Tungsten(IV) chloride
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
tungsten tetrachloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.157.353 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| Cl4W | |
| Molar mass | 325.65 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | black solid |
| Density | 4.62 g·cm−3 |
| Melting point | 450 °C (842 °F; 723 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+P312, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P330, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Tungsten(IV) fluoride |
Related compounds
|
Tungsten(V) chloride Tungsten hexachloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tungsten(IV) chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula WCl4. It is a diamagnetic black solid. The compound is of interest in research as one of a handful of binary tungsten chlorides.
Structure and preparation
[edit]WCl4 is usually prepared by reduction tungsten hexachloride. Many reductants have been reported, including red phosphorus, tungsten hexacarbonyl, gallium, tin, and antimony. The latter is reported to be optimal:[1]
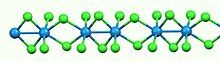
Like most binary metal halides, WCl4 is polymeric. It consists of linear chains of tungsten atoms each in octahedral geometry. Of six chloride ligands attached to each W center, four are bridging ligands. The W-W separations are alternatingly bonding (2.688 Å) and nonbonding (3.787 Å).
Reactions
[edit]Reduction of tungsten(IV) chloride with sodium yields the ditungsten(III) heptachloride derivative:[2]
- 2 WCl4 + 5 thf + 2 Na → [Na(thf)3][W2Cl7(thf)2] + NaCl
References
[edit]- ^ Zhou, Yibo; Kolesnichenko, Vladimir; Messerle, Louis (2014). "Crystalline and Amorphous Forms of Tungsten Tetrachloride". Inorganic Syntheses: Volume 36. Vol. 36. pp. 30–34. doi:10.1002/9781118744994.ch6. ISBN 978-1-118-74499-4.
- ^ Broderick, Erin M.; Browne, Samuel C.; Johnson, Marc J. A. (2014). "Dimolybdenum and Ditungsten Hexa(Alkoxides)". Inorganic Syntheses: Volume 36. Vol. 36. pp. 95–102. doi:10.1002/9781118744994.ch18. ISBN 978-1-118-74499-4.

