User:Jcuthbert/sandbox
Electrostatic Stabilization
Electrostatic repulsive forces dominate in polyelectrolyte stabilized emulsions. Although there are steric interactions, they are negligible in comparison. As the concentration of polyelectrolyte increases, repulsive forces increase. When there are polyelectrolyte molecules, the distance between individual particles decreases.
The general equation for repulsion energy assuming spherical particles:
where R = particle radius
C = bulk concentration of ions
k_b = Boltzmann constant
Γ relates the equation to thermal energy
h is the surface to surface distance of the spherical particles
K is the Debye length
As the distance h decreases, the exponential term becomes greater. Consequently, the repulsion energy also increases.
In addition, pH and ionic strength have a great influence on electrostatic interactions because these affect the "magnitude of electrical charge" in solution. (**impact of electrostatic interactions article**) As can be seen from the above equation, the repulsion energy depends on the square of the wikipedia:Debye length From the equation for the debye length, it is demonstrated how ionic strength can ultimately affect the electrostatic interactions in a solution.

| Polyelectrolyte | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Degree of polymerization |
|---|---|---|
| NAPSS | 70,000 | 340 |
| PAA | 10,000 | 140 |
| aPMA | 131,000 | 1528 |
| iPMA | 590,000 | 6900 |
| aPEA | 3600 | 36 |
| PVP | 168000 | 4000 |
| Poly-L-arginine | 15,000-70,000 | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
| Example | Example | Example |
1-5 found in Association and structure formation in oppositely charged polyelectrolyte–surfactant mixtures Ksenija Kogej ! 6 found in The electrostatic expansion of linear polyelectrolytes 7 found in Spontaneous formation of nanoparticle vesicles from Homopolymer Polylelectrolytes

Food Technology
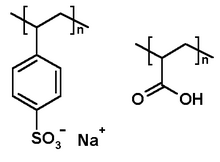
Because polyelectrolytes may be biocompatible, it follows that they can be used to stabilize emulsion in foods. Dextran sulfate (DSS), for instance, has been successfully used to induce mixing of proteins and polysaccharides in aqueous emulsions. (5)
Other studies have focused on stabilizing oil-in-water emsulsions using β-lactoglobulin (β-Lg), a globular protein, and pectin, an anionic polysaccharide. β-lactoglobulin is an important ingredient in whey protein, which is commonly used in the food industry as an emulsifier. ((**impact of electrostatic interactions article**))
[[File:Electrostaic repulsive force vs distance for polyelectrolytes.png|thumb|This graph illustrates eq. 1. It can be seen that as the surface to surface particle distance decreases, the electrostatic repulsive force decreases exponentially.[1]
- ^ Adapted from Philip, J.; Mondain-Monval, O.; Calderon, F. L. and Bibette, J. (1997). "Colloidal Force Measurements in the Presence of a Polyelectrolyte". Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics. 30: 2798–2803.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)

