User:Atomic7732/Sandboxes/List of tropical cyclones
| Part of a series on |
| Tropical cyclones |
|---|
 |
|
Outline Media coverage |
This is a list of notable tropical cyclones, subdivided by basin and reason for notability.
North Atlantic basin
[edit]These records are held by Atlantic hurricanes.
| Rank | Hurricane | Season | Damage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 Katrina | 2005 | $125 billion |
| 4 Harvey | 2017 | ||
| 3 | 4 Helene | 2024 | $124 billion |
| 4 | 4 Ian | 2022 | $113 billion |
| 5 | 4 Maria | 2017 | $90 billion |
| 6 | 3 Milton | 2024 | $85 billion |
| 7 | 4 Ida | 2021 | $75 billion |
| 8 | ET Sandy | 2012 | $65 billion |
| 9 | 4 Irma | 2017 | $52.1 billion |
| 10 | 2 Ike | 2008 | $30 billion |
| Deadliest Atlantic hurricanes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Hurricane | Season | Fatalities |
| 1 | ? "Great Hurricane" | 1780 | 22,000–27,501 |
| 2 | 5 Mitch | 1998 | 11,374+ |
| 3 | 2 Fifi | 1974 | 8,210–10,000 |
| 4 | 4 "Galveston" | 1900 | 8,000–12,000 |
| 5 | 4 Flora | 1963 | 7,193 |
| 6 | ? "Pointe-à-Pitre" | 1776 | 6,000+ |
| 7 | 5 "Okeechobee" | 1928 | 4,112+ |
| 8 | ? "Newfoundland" | 1775 | 4,000–4,163 |
| 9 | 3 "Monterrey" | 1909 | 4,000 |
| 10 | 4 "San Ciriaco" | 1899 | 3,855 |
| Largest Atlantic hurricanes By diameter of gale-force winds | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | System | Season | Diameter | |
| mi | km | |||
| 1 | Sandy | 2012 | 1,150 | 1,850 |
| 2 | Martin | 2022 | 1,040 | 1,670 |
| 3 | Igor | 2010 | 920 | 1,480 |
| 4 | Olga | 2001 | 865 | 1,390 |
| 5 | Teddy | 2020 | 850 | 1,370 |
| Sources: [1][2][3][4] [5] | ||||
| Most intense landfalling tropical cyclones in the United States Intensity is measured solely by central pressure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | System | Season | Landfall pressure |
| 1 | "Labor Day" | 1935 | 892 mbar (hPa) |
| 2 | Camille | 1969 | 900 mbar (hPa) |
| Yutu | 2018 | ||
| 4 | Michael | 2018 | 919 mbar (hPa) |
| 5 | Katrina | 2005 | 920 mbar (hPa) |
| Maria | 2017 | ||
| 7 | Andrew | 1992 | 922 mbar (hPa) |
| 8 | "Indianola" | 1886 | 925 mbar (hPa) |
| 9 | "Guam" | 1900 | 926 mbar (hPa) |
| 10 | "Florida Keys" | 1919 | 927 mbar (hPa) |
| Source: HURDAT,[3] Hurricane Research Division[4] | |||
| Most intense landfalling Atlantic hurricanes Intensity is measured solely by central pressure | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Hurricane | Season | Landfall pressure |
| 1 | "Labor Day"[nb 2] | 1935 | 892 mbar (hPa) |
| 2 | Camille | 1969 | 900 mbar (hPa) |
| Gilbert | 1988 | ||
| 4 | Dean | 2007 | 905 mbar (hPa) |
| 5 | "Cuba" | 1924 | 910 mbar (hPa) |
| Dorian | 2019 | ||
| 7 | Janet | 1955 | 914 mbar (hPa) |
| Irma | 2017 | ||
| 9 | "Cuba" | 1932 | 918 mbar (hPa) |
| 10 | Michael | 2018 | 919 mbar (hPa) |
| Sources: HURDAT,[3] AOML/HRD,[6] NHC[7] | |||
| Rank | Hurricane | Season | Damage | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Irma | 2017 | $13.2 billion | [8] |
| 2 | Ike | 2008 | $7.3 billion | [9] |
| 3 | Matthew | 2016 | $2.58 billion | [10] |
| 4 | Gustav | 2008 | $2.1 billion | [9] |
| 5 | Michelle | 2001 | $2 billion | [11] |
| Sandy | 2012 | [12] | ||
| 7 | Dennis | 2005 | $1.5 billion | [13] |
| 8 | Ivan | 2004 | $1.2 billion | [14] |
| 9 | Charley | 2004 | $923 million | [14] |
| 10 | Wilma | 2005 | $700 million | [15] |
South Atlantic basin
[edit]Tropical cyclones rarely form in the South Atlantic Basin. Only seven South Atlantic tropical cyclones in the area have been confirmed.
- The 1974 Subtropical Cyclone, 1974 - a subtropical storm formed in March off the coast of Brazil.
- The Angola Cyclone, 1991 - a tropical storm formed off Angola in April.
- The Brazil Cyclone, 2004 - a cyclone of depression and possibly storm strength formed in January.
- Cyclone Catarina, 2004 - first positively observed cyclone in the South Atlantic Ocean, and the first one to make landfall as a cyclone.
- The February Cyclone, 2006 - a small cyclone of tropical storm strength that formed 600 miles off the coast of Rio de Janeiro.
- The 2009 Suptropical Cyclone, 2009 - a subtropical storm formed in January off the coast of Uruguay.
- Tropical Storm Anita, 2010 - The second properly named South Atlantic storm, formed in March 2010.
Eastern Pacific basin
[edit]These records are held by Pacific hurricanes.
| Rank | Cyclone | Season | Damage | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Otis | 2023 | $12–16 billion | [16] |
| 2 | Manuel | 2013 | $4.2 billion | [17] |
| 3 | Iniki | 1992 | $3.1 billion | [1] |
| 4 | John | 2024 | $2.5 billion | [18] |
| 5 | Odile | 2014 | $1.25 billion | [19] |
| 6 | Agatha | 2010 | $1.1 billion | [20] |
| 7 | Hilary | 2023 | $915 million | [21] |
| 8 | Willa | 2018 | $825 million | [22] |
| 9 | Madeline | 1998 | $750 million | [23] |
| 10 | Rosa | 1994 | $700 million | [24] |
| Hurricane | Season | Fatalities | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| "Mexico" | 1959 | 1,800 | [25] |
| Paul | 1982 | 1,625 | [26][27][28][29] |
| Liza | 1976 | 1,263 | [30][31][32] |
| Tara | 1961 | 436 | [33] |
| Pauline | 1997 | 230–400 | [34] |
| Agatha | 2010 | 204 | [35][36] |
| Manuel | 2013 | 169 | [37] |
| Tico | 1983 | 141 | [38][39] |
| Ismael | 1995 | 116 | [40] |
| "Lower California" | 1931 | 110 | [41][42] |
| "Mazatlán" | 1943 | 100 | [43] |
| Lidia | 1981 | 100 | [36] |
| Hurricane | Season | Wind speed | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Otis | 2023 | 160 mph (260 km/h) | [44] |
| Patricia | 2015 | 150 mph (240 km/h) | [45] |
| Madeline | 1976 | 145 mph (230 km/h) | [46] |
| Iniki | 1992 | [47] | |
| Twelve | 1957 | 140 mph (220 km/h) | [48] |
| "Mexico" | 1959 | [48] | |
| Kenna | 2002 | [49] | |
| Lidia | 2023 | [50] |
Western Pacific basin
[edit]These records are held by: Pacific typhoon
Retired names
[edit]| Saffir–Simpson scale | ||||||
| TD | TS | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
Names retired before 2000 were done so by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Names during and after that year were retired by the Japan Meteorological Agency.
PAGASA also retires names for typhoons and tropical storms that affect the Philippines.
Significant typhoons with special names
[edit]Eight especially significant typhoons were named by Japan Meteorological Agency according to the area where they caused most damage.
| Name | Number | Japanese name |
|---|---|---|
| Ida | T4518 | Makurazaki Typhoon (枕崎台風)[52][53] |
| Louise | T4523 | Akune Typhoon (阿久根台風) |
| Marie | T5415 | Tōya Maru Typhoon (洞爺丸台風) |
| Ida | T5822 | Kanogawa Typhoon (狩野川台風) |
| Sarah | T5914 | Miyakojima Typhoon (宮古島台風) |
| Vera | T5915 | Isewan Typhoon (伊勢湾台風) |
| Nancy | T6118 | 2nd Muroto Typhoon (第2室戸台風) |
| Cora | T6618 | 2nd Miyakojima Typhoon (第2宮古島台風) |
| Della | T6816 | 3rd Miyakojima Typhoon (第3宮古島台風) |
| Babe | T7709 | Okinoerabu Typhoon (沖永良部台風) |
| Faxai | T1915 | Reiwa 1 Bōsō Peninsula Typhoon (令和元年房総半島台風) |
| Hagibis | T1919 | Reiwa 1 East Japan Typhoon (令和元年東日本台風) |
Other notable named storms
[edit]- Typhoon Wanda, 1962, Hong Kong - Often cited by Hong Kong residents as an example of a deadly storm. Although it ranked only as Category 2 on the Saffir-Simpson scale, the deficient warning system at the time led to many deaths in the villages of the New Territories unaware of the storm surge.
- Typhoon Ruby, 1964 - the strongest and worst of named typhoons to hit Hong Kong in recorded history. Killed over 700 and caused widespread damage.
- Typhoon Nina, 1975 - Dropped rain over eastern China, contributing to the collapse of the Banqiao Dam which killed at least 170,000
- Typhoon Tip, 1979, Japan - Most intense and largest tropical cyclone on record
- Typhoon Wayne, 1986 - The longest-lived Northwest Pacific tropical system ever observed in recorded history lasting 22 days throughout its lifetime.
- Typhoon Gay, 1989 - Rare typhoon that crossed Thailand as a 120 mph (190 km/h) cat 3 typhoon; crossed into North Indian Ocean Basin and hit India as a cat. 5, killing 39.
- Typhoon Herb, 1996, Taiwan and China - The strongest and the largest storm of this year, dropped heavy rain over Taiwan and China, killing hundreds.
- Typhoon Ivan and Typhoon Joan, 1997 - two of the most intense cyclones ever recorded at 872 mb; reached extreme intensities at close distance to each other.
- Typhoon Zeb, 1998 cat. 5 with 872 milibars of pressure; caused severe damage in the Philippines, killing nearly 100.
- Typhoon Maggie, Typhoon Sam, Typhoon York and Tropical Storm Cam 1999, Hong Kong - Four storms to directly strike the vicinity of Hong Kong within one typhoon season
- Typhoon Fengshen, 2008 - is a typhoon that struck the Philippines with an unusual path hence was poorly forecasted throughout its lifetime. 800 of the 856 people on board the MV Princess of the Stars were killed when the ship capsized at the height of the typhoon. Testimonies from survivors of the maritime tragedy suggest that the ferry have actually passed the typhoon's eye directly.[54] There is a total of 1371 direct fatalities and 87 people missing during the storm's lifetime.
- Tropical Storm Nangka, 2009 - while not a strong storm, it managed to spawn a tornado and a hail with the latter being extremely rare in the Philippines.[55]
- Typhoon Parma, 2009 - is another unusual typhoon to strike Philippines. It made an unprecedented three consecutive landfalls in the same area in Northern Luzon, Philippines alone and had moved very slowly and at times, almost stationary in its second and third landfalls which resulted in heavy flooding and constant wind damage[56][57]. Ilocos provinces and Abra (province) reportedly experienced typhoon-force winds and heavy rains for 15 hours straight.[58]
Notable unnamed storms
[edit]- The Kamikaze, 1281, destroyed a Mongol invasion fleet attacking Japan.
- A system of unknown intensity that hit Haiphong in 1881, killing 300,000 people.
- The 1922 Swatow Typhoon, a system of unknown intensity that struck Swatow, China late on August 2, 1922, killing more than 50,000 people.[59]
- Typhoon Muroto, 1934 — killing at least 3,036, another 15,361 are injured, with 92,323 houses are lost.
- The Great Hong Kong Typhoon of 1937 - killed 11,000
- Typhoon Cobra (Typhoon of 1944), 17–18 December, three US destroyers lost
- 1945 Makurazaki Typhoon — killing at least 3,756, another 2,452 are injured, with 116,491 houses are lost.
- Typhoon of July 1949 - killed 1,600 in Shanghai, making it the deadliest typhoon in the city's history.
Most active West Pacific seasons
[edit]The following are the most active Western Pacific seasons, according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center best track. Only seasons with at least 30 storms are included.
| Total Storms |
Year | Tropical Storms |
Typhoons | Super Typhoons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 39 | 1964 | 13 | 19 | 7 |
| 35 | 1965 1967 1971 |
14 15 11 |
10 16 16 |
11 4 4 |
| 34 | 1994 | 14 | 14 | 6 |
| 33 | 1996 | 12 | 15 | 6 |
| 32 | 1974 | 16 | 16 | 0 |
| 31 | 1989 1992 |
10 9 |
15 17 |
6 5 |
| 30 | 1962 1966 1972 1990 2004 |
7 10 8 9 10 |
17 17 20 17 13 |
6 3 2 4 7 |
Northern Indian Ocean
[edit]This region has had some of the world's deadliest cyclones, but there is a shortage of organized information about them. Only cyclones which caused fatalities over 3000 people have been included.[60][61][62] [63] [64]
- 1584 Backerganj Cyclone killed around 200,000 people.
- 1737 Calcutta cyclone, caused death and destruction around Calcutta, India.
- 1789 Indian Cyclone, killed 20,000 in Coringa, India.
- 1839 Indian Cyclone - caused a massive storm surge hit Coringa, India on November 25 killed 300,000 people.
- 1864 Calcutta Cyclone, killed around 60,000 people in Calcutta, India.
- 1876 Great Backerganj Cyclone hit the Meghna River Delta area of India, the storm surge killed 100,000, and the disease after the storm killed another 100,000.
- 1882 Great Bombay Cyclone killed around 200,000 people in Bombay, India.
- 1897 Chittagong cyclone killed around 175,000 in Chittagong, Bangladesh.
- 1942 Bengal Cyclone hit near the India/Bangladesh border, resulting in around 40,000 fatalities.
- 1960 East Pakistan I Cyclone 6,000 deaths can be attributed to a cyclone that hit the eastern portion of Bangladesh what was known then as East Pakistan on October 10
- 1963 East Pakistan II Cyclone on May 23, a cyclone hit present-day Bangladesh (then known as East Pakistan province), causing 22,000 fatalities due to storm surge and flooding.
- 1965 Pakistani Bengali Cyclones Two cyclones that hit on May 11 and June 1 killed a total of 47,000 people.
- 1965 Pakistani Cyclone hit near Karachi, Pakistan on December 15, causing about 10,000 casualties.
- 1970 Bhola cyclone, killed between 300,000 to 500,000 people in East Pakistan (now Bangladesh).
- 1971 Orissa Cyclone killed around 10,000 people in Cuttack, India.
- 1977 Andhra Pradesh Cyclone, killed 10,000 people in Andhra Pradesh, India.
- 1985 Cyclone 01B on May 25. Bangladesh, Meghna River Delta a cyclone created a surge 15-to 20-foot high killing around 6,000 - 10,000 people.
- 1988 Cyclone 04B on November 26 the cyclone hit the Sundarbans part of Bangladesh. Heavy storm surge killed 2000 people (with 6000 missing). In addition, the storm caused 1000 fatalities in Malaysia, Thailand, and western Indonesia.
- 1991 Bangladesh cyclone, killed 138,000 people in the Chittagong region of Bangladesh.
- 1999 Orissa cyclone, killed around 10,000 people in the Orissa state of India.
- 2007: Cyclone Sidr, struck Bangladesh on 15 November, has killed at least 3,500 people.
- 2008: Cyclone Nargis, struck the Irrawaddy Delta in Burma killing over 145,000 people and devastating the country's former capital and largest city, Rangoon, making it Burma's deadliest natural disaster in history, the costliest North Indian cyclone on record, and the second deadliest North Indian cyclone in recorded history.
Most active seasons
[edit]| Total Storms | Year | Tropical Depressions | Tropical Storms | Tropical Cyclones (>64kt) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | 1992 | 2 | 8 | 3 |
| 8 | 1987 | 0 | 8 | 0 |
| 8 | 1996 | 0 | 4 | 4 |
| 8 | 1998 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| 8 | 2005 | 1 | 6 | 1 |
Australian tropical cyclones
[edit]See[65] See also Australian Bureau of Meteorology - Severe Weather Events
- Cyclone Mahina, March 4, 1899 - 410 people died.
- 1918 Mackay cyclone, 1918 - 30 dead, extensive damage.
- 1949 Rockhampton cyclone, 1949 - 6 dead, 1,000 houses damaged and 500 totally wrecked.
- Cyclone Ada, 1970 - struck Whitsunday Island resorts and Whitsunday coast mainland. 14 people died and cost approximately AU$390 million.
- Cyclone Althea, 1971 - struck Magnetic Island and Townsville, Queensland on Christmas Day
- Cyclone Wanda, 1974 - caused extensive flooding in south-eastern Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales
- Cyclone Tracy, 1974 - 71 people died when the city of Darwin, Northern Territory, was devastated on Christmas Day. It is the costliest Australian cyclone on record.
- Cyclone Alby, 1978 - 5 people died in south-western parts of Western Australia. Albany recorded one of the strongest wind gusts on record.
- Cyclone Bobby, 1995 - 7 people died on two fishing trawlers sunk off the coast of Onslow; the cyclone then became a depression which caused heavy rain and flooding in inland WA, washing out the Eyre Highway and the Trans-Australian Railway for several days.
- Cyclone Justin, 1997 - 7 people died and damage came to approximately 190 million AUD.
- Cyclone Thelma, 1998 - intense Category 5 system that hit the Kimberley region of Western Australia causing extensive damage and flooding near Darwin.
- Cyclone Vance, 1999 - Category 5 system that caused extensive damage to the Western Australian towns of Exmouth and Onslow.
- Cyclone Steve, 2000 - A long-lived Category 2 storm, causing flooding in Queensland, Northern Territory and Western Australia.
- Cyclone Rosita, 2000 - Category 5, made a destructive landfall near Broome, Western Australia.
- Cyclone Ingrid, 2005 - Category 5 cyclone which took a long track over Northern Australia.
- Cyclone Larry, 2006 - Category 4 which crossed the Queensland coast at Innisfail, causing $1 billion in damage.
- Cyclone Glenda, 2006 - Category 5 which crossed the West Australian coast as Category 3 near Onslow
- Cyclone Monica, 2006 - Category 5; strongest cyclone ever recorded in the Southern Hemisphere (in terms of wind speed). Arguably the world's strongest cyclone, based on a Dvorak estimation, which suggested central pressure reached a low of 869 hPa. The official JTWC pressure was 879hPa.
- Cyclone George, 2007 - Category 5 which struck east of Port Hedland causing 3 fatalities.
- Cyclone Guba, 2007 - Category 1 cyclone (SSHS) which struck Papua New Guinea causing over 170 fatalities.
- Cyclone Hamish, 2009 - Category 5 cyclone (SSHS) which hovered off the southeast coast of Queensland near Mackay in March 2009. Two crew members from a capsised fishing trawler were never found.
- Cyclone Laurence, 2009 - First Category 5 cyclone to make landfall in Australia since Cyclone George, crossing the coast near Wallal in the Pilbara region of Western Australia. No fatalities or injuries were reported, however there was extensive damage to property and an estimated 1500 head of livestock were killed.
Size extremes
[edit]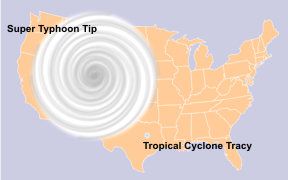
- Typhoon Tip is the largest tropical cyclone on record at 1350 miles (2170 km) wide, October (1979)
- Tropical Storm Marco is the smallest significant tropical cyclone on record at 10 miles (20 km) wide, October 2008.
These sizes indicate the distance from the center at which gale-force winds could be found.[66]
Highest storm surge
[edit]The four powerful hurricanes listed below caused very high storm surge. Hurricane Katrina had the highest recorded storm surge of any Atlantic hurricane, Hurricane Camille had the second-highest, and Hurricane Ike the third-highest. Worldwide storm surge data is sparse. Cyclone Mahina is generally regarded as having had the highest storm surge ever recorded, although measurements from before modern times must be viewed with some skepticism.
Storm surge is enhanced by high winds and greater storm size. The shape of the coastline and the contour of the bottom near the coast are also significant factors.
- Cyclone Mahina: 48 feet (15 m), South Pacific, 1899
- Hurricane Katrina: 28 feet (8.5 m), Atlantic Ocean, 2005[67]
- Hurricane Camille: 24 feet (7.3 m), Atlantic Ocean, 1969
- Hurricane Ike: 22 feet (6.7 m), Atlantic Ocean, 2008[68][69]
Unusual landfalls
[edit]For unusual landfalls in the Atlantic basin, see List of notable Atlantic hurricanes. For unusual tropical cyclone formation areas, see list of unusual areas of formation.
Morocco
[edit]- 2005 - Tropical Storm Delta hit the Canary Islands of Spain and then took a northeastern turn making landfall in Morocco.
Arabian Peninsula
[edit]- October, 1948 - Tropical Cyclone struck Salalah in Oman.
- May, 1959 - Tropical Cyclone struck Salalah in Oman
- June, 1977 - Tropical Storm struck Oman
- 1983 - Tropical Storm 01-A struck Oman.
- May, 1984 - Tropical Storm 01-A transited the Gulf of Aden and made landfall in northwest Somalia, the first tropical cyclone on record to do so.
- October, 1992 - Tropical Storm 06-A struck Oman.
- June, 1996 - Tropical Storm 02-A struck Oman.
- May, 2002 - Tropical Storm struck Salalah in Oman.
- June, 2007 - Cyclone Gonu struck parts of Oman, causing catastrophic damage.
- October, 2008 - Cyclone 03B struck southeast of Yemen, killing 184 people.
- June, 2010 - Cyclone Phet struck Omen as a Very Severe Cyclonic Storm, killing 24.
- November, 2011 - Cyclone Kelia struck Omen as a tropical storm, killing 14.
Brazil
[edit]- 2004 - A tropical depression hit eastern Brazil in January 2004, causing torrential flooding.
- 2004 - The only hurricane-strength tropical system ever observed in the South Atlantic, Cyclone Catarina, made landfall in the Brazilian state of Santa Catarina.
California
[edit]- 1858 - A hurricane just barely missed landfall in San Diego, causing considerable damage.
- 1939 - A tropical storm struck Long Beach killing 45 people.
- 1972 - Tropical Depression Hyacinth made landfall near Los Angeles and brought rain around the area.
Somalia
[edit]- 1984 - A tropical storm struck Somalia,
- 1984 - A late season cyclone slammed Somalia.
- 1994 - Somalia was hit by a tropical storm that brought 65 mph (105 km/h) winds and heavy rains.
- 1997 - A weak November storm made landfall in Eastern Somalia.
Spain
[edit]- 2005 - Hurricane Vince Made landfall in southwestern Spain as a tropical depression. Vince is the only recorded tropical system to make landfall on Spain.
Southern Western Australia
[edit]- 1956 - A cyclone made a close track along the whole Western Australian coast, and made a near landfall near Perth.
- 1978 - Cyclone Alby made a close encounter to the south-west of Western Australia as a strong extratropical system in the vicinity of Perth and Albany, causing extensive damage and five deaths. Albany recorded one of its highest wind gusts on record from Cyclone Alby.
- 1989 - Cyclone Ned passed almost directly over Perth.
Extreme latitudes
[edit]This list contains tropical cyclones that formed or moved to an extraordinary latitude. It can be extreme north (or south) latitude, or very equatorial cyclones.
- 1966 - Hurricane Faith reached an unprecedented northerly latitude of 62.5 degrees, just north of the Faroe Islands in the Norwegian Sea. Faith degenerated over Scandinavia, and the remnant low pressure area eventually reached Franz Josef Land, only 600 miles (970 km) from the North Pole.
- 1975 - A central Pacific unnamed hurricane formed at a record north latitude for the Central and East Pacific (tropical storm at 32N and hurricane at 40N)
- 2000 - Hurricane Alberto persisted north while tropical until a latitude of about 53°N.
- 2001 - Typhoon Vamei formed 85 miles (137 km) from the equator, the closest recorded formation location of a storm of hurricane strength.
- 2004 - Cyclone Agni reached a location of only 40 miles (64 km) from the equator, the closest to the equator any tropical cyclone has been recorded to have reached. However, Vamei retained the record for the most equatorial formation as Agni formed farther from the equator than Vamei and moved towards it.
The most intense tropical cyclones
[edit]| # | Cyclone | Season | Pressure | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hPa | inHg | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | Tip | 1979 | 870 | 25.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | Nora | 1973 | 875 | 25.8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June | 1975 | 875 | 25.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | Ida | 1958 | 877 | 25.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | Kit | 1966 | 880 | 26.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rita | 1978 | 880 | 26.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vanessa | 1984 | 880 | 26.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | Wilma | 2005 | 882 | 26.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | Nina | 1953 | 885 | 26.1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Joan | 1959 | 885 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Irma | 1971 | 885 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Forrest | 1983 | 885 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Megi | 2010 | 885 | 26.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: The International Best Track Archive for Climate Stewardship[70]|} Year-crossing Northern Hemisphere storms[edit]This is a list of Northern Hemisphere storms that have crossed two calendar years. Because the Southern Hemisphere cyclone season runs across the New Year, Southern Hemisphere storms that cross calendar years are not unusual, so they are not included here.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cite error: There are <ref group=nb> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist|group=nb}} template (see the help page).
