2024 Pacific typhoon season
| 2024 Pacific typhoon season | |
|---|---|
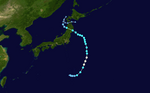
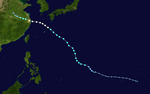
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 23, 2024 |
| Last system dissipated | December 26, 2024 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Yagi |
| • Maximum winds | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 915 hPa (mbar) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 39 |
| Total storms | 26 |
| Typhoons | 13 |
| Super typhoons | 6 |
| Total fatalities | 1,255 total |
| Total damage | $26.8 billion (2024 USD) (Fourth-costliest Pacific typhoon season on record) |
| Related articles | |
The 2024 Pacific typhoon season was the fifth-latest starting Pacific typhoon season on record, yet featured average activity, ending the streak of below average typhoon seasons that started in 2020. It was also the deadliest season since 2013, and became the fourth-costliest Pacific typhoon season on record, mostly due to Typhoon Yagi. This season saw an unusually active November, with the month seeing four simultaneously active named storms. The season runs throughout 2024, though most tropical cyclones typically develop between May and October. The season's first named storm, Ewiniar, developed on May 25, and eventually intensified into the first typhoon of the season, while the last named storm, Pabuk, dissipated on December 26. This season was an event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation in the western Pacific Ocean.
The scope of this article is limited to the Pacific Ocean to the north of the equator between 100°E and 180th meridian. Within the northwestern Pacific Ocean, there are two separate agencies that assign names to tropical cyclones which can often result in a cyclone having two names. The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA)[nb 1] will name a tropical cyclone if it has 10-minute sustained wind speeds of at least 65 km/h (40 mph) anywhere in the basin. The Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assigns names to tropical cyclones which move into or form as a tropical depression in the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N–25°N, regardless of whether or not a tropical cyclone has already been given a name by the JMA. Tropical depressions that are monitored by the United States' Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC)[nb 2][nb 3] are given a number with a "W" suffix; W meaning west, a reference to the western Pacific region.
Seasonal forecasts
[edit]| TSR forecasts Date |
Tropical storms |
Total Typhoons |
Intense TCs |
ACE | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average (1991–2020) | 25.5 | 16.0 | 9.3 | 301 | [3] |
| May 7, 2024 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 225 | [3] |
| July 5, 2024 | 24 | 14 | 7 | 211 | [4] |
| August 7, 2024 | 24 | 14 | 7 | 177 | [5] |
| Other forecasts
Date |
Forecast
Center |
Period | Systems | Ref. | |
| January 15, 2024 | PAGASA | January–March | 0–2 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| January 15, 2024 | PAGASA | April–June | 2–4 tropical cyclones | [6] | |
| June 26, 2024 | PAGASA | July–September | 6–10 tropical cyclones | [7] | |
| June 26, 2024 | PAGASA | October–December | 4–7 tropical cyclones | [7] | |
| 2024 season | Forecast Center |
Tropical cyclones |
Tropical storms |
Typhoons | Ref. |
| Actual activity: | JMA | 39 | 26 | 13 | |
| Actual activity: | JTWC | 28 | 22 | 14 | |
| Actual activity: | PAGASA | 18 | 13 | 10 | |
During the year, several national meteorological services and scientific agencies forecast how many tropical cyclones, tropical storms, and typhoons will form during a season and/or how many tropical cyclones will affect a particular country. These agencies included the Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) Consortium of University College London, PAGASA, Vietnam's National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting and Taiwan's Central Weather Administration.
Tropical Storm Risk (TSR) released their first forecast on May 7, predicting below average activity with 25 named storms, 15 typhoons and 7 intense typhoons. This was primarily due to the dominant El Niño event at the time, which was expected to transition into a weak or moderate La Niña by mid-2024.[3] TSR released their early July forecast on July 5, where they slightly decreased the amount of storms and typhoons, mentioning the same factors as their previous forecast.[4] On August 7, TSR released their final forecast for the season, retaining the same number of storms. However, they further decreased the predicted ACE index, due to a slow start of the season and decreased tropical activity as of early August.[5] Moreover, with the Pacific Decadal Oscillation being in a negative phase since the beginning of 2020, they also mentioned how this season could become the lowest five-year activity since 1965.[5]
Seasonal summary
[edit]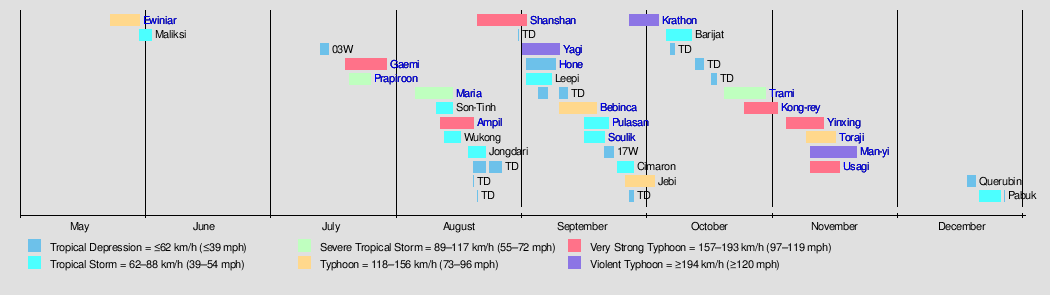
Background
[edit]Officially, the 2024 Pacific typhoon season had thirty-nine tropical depressions form; twenty-six became named storms. Thirteen became typhoons, six of which intensified into a super typhoon. This season's ACE index is approximately 210.1 units.[8] This number represents sum of the squares of the maximum sustained wind speed (knots) for all named storms while they are at least tropical storm intensity, divided by 10,000. Therefore, tropical depressions are not included.
| Rank | Total damages | Season |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | ≥ $38.96 billion | 2019 |
| 2 | ≥ $37.63 billion | 2023 |
| 3 | ≥ $30.54 billion | 2018 |
| 4 | ≥ $26.8 billion | 2024 |
| 5 | ≥ $26.43 billion | 2013 |
| 6 | ≥ $20.79 billion | 2012 |
| 7 | ≥ $18.77 billion | 2004 |
| 8 | ≥ $18.36 billion | 1999 |
| 9 | ≥ $17.69 billion | 2016 |
| 10 | ≥ $15.1 billion | 2017 |
Early season activity
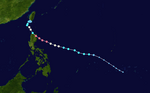
[edit]The Pacific typhoon season began on May 23, when a tropical storm named Ewiniar formed southeast of Palau, marking it as the fifth-latest start of a Pacific typhoon season since reliable records began.[9] Ewiniar tracked toward the Philippines, where it made nine landfalls in Homonhon Island; Giporlos, Eastern Samar; Basiao Island; Cagduyong Island; Batuan, Masbate; Masbate City; Torrijos, Marinduque; Lucena, Quezon and Patnanungan. It began to move over the warm tropical waters of Lamon Bay, where the JTWC and the JMA upgraded Ewiniar into a minimal typhoon. Ewiniar began transitioning to an extratropical cyclone while it is 719 km (447 mi) east-northeast of Kadena Air Base in Okinawa, Japan. On June 6, another extratropical cyclone[which?] would absorb the remnants of Ewiniar, just off the coast of Alaska. On May 30, another tropical depression formed southeast of Haikou, China. The next day, at 03:00 UTC, JTWC designated the disturbance as Tropical Depression 02W. A few hours later, JMA assigned the name Maliksi as they upgraded 02W into a tropical storm. Shortly after being named, on May 31, Maliksi made landfall in Yangjiang, Guangdong. The JMA and JTWC discontinued warnings as Maliksi moved inland and dissipated on June 2. No storms formed in June for the first time since 2010.

After many weeks of inactivity, on July 13, a tropical depression formed east of Vietnam, designated as 03W. Shortly after, it tracked into Vietnam, dissipating soon after. On July 19, two tropical disturbances recognized by the JTWC: one southeast of Manila and another east of Palau. Soon after, both disturbances developed into a depression, being named by PAGASA. The first one, west of Batangas, was named Butchoy while the second, east of Virac, was called Carina. Later that day, the JTWC followed suit, designating them both as depressions, with Butchoy being 04W and Carina as 05W. The next day, the easternmost disturbance, Carina was named Gaemi by the JMA. On July 21, Butchoy also intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name Prapiroon from the JMA. Prapiroon moved through the South China Sea as a mild tropical storm before landfall over Wanning, Hainan. Prapiroon moved through Gulf of Tonkin, where it further intensified into a severe tropical storm. Early on July 23, Prapiroon made its second and final landfall in Quảng Ninh, Vietnam.
Being in a favorable environment in the Philippine Sea, Gaemi continued to strengthen and became a typhoon, the second to occur this season. Gaemi rapidly intensified into a very strong typhoon, with 10-minute sustained winds of 165 km/h (105 mph). Gaemi stalled and executed a counterclockwise loop near the coast, slightly weakening before making landfall over Hualien, Taiwan. Weakened by the landfalls, the storm accelerated across the island and emerged into the Taiwan Strait, six hours after landfall. The next day, Gaemi made its final landfall at Xiuyu, Putian at Fujian Province as a weakening tropical storm. Moving inland, the storm rapidly weakened until it dissipated on July 27.
Even though Gaemi never made landfall in the Philippines, the storm's moisture would enhance the southwest monsoon. Heavy rainfalls were felt over Luzon and some parts of Visayas, leaving each region flooded. Overall, Gaemi caused 126 fatalities and $2.31 billion worth of damages throughout its track.
Peak season activity
[edit]
On August 3, a low-pressure area developed east of Kadena Air Base. At 00:00 UTC, JMA recognize the disturbance as a depression. However, it downgraded to a remnant low on August 7. The convection later meandered south of Ryukyu Islands for a few days before JMA reclassified it again as a depression on August 11. JMA issued a gale warning the next day, citing that it would intensify in the following days. JTWC later followed suit and upgraded into a tropical depression, 08W. On August 13, the depression became a tropical storm, receiving the name Ampil from the JMA. Ampil gradually intensified in the Pacific Ocean, becoming a severe tropical storm. JMA upgraded Ampil into a typhoon two days later, and the JTWC classified it as a Category 2-equivalent typhoon. The next day, it strengthened into a Category 4-equivalent typhoon. The typhoon passed just south of Greater Tokyo Area before weakening and transitioning to an extratropical cyclone.
On August 5, a low-pressure area was formed in Bonin Islands. The disturbance was in an environment with low to moderate wind shear and warm SSTs. JTWC later classified the disturbance into a depression the next day, giving the designation 06W. Early on August 8, JMA upgraded the depression into a storm, naming it Maria. The storm further strengthened into a severe tropical storm on the same day. At the same time, JTWC reported that Maria had rapidly intensified into a typhoon due to strong equatorward and poleward outflow. However, on August 9, Maria weakened into a tropical storm as it moved northeastwards. On August 10, another area of low pressure formed just southeast of Maria. The JTWC would classify the disturbance as a subtropical depression in their next bulletin. Despite being in a marginal environment and high wind shear, JMA upgraded into a tropical storm, assigning the name Son-Tinh. The next day, JTWC announced that Son-Tinh became tropical, designating it as 07W. Son-Tinh weakened back into a depression before it dissipated on August 14.
On the morning of August 12, Maria made landfall in Iwate Prefecture as a tropical storm, bringing strong winds and dumping heavy rains in northern Japan. Maria then weakened into a depression after moving inland. The storm entered through the Sea of Japan, weakening further the next day. The JTWC issued its final warning after Maria was last noted west-northwest of Misawa, Japan. JMA continued to track as a depression before they issued their final warning at 04:15 UTC.
Activity became more active when an area of convection was formed on August 12 near the southwest of a nearby storm Son-Tinh. JMA would immediately recognize the disturbance as a depression. The next day, JTWC went to give its identifier of the depression, which was Tropical Depression 09W. Just like Ampil, on August 13, 09W intensified into a tropical storm, attaining the name Wukong from the JMA. Wukong was short-lived due to its poorly organized cloud tops. JTWC made its final warning on Wukong as it moved through cooler waters and dissipated on August 15.
On August 17, JMA recognized a tropical depression that formed east of Taiwan. The next day, PAGASA declared the system a tropical depression, assigning the name Dindo. The depression was named Jongdari three hours later upon formation. JTWC later followed suit and upgraded into a tropical storm, with the designation of 10W. However, it did not last long and weakened into a depression as it nears the Korean Peninsula. On August 21, JMA and JTWC reported that Jongdari had dissipated as its low-level circulation center faded when it moved over land, after Jongdari, a low-pressure area formed in the Northern Mariana Islands on the same day. The system intensified into a tropical storm the next day, and the name Shanshan was picked up by the JMA. JTWC gave the designation of 11W to Shanshan.
Shanshan later strengthened into a Category 1-equivalent typhoon. It remained at that intensity as it battled through wind shear. As it nears the Amami Islands, it strengthened into a Category 4-equivalent typhoon. The approach of the typhoon caused the issuance of a special warning system in Kagoshima Prefecture, the first time issued in the area since Nanmadol of 2022. Around 08:00 JST on August 29, Shanshan made landfall near Satsumasendai, making the third tropical cyclone impact mainland Japan this season. Rapid erosion later ensued as it moved eastward over inland. Shanshan heads over Seto Inland Sea before it makes another landfall in Shikoku on the next day. Shanshan's convection began to be disorganized, causing it to weaken into a remnant low. However, it regained back into a depression as it moved east southeastward through open waters. JMA continued to track Shanshan until it dissipated on September 1.

Nearing the end of August, a tropical disturbance formed near Palau. On the same day, JMA started to issue advisories for the system as a depression. As it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), the agency gave it the name Enteng on the first day of September. JTWC followed suit and was classified as a depression, with its designation of 12W. At 21:00 JST (13:00 UTC), JMA developed into a tropical storm, naming the system Yagi. The storm made its first landfall in Casiguran in the province of Aurora. The mountainous terrain of the Cordillera Central had made Yagi weakened as it moved inland. It left PAR on early September 4 as it continues to intensify in the South China Sea.
Yagi later strengthened into a typhoon due to its highly favorable environmental conditions. The following day, it rapidly intensified, developing a distinct eye and briefly reaching Category 5-equivalent super typhoon status as it approached Hainan. The whole cloud system of Yagi covered the entire South China Sea. Although Yagi slightly weakened, it made its second landfall over Wenchang City in Hainan. The storm then moved over Haikou, China, and continued to make another landfall in Xuwen County, Guangdong. Afterward, Yagi entered the open waters of the Gulf of Tonkin.
Yagi became one of only four Category-5 typhoons recorded in the South China Sea, alongside Pamela (1954), Rammasun (2014), and Rai (2021). It also marked the most powerful typhoon to strike Hainan in autumn since Typhoon Rammasun in 2014. On September 7, Yagi underwent a period of reorganization and regained Category 4 status before making a historic landfall between Haiphong and Quang Ninh in Vietnam. Upon landfall, Yagi became the strongest storm to impact Northern Vietnam. The typhoon then weakened rapidly into a remnant low as it moved inland, dissipating on September 8. Even after dissipation, it still wreaked havoc, bringing heavy floods to Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand.
While Yagi was on its way to making landfall in the Philippines, JTWC announced another formation of a tropical disturbance in the open Pacific Ocean on September 2. JMA also started issuing advisories, and it was recognized as a tropical depression in the same location. Two days later, as JTWC upgraded it into a depression, it received its designation as 13W. A day later, JMA reported that 13W developed into a tropical storm, giving the name Leepi as the twelfth named storm of this season. Leepi then accelerated northeastwards before it became an extratropical cyclone on September 6.
On September 9, a tropical depression formed over the Micronesian Islands. The following day, the JTWC designated it as 14W. As it moved over Guam, 14W intensified into a tropical storm and was named Bebinca by the JMA. Despite encountering dry air, Bebinca strengthened as it began its northwestward movement. At 18:00 PHT on September 13, Bebinca entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility and was named Ferdie by PAGASA. Bebinca later strengthened into a minimal typhoon on the next day. On September 16, Bebinca made landfall in Lingang New City in Shanghai, China as a weakening Category-1 typhoon, and became the strongest typhoon to hit Shanghai since Typhoon Gloria of 1949.
As Bebinca moved toward eastern China, two tropical depressions formed in the Pacific on September 15—one near Guam and another within the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR). The JTWC designated the depression near Guam as 15W. It soon intensified into a tropical storm and was named Pulasan by the JMA. The PAR tropical depression was given the name Gener by PAGASA. At 02:00 PHT the following day, Gener landed over Palanan, Isabela. The storm continued to move westward over Northern Luzon, maintaining its strength as a depression. Meanwhile, Pulasan briefly entered the PAR at 18:30 PHT (10:30 UTC) and was assigned the name Helen. On September 18, two disturbances in the South China Sea near 98W and 99W were expected to merge and strengthen at 98W, closer to Vietnam. Shortly after, Gener was upgraded by the JTWC into a tropical depression, getting the designation 16W. On September 19, 16W was upgraded to a tropical storm and named Soulik by the JMA. Soulik made landfall over Vĩnh Linh District, Quảng Trị, in Vietnam. Meanwhile, Pulasan also made landfall over Zhoushan, China, similar to where Bebinca had made landfall three days earlier. After that, it made a second landfall over Shanghai, marking the first time since reliable meteorological records exist that two typhoons make landfall over Shanghai with only two days in between.
On September 20, a low-pressure area formed over Northern Luzon. The JTWC later designated the disturbance as Invest 90W upon its formation. Being inside the PAR, PAGASA initiated advisories and named the system Igme. The JTWC soon upgraded it into a tropical depression, designating it as 17W. Igme later curved southwestwards, passing closely to Taiwan. The storm later dissipated on September 22 after topographical interaction and high vertical wind shear had weakened the system significantly.
Following, on September 24, a tropical depression formed in the Pacific south of Japan. That day, JTWC designated the system as 18W. The following day, the JMA upgraded the depression into a tropical storm, earning the name Cimaron. The storm moved southwestwards, maintaining its intensity. As it moved westwards, Cimaron weakened into a tropical depression as an unfavorable environment hindered any intensification. Cimaron later dissipated on September 27. Shortly later the same day, another low-pressure area formed near the Northern Mariana Islands. Despite being in a marginal environment, the disturbance managed to be organized and designated as 19W by the JTWC. On September 27, the JMA upgraded 19W into a tropical storm, naming it Jebi. At first, Jebi struggled to organize due to the presence of moderate low-level windshear, causing to downgrade Jebi as a depression. However, Jebi redeveloped back into a tropical storm after. The storm continued to organize until it further intensified into a Category-1 typhoon by the JTWC, while JMA only reached the intensity of a severe tropical storm. Jebi later transitioned to an extratropical cyclone, causing both agencies to issue their final warning on October 2.
Shortly after Cimaron weakened into a depression, an area of low pressure formed in the Philippine Sea near extreme Northern Luzon on September 26, PAGASA shortly issued bulletins regarding the disturbance and was named Julian as it developed into a depression. The following day, the JTWC designated Julian as 20W, upgrading it into a tropical depression. On September 28, the JMA upgraded 20W into a tropical storm, naming it Krathon, a replacement name for Mangkhut. It then intensified into a Category-1 typhoon, heading towards Sabtang, Batanes. Shortly after, the typhoon began its rapid intensification and in two days, the system reached its peak intensity equivalent to a Category-4 super typhoon. On October 3, Krathon made landfall over Siaogang District in Kaohsiung, Taiwan. The typhoon became the first storm to make landfall in Taiwan's densely populated western plains since Typhoon Thelma in 1977. The storm weakened while moving inland, marking the first time it had happened in Taiwan since Tropical Storm Trami in 2001. The JMA continued to track the system to the South China Sea before it dissipated on October 4.
Late season activity
[edit]On October 5, a tropical depression formed near Guam. The following day, the JTWC designated it as 21W. Despite moving through warm waters, high wind shear hindered any further development, causing it to weaken back into a disturbance. On October 8, the JTWC issued its final warning, with dissipation expected in the next 12 hours. The next day, 21W intensified into a tropical storm, receiving the name Barijat from the JMA. Later in the day, JTWC reissued advisories on Barijat and strengthened into a tropical storm. However, both agencies later made their final warning for the last time as the storm dissipated on October 11.

On October 19, a tropical depression formed nearby Yap. The next day, it was assigned as 22W by the JTWC, acknowledged as a tropical depression. Then, it moved into the PAR and was named Kristine by PAGASA. Soon after, the JMA upgraded it to tropical storm status and was given the name Trami. Many parts of the Philippines were issued wind storm signals prior to its approach to the country. On October 23, Trami later strengthened into a severe tropical storm, causing some northern and central Luzon areas to upgrade to Tropical Cyclone Wind Signal No. 3. At 04:30 UTC the next day, Trami made landfall over the province of Divilacan, Isabela. The following day, Trami emerged above the coastal waters of southern Ilocos Sur, leaving the remnants of a circulation center over Northern Luzon. This caused a lot of areas in the country to bring torrential rains with gusty winds throughout the day.
Trami continued crossing the South China Sea, maintaining severe tropical storm strength. Trami later encountered strong easterly vertical wind shear as it approached the coast of Vietnam. The storm later made another landfall in Da Nang at 10 AM local time on October 27. Trami then moved southwestwards due to weak steering flow before making a U-turn over the coastal regions of Vietnam. Trami later weakened into a low-pressure area before the agencies made its last warning on October 29.
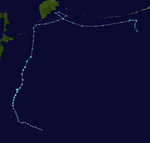
As Trami crossed through the Cordilleras, another tropical disturbance was formed southeast of Guam on October 24. JMA began to track the system thereafter as a tropical depression, with a gale warning also being issued. The next day, JMA upgraded the disturbance into a tropical storm, assigning the name Kong-rey. Since another disturbance was formed as Invest 99W on the northern side, the JTWC canceled warnings on the southern side, designated as 98W and issued Kong-rey at 99W, located in the north side. Kong-rey was later designated as Tropical Depression 23W by the JTWC. The storm entered PAR, receiving the local name Leon. On October 29, Kong-rey started undergoing rapid intensification and became a Category-4 super typhoon the following day. With that, Kong-rey achieved a peak intensify of 1-minute sustained winds of 240 km/h (150 mph) and a central pressure of 925 hPa (27.32 inHg).
Shortly after reaching its peak intensity, Kong-rey started to slightly weaken as it went through eyewall replacement cycle moving northwestwards. The storm later made a historic landfall over Chenggong, Taitung in Taiwan, marking the first major typhoon to make landfall in the country after mid-October, and the largest typhoon to hit since Typhoon Herb of 1996. Kong-rey later reemerged through the Taiwan Strait with a weakened convective structure around the center. Kong-rey weakened and transitioned to an extratropical cyclone over Sasebo, Japan, causing both agencies to cease advisories on November 1.

Just after Kong-rey transitioned to a post-tropical cyclone, an area of low pressure was formed near Palau on November 1. However, JTWC discontinued issuing advisories as unfavorable conditions hindered the development. Two days later, JTWC reissued advisories as signs of organization of the disturbance continued to form. At 14:00 UTC, the JTWC along with JMA upgraded the system to a tropical depression, assigning it the designation Tropical Depression 24W. Later at 18:00 UTC of November 3, 24W intensified into a tropical storm, gaining the name Yinxing by the JMA. Yinxing would enter the Philippine Area of Responsibility, receiving the name Marce by PAGASA. The storm would continue to intensify over the Philippine Sea until the agencies were prompted to classify as a typhoon on the following day. It then reached its peak intensity of a Category-4 typhoon, with 1-minute sustained winds of 230 km/h (145 mph) and a central pressure of 940 hPa (27.76 inHg). Around 3:40 PM PHT (07:40 UTC) of November 7, Yinxing made landfall over Santa Ana, Cagayan. After crossing through Babuyan Channel, the storm made its second landfall over Sanchez Mira, Cagayan. Yinxing slightly weakened into a Category-2 typhoon after making landfall, but eventually regained as a Category-3 typhoon as it reemerged through South China Sea.
On November 8, a tropical disturbance formed east of Southern Luzon. The disturbance was moving westward as it continues to organize itself in a favorable environment. At 8:00 AM PHT (00:30 UTC) of the following day, it entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), where it attained the name Nika by PAGASA. Not long after Nika formed, another area of low pressure formed near Marshall Islands on the following day, designated as Invest 93W. The low pressure was also located in a favorable development and low vertical wind shear, causing to issue of a TCFA regarding the disturbance. Hours later, 93W became a tropical depression, giving the identifier 25W. The JTWC also upgraded Nika into a depression, designated as 26W.

Later that day, both depressions strengthened into tropical storms and were named Toraji for 26W and Man-yi for 25W by the JMA. On November 10, Toraji further intensified into a severe tropical storm by the JMA, while JTWC automatically upgraded the system into a Category-1 typhoon as the outer bands of the system continues to tighten up. JMA later followed suit and granted Toraji to intensify into a minimal typhoon before it struck the province of Dilasag, Aurora. It later emerged over South China Sea, just off the coast of Magsingal, Ilocos Sur, with satellite imagery showing a tightly wrapped low-level circulation. As it moved northwestwards, a small patch of deep convection developed over the northern portion of a partially exposed low-level circulation, resulting in the system weakening into a tropical storm on November 11.
Meanwhile, on November 9, a tropical depression formed near Micronesia. The following day the JMA issued a warning on the system. On November 11, the JTWC upgraded it into a tropical depression, designating it as 27W. In early morning the next day, 27W strengthened into a tropical storm, prompting the JMA to name it Usagi. This marks the first time in this basin since reliable meteorological records that four active systems existed simultaneously in November.[10] Meanwhile, Usagi entered Philippine Area of Responsibility (PAR), getting the name Ofel from PAGASA. Usagi continued to strengthen until it underwent rapid intensification, prompting it to upgrade into a Category-4 super typhoon on November 14. At 1:30 PM PHT (05:30 UTC) of the same day, the storm made landfall over Baggao, Cagayan. Usagi later weakened as the eye began to disappear after having land interaction with the mountains.
Upon giving the name Usagi as 27W, the Northwest Pacific witnessed a historical rarity on November 12, witnessing double typhoons in the South China Sea for the first time since 1992 by Angela and four storms simultaneously active in November since records began in 1951 and the basin for the first time since 1970.
Meanwhile, after Man-yi maintained tropical storm strength for five days, JMA upgraded it into a severe tropical storm as it moved into a more favorable environment. At 20:00 PHT (12:00 UTC) on November 14, Man-yi briefly entered PAR, gaining the name Pepito by PAGASA. Early November 16, Man-yi peaked as a super typhoon, with estimated 1-minute maximum sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph) and a central pressure of 920 hPa (27.17 inHg). At 9:40 PM PHT (05:40 UTC) of the same day, Man-yi made its first landfall over the province of Panganiban, Catanduanes, packing strong winds and heavy rains all over the area. The following day, Man-yi made its second landfall in Dipaculao, Aurora, on Luzon Island at around 3:20 PM PHT (07:20 UTC).[11] The Sierra Madre mountain range caused the eye of the typhoon to close as it rapidly moved inland. Man-yi later accelerated northwestward over the South China Sea, weakening into a severe tropical storm. It then continued to deteriorate as it moved through increased vertical wind shear. JTWC issued its final warning on Man-yi on November 19 as the system weakened to a tropical depression, while the JMA continued to monitor it until it was last noted at 06:00 UTC on the following day.
After weeks of inactivity, on December 17, a low-pressure area was formed southeast of Mindanao. The next day, the disturbance entered PAR, where it became a depression. It was later given the local name Querubin by PAGASA, the replacement name for Quinta. Although in a favorable environment, Querubin struggled to organize itself due to its movement, which tried to move closely inland, hindering its development. With JTWC, the TCFA was initiated twice, citing a high chance of development, however, as it crossed between Visayas and Mindanao, PAGASA issued its final warning for Querubin on December 18 as it downgraded into a well-marked disturbance. JTWC continued to monitor Querubin despite being downgraded to low chance, but it eventually ceased bulletins the next day after the agency last noted as a disturbance.
The last tropical cyclone of 2024 developed on December 20 over northeast Malaysia, designated as 98W. The low-pressure area had brought gusty conditions to Sarawak, Sabah, and Brunei throughout the formation. The next day, the JTWC issued a TCFA warning, citing a high chance of development. However, another disturbance, designated as 99W was also present in the basin. This caused JTWC to downgrade 98W to a low chance and instead give bulletins at 99W. Despite not being present inside PAR, PAGASA named the disturbance Romina, the replacement name for Rolly, as it threatens the Kalayaan Islands. The JTWC later designated Romina as 28W. Hours later, JMA upgraded 28W into a tropical storm, assigning the name Pabuk. It then moved westward and turned toward Vietnam, weakening back to a depression due to low-level flow associated with a northeasterly cold surge along the eastern coast of Vietnam. Pabuk made its last warning on 18:00 UTC of December 26 as it further downgraded into a well-marked disturbance.
Systems
[edit]Typhoon Ewiniar (Aghon)
[edit]| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 2 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 23 – May 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min); 970 hPa (mbar) |
On May 21, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) began tracking an area of atmospheric convection 441 km (274 mi) southeast of Palau, noting that the system was moving northwestward towards an environment favorable for tropical cyclogenesis.[12] By May 23, the disturbance became a tropical depression.[13] The depression would later enter PAR, assigning the name Aghon, a replacement name for Ambo.[14] At 18:00 UTC, the JTWC designated the depression as 01W, based on surface observations from Guiuan.[15] Aghon made landfall over Homonhon Island and subsequently Giporlos, Eastern Samar in the early morning of May 25 (PHT).[16] It made five more landfalls over Basiao and Cagduyong Islands of Catbalogan; Batuan in Ticao Island; Masbate City; and Torrijos, Marinduque.[17] At 12:00 UTC, 01W intensified into a tropical storm while it was still in Tayabas Bay, prompted the JMA to name the storm as Ewiniar.[18] In the morning of May 26 (PHT), the storm made its eighth landfall over Lucena, Quezon in Luzon island.[17] Ewiniar later intensified into a typhoon over Lamon Bay[19] The storm made its final landfall over Patnanungan in the Polillo Islands.[20] The typhoon left the PAR on May 29 and continued to weaken due to subsidence around the mid-latitude.[19][16] On May 30, Ewiniar transitioned into an extratropical cyclone south-southwest of Yokosuka, Japan.[21] Then at 18:00 UTC on May 31, Ewiniar entered the baroclinic zone and an area of high wind shear.[19]
Typhoon Ewiniar resulted in ₱1.03 billion (US$20.88 million) in total damages in the Philippines, with ₱85.63 million (US$1.74 million) to agriculture and ₱942.55 million (US$19.14 million) to infrastructure, while also causing six deaths, injuring eight people, and impacting around 152,266 others. In Japan, heavy rainfall was observed in several regions, with a maximum of 52.5 mm (2.07 in) of rain being recorded in Miyake, Tokyo.[22][23]
JMA has upward the wind of Ewiniar to 140 km/h (85 mph) and downward it pressure to 970 hPa (28.64 inHg) in post analysis.
Tropical Storm Maliksi
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 30 – June 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
On May 29, the JTWC began tracking an area of convection located 406 km (252 mi) southeast of Haikou, China. Being in an area of warm waters and low vertical shear and having southerly outflow, the system sustained a weak circulation, inhibited from development by another area of convection near Mainland China.[24] It was recognized as a low-pressure area by the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) early the next day,[25] before the agency upgraded it to a tropical depression at 06:00 UTC.[26] Later that day, the JTWC issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) on the depression since it had rapidly developed.[27] At 00:00 UTC the next day, the JTWC upgraded the system into a tropical depression, designating it as 02W.[28] Later, the JMA upgraded it into a tropical storm, and it was given the name Maliksi.[29] However, the JTWC reported that it did not intensify into a tropical storm as it was disorganized, with the circulation elongating.[30][31] At 21:00 UTC on May 31, the JTWC discontinued warnings on the system as it made landfall in Yangjiang, Guangdong.[32] Soon after, the JMA last noted Maliksi as a depression on June 1 before weakening further into a low-pressure area the next day, as it tracked inland.[33][34][35]
On May 30, the Hong Kong Observatory issued a No. 1 standby signal as the depression neared Hong Kong.[36] The next day, it upgraded the warnings into a No. 3 Strong Wind signal.[37] Although it was likely to not directly affect Taiwan, the Central Weather Administration noted that Maliksi's remnants were likely to merge with a frontal system and bring heavy rains to Taiwan over the weekend.[38] In Macau, the storm caused unstable weather, with the Meteorological and Geophysical Bureau issuing Typhoon Signal No. 3.[39][40] In China, torrential rainfall occurred, peaking at 272.3 mm (10.72 in) somewhere in the Leizhou Peninsula. Additionally, heavy rain was recorded in Fujian, Zhejiang and Jiangxi.[41]
Tropical Depression 03W
[edit]| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 13 – July 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
On July 13, the JTWC began tracking an area of convection 423 mi (682 km) east-southeast of Da Nang, Vietnam. At the time, the disturbance was in a marginal environment for development, with high vertical wind shear offsetting good divergence aloft alongside warm sea surface temperatures.[42] At 06:00 UTC of that day, the JMA designated the system as a tropical depression.[43] The JTWC then issued a TCFA on the system the next day, noting its symmetrical center had improved as it moves northwest, though convection was disorganized.[44] By 18:00 UTC the next day, the JTWC upgraded the system into a tropical depression, designating it 03W.[45] However, they issued their last warning on the depression early the next day as it moved over Vietnam and rapidly weakened.[46] Later that day, the JMA stopped tracking the depression as it dissipated.[47]
Typhoon Gaemi (Carina)
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 19 – July 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 km/h (105 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
On July 17, the JMA reported that a low-pressure area had formed east of Palau.[48] Shortly after, both the JMA and the JTWC followed suit and upgraded the tropical depression,[49] with the latter designating the system as 05W.[50] The PAGASA followed suit a few hours later, recognizing the system as a tropical depression and naming it Carina.[51] Early the next day, the depression intensified into a tropical storm, and was given the name Gaemi by the JMA.[52] Due to a weak steering environment between the subtropical ridge to the northwest and east, the JTWC upgraded Gaemi to minimal typhoon around 21:00 UTC that day.[53] On July 24, Gaemi later rapidly intensified and peaked at Category 4-equivalent intensity on the Saffir-Simpson scale at 21:00 UTC on 23 July, with 1-minute sustained winds of 230 km/h (145 mph) by the JTWC, 10-minute sustained winds of 165 km/h (105 mph) by the JMA, and a central pressure of 935 hPa (27.61 inHg).[54][55] After stalling and executing a tight counter-clockwise loop near the coast,[56] Gaemi slightly weakened into a below-equivalent typhoon status due to land interaction before it made landfall on the northeastern coast of Taiwan on July 24.[57] Gaemi accelerated as it moved across the island and emerged into the Taiwan Strait just six hours after making landfall.[58] Soon after,[59] the JTWC ceased issuing advisories on the system as it made its final landfall at Xiuyu, Putian in Fujian Province.[60] Once inland, the JMA downgraded Gaemi into a tropical depression on July 26[61] and continued tracking the system until it dissipated at 18:00 UTC of July 29.[62]
The southwest monsoon, combined with Tropical Storm Prapiroon, brought heavy rains to southern and northern Luzon, triggering widespread flash floods that resulted in at least 126 deaths and caused damage estimated at US$2.31 billion across several countries.[63][64][65]
JMA has downward the pressure of Gaemi to 935 hPa (27.61 inHg) in post analysis.
Severe Tropical Storm Prapiroon (Butchoy)
[edit]| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 20 – July 25 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 985 hPa (mbar) |
On July 15, the JTWC started to monitor a persistent area of convection roughly 623 km (385 mi) southeast of Manila, Philippines. At that time, the disturbance was in a favorable environment for development, with warm 29–30 °C (84–86 °F), sea surface temperatures, low wind shear and good equatorial outflow.[66] At 06:00 UTC the same day, the JMA designated the system as a low-pressure area.[67] Shortly after, the JMA designated it as a tropical depression.[49] The PAGASA declared the system a tropical depression a few hours later. Since the storm formed within the Philippine Area of Responsibility, the agency named it Butchoy.[68] The JTWC began issuing advisories on the system, classifying it as 04W.[69] It intensified into a tropical storm and was named Prapiroon by the JMA on July 21.[70][71] The center of Prapiroon made landfall near Wanning, Hainan, with 1-minute sustained winds of 95 km/h (60 mph) on July 22.[72] After making landfall, the storm maintained its well-defined eye while moving across central Hainan.[73] Prapiroon soon encountered high wind shear and a dry environment,[74] and by 6:30 a.m. local time on July 23, it made its second landfall in Quảng Ninh, Vietnam.[75][76] After the system moved inland, both the JMA and the JTWC ceased monitoring it on July 24.[77][78]
Typhoon Gaemi and Prapiroon, along with its precursor, significantly impacted the southwest monsoon over the Philippines, leading to heavy rainfall that caused 23 deaths, 9 people missing, and US$32.9 million in damages across several countries.[79][80][81]
JMA has downward the wind of Prapiroon to 100 km/h (65 mph) and upward it pressure to 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) in post analysis. However, JMA also advanced it formed date to July 20.
Severe Tropical Storm Maria
[edit]| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 5 – August 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 100 km/h (65 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
On August 5, the JMA stated that a tropical depression had formed.[82] Later that day, the JTWC began tracking it, noting the depression was in an environment with low to moderate wind shear, warm sea surface temperatures, and good equatorward outflow aloft.[83] At 09:00 UTC on August 6, the JTWC issued a TCFA on the disturbance, which was located 423 mi (682 km) north-northwest of Iwo Jima, along the eastern periphery of the monsoon gyre,[84] prior to it being designated as 06W.[85] The development of a central dense overcast and a ragged eye feature signified its intensification into a tropical storm,[86] leading the JMA to name it Maria on August 7.[87] Maria then turned northeastward,[88] and intensified into a severe tropical storm on August 8 due to a favorable environment for development.[89] Concurrently, the JTWC then reported that Maria had rapidly intensified into a minimal typhoon due to strong equatorward and poleward outflow.[90] However, Maria's wind field became more asymmetric, with its associated convection shifting northward,[91] causing Maria to weaken into a tropical storm on August 9.[92] Around 00:00 UTC on August 12, the storm made landfall Ōfunato,[93] a city in Iwate Prefecture, Japan with winds of 85 km/h (50 mph) before traversing northern Honshu and emerging into the Sea of Japan.[94] The JMA continued to monitor the system until it was last noted at 18:00 UTC on August 14.[95]
Record-breaking rainfall in Iwate Prefecture, with 19 inches (482.6 mm) in Kuji and 12.6 inches (320.0 mm) in Otsuchi—nearly double the average for August—led to controlled releases from the Taki Dam in Kuji, necessitating the evacuation of 8,300 people and the issuance of the highest evacuation alert level, though no damage or injuries were reported in association with Maria.[96]
Tropical Storm Son-Tinh
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 10 – August 14 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 994 hPa (mbar) |
On August 10, the JMA noted that a tropical depression had formed southeast of Severe Tropical Storm Maria.[97] A few hours later, the JTWC began tracking the system, noting that it could transition into a tropical cyclone despite intense wind shear.[98] Early the next day, they noted that the depression had transitioned into a subtropical cyclone.[99] As a result, a few hours later, the JMA named it Son-Tinh.[100] The next day, the JTWC noted that it had transitioned into a tropical storm, designating it 07W.[101] Soon after, the low-level circulation center became fully exposed with no deep convection existing near the center.[102] On August 13, Son-Tinh turned northwest along the western edge of a subtropical ridge.[103] Both the JMA and the JTWC stopped monitoring it as a tropical depression that day,[104] though the JMA continued to track it until it was last noted the following day.[95]
JMA has upward the wind of Son-Tinh to 75 km/h (45 mph) in post analysis.
Typhoon Ampil
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 11 – August 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 155 km/h (100 mph) (10-min); 950 hPa (mbar) |
On August 3, the JTWC began tracking an area of convection 976 km (606 mi) east of Kadena Air Base on August 3.[105] At 18:00 UTC the same day, the JMA designated the system as a low-pressure area.[106] However, the following day, the system was upgraded to a tropical depression.[107] The depression weakened and was last noted by the JMA on August 7.[108] The disturbance later meandered south of the Ryukyu Islands for a few days before it was re-designated by the JMA as a tropical depression on August 11.[109] A few hours later, they recognized the system as a tropical depression, designating it as 08W.[110] Soon after, the JMA noted that it had intensified into a tropical storm and named it Ampil.[111] The JMA then reported that Ampil had intensified into a typhoon due to warm sea surface temperatures and low vertical wind shear on August 15.[112] The JMA reported that Ampil reached its peak intensity at 12:00 UTC that day with 10-minute sustained winds of 155 km/h (100 mph) and a central pressure of 950 hPa (28.05 inHg) before making its closest approach to Japan, and transitioned into an extratropical low on August 19.[113]
Ampil brought strong winds and coastal waves to western Alaska, while Tokyo experienced minimal damage according to NHK, although Kanagawa Prefecture saw several injuries; the remnants of Ampil also contributed to an atmospheric river as its moist core flowed into a low-pressure system, ultimately being absorbed into the Pacific jet stream and anticipated to impact California.[114]
Tropical Storm Wukong
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 11 – August 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
On 12 August, the JMA noted that a tropical depression formed southwest of Tropical Storm Son-Tinh.[115] A few hours later, strong convection south of the system's low-level circulation center consolidated, which prompted the JTWC to issue a TCFA for the disturbance.[116] Soon after, they recognized the system as a tropical depression, designating it as 09W.[117] Satellite imagery revealed that a central dense overcast obscured the center, leading to the depression strengthening into a tropical storm named Wukong by the JMA,[118] although moderate vertical wind shear displaced the deep convection to the southeast.[119][120] Wukong then shifted northwestward, following the eastern edge of a subtropical ridge, while also being affected by the shear and outflow from Typhoon Ampil to the southwest.[121] On August 15, both the JMA and the JTWC ceased monitoring the system, with the JMA reporting that Wukong had transitioned into an extratropical low due to moderate vertical wind shear and cooler sea surface temperatures.[122][123]
Tropical Storm Jongdari (Dindo)
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 18 – August 22 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 996 hPa (mbar) |
On August 17, a low-pressure area east of Taiwan developed into a tropical depression.[124][125] Soon after the development of a low-level circulation center and deep convection, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the disturbance.[126] A few hours later, PAGASA declared the system a tropical depression and named it Dindo,[127] while the JMA reported it had intensified into a tropical storm and named it Jongdari,[128] and the following day, the JTWC recognized it and designated it as 10W.[129] Jongdari became devoid of convection as it was displaced from its exposed low-level circulation center and turned north-northeastward along the western edge of a subtropical ridge.[130] Jongdari then weakened as it moved into the Yellow Sea and made landfall over the Korean Demilitarized Zone on August 20 before emerging into the Sea of Japan.[131][132] The JTWC assessed the cyclone as having dissipated and ceased issuing advisories on the system,[133] while the JMA continued to monitor the system until it was last noted on August 21.[134]
In some parts of the southern islands of Jeju, Jongdari accumulated 60–130 millimetres (2.4–5.1 in) of rain as it moved closer to the coast.[135] One person was killed as a result of Jongdari, when a 60-year-old man drowned in a port located on Heuksando, Sinan County. He was a 43-ton fishing boat crew member that docked in the port to seek refuge from the storm.[136]
JMA has advanced the formed date of Jongdari to August 18 in post analysis. However, JMA also downward it pressure to 996 hPa (29.41 inHg).
Typhoon Shanshan
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 20 – September 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 935 hPa (mbar) |
On August 20, the JMA reported that a low-pressure area had formed near the Mariana Islands.[137] At midnight on August 21, both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded the tropical depression, with the latter designating the system as 11W.[138][139] Shortly after, the depression intensified into a tropical storm and was named Shanshan by the JMA due to low vertical wind shear and warm sea surface temperatures.[140] A ragged eye-like feature appeared on satellite imagery, and on August 24,[141] both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded it to a minimal typhoon.[142] The JMA reported that Shanshan reached its peak intensity at 15:00 UTC on August 27, with 10-minute sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph) and a central pressure of 935 hPa (27.61 inHg).[143] Shanshan then turned northward and made landfall near Satsumasendai in Kagoshima Prefecture on August 29.[144][145] It then turned eastward along the northern periphery of a subtropical high,[146] quickly crossed the Seto Inland Sea, and made landfall over the northern tip of Shikoku on August 30.[147] Shanshan's circulation later diminished as its LLCC became disorganized.[148] However, convection slightly increased after six hours as Shanshan's circulation moved back over open water and began moving east-southeastward, causing to regenerate back to a depression.[149][150] The JMA continued to monitor the system until it dissipated at 18:00 UTC that day.[151]
The JMA issued special weather warnings for Kagoshima Prefecture, marking the first such emergency alert since Typhoon Nanmadol in 2022.[152] Shanshan caused six fatalities and damaged hundreds of structures throughout Japan.[153] In response to the severe weather, evacuation orders were issued for 996,299 people in Miyazaki Prefecture and 982,273 people in Kagoshima Prefecture.[154]
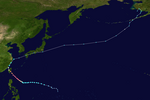
Typhoon Yagi (Enteng)
[edit]| Violent typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 31 – September 9 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-min); 915 hPa (mbar) |
On August 30, the JMA reported the formation of a low-pressure area approximately 540 km (330 mi) northwest of Palau.[155][156] This broad low-pressure system began to organize and developed into a tropical depression on August 31.[157] The following day, PAGASA designated the system as a tropical depression and named it Enteng, as it formed within the Philippine Area of Responsibility.[158] Shortly after, the system was classified as Tropical Depression 12W.[159] As it intensified into a tropical storm, the JMA named it Yagi.[159][160] At 14:00 PHT (06:00 UTC) on September 2, Yagi made landfall in Casiguran, Aurora.[161] Early the next day, both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded the storm to a typhoon as satellite imagery revealed the formation of an eye. On September 5, Yagi reached peak intensity as a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon, with 1-minute sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph) and a central pressure of 915 mbar (27.0 inHg).[162] It made landfall in Wenchang City, Hainan, and passed directly over Haikou, China, before moving into the open waters of the Gulf of Tonkin and making landfall over Xuwen County in Guangdong.[163] On September 7, Yagi reorganized and restrengthened into a Category 4-equivalent typhoon before making its final landfall over Haiphong and Quảng Ninh, Vietnam.[164] It continued to weaken rapidly as it moved southwest along the southeastern edge of a mid-level subtropical high,[165] becoming a tropical depression on September 8. The JMA monitored Yagi until it was last noted at 18:00 UTC that day.[166]
Yagi, combined with the effects of the southwest monsoon, resulted in at least 21 deaths, 22 injuries and 26 missing people in the Philippines.[167] Yagi also caused extensive damages, landslides and floods in Vietnam, Laos, Thailand and Myanmar and left 815 people dead.[168]
Tropical Depression Hone
[edit]| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Subtropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 1 (Entered basin) – September 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
On September 1 at 21:00 UTC, the remnants of Hurricane Hone moved into the basin from the Central Pacific about 280 km (150 nmi; 175 mi) to the southwest of Midway Atoll,[169][170] where it was classified as a tropical depression by the JMA and as a subtropical depression by the JTWC the next day.[171] Soon after, Hone began exhibiting a highly asymmetric convective structure, characterized by convective bands encircling a broad center, while being located under a deep subtropical trough with low to moderate vertical wind shear.[172][173] The JTWC stopped tracking it on September 4, determining the system had dissipated,[174] while the JMA continued to maintain Hone as a depression until it was last noted by the agency at 06:00 UTC on September 8.[175]
Tropical Storm Leepi
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 1 – September 7 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
On September 2, the Japan Meteorological Agency noted that a tropical depression had formed over the open Pacific.[170] Despite unfavorable conditions, JTWC later issued a TCFA warning, citing that it will intensify in the upcoming days. Two days later, the JTWC designated the system as Tropical Depression 13W. A day later, JMA reported that it intensified into a tropical storm, assigning the name Leepi. Although the storm was in a high wind shear and unfavorable environment, Leepi continued to maintain that intensity as it accelerated northeastward. Satellite imagery depicted that the low-level circulation center (LLCC) of Leepi passed under strong upper-level southwesterly flow, indicated by a broad region of cirrus streamers. The storm did not last long, and JTWC later announced its final warning on September 6 as the system transitioned to an extratropical cyclone. The JMA later followed suit and issued its final advisory on 18:00 UTC of September 6.[citation needed]
Typhoon Bebinca (Ferdie)
[edit]| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 9 – September 18 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 140 km/h (85 mph) (10-min); 965 hPa (mbar) |
On September 5, the JTWC noted an area of atmospheric convection 385 km (239 mi) east-northeast of Kosrae.[176] At 02:30 UTC on September 9, the JTWC issued a TCFA, noting that the system had become well-defined with formative banding in the eastern quadrants.[177] A few hours later, both the JMA and the JTWC followed suit and upgraded the tropical depression, with the latter designating the system as 14W.[178][179] On September 10, the depression intensified into a tropical storm and was named Bebinca by the JMA.[180] By 06:00 PHT (10:00 UTC) on September 13, Bebinca had entered the PAR and was subsequently named Ferdie by the PAGASA,[181] but just a few hours later, it exited the PAR.[182] The JMA reported that Bebinca reached its peak intensity at 00:00 UTC on September 15 with 10-minute sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph) and a central pressure of 965 hPa (28.50 inHg),[183] before eventually peaking at Category 1-equivalent intensity on the Saffir-Simpson scale with 1-minute sustained winds of 140 km/h (85 mph).[184] On September 16, at around 07:30 CST,[185] Bebinca made landfall in Lingang New City, Shanghai, China.[186] Shortly after landfall, the JTWC discontinued warnings on the system.[187] Inland, Bebinca quickly diminished to a severe tropical storm due to land interaction,[188] with the JMA tracking the system until it was last noted on September 18.[189]
Bebinca became the second storm to hit China within a few weeks, following Typhoon Yagi's landfall on Hainan Island in the southern part of the country.[190] At least 30,000 households lost power.[191] Four homes were damaged, over 10,000 trees were damaged or uprooted and 53 hectares (132 acres) of farmland were flooded.[192] In China, two people were killed, while one person was injured.[193] The storm also left six people dead, eleven others injured and two people missing in the Philippines.[194]
Tropical Storm Pulasan (Helen)
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
On September 14, the JTWC noted an area of atmospheric convection 196 km (122 mi) west-southwest of Andersen Air Force Base, Guam.[195] At 00:00 UTC on September 15, the JMA designated the system as a low-pressure area, having previously identified it as a tropical depression.[196][197] Shortly after, the depression intensified into a tropical storm and was named Pulasan by the JMA.[198] Pulasan was characterized by a large cyclonic circulation exceeding 690 miles (1,111 km) and extensive gale-force winds, leading the JTWC to classify it as a monsoon depression at 06:00 UTC on September 16,[199] before later upgrading it to a tropical storm and designating it as 15W.[200] By 11:00 PHT (03:00 UTC) on September 17, Pulasan had entered the PAR and was subsequently named Helen by the PAGASA.[201] Pulasan exited the PAR on September 18 while traversing Okinawa Island in Japan's Ryukyu Archipelago as its circulation center strengthened with persistent convection.[202] On September 19, Pulasan made landfall in Zhoushan, Zhejiang, followed by a second landfall in Shanghai, just days after Typhoon Bebinca affected the Shanghai area.[203][204] Pulasan reemerged over the East China Sea, just off the coast of Jiangsu, China, showcasing a large, near-symmetric area of deep convection to the southeast on September 20.[205] By 06:00 UTC on September 21, the JMA reported that Pulasan had transitioned into an extratropical low as it moved east-northeastward and became embedded within the polar front jet to the north.[206][207]
Heavy rains from Pulasan caused major flooding and landslides across the Noto Peninsula in Japan, leaving one missing, destroying many buildings and forcing 60,700 residents to be evacuated. The town of Wajima was especially affected.[208]
Tropical Storm Soulik (Gener)
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 992 hPa (mbar) |
On September 14, the JMA reported that a low-pressure area had formed approximately 596 km (371 mi) east-northeast of Manila, Philippines.[209][210] At 00:00 UTC on September 15, the JMA identified the system as a tropical depression.[196] On September 16, the PAGASA announced that the system had developed into a tropical depression and named Gener, as it formed within the PAR.[211] At 23:00 PHT (15:00 UTC) of the same day, the storm made landfall in Palanan, Isabela.[212][213] As it emerged over the South China Sea at 14:00 PHT (06:00 UTC) on the next day, the system displayed a broad disorganized low-level circulation.[214][215] On September 18, the JTWC canceled their TCFA due to an obscured low-level circulation with flaring convection, while the depression had drifted into an area of moderate vertical wind shear.[216] Earlier, two disturbances in the South China Sea near 98W and 99W were expected to merge and strengthen at 98W, closer to Vietnam, and shortly after, the system was classified as tropical depression 16W[217] Early the following day, the depression intensified into a tropical storm named Soulik, according to the JMA, while heading towards the northern coast of Vietnam, though it was gradually weakening.[218][219] Soulik made landfall in Vĩnh Linh District, Quảng Trị, Vietnam, at around 2 p.m. local time that day,[220] Soulik quickly weakened to a tropical depression due to land interaction,[221] and the JMA continued to monitor the system until it dissipated on September 20.[222]
Heavy rain and flooding in Central Vietnam caused by Soulik killed three people in Nghe An and injured one person in Thua Thien Hue.[223]
Tropical Depression 17W (Igme)
[edit]| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 20 – September 21 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1002 hPa (mbar) |
On September 20, a tropical depression formed near northern Luzon. The disturbance was in a marginal environment, with moderate to high wind shear and warm sea surface temperature. Hours later, JMA later recognized the LPA as a depression. At 14:00 PHT of the same day, PAGASA followed suit and named the system as Igme.[224] JTWC later issued a TCFA warning as the LLCC started to organize. The next day, the JTWC upgraded Igme as a tropical depression and designated it as 17W.[225] Igme later curved southwestwards, passing closely through Taiwan with the JMA last noting it as it became embedded in a front.[225] On September 22, the JTWC reported that Igme had strengthened into a tropical storm as it nears China, though reanalysis showed that it remained as a depression throughout its track.[225] JTWC later discontinued issuing bulletins on Igme after high vertical wind shear and the topographic interaction had caused to weaken significantly and dissipated after.[226]
Tropical Storm Cimaron
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 23 – September 27 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 km/h (40 mph) (10-min); 998 hPa (mbar) |
On September 24, a tropical depression formed south of Japan, designated as 18W by the JTWC later that same day. The following day, 18W was upgraded by the JMA to become a tropical storm, thereby earning the name Cimaron. JTWC later followed suit and upgraded into a storm as it moved westward. Cimaron later moved northeastward, with the presence of moderate and high shear, which caused a weakening of a tropical depression. The environmental analysis also depicted that Cimaron is in an unfavorable environment, characterized by moderate poleward outflow and the presence of dry air.[227] At the latter part of September 27, JTWC reported that Cimaron became a remnant low due to its increasing vertical wind shear, resulted of eroding of the low-level circulation center (LLCC). The agency made its final warning as it absorbed within the frontal boundary.[228] The JMA downgraded the system to a low-pressure area on 18:00 UTC of the same day.
JMA has advanced formed date of Cimaron to September 23 in post analysis. However, JMA also downward it pressure to 998 hPa (29.47 inHg).
Typhoon Jebi
[edit]| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 25 – October 2 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 120 km/h (75 mph) (10-min); 980 hPa (mbar) |
On September 25, a tropical depression formed near the Northern Mariana Islands. Later that day, JTWC started issuing advisories, stating that it would gradually intensify in the upcoming days. On September 26, it was classified as 19W by the JTWC as it was in a marginally favorable environment.[229] 19W developed into a tropical storm, thus gaining the name Jebi by the JMA. Satellite imagery shows that Jebi struggled to organize as moderate low-level wind shear was present.[230] The storm was downgraded back into a depression on September 28. However, Jebi regained tropical storm status for the second time as it moved northeastwards. On October 1, Jebi further strengthened into a Category 1-equivalent typhoon according to the JTWC, while JMA retained severe tropical storm status. Both agencies later issued their final warning the next day, as Jebi became an extratropical cyclone.
JMA has upgraded Jebi into a typhoon in post-analysis and it pressure has downward to 980 hPa (28.94 inHg).
Typhoon Krathon (Julian)
[edit]| Violent typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 26 – October 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-min); 920 hPa (mbar) |
On September 26, the JMA reported a tropical depression 250 km (155 mi) south-southwest of Kadena Air Base, Japan,[231] characterised by a partially exposed low-level circulation centre with persistent deep convection in the southern semicircle and formative banding to the north.[232] On the next day, the PAGASA announced that the system had developed into a tropical depression, naming it Julian.[233] At 09:00 UTC, the JTWC upgraded the tropical depression, designating the system as 20W.[234] On September 28, the depression intensified into a tropical storm named Krathon by the JMA as it moves southwestward along the southeastern periphery of a mid-level subtropical high.[235] Early the next day, both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded it to a minimal typhoon after it had opened a broad, raggedly-defined eye.[236] which had since become cloud-filled,[237] Early on October 1, the JMA upgraded Krathon to a violent typhoon, estimating its peak intensity with a minimum central pressure of 915 hPa (27.02 inHg) and 10-minute maximum sustained winds of 195 km/h (120 mph).[238] On October 3 at 12:40 p.m. local time, Krathon made landfall near Siaogang District in Kaohsiung, Taiwan as a weakening Category-1 typhoon.[239] After making landfall, the system rapidly slowed down and deteriorated, weakening rapidly to a depression.[240] The JMA continued to monitor the system as it emerged into the South China Sea before dissipating on October 4.[241][242]
Krathon caused landslides and flooding in parts of the Philippines, leaving five people dead and another missing. Eight others were injured.[243] Four deaths, 714 injuries and one missing person was also reported in Taiwan.[244]
JMA has upward the pressure of Krathon to 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) in post analysis.
Tropical Storm Barijat
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 5 – October 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 km/h (50 mph) (10-min); 990 hPa (mbar) |
A tropical depression formed near Guam on October 5. The following day, the JTWC issued a TCFA on the system and later upgraded it to Tropical Depression 21W. With convection flaring and persisting to the east of a partial low-level circulation center, the JTWC upgraded it to a tropical storm on October 7. Despite moving over warm waters, high wind shear further displaced the convection, weakening 21W to a tropical depression a few hours later. On October 8, the JTWC issued its last warning on 21W as it further weakened, with the agency expecting it to dissipate within the next 12 hours. The next day, the JMA upgraded 21W to a tropical storm, naming it Barijat. After a few hours, the JTWC reissued warnings for it. However, Barijat would begin its extratropical transition, prompting the said weather agency to issue its last warning the following day, at 09:00 UTC.
Severe Tropical Storm Trami (Kristine)
[edit]| Severe tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 19 – October 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 110 km/h (70 mph) (10-min); 970 hPa (mbar) |
On October 19, the JMA reported a low-pressure area located 633 km (394 mi) west of Guam. The low-pressure area later moved westward slowly before it was designated as a tropical depression by the JMA.[245] The following day, the JTWC designated the system as 22W, as low-level banding wrapped into the circulation center.[246] At 18:00 UTC that day, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm and named it Trami.[247] At around 06:00 UTC on October 23, the JMA reported that Trami had intensified into a severe tropical storm as it was moving west-northwestward along the southwestern edge of a mid-level subtropical high,[248] At 12:30 AM PHT of October 24 (16:30 UTC on October 23), the storm made landfall in Divilacan, Isabela,[249] The following day, Trami emerged over the coastal waters of southern Ilocos Sur and encountered easterly vertical wind shear as it approached the coast of Vietnam.[250] It made landfall in Thua Thien-Hue and Da Nang at about 10 AM local time on October 27,[251] before drifting slowly inland while moving southwestward over the past few hours.[252] The storm rapidly weakened as it moved around the Laos–Vietnam border.[253] It then moved southwestward before making a U-turn and gradually moving toward the coastal regions of Vietnam.[254] The JMA continued to monitor the system, which further weakened into a low-pressure area at 18:00 UTC the following day.[255]
Overall, Trami was responsible for 178 deaths, with 23 people reported missing and 151 others injured, causing approximately US$426 million in damages.[256] In Vietnam, Trami's strong winds caused trees and billboards to fall in Da Nang,[257][258] while heavy rainfall in Quang Tri province resulted in severe flooding of several bridges and left 18,000 people without power.[259]
Typhoon Kong-rey (Leon)
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 24 – November 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 185 km/h (115 mph) (10-min); 925 hPa (mbar) |
On October 22, the JTWC started monitoring a weak exposed low-level circulation at 14°54′N 141°24′E / 14.9°N 141.4°E, about 394 km (245 mi) west-northwest of Guam.[260] The JMA designated the disturbance as a low-pressure area the following day,[261] and on October 24, it was upgraded to a tropical depression.[262] At 00:00 UTC on October 25, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm named Kong-rey,[263] which the JTWC later designated as 23W. On October 30, the JTWC reported that the system had peaked as a Category 4-equivalent super typhoon after Kong-rey attained 1-minute sustained winds of 240 km/h (150 mph),[264] and a 10-minute sustained winds of 185 km/h (115 mph) and a central pressure of 925 hPa (27.32 inHg).[265] The following day at 1:40 p.m. local time, Kong-rey made landfall in Chenggong, Taitung in eastern Taiwan.[266] It was later reemerged over the Taiwan Strait with a weakened convective structure, and its rapid movement across Taiwan may be attributed to a lee-side jump.[267] It moved along the eastern coast of China as it began its extratropical transition[268] On November 1, JMA reported that Kong-rey had transitioned into an extratropical low as it moved north-northeastward, with JTWC alongside discontinued the warnings as it completed its extratropical transition.[269]
Kong-rey triggered strong winds and storm surges that flooded several houses in Gonzaga, Cagayan and Batanes,[270] and destroyed the historic Itbayat Church, the oldest church in Itbayat, Batanes.[271] In Taiwan, typhoon warnings were issued all around the country.[272] Multiple large wave warnings and a singular surge warnings were issued, all in the eastern coast of Taiwan.[273] At least three people were killed and 690 others were injured in Taiwan.[274]
Typhoon Yinxing (Marce)
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 3 – November 12 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
Yinxing emerged from an area of convection 494 km (307 mi) east of Yap, with satellite imagery showing the lower-level winds beginning to consolidate as the convective banding wraps around the low-level circulation center on November 2.[275] At 00:00 UTC the following day, the JMA classified the system as a tropical depression,[276] and by 03:00 UTC, the JTWC issued a TCFA for the disturbance, citing a favorable environment for development characterized by low to moderate vertical wind shear, good divergence aloft, and warm sea surface temperatures of 29–30 °C (84–86 °F).[277] Later that same day, the JTWC designated the system as 24W, due to its compact structure and a small burst of deep convection occurring near the circulation center,[278] which revealed a nearly symmetrical and compact CDO with extremely cold cloud tops of −70 °C (−94 °F).[279] At 18:00 UTC that same day, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm named Yinxing,[280] as it exhibited improved convective banding tightly wrapping around the obscured low-level circulation center.[281] Microwave imaging revealed the development of a nascent microwave eye as Yinxing moved west-northwestward along the southwestern edge of a mid-level subtropical high,[282][283] with the system being very compact and displaying a symmetrical and persistent CDO that obscured the circulation center.[284] A pinhole eye also began to form, prompting the JMA to upgrade it to a typhoon at 00:00 UTC on November 5.[285] As it moved slowly west-northwestward,[286] the typhoon's eye, which measured 23 miles (37 km) in diameter, became more circular in shape as it approached northeastern Cagayan.[287]
On November 7, the JTWC reported that the system had peaked as a Category 4-equivalent super typhoon after Yinxing attained 1-minute sustained winds of 240 km/h (150 mph),[288] while the JMA indicated that Yinxing reached its peak intensity with 10-minute sustained winds of 175 km/h (110 mph) and a central pressure of 940 hPa (27.76 inHg).[289] Later that day, Yinxing made landfall on Santa Ana, Cagayan on Luzon island, around 3:40 PM PHT (07:40 UTC).[290] After crossing the Babuyan Channel, Yinxing made its second landfall in Sanchez Mira, Cagayan, also in Luzon, at 9:00 PM PHT (13:00 UTC).[291] As the typhoon accelerated westward over the South China Sea, it weakened due to interactions with the terrain.[292] It later developed into a more compact cold central cover with deepening overshooting cloud tops and a 22 miles (35 km) diameter eye that became increasingly symmetrical and sharply defined.[293] Yinxing restrengthened, featuring a 22 miles (35 km) oblong eye and an eye temperature of 11.8 °C (53.2 °F). As a result, the JTWC assessed the storm's winds to have reached 205 km/h (125 mph) on November 9.[294] The next day, it was steadily weakening, with the CDO becoming more asymmetric due to cooler sea surface temperatures around 26 °C (79 °F) and increasing vertical wind shear.[295] Moving southwestward between two mid-level subtropical high, the system's cold central cloud cover was quickly disrupted by strong southwestward vertical wind shear, which partially exposed the low-level circulation.[296] The system had a compact circulation center just offshore of the southern coast of Vietnam, with an eye-like feature surrounded by weak to moderate convective activity.[297] Afterward, the JMA continued to track the system until it dissipated at 18:00 UTC on the same day.[298] Overall, Yinxing was responsible for one person reported dead, another injured, and one more reported missing, causing approximately US$9.63 million in damages.[299]
Typhoon Toraji (Nika)
[edit]| Typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 1 typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 8 – November 15 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 130 km/h (80 mph) (10-min); 975 hPa (mbar) |
On November 8, the JMA reported that a low-pressure area had formed 620 km (386 mi) north of Yap,[300] with satellite imagery showing an organizing low-level circulation center, obscured by flaring convection wrapping around its southern and western peripheries. Environmental analysis indicated a favorable environment for further development, with sea surface temperatures of 30–31 °C (86–88 °F), strong poleward outflow aloft, and low vertical wind shear.[301] At 18:00 UTC on the same day, the JMA classified the system as a tropical depression.[302] At 06:00 UTC the same day, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm named Toraji,[303] which the JTWC later designated as 26W.[304] Satellite imagery shows that Toraji was undergoing rapid intensification, with a small system displaying an elongated, compact CDO feature, measuring around 81–92 miles (130–148 km) in diameter. A microwave imaging reveals a complete eyewall surrounding a small microwave eye feature, along with a deep convective band over the southern quadrant.[305]
Early the next day, the JMA upgraded it to a severe tropical storm as it moved west-northwestward, with formative bands wrapping tighter around the obscured low-level circulation.[306][307] At 09:00 UTC on that day, the JTWC upgraded the storm to a minimal typhoon, noting a more asymmetric CDO in the eastern quadrant.[308] Satellite imagery reveals a decrease in easterly vertical wind shear, with the CDO becoming more symmetric and building back over the low-level circulation center.[309] At 15:00 UTC on the same day, the JMA upgraded Toraji to a typhoon.[310] On November 11, Toraji made landfall on Dilasag, Aurora, on Luzon Island at around 8:10 AM PHT (00:10 UTC),[311] before moving inland over mountainous terrain, which caused significant weakening.[312] Later that evening, Toraji emerged over the South China Sea off the coast of Magsingal, Ilocos Sur, with satellite imagery showing a tightly wrapped low-level circulation and fragmented deep convection beginning to reorganize over the northern semicircle.[313][314] As it moved northwestward along the southwestern periphery of a mid-level subtropical high, a small patch of deep convection developed over the northern portion of a partially exposed low-level circulation, resulting in the system weakening into a tropical storm on November 11.[315][316] Satellite imagery showed a weakening of deep convection at the storm's center, with low-level cloud banding around the center and along the southern edge of the circulation, resulting from strong southerly vertical wind shear as it became embedded in the low-level northeasterly flow associated with a cold surge.[317][318] The JMA continued to monitor the system until it was last noted at 06:00 UTC on November 15.[319]
Typhoon Man-yi (Pepito)
[edit]| Violent typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 5 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 9 – November 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 195 km/h (120 mph) (10-min); 920 hPa (mbar) |
Man-yi emerged from an area of convection 220 km (140 mi) east of Kwajalein Atoll, with satellite imagery showing a more organized low-level circulation center and a persistent area of deep convection on the southwestern periphery on November 8.[320] The JMA designated the disturbance as a low-pressure area on the same day,[321] and the next day, it was upgraded to a tropical depression.[322] Later that same day, the JTWC assigned the system the designation 25W, noting that it was a consolidating system with formative bands wrapping in from the north and a deepening cold central core that was obscuring the low-level circulation.[323] As the system moved northwestward along the southern edge of a mid-level subtropical high, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm named Man-yi at 06:00 UTC on the same day,[324] with satellite imagery revealing a very compact system and the low-level circulation center partially exposed on the northwestern edge of a small CDO.[325] Man-yi wrapped around the northern and eastern quadrants of the circulation center, growing more intense as the vertical structure continued to align.[326] The system became disorganized, with convection displaced to the southeast, but it eventually coalesced,[327] as evidenced by cooling cloud tops in the central cold cover and a tightening wrap of the feeder band around the obscured circulation center,[328] as the system passed Guam on November 13.[329] On November 15, the JMA upgraded the storm to a minimal typhoon, and the JTWC followed suit,[330] with satellite imagery revealing a symmetric eyewall surrounding an oblong eye and spiral banding extending over the eastern semicircle.[331][332]
Early the next day, the JTWC upgraded the system to super typhoon status, with estimated 1-minute maximum sustained winds of 260 km/h (160 mph), making it a Category 5-equivalent super typhoon.[333] Meanwhile, the JMA upgraded Man-yi to a violent typhoon, estimating its peak intensity with a minimum central pressure of 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) and 10-minute maximum sustained winds of 195 km/h (120 mph).[334] Man-yi made its first landfall in Panganiban, Catanduanes, at around 9:40 PM PHT (13:40 UTC).[335] After making landfall in Catanduanes, the system slightly degraded in appearance,[336] with the western semicircle becoming less organized and the cloud tops warming as it passed north of the Calaguas Islands.[337] The following day, Man-yi made its second landfall in Dipaculao, Aurora, on Luzon Island at around 3:20 PM PHT (07:20 UTC) and quickly moved inland.[338][339] Man-yi accelerated northwestward over the South China Sea, with its low-level circulation center partially exposed and fragmented convective bands occurring along the southern and eastern edges of the system.[340][341] Satellite imagery revealed a rapidly weakening system, with the low-level circulation center partially exposed to the south of intense deep convection, leading the JMA to report that the storm had weakened into a severe tropical storm at 12:00 UTC on November 18.[342][343] Man-yi rapidly deteriorated as the storm encountered a low-level northeasterly cold surge across the northern South China Sea and experienced increased vertical wind shear.[344] The system became fully exposed, with the central convection completely eroded.[345] The JTWC issued its final warning on the same day as the system weakened to a tropical depression, while the JMA continued to monitor it until it was last noted at 06:00 UTC on November 20.[346]
Typhoon Usagi (Ofel)
[edit]| Very strong typhoon (JMA) | |
| Category 4 super typhoon (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 9 – November 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 175 km/h (110 mph) (10-min); 940 hPa (mbar) |
Usagi emerged from an area of convection 494 km (307 mi) east of Chuuk, with satellite imagery showing a broad area of persistent convection that began to consolidate on November 8.[347] At 12:00 UTC the following day, the JMA classified the system as a tropical depression, citing a favorable environment for development, with low to moderate vertical wind shear, moderate divergence aloft, and warm sea surface temperatures.[348] The next day, the JTWC designated the system as 27W as it became a depression off the northeast coast of Luzon.[349] At 18:00 UTC of November 10, the JMA upgraded the system to a tropical storm and named it Usagi.[350] On November 12, both the JMA and the JTWC upgraded the system to a minimal typhoon, as it exhibited well-defined of well-defined convective banding tightly wrapping around an obscured LLCC.[351]
On November 13, the JTWC reported that the system had peaked as a Category 4-equivalent super typhoon after Usagi attained 1-minute sustained winds of 240 km/h (150 mph) [352] and a central pressure of 940 hPa (27.76 inHg).[353] Usagi made landfall in Baggao, Cagayan, on Luzon Island at around 1:30 PM PHT (05:30 UTC) on November 14.[354] After crossing northern Luzon, Usagi emerged into the Babuyan Channel, passing close to the Babuyan Islands and northern Cagayan.[355] This later announced that the JMA would downgrade the system to a severe tropical storm.[356] Usagi weakened significantly due to increasing wind shear as it nears Taiwan.[357] Afterward, the JMA continued to track the system until it dissipated at 12:00 UTC on the same day.[358]
Tropical Depression Querubin
[edit]| Tropical depression (JMA) | |
| Duration | December 17 – December 19 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 55 km/h (35 mph) (10-min); 1004 hPa (mbar) |
After a month of inactivity, at 15:00 UTC on December 16, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert, designating the system as Invest 96W.[359] The next day, it became a depression and entered the Philippine Area of Responsibility, which PAGASA named Querubin[360], a replacement name for Quinta. On 17:00 PHT (09:00 UTC), PAGASA declared Signal No. 1 to Davao Oriental.[361] Six hours later, the JTWC issued a TCFA to Querubin, citing that it will strengthen for the next couple of days. Satellite imagery shows the banding organizing, with Querubin inside a favorable environment.[362] At 11:00 PHT (03:00 UTC) in December 18, PAGASA also placed Signal No. 1 in Surigao del Sur.[363] At 17:00 PHT (09:00 UTC), PAGASA downgraded it to a low pressure area.[364] On 13:00 UTC, JTWC cancelled TCFA for the system. However, the agency reissued it for the second time on 19:30 UTC, citing a high chance of formation of a tropical cyclone. Later that day JTWC cancelled TCFA downgraded it to a low chance before dissipated. Its remnants’ energy later re-formed into Pabuk.
Tropical Storm Pabuk (Romina)
[edit]| Tropical storm (JMA) | |
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | December 20 – December 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 75 km/h (45 mph) (10-min); 1000 hPa (mbar) |
On December 20, the JMA reported a low-pressure area located 460 km (290 mi) west-southwest of Brunei,[365] which was later upgraded to a tropical depression.[366][367] At 06:00 UTC the following day, the JTWC issued a TCFA, noting that formative banding was organizing around the circulation and deep convection was building over the center.[368] However, due to its imminent threat to the Kalayaan Islands, PAGASA named the depression Romina, a replacement name for Rolly, even though it was still outside the PAR, at 11:00 PHT (03:00 UTC) on December 22, and began issuing advisories on it.[369] This marked the first time since 1963 that PAGASA named a tropical cyclone outside the PAR.[370] Later that same day, the JTWC assigned the system the designation 28W, noting a strong northeast surge was occurring with winds shifting from north-northeasterly to northerly, while Invest 98W, which had formed near the storm, rapidly weakened and was absorbed into the storm's southeastern periphery.[371] Pabuk showed deep convection flaring on the northwestern periphery of a low-level circulation that was mostly exposed.[372] On December 23, PAGASA issued its final advisory on Romina as it moved away from the Kalayaan Islands and lifted the wind signals.[373] On 06:00 UTC, the JMA upgraded the storm to a tropical storm and named it Pabuk, following the observation of a favorable environment as it moved westward along the southern periphery of a mid-level subtropical high.[374] Pabuk moved westward and turned toward Vietnam as it lost its vertical structure, steered by the low-level flow associated with a northeasterly cold surge along the eastern coast of Vietnam.[375] The system was last noted by the JMA on 18:00 UTC of December 26.
On December 22, the Kalayaan Islands were issued Signal No. 1, where a wind speed of 39 kilometres per hour (24 miles per hour) to 61 km/h (38 mph) is expected.[376] That same day, the municipality of Balabac, Palawan was added to Signal No. 1.[377] A few hours later, Balabac was removed.[378] On December 23, all signals were removed as Pabuk moved away from the Philippines.[379] Online, rumors were made that Pabuk would make landfall over Thailand on December 20, 2024, though the national agency said that the rumors were false.[380] On December 23, 2024, heavy rain was recorded in the South Central Coast and Central Highlands of Vietnam.[381] On December 24, an advisory was made by the Malaysian Meteorological Department for Pabuk, noting that rough seas are expected within the South China Sea.[382] Heavy rains caused 36,900 affected people in the Philippines, mostly in Palawan and Oriental Mindoro. A total of 12,200 families were affected. 799 displaced people were recorded, and eight evacuation centers were used.[383] Pabuk also caused Baco, Oriental Mindoro to issue a state of calamity due to intense flooding. A total of 4,300 families or 20,000 people have been displaced in Baco.[384]
Other systems
[edit]
- On August 18, the JMA reported the formation of a low-pressure area over the Philippine Sea.[385] The next day, it was designated as a tropical depression but weakened to a low-pressure area by August 22.[386] The following day, the JMA re-designated it as a tropical depression as it turned southward.[387] Over the next few days, the depression gradually moved southwestward while Typhoon Shanshan approached Japan from the west.[388] The JMA continued to monitor the depression until it dissipated on August 26.[389]
- A tropical depression briefly formed south of South Korea on August 19 and was last noted by the JMA at 18:00 UTC as it moved northward.[390][391]
- A tropical depression briefly developed southeast of Japan on August 20.[137] Thereafter, it was designated as an extratropical low while drifting southeastward.[392]
- A tropical depression briefly formed southeast of Typhoon Shanshan on August 30 and was last noted by the JMA at 18:00 UTC.[393][155]
- A tropical depression formed over the Philippine Sea on September 4. Two days later, it degenerated into a low-pressure area as it slowly turned to the west. On September 9, it re-strengthened back into a tropical depression as it moved west-northwest towards Eastern China where it made landfall before dissipating.
- On September 25, the JTWC marked a subtropical storm near Tokyo and designated it with an invest tag 96W, stating the system has a low chance of transitioning to a tropical system. The next day, the agency last noted the system as it merged with a frontal boundary while moving to the east. The JMA did not recognize the system.
- A tropical depression formed west of Guam on September 26. The depression did not last long, dissipating the next day, with its remnants moving northwards across the Philippine Sea.
- Another tropical depression formed west of Guam on October 6. The depression moved eastwards as it interacted with a nearby Tropical Depression that would later become Tropical Storm Barijat. The JMA last noted it the next day as the depression became embedded in the latter's circulation.
- A tropical depression formed in northeast of Mukojima on October 12. JTWC classified it as a subtropical depression on October 13. JTWC upgraded it into a subtropical storm on October 14. At the same time, JMA declared the system had transitioned to a developing extratropical low.
- A tropical depression formed north of Micronesia on October 16. The depression did not last long, and JMA downgraded the system into a low pressure area the next day.
- A tropical depression formed north of Malaysia on December 21,[394] before being absorbed into Tropical Storm Pabuk on December 22.[395]
Storm names
[edit]Within the basin, both the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) and the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration (PAGASA) assign names to tropical cyclones that develop in the Western Pacific, which can result in a tropical cyclone having two names.[396] The Japan Meteorological Agency's RSMC Tokyo — Typhoon Center assigns international names to tropical cyclones on behalf of the World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee when they have 10-minute sustained winds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[397]
PAGASA names tropical cyclones which are active in their area of responsibility located between 135°E and 115°E and between 5°N and 25°N even if the cyclone has already been named.[396] If the list of names for the Philippine region are exhausted, then names will be taken from an auxiliary list of which the first ten are published each season. Unused names are marked in gray. The names of significant tropical cyclones will be retired by both PAGASA and the Typhoon Committee in the spring of 2025.[397]
International names
[edit]During the season, 26 tropical storms developed in the Western Pacific and all of them were named by the JMA once they had 10-minute sustained winds of 65 km/h (40 mph).[398] The JMA selected the names from a list of 140 names, that had been developed by the 14 members nations and territories of the ESCAP/WMO Typhoon Committee.[399] Retired names, if any, will be announced by the WMO in 2025, though replacement names will be announced in 2026. During the season, the names Pulasan, Krathon and Yinxing were used for the first time after they replaced Rumbia, Mangkhut and Yutu, which were retired following the 2018 season. The next 28 names on the naming list are listed here along with their international numeric designation, if they are used.
| Ewiniar | Maliksi | Gaemi | Prapiroon | Maria | Son-Tinh | Ampil | Wukong | Jongdari | Shanshan | Yagi | Leepi | Bebinca |
| Pulasan | Soulik | Cimaron | Jebi | Krathon | Barijat | Trami | Kong-rey | Yinxing | Toraji | Man-yi | Usagi | Pabuk |
Other names
[edit]If a tropical cyclone enters the Western Pacific basin from the Eastern and Central Pacific basin (west of 180°E), it will retain the name assigned to it by the National Hurricane Center (NHC) and Central Pacific Hurricane Center (CPHC). The following storms were named in this manner.
Philippines
[edit]| Main list | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aghon | Butchoy | Carina | Dindo | Enteng |
| Ferdie | Gener | Helen | Igme | Julian |
| Kristine | Leon | Marce | Nika | Ofel |
| Pepito | Querubin | Romina | Siony (unused) | Tonyo (unused) |
| Upang (unused) | Vicky (unused) | Warren (unused) | Yoyong (unused) | Zosimo (unused) |
| Auxiliary list | ||||
| Alakdan (unused) | Baldo (unused) | Clara (unused) | Dencio (unused) | Estong (unused) |
| Felipe (unused) | Gomer (unused) | Heling (unused) | Ismael (unused) | Julio (unused) |
During the season, PAGASA used its own naming scheme for the 18 tropical cyclones, that either developed within or moved into their self-defined area of responsibility.[400] The names were taken from a list of names, that was last used during 2020 and are scheduled to be used again during 2028.[400] All of the names are the same except Aghon, Querubin, Romina and Upang which replaced the names Ambo, Quinta, Rolly and Ulysses after they were retired.[400] The names Aghon, Querubin and Romina were used for the first time this year.
Season effects
[edit]This table summarizes all the systems that developed within or moved into the North Pacific Ocean, west of the International Date Line during 2024. The table also provide an overview of a system's intensity, duration, land areas affected, and any deaths or damages associated with the system.
| Name | Dates | Peak intensity | Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Refs | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Category | Wind speed | Pressure | ||||||
| Ewiniar (Aghon) | May 23–30 | Typhoon | 140 km/h (85 mph) | 970 hPa (28.64 inHg) | Philippines, Japan, Alaska | $20.88 million | 6 | [22] |
| Maliksi | May 30–June 2 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | South China, Taiwan | Unknown | None | [401] |
| 03W | July 13–15 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | Vietnam, Laos, Thailand | None | None | |
| Gaemi (Carina) | July 19–29 | Very strong typhoon | 165 km/h (105 mph) | 935 hPa (27.61 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, Yaeyama Islands, East China, Indonesia, North Korea | $1.66 billion | 107 | [63][402][403][404] |
| Prapiroon (Butchoy) | July 20–25 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 985 hPa (29.09 inHg) | Philippines, Vietnam, South China, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia | >$32.9 million | 23 | [79][405][406] |
| Maria | August 5–14 | Severe tropical storm | 100 km/h (65 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Bonin Islands, Japan | None | None | [407] |
| Son-Tinh | August 10–14 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 994 hPa (29.35 inHg) | Alaska | None | None | |
| Ampil | August 11–19 | Very strong typhoon | 155 km/h (100 mph) | 950 hPa (28.05 inHg) | Bonin Islands, Japan, Alaska | Minimal | None | |
| Wukong | August 11–16 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Jongdari (Dindo) | August 18–22 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 996 hPa (29.41 inHg) | Miyako Islands, Yaeyama Islands, Korean Peninsula | None | 1 | [408] |
| TD | August 19–26 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | August 19 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | August 20 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1012 hPa (29.88 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Shanshan | August 20–September 1 | Very strong typhoon | 175 km/h (110 mph) | 935 hPa (27.61 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Japan, South Korea | >$6 billion | 8 | [409] |
| TD | August 30 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | Japan | None | None | |
| Yagi (Enteng) | August 31–September 9 | Violent typhoon | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 915 hPa (27.02 inHg) | Palau, Philippines, South China, Hong Kong, Macau, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, Myanmar | $16.9 billion | 844 | [410][411][412] |
| Hone | September 1–8 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Hawaii (before crossover) | None | None | |
| Leepi | September 1–7 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | September 4–12 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | Okinawa Prefecture, Taiwan, East China | None | None | |
| Bebinca (Ferdie) | September 9–18 | Typhoon | 140 km/h (85 mph) | 965 hPa (28.50 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Philippines, Ryukyu Islands, East China | $1.42 billion | 8 | [413] |
| Pulasan (Helen) | September 15–21 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 992 hPa (29.29 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Philippines, East China, South Korea, Japan | $4.15 million | 15 | |
| Soulik (Gener) | September 15–20 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 992 hPa (29.29 inHg) | Philippines, Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, Cambodia, Myanmar | $22.63 million | 29 | [414][223] |
| 17W (Igme) | September 20–22 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1002 hPa (29.59 inHg) | Philippines, Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan, East China | Unknown | None | |
| Cimaron | September 23–27 | Tropical storm | 65 km/h (40 mph) | 998 hPa (29.47 inHg) | None | Unknown | None | |
| Jebi | September 25–October 2 | Typhoon | 120 km/h (75 mph) | 980 hPa (28.94 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Japan, Kuril Islands | Unknown | None | |
| TD | September 26–27 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Krathon (Julian) | September 26–October 3 | Violent typhoon | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan, Ryukyu Islands | $48.1 million | 18 | |
| Barijat | October 5–11 | Tropical storm | 85 km/h (50 mph) | 990 hPa (29.23 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Kuril Islands, Kamchatka Peninsula | None | None | |
| TD | October 6–7 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | October 12–14 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1006 hPa (29.71 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| TD | October 16–17 | Tropical depression | Not specified | 1008 hPa (29.77 inHg) | None | None | None | |
| Trami (Kristine) | October 19–29 | Severe tropical storm | 110 km/h (70 mph) | 970 hPa (28.64 inHg) | Palau, Philippines, Taiwan, South China, Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand | $426.34 million | 178 | [415] |
| Kong-rey (Leon) | October 24–November 1 | Very strong typhoon | 185 km/h (115 mph) | 925 hPa (27.32 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Philippines, Taiwan, East China, South Korea, Japan | $149.4 million | 3 | [416] |
| Yinxing (Marce) | November 3–12 | Very strong typhoon | 175 km/h (110 mph) | 940 hPa (27.76 inHg) | Caroline Islands, Philippines, South China, Vietnam, Cambodia | $3.91 million | 1 | [299] |
| Toraji (Nika) | November 8–15 | Typhoon | 130 km/h (80 mph) | 975 hPa (28.79 inHg) | Philippines, South China, Taiwan, Hong Kong, Macau | $7.76 million | 4 | [417][418] |
| Man-yi (Pepito) | November 9–20 | Violent typhoon | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 920 hPa (27.17 inHg) | Guam, Northern Mariana Islands, Caroline Islands, Palau, Philippines, Taiwan, South China, Hong Kong, Macau | >$76.05 million | 14 | [419] |
| Usagi (Ofel) | November 9–16 | Very strong typhoon | 175 km/h (110 mph) | 940 hPa (27.76 inHg) | Philippines, Taiwan | $9.56 million | None | [420] |
| Querubin | December 17–19 | Tropical depression | 55 km/h (35 mph) | 1004 hPa (29.65 inHg) | Philippines | None | None | [421] |
| Pabuk (Romina) | December 20–26 | Tropical storm | 75 km/h (45 mph) | 1000 hPa (29.53 inHg) | East Malaysia, Indonesia, Brunei, Spratly Islands, Philippines, Vietnam | None | None | |
| Season aggregates | ||||||||
| 39 systems | May 23 – December 26 | 195 km/h (120 mph) | 915 hPa (27.02 inHg) | $26.8 billion | 1255 | |||
See also
[edit]- Weather of 2024
- Tropical cyclones in 2024
- Pacific typhoon season
- 2024 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2024 Pacific hurricane season
- 2024 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2023–24, 2024–25
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2023–24, 2024–25
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2023–24, 2024–25
Notes
[edit]- ^ The Japan Meteorological Agency is the official Regional Specialized Meteorological Center for the western Pacific Ocean.
- ^ The Joint Typhoon Warning Center is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force task force that issues tropical cyclone warnings for the western Pacific Ocean and other regions.[1]
- ^ A super typhoon is an unofficial category used by the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) for a typhoon with winds of at least 240 km/h (150 mph).[2]
References
[edit]- ^ "Joint Typhoon Warning Center Mission Statement". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. 2011. Archived from the original on July 26, 2007. Retrieved July 25, 2012.
- ^ Frequently Asked Questions (Report). Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2012. Archived from the original on October 4, 2013. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
- ^ a b c Lea, Adam; Wood, Nick (May 7, 2023). Extended Range Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2024 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Archived (PDF) from the original on May 6, 2023. Retrieved May 7, 2023.
- ^ a b Lea, Adam; Wood, Nick (July 5, 2024). Early July Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2024 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 20, 2024. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- ^ a b c Lea, Adam; Wood, Nick (August 7, 2024). Early August Forecast for Northwest Pacific Typhoon Activity in 2024 (PDF) (Report). Tropical Storm Risk Consortium.
- ^ a b Seasonal Climate Outlook January – June 2024 (PDF) (Report). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. January 15, 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 10, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ a b 161th Climate Forum July–December 2024 (PDF) (Seasonal Climate Outlook). Philippine Atmospheric Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. June 26, 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on July 19, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ "Real-Time Tropical Cyclone North Atlantic Ocean Statistics". Fort Collins, Colorado: Colorado State University. Retrieved January 1, 2025.
- ^ Wulfeck, Andrew (May 25, 2024). "Tracking the tropics: Northern Hemisphere finally sees its first tropical depression". FOX Weather. Retrieved May 25, 2024.
- ^ "Potential tropical storm could affect Taiwan: CWA - Taipei Times". www.taipeitimes.com. November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 12, 2024.
- ^ Mondoñedo-Ynot, Laureen (November 17, 2024). "'Pepito' makes 2nd landfall in Aurora". SunStar Publishing Inc. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 21 May 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 21, 2024. Archived from the original on May 21, 2024. Retrieved May 21, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 221800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. May 22, 2024. Archived from the original on May 22, 2024. Retrieved May 22, 2024.
- ^ "LPA develops into Tropical Depression east of Surigao del Sur". GMA Network. May 24, 2024. Retrieved May 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 24, 2024. Archived from the original on May 24, 2024. Retrieved May 24, 2024.
- ^ a b "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #7 for Tropical Depression 'Aghon'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 24, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 24, 2024. Retrieved May 24, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ a b "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #14 for Tropical Depression 'Aghon'" (PDF). PAGASA. May 26, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 25, 2024. Retrieved May 26, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tropical Depression 01W (One) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 25, 2024. Archived from the original on May 25, 2024. Retrieved May 25, 2024.
- ^ a b c Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 01W (Ewiniar) Warning No. 7 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 26, 2024. Archived from the original on May 26, 2024. Retrieved May 26, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #21 for Severe Tropical Storm 'Aghon' (Aghon)" (PDF). PAGASA. May 26, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on May 26, 2024. Retrieved May 26, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ "WTPQ50 RJTD 301800". Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 30, 2024.
- ^ a b Situational Report No. 12 for TC AGHON (2024) (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. June 6, 2024. Retrieved June 6, 2024.
- ^ Shimbun, The Yomiuri (May 31, 2024). "Typhoon Ewiniar Weakens into Extratropical Cyclone on Friday Predawn". Yomiuri Shimbun. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0230Z 30 May 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 30, 2024. Archived from the original on May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 30, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 300000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. May 30, 2024. Archived from the original on May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 300600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. May 30, 2024. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 94W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 30, 2024. Archived from the original on May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 30, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 02W (Two) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 31, 2024. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ TS 2402 Maliksi (2402) Upgraded from TD (RSMC Tropical Cyclone Advisory). Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 02W (Two) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 31, 2024. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 02W (Maliksi) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 31, 2024. Archived from the original on May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 02W (Maliksi) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. May 31, 2024. Archived from the original on June 1, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 010600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 1, 2024. Retrieved June 1, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 020000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. Archived from the original on June 2, 2024. Retrieved June 2, 2024.
- ^ Maliksi (2402) JMA Best Track (Report). National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. September 5, 2024. Archived from the original on September 5, 2024. Retrieved September 6, 2024.
- ^ "Hong Kong No 1 typhoon signal to remain in force until at least Friday morning". South China Morning Post. May 30, 2024. Retrieved May 30, 2024.
- ^ "Hong Kong Observatory says T3 signal to stay in force until early Saturday morning". South China Morning Post. May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical storm Maliksi forms, expected to bring rain to Taiwan". Focus Taiwan. May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ "MGTO calls for visitors' attention to typhoon updates and activity arrangements". Macao SAR Government Portal. May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Maliksi: Low possibility of No.8 alert". Macau Business. May 31, 2024. Retrieved May 31, 2024.
- ^ "Update: Typhoon Maliksi wanes upon landing in south China province". Xinhua. June 1, 2024. Retrieved June 1, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0230Z 13 July 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 13, 2024. Archived from the original on July 13, 2024. Retrieved July 13, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 130600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. May 30, 2024. Archived from the original on July 13, 2024. Retrieved July 13, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 99W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 14, 2024. Archived from the original on July 14, 2024. Retrieved July 14, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 03W (Three) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 14, 2024. Archived from the original on July 14, 2024. Retrieved July 14, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 03W (Three) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 15, 2024. Archived from the original on July 15, 2024. Retrieved July 14, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 151800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 15, 2024. Archived from the original on July 15, 2024. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 170600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 17, 2024. Archived from the original on July 17, 2024. Retrieved July 17, 2024.
- ^ a b Warning and Summary 190600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 19, 2024. Archived from the original on July 19, 2024. Retrieved June 19, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 05W (Five) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 19, 2024. Archived from the original on July 19, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Carina' (Carina)". PAGASA. July 19, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 19, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Gaemi (2403) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 20, 2024. Archived from the original on July 20, 2024. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 05W (Gaemi) Warning No. 13 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 23, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 05W (Gaemi) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2024. Archived from the original on July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 20 for TY Gaemi (2403) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ Cappucci, Matthew (July 25, 2024). "Why this deviant, looping typhoon is stunning meteorologists". Washington Post. ISSN 0190-8286. Archived from the original on July 26, 2024. Retrieved July 27, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 05W (Gaemi) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 05W (Gaemi) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 25, 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2024. Retrieved July 25, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Gaemi Reaches China as Cargo Ship Sinks Off Taiwan". The New York Times. July 25, 2024. Archived from the original on July 26, 2024. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 05W (Gaemi) Warning No. 24 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 24, 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 33 for TD Gaemi (2403) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 27, 2024. Archived from the original on July 27, 2024. Retrieved July 27, 2024.
- ^ "RSMC Tropical Cyclone Best Track Name 2403 Gaemi (2403)". Japan Meteorological Agency. October 21, 2024. Archived from the original on October 21, 2024. Retrieved October 21, 2024.
- ^ a b SS. Kurniawan (July 23, 2024). "Badai Siklon Tropis Gaemi Terus Meningkat, Cuaca Hujan Lebat di Provinsi Ini". Kontan (in Indonesian). Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ SitRep No. 42 for the Combined Effects of Southwest Monsoon and TC CARINA (2024) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. August 11, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ "Rainy Monday in Northern Luzon, Metro Manila due to TS 'Carina'". Philippines News Agency. July 21, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 09Z 15 July 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 15, 2024. Archived from the original on July 15, 2024. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 150600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 15, 2024. Archived from the original on July 15, 2024. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Butchoy' (Butchoy)". PAGASA. July 19, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on July 19, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 04W (Four) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 19, 2024. Archived from the original on July 20, 2024. Retrieved July 19, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2024. Archived from the original on July 21, 2024. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 20, 2024. Archived from the original on July 21, 2024. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 21, 2024. Archived from the original on July 22, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 22, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 12 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 22, 2024. Retrieved July 22, 2024.
- ^ "Storm Prapiroon hits Quang Ninh in northern Vietnam". VNExpress. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 31, 2024. Retrieved July 31, 2024.
- ^ "North VN hit by heavy rain from storm, harsh weather to continue due to La Nina". VietnamNet. July 23, 2024. Archived from the original on July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 24, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 241800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. July 15, 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2024. Retrieved July 15, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 04W (Prapiroon) Warning No. 14 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. July 23, 2024. Archived from the original on July 23, 2024. Retrieved July 23, 2024.
- ^ a b SitRep No. 7 for the Combined Effects of SW Monsoon and TD "Butchoy" (2024) (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. July 20, 2024. Retrieved July 20, 2024.
- ^ Kristine Daguno-Bersamima (July 20, 2024). "2 LPAs develop into Tropical Depressions Butchoy, Carina". The Philippine Star. Archived from the original on July 27, 2024. Retrieved July 27, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Prapiroon brings rainstorms, strong gusts to South China". Xinhua. China Daily. July 22, 2024. Archived from the original on July 25, 2024. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 050600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 5, 2024. Archived from the original on August 5, 2024. Retrieved August 5, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 2100Z 5 August 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 5, 2024. Archived from the original on August 5, 2024. Retrieved August 5, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 94W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 6, 2024. Archived from the original on August 6, 2024. Retrieved August 6, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 06W (Six) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 7, 2024. Archived from the original on August 7, 2024. Retrieved August 7, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 06W (Six) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 7, 2024. Archived from the original on August 7, 2024. Retrieved August 7, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Maria) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 8, 2024. Archived from the original on August 8, 2024. Retrieved August 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 6 for TS Maria (2405) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 7, 2024. Archived from the original on August 8, 2024. Retrieved August 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 8 for STS Maria (2405) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 8, 2024. Archived from the original on August 8, 2024. Retrieved August 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 06W (Maria) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 8, 2024. Archived from the original on August 8, 2024. Retrieved August 8, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Maria) Warning No. 12 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 9, 2024. Archived from the original on August 10, 2024. Retrieved August 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Maria) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 9, 2024. Archived from the original on August 9, 2024. Retrieved August 9, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Maria) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 06W (Maria) Warning No. 23 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ a b Warning and Summary 141800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 14, 2024. Archived from the original on August 15, 2024. Retrieved August 14, 2024.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- "Typhoon Maria Brings Record-breaking Rain to Japan's Tohoku Region; Akita Shinkansen Line Partially Closed (UPDATE1)". Yomiuri Shimbun. August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- Daniel Traylor (August 13, 2024). "Focus shifts to incoming typhoon as Tropical Storm Maria dissipates". The Japan Times. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- "Tropical Storm "Maria" makes landfall in Japan bringing record-breaking rainfall". The Watchers. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 17, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 for TD (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 10, 2024. Archived from the original on August 10, 2024. Retrieved August 10, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 1530Z 10 August 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 10, 2024. Archived from the original on August 11, 2024. Retrieved August 10, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0230Z 11 August 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 11, 2024. Archived from the original on August 11, 2024. Retrieved August 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 5 for TS Son-Tinh (2406) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 11, 2024. Archived from the original on August 11, 2024. Retrieved August 11, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 07W (Son-Tinh) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 07W (Son-Tinh) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 07W (Son-Tinh) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 13 for TD (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 3 August 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 3, 2024. Archived from the original on August 3, 2024. Retrieved August 3, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 031800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 3, 2024. Archived from the original on August 3, 2024. Retrieved August 3, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 040000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 4, 2024. Archived from the original on August 4, 2024. Retrieved August 4, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 071800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 10, 2024. Archived from the original on August 8, 2024. Retrieved August 7, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 110600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 11, 2024. Archived from the original on August 11, 2024. Retrieved August 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 08W (Eight) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Ampil (2407) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 8, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Ampil (2407) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 15, 2024. Retrieved August 15, 2024.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Prognostic Reasoning No. 15 for TY Ampil (2407) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 15, 2024. Archived from the original on August 15, 2024. Retrieved August 15, 2024.
- "Danger not over as typhoon passes Japan | NHK WORLD-JAPAN News". NHK WORLD. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- Tropical Cyclone Advisory for Developing Low Former STS Ampil (2407) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 19, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- ^ Multiple sources:
- Purcell, Jackie (August 23, 2024). "A sunny break again Friday for southcentral". Archived from the original on August 23, 2024. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- Traylor, Daniel; Kaneko, Karin; Speed, Jessica (August 16, 2024). "Typhoon Ampil lashes eastern Japan with heavy rain and wind". The Japan Times. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 17, 2024.
- Porter, Greg (August 21, 2024). "Typhoon's remnants to trigger California storm, bringing a shift to cooler weather". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 120000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 96W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 09W (Nine) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 09W (Wukong) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 14, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 09W (Nine) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 2 for TS Wukong (2408) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 13, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 09W (Wukong) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 14, 2024. Archived from the original on August 14, 2024. Retrieved August 14, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 09W (Wukong) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 15, 2024. Archived from the original on August 15, 2024. Retrieved August 15, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for Developing Low Former TS Wukong (2410) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 15, 2024. Archived from the original on August 15, 2024. Retrieved August 15, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 170000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 17, 2024. Archived from the original on August 17, 2024. Retrieved August 17, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 170600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 17, 2024. Archived from the original on August 17, 2024. Retrieved August 17, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 18, 2024. Archived from the original on August 18, 2024. Retrieved August 18, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Dindo'" (PDF). PAGASA. August 18, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on August 24, 2024. Retrieved August 18, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TS Jongdari (2409) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 18, 2024. Archived from the original on August 18, 2024. Retrieved August 18, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Ten) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 13, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 10W (Jongdari) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 19, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 211200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Jongdari) Warning No. 7 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 20, 2024. Archived from the original on August 20, 2024. Retrieved August 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 10W (Jongdari) Warning No. 8 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 20, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 20, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 211800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 22, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical storm Jongdari weakens as it nears South Korea with heavy rain and winds". AP News. August 20, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Geun-yeong, Jo (August 21, 2024). "60-year-old sailor found dead after entering Heuksando port due to typhoon damage". Yonhap News. Retrieved September 29, 2024.
- ^ a b WWJP27 RJTD 201800. Japan Meteorological Agency (Report). August 20, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 22, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Six) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Shanshan (2410) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Shanshan (2407) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 23, 2024. Archived from the original on August 24, 2024. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 23, 2024. Archived from the original on August 23, 2024. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Shanshan (2410) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 27, 2024. Archived from the original on August 28, 2024. Retrieved August 27, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 31 for TY Shanshan (2410) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 28, 2024. Archived from the original on August 28, 2024. Retrieved August 28, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Shanshan makes landfall in Kagoshima, southwestern Japan | NHK WORLD-JAPAN News". NHK WORLD. Retrieved August 29, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 36 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 30, 2024. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 37 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 30, 2024. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 39 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 30, 2024. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tropical Depression 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 42 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2024. Archived from the original on September 1, 2024. Retrieved September 1, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 11W (Shanshan) Warning No. 41 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2024. Archived from the original on September 1, 2024. Retrieved September 1, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 011800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 1, 2024. Archived from the original on September 1, 2024. Retrieved September 1, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Shanshan churns up Japan, up to six dead". Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024.
- ^ "鹿児島県に暴風・波浪の特別警報発表 台風10号で気象庁". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). Archived from the original on August 28, 2024. Retrieved August 28, 2024.
- ^ 令和6年台風第10号による被害及び 消防機関等の対応状況(第5報) (PDF) (Report) (in Japanese). Fire and Disaster Management Agency. August 28, 2024. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 28, 2024.
- ^ a b Warning and Summary 301800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 30, 2024. Archived from the original on August 31, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 31 August 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. August 31, 2024. Archived from the original on August 31, 2024. Retrieved August 31, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 310000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 31, 2024. Archived from the original on August 31, 2024. Retrieved August 31, 2024.
- ^ Cabato, Luisa (September 1, 2024). "LPA east of Eastern Visayas has become tropical depression Enteng". INQUIRER.net. Retrieved September 1, 2024.
- ^ a b Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 12W (Yagi) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 1, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 1, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 3 for TS Yagi (2411) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 1, 2024. Archived from the original on September 2, 2024. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ Salcedo, Mary Joy (September 2, 2024). "Bagyong Enteng, nag-landfall na sa vicinity ng Casiguran, Aurora". Balita (in Filipino). Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 12W (Yagi) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 5, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 12W (Yagi) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 6, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 6, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 12W (Yagi) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 7, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 7, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 28 for STS Yagi (2411) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 7, 2024. Archived from the original on September 8, 2024. Retrieved September 7, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 081800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 8, 2024. Archived from the original on September 8, 2024. Retrieved September 8, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Yagi toll rises to 16, affects 1.7 million in the Philippines". Borneo Bulletin. September 5, 2024. Archived from the original on September 5, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- ^ "Floods and mudslides kill more than 300 in Myanmar". BBC. Retrieved September 17, 2024.
- ^ Post-Tropical Cyclone Hone Advisory Number 42 (Report). Honolulu, Hawaii: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. September 1, 2024. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ a b WWJP27 Warning and Summary September 2, 2024 00z (Report). Japan Meteorological Agency. September 2, 2024. Archived from the original on September 2, 2024. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0030Z 2 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2024. Archived from the original on September 2, 2024. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0600Z 2 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 2, 2024. Archived from the original on September 2, 2024. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0600Z 3 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 3, 2024. Archived from the original on September 3, 2024. Retrieved September 3, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 0330Z 4 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 4, 2024. Archived from the original on September 3, 2024. Retrieved September 4, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 086000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 8, 2024. Archived from the original on September 8, 2024. Retrieved September 8, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 23Z 5 September 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 5, 2024. Archived from the original on September 5, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 95W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 9, 2024. Archived from the original on September 9, 2024. Retrieved September 9, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 091200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 9, 2024. Archived from the original on September 9, 2024. Retrieved September 9, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 14W (Fourteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 10, 2024. Archived from the original on September 10, 2024. Retrieved September 10, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Bebinca (2413) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 10, 2024. Archived from the original on September 10, 2024. Retrieved September 10, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Storm 'Ferdie' (Bebinca)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 13, 2024. Retrieved September 13, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #2F for Tropical Storm 'Ferdie' (Bebinca)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 13, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 14, 2024. Retrieved September 13, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 22 for TY Bebinca (2413) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on October 4, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 14W (Bebinca) Warning No. 22 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tianchi, Zhang. "暴风雨圈直击!"贝碧嘉"或为1949年以来登陆上海最强台风" [Storm circle hits! "Bebejia" may be the strongest typhoon to land in Shanghai since 1949]. MSN. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Shanghai hit by strongest typhoon in more than 70 years as Bebinca makes landfall". France 24. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ Typhoon 14W (Bebinca) Warning No. 25 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for STS Bebinca (2413) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 16, 2024. Archived from the original on September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 180000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 18, 2024. Archived from the original on September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 18, 2024.
- ^ "Shanghai slammed by biggest typhoon to hit city since 1949". The Japan Times. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Strongest typhoon to hit Shanghai since 1949 shuts down megacity". France 24. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon knocks out power to some homes in Shanghai". Shropshire Star. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "2 people reported dead in China as Typhoon Bebinca is downgraded to a tropical storm". Associated Press. September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024.
- ^ SitRep No. 5 for the Effects of Trough of TC Ferdie (Bebinca) and Enhanced Southwest Monsoon (2024) (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 19Z 14 September 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 14, 2024. Archived from the original on September 14, 2024. Retrieved September 14, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ a b Warning and Summary 150000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TS Pulasan (2414) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 16 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 15W (Pulasan) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 16, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Storm 'Helen' (Pulasan)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #5F for Tropical Storm 'Helen' (Pulasan)" (PDF). PAGASA. September 18, 2024. Retrieved September 18, 2024.
- ^ Yoon, John (September 19, 2024). "Tropical Storm Pulasan Strikes Near Shanghai, Days After Typhoon Hit". The New York Times. Retrieved September 19, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Pulasan makes 2nd landfall in China". english.shanghai.gov.cn. Retrieved September 28, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 15W (Pulasan) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 20, 2024. Archived from the original on September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 15W (Pulasan) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 21, 2024. Archived from the original on September 21, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 25 for Extropical Cyclone located at 34N 125E (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 21, 2024. Archived from the original on September 21, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ "Japan orders evacuations as heavy rains trigger floods in earthquake-hit region". Manila Standard. September 21, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 141800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 14, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 14, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 15 September 2024 Reissued (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 15, 2024. Archived from the original on September 15, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Gener'" (PDF). PAGASA. September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 2 for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 16, 2024. Archived from the original on September 16, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #7 for Tropical Depression 'Gener'" (PDF). PAGASA. September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #11 for Tropical Depression 'Gener'" (PDF). PAGASA. September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 17, 2024. Archived from the original on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 18, 2024. Archived from the original on September 18, 2024. Retrieved September 17, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 18, 2024. Archived from the original on September 18, 2024. Retrieved September 18, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 16W (Sixteen) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 18, 2024. Archived from the original on September 19, 2024. Retrieved September 18, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 13 for TS Soulik (2415) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 19, 2024. Archived from the original on September 19, 2024. Retrieved September 16, 2024.
- ^ "Storm Soulik enters central Vietnam". VnExpress. September 19, 2024. Archived from the original on September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 16 for tropical depression located at 17N 107E (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 19, 2024. Archived from the original on September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 200600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 20, 2024. Archived from the original on September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 20, 2024.
- ^ a b "Báo cáo nhanh công tác trực ban PCTT ngày 22/9/2024".
- ^ "LPA strengthens into tropical depression Igme". ABS-CBN. September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 20, 2024.
- ^ a b c Tropical Storm 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 21, 2024. Retrieved September 21, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 17W (Seventeen) Warning No. 7 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 22, 2024. Retrieved September 22, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 18W (Cimaron) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 27, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 18W (Cimaron) Warning No. 11 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 27, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 19W (Nineteen) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 27, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 19W (Jebi) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 26 September 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 26, 2024. Archived from the original on September 26, 2024. Retrieved September 26, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Warning and Summary 260600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 26, 2024. Archived from the original on September 26, 2024. Retrieved September 26, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Julian'" (PDF). PAGASA. September 27, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 20W (Twenty) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 27, 2024. Archived from the original on September 27, 2024. Retrieved September 27, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 6 for TS Krathon (2418) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 28, 2024. Archived from the original on September 28, 2024. Retrieved September 15, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 20W (Krathon) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. September 29, 2024. Archived from the original on September 29, 2024. Retrieved September 29, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Krathon (2418) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. September 17, 2024. Archived from the original on October 4, 2024. Retrieved September 29, 2024. Alt URL
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 18 for TY Krathon (2418) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 1, 2024. Archived from the original on October 1, 2024. Retrieved October 1, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Krathon makes landfall in Kaohsiung". Focus Taiwan. October 3, 2024. Retrieved October 3, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Category 4-Equivalent Super Typhoon 20W (Krathon) Warning No. 26 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 3, 2024. Archived from the original on October 3, 2024. Retrieved October 3, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 041200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 4, 2024. Archived from the original on October 4, 2024. Retrieved October 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 29 for TS Krathon (2418) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 3, 2024. Archived from the original on October 4, 2024. Retrieved October 3, 2024.
- ^ "NDRRMC: 5 reported dead due to Julian". GMA News. October 4, 2024. Retrieved October 4, 2024.
- ^ "Torrential rain from storm Krathon kills two more". Focus Taiwan. October 5, 2024. Retrieved October 5, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 191800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 19, 2024. Archived from the original on October 20, 2024. Retrieved October 19, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Twenty-Two) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 20, 2024. Retrieved October 20, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 7 for TS Trami (2420) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 21, 2024. Archived from the original on October 21, 2024. Retrieved October 21, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 13 for STS Trami (2420) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 23, 2024. Archived from the original on October 23, 2024. Retrieved October 23, 2024.
- ^ "'Kristine' makes landfall in Isabela: PAGASA". ABS-CBN News. October 23, 2024. Retrieved October 23, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #20 for Severe Tropical Storm 'Kristine' (Trami)" (PDF). PAGASA. October 24, 2024. Retrieved October 24, 2024.
- ^ "Storm Trami makes landfall in central Vietnam". e.vnexpress.net. October 26, 2024. Retrieved October 26, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Trami) Warning No. 28 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 26, 2024. Retrieved October 26, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 29 for TS Trami (2420) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 27, 2024. Archived from the original on October 27, 2024. Retrieved October 27, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 22W (Trami) Warning No. 31 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 28, 2024. Retrieved October 28, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 291800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 29, 2024. Archived from the original on October 30, 2024. Retrieved October 29, 2024.
- ^ "Agri damage due to Kristine, Leon breaches P4B —NDRRMC". GMA News. November 1, 2024. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ "Ít nhất ba người chết do bão Trà Mi". rfa.org. October 27, 2024. Retrieved October 27, 2024.
- ^ "Heavy rain due to storm Tra Mi, some mountainous areas of Quang Tri are isolated". laodong.vn. Retrieved October 27, 2024.
- ^ "Storm Trami lands in central Vietnam posing flood risks". Free Malaysia Today. Reuters. October 27, 2024. Retrieved October 27, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 22 October 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 22, 2024. Archived from the original on October 22, 2024. Retrieved October 22, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 231800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 23, 2024. Archived from the original on October 24, 2024. Retrieved October 23, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 24, 2024. Archived from the original on October 24, 2024. Retrieved October 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 5 for TS Kong-rey (2421) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 25, 2024. Archived from the original on October 25, 2024. Retrieved October 25, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Category 4-Equivalent Super Typhoon 22W (Kong-rey) Warning No. 21 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 30, 2024. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 25 for TY Kong-rey (2421) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 30, 2024. Archived from the original on October 30, 2024. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Kong-rey makes landfall in Taitung - Focus Taiwan". Focus Taiwan - CNA English News. October 31, 2024. Retrieved October 31, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 22W (Kong-rey) Warning No. 27 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. October 31, 2024. Retrieved October 31, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 22W (Kong-rey) Warning No. 30 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 1, 2024. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Storm 22W (Kong-rey) Warning No. 32 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 1, 2024. Retrieved November 1, 2024.
- ^ "Fierce winds, coastal flooding batter Batanes due to Leon". GMA News. October 30, 2024. Retrieved October 30, 2024.
- ^ "Philippines: Supertyphoon destroys old church, houses, infrastructure". gulfnews.com. October 31, 2024. Retrieved October 31, 2024.
- ^ "Sea and Land Typhoon Warning". Central Weather Administration. August 14, 2024. Archived from the original on October 31, 2024. Retrieved October 31, 2024.
- ^ "Waves and Tides Monitoring". Central Weather Administration. August 14, 2024. Archived from the original on October 31, 2024. Retrieved October 31, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Kong-rey causes 3 deaths, 690 injuries". Focus Taiwan. November 2, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 18Z 2 November 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 2, 2024. Archived from the original on November 2, 2024. Retrieved November 2, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 1 for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 3, 2024. Archived from the original on November 3, 2024. Retrieved November 3, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 90W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 2, 2024. Archived from the original on November 2, 2024. Retrieved November 2, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 24W (Twenty-Four) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 3, 2024. Retrieved November 3, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 24W (Twenty-Four) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 3, 2024. Retrieved November 3, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Yinxing (2422) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 3, 2024. Archived from the original on November 4, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 4, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 4, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 4 for TS Yinxing (2422) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 4, 2024. Archived from the original on November 4, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 4, 2024. Retrieved November 4, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 9 for TY Yinxing (2422) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 5, 2024. Archived from the original on November 5, 2024. Retrieved November 5, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #19 for Typhoon 'Marce' (Yinxing)" (PDF). PAGASA. November 7, 2024. Retrieved November 7, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 15 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 6, 2024. Retrieved November 6, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 16 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 7, 2024. Retrieved November 7, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 17 for TY Yinxing (2422) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. October 30, 2024. Archived from the original on November 7, 2024. Retrieved November 7, 2024.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (November 7, 2024). "Typhoon Marce makes landfall in Cagayan". Rappler. Retrieved November 7, 2024.
- ^ Casucian, Jiselle Anne (November 7, 2024). "PAGASA: Marce makes 2nd landfall over Sanchez-Mira, Cagayan". GMA News. Retrieved November 7, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #26 for Typhoon 'Marce' (Yinxing)" (PDF). PAGASA. November 8, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 23 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 8, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 25 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 29 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 31 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 37 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 12, 2024. Retrieved November 12, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 24W (Yinxing) Warning No. 38 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 12, 2024. Retrieved November 12, 2024.
- ^ a b Situational Report No. 11 for TCs Marce (2024) (PDF) (Report). Quezon City, Philippines: National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. November 13, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 080000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 8, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 01Z 8 November 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 8, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 081800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 8, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 3 for TS Toraji (2423) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for STS Toraji (2423) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 10, 2024. Archived from the original on November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 4 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 5 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 10, 2024. Archived from the original on November 10, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Toraji (2423) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 10, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 10, 2024.
- ^ "Typhoon Nika makes landfall in Aurora, PAGASA issues severe weather warnings". Brigada News FM. November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 9 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ "Nika weakens into severe tropical storm, exits land via Ilocos Sur". Rappler. November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 11 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 12, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 11 for TS Yinxing (2422) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 12, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 17 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 13, 2024. Archived from the original on November 13, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 26W (Toraji) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 13, 2024. Archived from the original on November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 150600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 15, 2024. Archived from the original on November 15, 2024. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 01Z 8 November 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 8, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 081800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 8, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for tropical depression (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 25W (Twenty-Five) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 2 for TS Man-yi (2424) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 3 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 10 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 13, 2024. Archived from the original on November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 19 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 13, 2024. Archived from the original on November 13, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ John O'Connor (November 13, 2024). "Tropical storm spares Guam". The Guam Daily Post. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 25 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 15, 2024. Archived from the original on November 15, 2024. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Man-yi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 15, 2024. Archived from the original on November 15, 2024. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 27 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 15, 2024. Archived from the original on November 15, 2024. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 30 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Man-yi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 16, 2024. Archived from the original on November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ "Super Typhoon Pepito slams Catanduanes: Torrential rains, deadly winds, and storm surges threaten Bicol region overnight". Brigada News. November 16, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 32 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #16 for Super Typhoon 'Pepito' (Man-yi)" (PDF). PAGASA. November 17, 2024. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Mondoñedo-Ynot, Laureen (November 17, 2024). "'Pepito' makes 2nd landfall in Aurora". SunStar Publishing Inc. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 35 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 17, 2024. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 37 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 18, 2024. Retrieved November 18, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #22 for Typhoon 'Pepito' (Man-yi)" (PDF). PAGASA. November 17, 2024. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 38 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 18, 2024. Archived from the original on November 18, 2024. Retrieved November 18, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for STS Man-yi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 18, 2024. Archived from the original on November 18, 2024. Retrieved November 18, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 40 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 18, 2024. Archived from the original on November 19, 2024. Retrieved November 18, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Depression 25W (Man-yi) Warning No. 43 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 19, 2024. Archived from the original on November 19, 2024. Retrieved November 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 200600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 20, 2024. Archived from the original on November 20, 2024. Retrieved November 20, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 01Z 8 November 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 8, 2024. Retrieved November 8, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 091200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 9, 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 27W (Twenty-Seven) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 11, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 8 for TS Usagi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 4, 2024. Archived from the original on November 11, 2024. Retrieved November 11, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Usagi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 12, 2024. Archived from the original on November 13, 2024. Retrieved November 12, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Category 4-Equivalent Super Typhoon 27W (Usagi) Warning No. 12 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 13, 2024. Archived from the original on November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 13, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Advisory for TY Usagi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 14, 2024. Archived from the original on November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
- ^ Arceo, Acor (November 14, 2024). "Ofel weakens into typhoon, makes landfall in Cagayan". Rappler. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Typhoon 27W (Usagi) Warning No. 15 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 14, 2024. Archived from the original on November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 20 for STS Usagi (2425) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 14, 2024. Archived from the original on November 15, 2024. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Storm 27W (Usagi) Warning No. 20 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. November 15, 2024. Archived from the original on November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 15, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 161200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. November 16, 2024. Archived from the original on November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 16, 2024. Archived from the original on December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- ^ "LPA off Mindanao strengthens into tropical depression Querubin". ABS-CBN. December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 17, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Querubin'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 17, 2024. Archived from the original (PDF) on December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 17, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 96W) Reissued". Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 17, 2024. Archived from the original on December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #4 for Tropical Depression 'Querubin'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 18, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #5-FINAL for Low Pressure Area (formerly 'Querubin')" (PDF). PAGASA. December 18, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 200600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. December 20, 2024. Archived from the original on December 21, 2024. Retrieved December 21, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 201800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. December 20, 2024. Archived from the original on December 21, 2024. Retrieved December 21, 2024.
- ^ Significant Tropical Weather Advisory for the Western and South Pacific Oceans, 06Z 20 December 2024 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 20, 2024. Archived from the original on December 20, 2024. Retrieved December 20, 2024.
- ^ Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (Invest 98W) (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 21, 2024. Retrieved December 21, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Romina'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ Rojas, Ariel (December 22, 2024). "For the first time, PAGASA names tropical depression that may not enter PAR". ABS-CBN. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 28W (Twenty-Eight) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 22, 2024. Archived from the original on December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 28W (Twenty-Eight) Warning No. 2 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 22, 2024. Archived from the original on December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #6-FINAL for Tropical Depression 'Romina'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning No. 6 for TS Pabuk (2426) (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. December 23, 2024. Archived from the original on December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 28W (Pabuk) Warning No. 6 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 23, 2024. Archived from the original on December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #1 for Tropical Depression 'Romina'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #3 for Tropical Depression 'Romina' (Pabuk)" (PDF). PAGASA. December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ "Severe Weather Bulletin #4 for Tropical Depression 'Romina' (Pabuk)" (PDF). PAGASA. December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Bulletin #6-FINAL for Tropical Depression 'Romina'" (PDF). PAGASA. December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ "Pabuk storm heading to Thailand is fake news". The Star. December 20, 2024. Retrieved December 24, 2024.
- ^ "TIN DỰ BÁO MƯA LỚN Ở KHU VỰC TRUNG VÀ NAM TRUNG BỘ" [Heavy Rain Forecast in the Central and South Central Regions]. National Center for Hydro-Meteorological Forecasting. December 24, 2024. Retrieved December 24, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Advisory issued at 5:45AM 24 December 2024". Malaysian Meteorological Department. December 24, 2024. Archived from the original on December 24, 2024. Retrieved December 24, 2024.
- ^ "Flash Update: No. 01 – Tropical Cyclone Pabuk – 23 December 2024". ASEAN Coordinating Centre for Humanitarian Assistance. December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ "Oriental Mindoro town under state of calamity due to flooding". Manila Bulletin. December 25, 2024. Retrieved December 26, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 181800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 18, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 18, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 190000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 19, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 230000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 23, 2024. Archived from the original on August 23, 2024. Retrieved August 23, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 241200 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 24, 2024. Archived from the original on August 24, 2024. Retrieved August 24, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 260600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 26, 2024. Archived from the original on August 26, 2024. Retrieved August 26, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 190600 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 19, 2024. Archived from the original on August 19, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 191800 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 19, 2024. Archived from the original on August 20, 2024. Retrieved August 19, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 210000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 21, 2024. Archived from the original on August 21, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Warning and Summary 300000 (Report). Tokyo, Japan: Japan Meteorological Agency. August 30, 2024. Archived from the original on August 30, 2024. Retrieved August 30, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 98W (Invest 98W) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 21, 2024. Archived from the original on December 21, 2024. Retrieved December 24, 2024.
- ^ Prognostic Reasoning for Tropical Depression 28W (Twenty-Eight) Warning No. 1 (Report). United States Joint Typhoon Warning Center. December 22, 2024. Archived from the original on December 22, 2024. Retrieved December 24, 2024.
- ^ a b Padgett, Gary. "Monthly Tropical Cyclone Summary December 1999". Australian Severe Weather. Archived from the original on February 11, 2012. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ a b The Typhoon Committee (February 21, 2013). "Typhoon Committee Operational Manual 2013" (PDF). World Meteorological Organization. pp. 37–38. Archived (PDF) from the original on August 1, 2013. Retrieved October 1, 2013.
- ^ "Review of the 2015 Pacific typhoon season" (PDF). www.typhooncommittee.org. January 25, 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on March 24, 2016. Retrieved April 8, 2022.
- ^ Zhou, Xiao; Lei, Xiaotu (2012). "Summary of retired typhoons within the Western North Pacific Ocean". Tropical Cyclone Research and Review. 1 (1). The Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific/World Meteorological Organization's Typhoon Committee: 23–32. doi:10.6057/2012TCRR01.03. ISSN 2589-3025. Archived from the original on August 12, 2017. Retrieved December 21, 2014.
- ^ a b c "Philippine Tropical Cyclone Names". Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration. Archived from the original on December 28, 2016. Retrieved April 18, 2015.
- ^ "Typhoon Maliksi wanes upon landing in Guangdong". ChinaDaily. June 1, 2024. Retrieved June 1, 2024.
- ^ "Severe weather causes fatal Tuk-Tuk accident in Siem Reap (VIDEO)". Khmer Times. July 24, 2024. Retrieved July 26, 2024.
- ^ SitRep No. 44 for the Combined Effects of Southwest Monsoon and TC CARINA (2024) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. August 16, 2024. Retrieved August 16, 2024.
- ^ "2024年7月全國自然災害狀況". Ministry of Emergency Management (MEM) (China) (in Chinese). August 8, 2024. Archived from the original on November 18, 2024. Retrieved December 10, 2024.
- ^ Khanh Vu (July 26, 2024). "Floods, landslides kill 10, leave 9 missing in northern Vietnam". Reuters. Retrieved July 25, 2024.
- ^ Chanlivong, Kheuakham (September 19, 2024). "Communities in Laos Come Together for Flood Recovery". Laotian Times. Retrieved September 22, 2024.
- ^ "Tropical Storm "Maria" makes landfall in Japan bringing record-breaking rainfall". The Watchers. August 12, 2024. Archived from the original on August 12, 2024. Retrieved August 17, 2024.
- ^ "A sailor in his 60s was found dead at the port of Heuksando Island, affected by the typhoon". Yonhap News Agency. September 22, 2024. Retrieved August 21, 2024.
- ^ Steve Evans (August 30, 2024). "Typhoon Shanshan seen as unlikely to trouble cat bonds or ILS positions". Artemis.bm. Retrieved September 2, 2024.
- ^ SitRep No. 11 for the Combined Effects of TC ENTENG (2024) and Southwest Monsoon (PDF) (Report). National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. September 7, 2024. Retrieved September 7, 2024.
- ^ "Bão số 3 tàn phá mạnh nhất trong 70 năm qua, gây thiệt hại nặng nề". VietNamNet (in Vietnamese). December 23, 2024. Archived from the original on December 23, 2024. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ "Public Announcement on Response Efforts and Damage from Typhoon Yagi - Global New Light Of Myanmar". December 8, 2024. Retrieved December 25, 2024.
- ^ "Watch Counting China's Economic Losses From Typhoon Bebinca". Bloomberg. September 17, 2024. Retrieved September 19, 2024.
- ^ "NDRRMC: Death toll due to Habagat, Ferdie, Gener, Helen now 24". GMA News. September 20, 2024. Retrieved September 20, 2024.
- ^ Phuc, Hoang (October 31, 2024). "Quảng Bình: Mưa lũ gây thiệt hại 500 tỉ đồng, 14 người thương vong". Người Lao Động (in Vietnamese). Archived from the original on December 9, 2024. Retrieved December 9, 2024.
- ^ "2024年11月全國自然災害狀況". Ministry of Emergency Management (MEM) (China) (in Chinese). December 17, 2024. Archived from the original on December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- ^ "Nika, Ofel cause P320M in infra damage, 300K people affected". GMA News. November 14, 2024. Retrieved November 14, 2024.
- ^ "Higit P50 Milyon naitalang pinsala sa imprastraktura sa pananalasa ng bagyong Nika sa Region 2 – DPWH". Bombo Radyo (in Filipino). November 16, 2024. Retrieved November 16, 2024.
- ^ Situational Report No. 34 for the Combined Effects TCs Nika, Ofel, and Pepito (2024) (PDF) (Report). Quezon City, Philippines: National Disaster Risk Reduction and Management Council. December 4, 2024. Retrieved December 10, 2024.
- ^ Ombay, Giselle (November 17, 2024). "Infra damage due to Nika, Ofel, Pepito hits P469M —NDRRMC". GMA News. Retrieved November 17, 2024.
- ^ "Warning and Summary 170600". Japan Meteorological Agency. December 17, 2024. Archived from the original on December 17, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
External links
[edit]- China Meteorological Agency
- Digital Typhoon
- Hong Kong Observatory
- Japan Meteorological Agency
- Joint Typhoon Warning Center
- Korea Meteorological Administration
- Malaysian Meteorological Department
- National Weather Service Guam
- Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
- Taiwan Central Weather Bureau
- TCWC Jakarta
- Thai Meteorological Department
- Typhoon2000
- Vietnam's National Hydro-Meteorological Service