User:Persept/sandbox
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
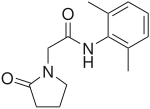
| Formula | C14H18N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 246.305 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Nefiracetam is a nootropic antidementia drug of the racetam family.[1]
Nefiracetam's cytoprotective actions are mediated by enhancement of GABAergic, cholinergic, and monoaminergic neuronal systems that give antiamnesia effects to the Alzheimer's type and cerebrovascular type of dementia.[2][3]
Concerns
[edit]Animals which metabolize nefiracetam differently than humans and primates are at risk for renal [4][5] and testicular [6] [7] toxicity. Dogs especially are particularly sensitive, which has been shown to be caused by a specific metabolite, M-18[5]. Higher doses than those in dogs were needed to cause testicular toxicity in rats, although no toxicity [9] and [10]., however, was seen in monkeys. Additionally, there has been no evidence of toxicity during clinical trials [8][9] <ref name=Shimomura>
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Murphy, Keith (22 July 2004). "Chronic Exposure of Rats to Cognition Enhancing Drugs Produces a Neuroplastic response" (PDF). Neuropsychopharmacology. Retrieved 1 September 2010.
- ^ Robinson RG, Jorge RE, Clarence-Smith K, Starkstein S (2009). "Double-blind treatment of apathy in patients with poststroke depression using nefiracetam". The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 21 (2): 144–51. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.21.2.144. PMID 19622685.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Robinson RG, Jorge RE, Clarence-Smith K (2008). "Double-blind randomized treatment of poststroke depression using nefiracetam". The Journal of Neuropsychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences. 20 (2): 178–84. doi:10.1176/appi.neuropsych.20.2.178. PMID 18451188.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Cite error: The named reference
Tsuchiyawas invoked but never defined (see the help page). - ^ a b Goto, Koichi; Ishii, Yoshikazu; Jindo, Toshimasa; Furuhama, Kazuhisa (3). "Effect of Nefiracetam, a Neurotransmission Enhancer, on Primary Uroepithelial Cells of the Canine Urinary Bladder". Toxicological Sciences. 1 (72): 164–70. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfg010. PMID 12604846.
{{cite journal}}: Check date values in:|date=and|year=/|date=mismatch (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Shimada, M; Shikanai, Y; Shimomura, K; Harada, S; Watanabe, G; Taya, K; Kato, M; Furuhama, K (2003). "Investigation of testicular toxicity of nefiracetam, a neurotransmission enhancer, in rats". Toxicology Letters. 143 (3): 307–15. doi:10.1016/s0378-4274(03)00197-8. PMID 12849691.
- ^ Shimomura, K; Shimada, M; Hagiwara, M; Harada, S; Kato, M; Furuhama, K (2004). "Testicular toxicity induced in dogs by nefiracetam, a neutrotransmission enhancer". Reproductive Toxicology (Elmsford, N.Y.). 18 (3): 423–30. doi:10.1016/j.reprotox.2004.01.008. PMID 15082078.
- ^ M Murasaki, M Inami, J Ishigooka, H Watanabe, M Utsumi, T Matsumoto; et al. (1994). "Phase I study on DM-9384 (nefiracetam)". Jpn. Pharmacol. Ther. 22: 3539–3587.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ E Otomo, K Kogure, S Hirai, F Goto, K Hasegawa, Y Tazaki; et al. (1994). "Clinical evaluation of DM-9384 in the treatment of cerebrovascular disorders: early phase II study". Jpn. Pharmacol. Ther. (22): 3589–3624.
{{cite journal}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
Category:Racetams
Category:Pyrrolidones
Category:Acetanilides
Category:Nootropics

