User:Lekah005/sandbox
Chromosome 9 open reading frame 25 (C9orf25) is a domain that encodes the FAM219A gene[1]. The terms FAM219A and C9orf25 are allieses and can be used interchangeably. The function of this gene is not yet understood.
Gene
[edit]
Location
[edit]C9orf25 is located on the short arm of chromosome 9 at the 9p13.3 position[2]. The gene is encoded on the sense strand (-) spanning the chromosomal locus from base pair 34,502,909 to 34,398,027[1][3].
Transcript Variants
[edit]In humans there are 8 main transcript variants of the FAM219A gene[3]. All of these transcripts have varying lengths and splice sites. Only four of these transcripts encode for a protein product.[4]
Homology
[edit]Orthologs
[edit]The C9orf25 gene has orthologs in a wide variety of Eukaryotic organisms, including invertebrates. This gene has not been found in plants, fungi or protists[5]. C9orf25 is a slowly evolving gene and is highly conserved though out all of its known orthologs.
Paralogs
[edit]C9orf25 has a paralog FAM219B which is located on the long arm of chromosome 9 and is 198 amino acids long.[6]The C9orf25 and FAM219B genes duplicated and diverged between 684 and 797 million years ago.
Protein
[edit]General Properties
[edit]The C9orf25 protein is composed of 185 amino acids. It has a molecular weight of 20.4 kilodaltons and an isoelectric point of 4.47[7]. It is a member of the FAM219 super family. The entire protein is still considered to be a domain of unknown function.
Protein Localization
[edit]C9orf25 has no signal sequence and remains in the cytosol.[7]
Conserved Motifs and Post-Translational Modifications
[edit]The following are experimental post-transitional modifications for the C9orf25 protein[8]:
- 6 predicted Serine phosphorylation sites
- 1 predicted Tyrosine phosphorylation site
- 1 predicted prenylation site
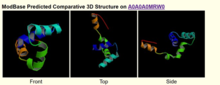
Secondary Structure
[edit]The secondary structure of the gene is predicted to have two stretches of alpha helices and one beta strand. The majority of the secondary structure of gene is random coils[9].
Expression
[edit]The C9orf25 gene has medium to high expression in most tissues of the body[10].The gene has particularly high expression in the nervous, digestive and male reproductive systems[11].
Interacting Proteins
[edit]The C9orf25 gene has many different interactions with a variety of other proteins that have an assortment of functions[12][13][14]. The main ones that are listed on at least two reviewed sources are shown below.
| Interactor Gene | Full Protein Name | Method | Description | Clinical Significance (Potential) |
| LIMS3 | LIM Zinc finger domain | Two hybrid pooling approach | Senescent cell antigen containing protein | |
| PDE6D | Rhodopsin sensitive cGMP phosphodiesterase subunit | Two hybrid pooling approach | Regulates the activity of the RAS protein in the cytosol | Joubert Syndrome |
| NIPSNAP3A | NipSnap homolog 3A | Two Hybrid | Involved in the Acetylation and phosphorylation process | |
| CSNK1A1 | Casein Kinase 1 Alpha 1 | Two Hybrid | Serine/Threonine protein kinase. Participates in S phase checkpoint arrest by phosphorylating Claspin | NSEOE |
| SPRY2 | Protein Sprouty Homolog 2 | Two Hybrid | Antagonist of fibroblast growth factor | IgA nephropathy 3 |
| BTRC | F-box/WD repeat containing protien | Affinity Capture | Substrate recognition component of SCF ubiquitin-protein ligase (phosphorolation dependent ubiquination) | CD4 (HIV-1) degregation |
| MTA1 | Metastasis Associated Protein 1 | Affinity Capture | Cancer associated. DNA binding transcription factor activity | Esophageal and Breast cancer |
| MTA3 | Metastasis Associated Protein 3 | Affinity Capture | Maintains epithelial architecture. Regulation of E-cadherin levels | Cancers related to epithelial cells |
References
[edit]- ^ a b "FAM219A family with sequence similarity 219 member A [Homo sapiens (human)] - Gene - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-05.
- ^ "Chromosome 9: 34,396,977-34,459,777 - Region in detail - Homo sapiens - Ensembl genome browser 92". useast.ensembl.org. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ a b mieg@ncbi.nlm.nih.gov, Danielle Thierry-Mieg and Jean Thierry-Mieg, NCBI/NLM/NIH,. "AceView: Gene:C9orf25, a comprehensive annotation of human, mouse and worm genes with mRNAs or ESTsAceView". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Database, GeneCards Human Gene. "FAM219A Gene - GeneCards | F219A Protein | F219A Antibody". www.genecards.org. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ "BLAST: Basic Local Alignment Search Tool". blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ "RecName: Full=Protein FAM219B - Protein - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ a b EMBL-EBI. "SAPS < Sequence Statistics < EMBL-EBI". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ "PTM prediction tools". www.cbs.dtu.dk. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ UCBL, Institut de Biologie et Chimie des Proteines - UMR5086 - CNRS -. "NPS@: Welcome to Network Protein Sequence @nalysis at IBCP, FRANCE". npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Home - GEO Profiles - NCBI". www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ "Tissue expression of FAM219A - Summary - The Human Protein Atlas". www.proteinatlas.org. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ Lab, Mike Tyers. "BioGRID | Database of Protein, Chemical, and Genetic Interactions". thebiogrid.org. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ "HitPredict - High confidence protein-protein interactions". hintdb.hgc.jp. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
- ^ IntAct. "https://www.ebi.ac.uk/intact/". www.ebi.ac.uk. Retrieved 2018-05-06.
{{cite web}}: External link in|title=
