 2016 Toronto, Canada, July 17-22, 2016, Proceedings, Part I. Springer. p. 61. ISBN 978-3-319-40349-6.
- ^ Hetherington, Stephen. "Knowledge". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 1. Kinds of Knowledge. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Gaskins, Irene West (3 May 2005). Success with Struggling Readers: The Benchmark School Approach. Guilford Press. p. 51. ISBN 978-1-59385-169-9.
- ^ a b Peels, Rik (2023). Ignorance: A Philosophical Study. Oxford University Press. p. 28. ISBN 978-0-19-765451-4.
- ^ Merriënboer, Jeroen J. G. van (1997). Training Complex Cognitive Skills: A Four-Component Instructional Design Model for Technical Training. Educational Technology. p. 32. ISBN 978-0-87778-298-8.
- ^ Pavese, Carlotta (2022). "Knowledge How". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 6.1 Knowledge-how and Belief: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Pritchard, Duncan (1 October 2013). "1 Some preliminaries". What is this thing called Knowledge?. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-57367-7. Archived from the original on 2 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ Heydorn, Wendy; Jesudason, Susan (18 July 2013). Decoding Theory of Knowledge for the IB Diploma. Cambridge University Press. p. 10. ISBN 978-1-107-62842-7.
- ^ Foxall, Gordon (16 October 2017). Context and Cognition in Consumer Psychology: How Perception and Emotion Guide Action. Routledge. p. 75. ISBN 978-1-317-67738-3.
- ^
- Hasan, Ali; Fumerton, Richard (2020). "Knowledge by Acquaintance vs. Description". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- Haymes, Brian; Özdalga, Elisabeth (3 January 2016). Concept Of The Knowledge Of God. Springer. pp. 26–8. ISBN 978-1-349-19066-9.
- Miah, Sajahan (30 May 2006). Russell's Theory of Perception. Continuum. pp. 19–20. ISBN 978-1-84714-284-9.
- Alter, Torin; Nagasawa, Yujin (1 April 2015). Consciousness in the Physical World: Perspectives on Russellian Monism. Oxford University Press. pp. 93–4. ISBN 978-0-19-992736-4.
- ^
- Woolfolk, Anita E.; Hughes, Malcolm; Walkup, Vivienne (2008). Psychology in Education. Pearson Longman. p. 307. ISBN 978-1-4058-3541-1.
- Dunlap, Linda L. (2004). What All Children Need: Theory and Application. University Press of America. pp. 144–5. ISBN 978-0-7618-2925-6.
- Earley, P. Christopher; Ang, Soon (2003). Cultural Intelligence: Individual Interactions Across Cultures. Stanford University Press. p. 109. ISBN 978-0-8047-4312-9.
- Woolfolk, Anita; Margetts, Kay (25 July 2012). Educational Psychology Australian Edition. Pearson Higher Education AU. p. 251. ISBN 978-1-4425-5145-9.
- ^
- Maedche, Alexander; Brocke, Jan vom; Hevner, Alan (22 May 2017). Designing the Digital Transformation: 12th International Conference, DESRIST 2017, Karlsruhe, Germany, May 30 – June 1, 2017, Proceedings. Springer. p. 403. ISBN 978-3-319-59144-5.
- Goldberg, Elkhonon (16 February 2006). The Wisdom Paradox: How Your Mind Can Grow Stronger As Your Brain Grows Older. Penguin. pp. 121–2. ISBN 978-1-4406-2695-1.
- Lalanda, Philippe; McCann, Julie A.; Diaconescu, Ada (13 May 2013). Autonomic Computing: Principles, Design and Implementation. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 187–8. ISBN 978-1-4471-5007-7.
- Chen, Fang; Terken, Jacques (18 August 2022). Automotive Interaction Design: From Theory to Practice. Springer Nature. p. 49. ISBN 978-981-19-3448-3.
- ^ Nguyen, Van Tham; Nguyen, Ngoc Thanh; Tran, Trong Hieu (30 December 2022). Knowledge Integration Methods for Probabilistic Knowledge-based Systems. CRC Press. ISBN 978-1-000-80999-2.
- ^ a b c Haskell, Robert E. (2001). Transfer of Learning: Cognition and Instruction. Academic Press. p. 101-3. ISBN 978-0-12-330595-4.
- ^ Stillings, Neil A.; Chase, Christopher H.; Weisler, Steven E.; Feinstein, Mark H.; Rissland, Edwina L. (1995). Cognitive Science: An Introduction. MIT Press. p. 370. ISBN 978-0-262-69175-8.
- ^ Cornelis, Gustaaf C.; Smets, Sonja; Bendegem, Jean-Paul van (11 November 2013). Metadebates on Science: The Blue Book of “Einstein Meets Magritte”. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 37. ISBN 978-94-017-2245-2.
- ^ a b Murphy, P. Karen; Alexander, Patricia A. (7 October 2005). Understanding How Students Learn: A Guide for Instructional Leaders. Corwin Press. pp. 38–9. ISBN 978-1-4833-6347-9.
- ^ a b Degenhardt, M. A. B. (13 August 2019). Education and the Value of Knowledge. Routledge. p. 1-6. ISBN 978-1-000-62799-2.
- ^ a b c Pritchard, Duncan (1 October 2013). "2 The value of knowledge". What is this thing called Knowledge?. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-134-57367-7. Archived from the original on 2 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ a b Olsson, Erik J (December 2011). "The Value of Knowledge: The Value of Knowledge". Philosophy Compass. 6 (12): 874–883. doi:10.1111/j.1747-9991.2011.00425.x. S2CID 143034920.
- ^ a b c d Smith, Patricia L.; Ragan, Tillman J. (7 December 2004). Instructional Design. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 152–4. ISBN 978-0-471-39353-5.
- ^ Soled, Suzanne Wegener (1995). Assessment, Testing, and Evaluation in Teacher Education. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 49. ISBN 978-1-56750-153-7.
- ^ Leung, Yee (29 November 2019). International Encyclopedia of Human Geography. Elsevier. p. 210. ISBN 978-0-08-102296-2.
- ^ Pritchard, Duncan; Turri, John; Carter, J. Adam (2022). "The Value of Knowledge". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ Plato (2002). Five Dialogues. Indianapolis, IN: Hackett Pub. Co. pp. 89–90, 97b–98a. ISBN 978-0-87220-633-5.
- ^ a b Dempsey, John V. (1993). Interactive Instruction and Feedback. Educational Technology. pp. 80–1. ISBN 978-0-87778-260-5.
- ^ a b Rhem, Anthony J. (21 November 2005). UML for Developing Knowledge Management Systems. CRC Press. p. 42-3. ISBN 978-1-135-48553-5.
- ^ Hetherington, Stephen. "Knowledge". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 3b. Observational Knowledge. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ O’Brien, Daniel. "The Epistemology of Perception". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Retrieved 25 October 2022.
- ^ a b Martinich, A. P.; Stroll, Ayrum. "Epistemology - Knowledge and certainty". www.britannica.com. Rationalism and empiricism. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5.2 Introspection: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Hohwy, Jakob (November 2013). The Predictive Mind. Oxford University Press. p. 245. ISBN 978-0-19-968273-7.
- ^ Audi, Robert (2002). "The Sources of Knowledge". The Oxford Handbook of Epistemology. Oxford University Press. pp. 71–94. ISBN 978-0-19-513005-8. Archived from the original on 12 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- ^ Gardiner, J. M. (29 September 2001). "Episodic memory and autonoetic consciousness: a first-person approach". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 356 (1413): 1351–1361. doi:10.1098/rstb.2001.0955. ISSN 0962-8436. PMC 1088519. PMID 11571027.
- ^ Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5.4 Reason: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Audi, Robert (20 June 2005). Epistemology: A Contemporary Introduction to the Theory of Knowledge. Routledge. p. 315. ISBN 978-1-134-79181-1.
- ^ Steup, Matthias; Neta, Ram (2020). "Epistemology". The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. 5.5 Testimony: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Leonard, Nick (2021). "Epistemological Problems of Testimony". Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction: Metaphysics Research Lab, Stanford University. Archived from the original on 10 July 2022. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ Green, Christopher R. "Epistemology of Testimony". Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy. introduction. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ Plantinga, Alvin (27 January 2000). Warranted Christian Belief. Oxford University Press. pp. 182–3. ISBN 978-0-19-803024-9.
Sources
[edit]- Zagzebski, Linda (1999). "What Is Knowledge?". In Greco, John; Sosa, Ernest (eds.). The Blackwell Guide to Epistemology. Malden, MA: Blackwell. pp. 92–116. doi:10.1002/9781405164863.ch3. ISBN 978-0-631-20290-5. OCLC 39269507. S2CID 158886670. Archived from the original on 2 June 2022. Retrieved 12 June 2022.
- Villoro, Luis (1998). Belief, personal, and propositional knowledge. Amsterdam: Rodopi. ISBN 9042007427.
