Transpennine Route Upgrade
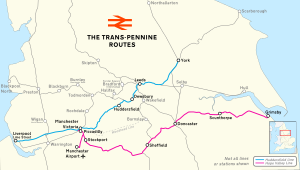
The Transpennine Route Upgrade (TRU) is a major investment being made in the railway between York and Manchester via Leeds and Huddersfield in the north of England. It is the 76 miles (122 km) northern route over the Pennines,[1] most of which is also known as the Huddersfield line. As of 2024[update], the line is heavily used but is slow and lacks capacity.[2] It has Victorian infrastructure, covers difficult terrain including the 3-mile (4.8 km) Standedge Tunnel, and has poor access roads.
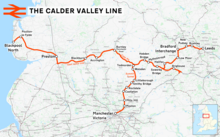
Since the closure of the Woodhead line, there are three remaining transpennine rail lines that connect Lancashire and Yorkshire. To the south of the Huddersfield line is the Hope Valley line which traverses even more difficult terrain including the 3.5-mile (5.6 km) Totley Tunnel, and which in 2021 was allocated £137 million investment to improve capacity and connectivity between Manchester and Sheffield.[3][4] To the north the Calder Valley line connects Manchester and Leeds via Rochdale and Bradford (where trains have to reverse). This line has been strengthened to allow its use as a diversionary route while the Huddersfield line is upgraded.[5]
Reopening the Woodhead line as a potential alternative Pennine crossing was ruled out early on.[6] The Skipton–East Lancashire Rail Action Partnership is a campaign that is seeking the reopening of the 12-mile (19 km) railway line that used to run between the Lancashire town of Colne and the Yorkshire town of Skipton. This could provide an additional transpennine route for both a commuter service and a relief transpennine freight route.[7][8]
Background
[edit]Since the rejection of Northern Powerhouse Rail's aspiration for a new high speed line within Yorkshire, it has been questioned whether an upgraded Huddersfield line will provide sufficient capacity for the region's needs.[9] However, the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands (IRP) that was announced in November 2021,[10][11] did include full electrification between Manchester and York,[12] and subsequently W12 loading gauge to accommodate 2.9 m × 2.6 m (9.5 ft × 8.5 ft) refrigerated shipping containers throughout.[13][14] The whole £9–11.5 billion programme has been defined as phase one of Northern Powerhouse Rail, and is claimed to be the biggest infrastructure project in the UK.[15] It consists of a succession of sub-projects[16] designed to give incremental benefits to rail users over a period of time, with an anticipated overall completion date of between 2036 and 2041. Following completion of the upgrade trains will be able to run at top speeds of 125 mph (201 km/h). [17][18][19] In Manchester, the project interfaces with the Northern Hub.
There were up to 50 million passenger journeys per year on this line pre COVID-19 on fast (including TransPennine Express), semi-fast and stopping trains, as well as freight trains. The existing passenger service is widely accepted as being very unsatisfactory in terms of journey time, frequency, punctuality and level of passenger comfort.[20][21] At its worst, 15% of passengers had to stand in peak times.[22] The 50-mile (80 km) railway line between Leeds and Manchester links two key population centres. Leeds is the largest city in Yorkshire, and forms the main area of the City of Leeds metropolitan borough. It is the central city of the Leeds City Region[23] which has a population of over 3 million, making it the second most populated metropolitan city region in the United Kingdom, behind Greater London.[24] Manchester is the most-populous city and metropolitan borough in North West England. It lies within the third most-populous county, at around 2.8 million people.[25][26] Manchester is often referred to as the second city of the United Kingdom,[27][28][29][30] although this is disputable.[31][32] York was voted European Tourism City of the Year in June 2007.[33] Linking these population centres together by a low-polluting, low-carbon mode of transport such as electric trains is now seen as both desirable and essential.[34]
The equivalent transpennine road link is the M62 motorway, which provides the most practical route for heavy goods vehicles and other commercial traffic between Manchester and Leeds. However, the section between junctions 18 and 29 through Greater Manchester and West Yorkshire has been identified as one of the most congested roads in Britain.[35][36] Three of the five largest metro areas in England that contain a significant number of warehouses requiring deliveries to and from the ports at Merseyside and the Humber, are linked by the M62. Annual average daily traffic flows of 100,000 were recorded east of the Pennines at junction 22 in 2006 and 78,000 west of the Pennines.[37] The UK government has long recognised the advantages of modal shift from road to rail.[38]
Most main railway lines in England radiate out from London with very few, such as the transpennine routes, going at right angles to these. It is widely accepted that there is a North–South divide in England,[39] with government spending per person on drivers of growth such as transport infrastructure, being far higher in the South-East than the North.[40][41] London has a directly elected mayor with control over public transport whilst most Northern cities have transport policies decided by Westminster. In 2021, the Conservative government launched a Levelling up policy to address the North–South divide as part of a broader objective.[42] All of the above factors mean the Transpennine Route Upgrade is high on the political agenda for all parties.
In March 2021, Parliament's Transport Select Committee published a report in the series of Trains Fit for the Future enquiry. It recommended a rolling programme of electrification. There was also a call for the Department for Transport (DfT) to publish without delay a list of “no regret” electrification schemes, and then for the industry to act on them.[43] The report also reached the mainstream media with headlines of “MPs call for a rolling programme of electrification”.[34]
Project history
[edit]Before 2020
[edit]The initial proposal in the 21st century was to electrify the line from Manchester Victoria to Leeds via Huddersfield, with some infill schemes around Manchester. This was announced in the 2011 Autumn Statement by the Chancellor of the Exchequer. The cost was cited as £290 million and the project was planned to start in 2014.[44] In the 2012 High Level Output Specification (HLOS), it was announced there would be additional electrification from Leeds to Selby.
Northern Powerhouse Rail (sometimes called High Speed 3) was established in 2014 to substantially enhance the economy of the North of England.[45][46] It would have provided new and significantly upgraded railway lines to transform rail services between the region's towns and cities.[47][48][49][50] The original scheme would have seen a new high-speed rail line from Liverpool to Warrington then joining the HS2 tunnel which it would share into Manchester Piccadilly. From there, the line would have continued via a new through station at Bradford, to Leeds.[51] However, in November 2021 the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands was published which removed all of the new line in Yorkshire, from the plan.[10]: 7
In March 2015, the Chancellor George Osborne announced there would be an additional rolling programme of improvement and electrification to Hull. In July 2012, the UK government announced £4.2 billion of 25 kV AC electrification schemes. The Transpennine Route Upgrade from Manchester to York and Selby via Leeds was announced at this time. In November 2014, the deputy prime minister Nick Clegg reported on the government's desire to see the whole route upgraded and electrified.[52]
Manchester Victoria has already had electrification equipment installed as part of the northwest programmes.[53][54][55] On other parts of the route, including between Leeds and York, bridge raising and other civil engineering works were started in March 2015.[56] Other bridges in Tameside between Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge were also worked on.[57][58][59] Further civil engineering contracts were awarded in 2017.[60] Various local authorities have also provided updates.[61][62] On a visit to Leeds on 2 March 2018, Transport Secretary Chris Grayling said the upgrade would continue.[63]
2020 and beyond
[edit]As of 2021[update], ten years after the Autumn Statement announcement, the line was still being upgraded in stages.[64] It has been stated that the delays are due to political dithering.[65] In 2021, considerable work was done in the Miles Platting area, to pave the way for wires all the way to Stalybridge, with a compound constructed.[66][67][68] Network Rail said that there would be significant disruption over at least a five year period.[69][70] However, in an order under the Transport and Works Act 1992 (TWAO) published in March 2021, it was said that work on some of the scheme would extend beyond 2029 i.e. into a later Network Rail Control Periods, CP8.[71] A total blockade took place on the route between Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge and Rochdale between 31 July and 15 August 2021.[72][73] This work was completed on time.[74] On 5 October 2021 Proofs of Evidence were submitted by Network Rail to the Department for Transport.[75]
On 26 May 2021, it was confirmed that a further £317 million was being spent on the upgrade, and confirmed the electrification of the line between York and Church Fenton,[76][77][78] although Network Rail had already started to install masts for overhead line electrification (OLE) on this route in February 2021.[79][80][81][82][83] On 4 June 2021, it was confirmed that the £317 million was in addition to the £589 million previously announced and further confirmed that electrification would go from Huddersfield to Leeds. It was also stated that work would begin immediately.[84] However, this is disputed according to one source.[85]
As of 2021[update], Network Rail are working on the sections between York and Church Fenton,[86] Huddersfield and Westtown (Dewsbury) and Manchester and Stalybridge.[87] It is planned to upgrade the signalling, to increase tracks from two to four in places, and to implement other track changes and renewals that improve line speed and hence give shorter journey times.[88][89] Parts of the cost of upgrading have been quoted at £2.9 billion and £3.1 billion in total.[90][91] In 2021, the government allocated £589 million of funding for the section between Leeds and Huddersfield.[92] The route has 285 overbridges and 6 miles (9.7 km) of tunnels including Standedge Tunnel.[93] There are a total of 23 stations including the Grade I listed Huddersfield station, and major viaducts at Dewsbury, Batley, Milnsbridge and Huddersfield. Nine structures along the route require listed building approval.[94][95]
The planned upgrade of the 8-mile (13 km) section between Huddersfield and Westtown (Dewsbury) is of particular significance.[96] It is the best place on the route to provide a facility for fast trains to overtake slower ones, by increasing the number of tracks from two to four. Also, by building a bridge that will provide grade separation at Thornhill L.N.W. Junction, it will eliminate conflicts between trains travelling along the Calder valley between Brighouse and Wakefield and those travelling between Huddersfield and Leeds.[22] On 27 June 2022, the Secretary of State for Transport's decision to grant the Order under the Transport and Works Act (the TWAO) for this section was published. This includes quadrupling the track across most of the route, the provision of grade separation at Ravensthorpe and works to the stations, as well as electrification throughout. [97]
On 18 November 2021 the Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands (IRP) was published. This included a commitment to the Transpennine north railway upgrade to include full electrification. The completion date for all works was cited as 2032.[10]: 133–136 However, the IRP did not include most of the eastern leg of HS2, nor the high speed rail line from Manchester all the way to Leeds. Instead, it says a high speed line would be built east from Manchester to Marsden, which is just over the border into West Yorkshire, at the eastern end of the Standedge Tunnels.[10]: 13 Cllr Louise Gittins, Interim Chair of Transport for the North, said that: “Today’s announcement is woefully inadequate. After decades of underfunding, the rail network in the North is not fit for purpose. It is largely twin-track Victorian infrastructure trying to cope with the demands of a 21st Century economy." The leaders of the upgrade held a round table conference November 2022 discussing progress and strategy for keeping disruption to a minimum.[98]
In September 2022 Boris Johnson ceased to be Prime Minister of the United Kingdom and was replaced by Liz Truss. In her bid to get that job, she had promised that the Transpennine route upgrade would be delivered in full, with electrification all the way between Liverpool and Hull including a stop in Bradford.[99] However, she was succeeded by Rishi Sunak in October 2022, and his government returned to the position of the Johnson administration.[100]
In November 2023, a Freedom of Information Request uncovered by The Northern Agenda newsletter revealed that the government-operated TransPennine Express spent almost £2 million securing advertising for the delayed TRU programme in 2022/23. [101]
Technical details
[edit]Anticipated benefits and timescales
[edit]Although the overall project completion date may be as late as 2041, some benefits should be felt in late 2024 or early 2025 when electric trains are due to run over the improved track layout between Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge (Projects W1/W2a), and bi-mode trains will be able to use electric traction between Church Fenton and York (Project E1). Benefits will also be available for users between Lancashire and Yorkshire from improvements to the Calder Valley line via Rochdale and the Hope Valley line to Sheffield, when these are used as diversionary routes because of work on the Huddersfield line.[102]
Funding approval for Projects E2/3/4 and W3 is to be sought in 2023. Projects E2/3/4 should lead to reduced journey times between Leeds and Church Fenton, with improvements at Leeds station, electrification and capacity improvements including reduced conflicts from Neville Hill depot.[102] Project W3 concerns the section between Huddersfield and Ravensthorpe. This will involve improvements to Huddersfield station including an increase from three to four through platforms, four-tracking between the two stations, with grade separation at Ravensthorpe, and the movement of Ravensthorpe station to serve trains on the Calder Valley line in addition to the Huddersfield line.[16]
Projects W2b/c concern the Stalybridge to Marsden and Marsden to Huddersfield sections. These include track realignment between Stalybridge and Diggle, and the provision of a third track to act as a "Crawler Lane" for freight trains climbing up from Huddersfield to Marsden.[16] Further benefits to the economy have also been touted.[103] In particular, sustainability has been emphasized.[104][105]
Transport Works Act Order
[edit]On 31 March 2021, a TWAO was published with plans showing the scope of the works.[106] The whole scheme document was split up into portions, with W referring to portions to the west, and E to portions to the east of Leeds.[107]
The TWAO covered the following sections:[108][109][110]
The scheme was further updated with the section between Stalybridge and Huddersfield being split further at Marsden.[111]
- W1 – Manchester Victoria to Stalybridge: line speed increases and electrification
- W2a – Stalybridge station: general improvements and remodelling of the junction at the west of the station
- W2b – Stalybridge to Marsden: electrification – including the 3 mi (5 km) long Standedge tunnel
- W2c – Marsden to Huddersfield
- W3 – Huddersfield to Ravensthorpe: line speed improvements and electrification
- W4 – Ravensthorpe to Leeds: line speed improvements and electrification
- W5 – Morley station: greater line speed and electrification
- E1 – North of Church Fenton to York: line speed improvements and electrification
- E2 – Leeds station improvements
- E3 – Crossgate to Micklefield
- E4 – Micklefield to Church Fenton
Under the order sections W1, W2a, W3, W4, W5 and E1 were permitted to proceed to the design stage. Sections W2b and E2-E4 were permitted to develop further to GRIP 3 status.[112] As part of the upgrade, eleven stations along the route will require a review of options for persons of reduced mobility such as step-free access and other enhancements.[22][113]
Power supply
[edit]The electrical power for the scheme on the west side of the scheme, is being provided from the grid feeder in the Stalybridge area at Heyrod. It was visited by Jonathan Reynolds, the local MP for the constituency on 27 May 2016.[114] The latest plans in the TWAO call for a SFC (Static Frequency Converter) in the Ravensthorpe vicinity rather than a normal grid feeder station.[115]
Bridges
[edit]There are a number of bridges being upgraded and strengthened or otherwise modified as part of the project.[116] In the Manchester area they include the bridge at Dantzic Street in the centre of Manchester. In the Miles Platting area, Queens Road bridge is being modified, as is the Bromley Street subway and also at Oldham Road.[117] In Ashton-under-Lyne in the Southampton Street[118] and Granville Street area, overbridges were raised in April and May 2022.[119][120] Between Huddersfield and Ravensthorpe, twelve bridges will be demolished and replaced, a small number will be adapted, and one will be removed altogether.[121][122]
Crossings
[edit]A consultation has been launched with residents on the plan to close Lady Anne level crossing and Batley signal box as part of the upgrade.[123] Consultations have also been launched on other crossings being considered for closure.[124][125][126][127] These consultations include discussion of environmental mitigation necessity.[128] A TWAO was submitted July 2022 to close three level crossings (Rose Lane, Adamsons and Poulters) and replace with one new road and bridge with pavement and mitigated for reduced mobility access. It has been called the Church Fenton Level Crossing Reduction, and will give access to the farms and homes in the area.[129] Other crossings are being modified and closed in the scope of these works, some of which affect public rights of way.[130]
Gantry design
[edit]As Huddersfield station is a Grade I listed building, a special design was submitted that precludes the use of headspan overhead line gantries and uses a bespoke design.[131] The planning application to Kirklees council shows total closure of the station for two 32-day periods from April to May 2024 and also April to May 2025.[132][133]
Timeline
[edit]- November 2011: Autumn statement announcing electrification of the line
- July 2012: Addition of Leeds to Selby announced as part of HLOS
- November 2014: Deputy prime minister states government's desire for the whole route to be electrified
- March 2015: Civil engineering including overbridge raising works start at various places
- March 2015: Chancellor announces extra electrification from Selby to Hull
- June 2015: work on the whole scheme paused by Secretary of State for Transport
- September 2015: work on the scheme resumed
- August 2016: GRIP 1 complete
- December 2016: GRIP 2 complete
- March 2017: various civil engineering contracts awarded
- December 2017: GRIP 3 complete
- March 2018: Transport Secretary confirms work on the upgrade would continue
- January 2021: Piling commences in two locations along the route
- March 2021: Transport Works Act Order published
- April 2021: Network Rail confirm piling in Miles Platting area to completed by end of 2021
- 4 June 2021: Confirmation of £317 million extra funding and work to begin immediately.
- 31 July – 15 August 2021: Blockade and blitz strategy Manchester Victoria to Stalybridge and Rochdale.[134] Completed on time and budget.
- 18 November 2021: The Integrated Rail Plan is published committing to the full upgrade and electrification.
- 27 June 2022: Yes decision published by the Department of Transport for the Ravensthorpe TWAO (W3).[135]
- 19 July 2022: House of Commons announcement by the Secretary of State for Transport that another £959 million of funding had been made available for the project.[136][137]
- 20 July 2022: National Audit Office publish a report into the upgrade saying the case had been firmly made for the upgrade but risks remain, money had been wasted, and was critical of the DfT taking so long to agree the scope of the works.[17]
- November 2022: Announcement that wires had started going up in the Stalybridge area.[138]
- January 2023: Announcement of a new managing director for the route upgrade project[139] and a major 26 day blockade and diversions for Stalybridge area[140] and other closures including Morley station,[141] in the February to April 2023 timeframe.[142][143]
- February 2023: Morley station blockade completed on schedule.[144] The new station is due to open in Summer 2023.[145][146]
- April 2023: Stalybridge station reopens after a 26 day blockade for major upgrades and renewals.[147]
- 26 June 2023: Morley station reopens on time after a 9 day blockade to rebuild.[148]
- 17 July 2023: Application for a TWAO made for the Leeds to Micklefield section of the upgrade including compulsory land purchases.[149][150]
- 4 December 2023: Announcement of £3.9 billion being injected to speed up the scheme and bring Hull into the scope.[151]
- 13 March 2024: A test train ran successfully between Manchester Victoria and Stalybridge.[152][153]
- 22 March 2024: Screening TWAO for Stalybridge to Standedge tunnel eastern portal published stating no further environmental impact screening necessary.[154]
- February - March 2024: Leeds to Micklefield Enhancements TWA Order Public Enquiry held[155]
- 9 April 2024: Ten-day closure of Huddersfield Railway Station completed although roof work postponed due to high winds[156]
- April 2024: Church Fenton Level Crossing Reduction TWA Order came into force[157]
- July 2024: Church Fenton to Colton Junction energised[158]
- 12 September 2024: A consortium including BAM and Amey announced as contractors for the section of the upgrade between Leeds and Huddersfield including signalling for 28 route miles (45 km)[159][160]
- 1 October 2024: The TWAO for the Leeds-Micklefield section of the upgrade is published.[161]
- October 2024: The October 2024 budget the new government confirmed support for the upgrade project.[162]
The Transport for the North State of Play document, issued in September 2024, gives the following timeline for the completion of each section:[163]
| TRU Segment | Finish Date |
|---|---|
| Manchester Victoria to Stalybridge Electrification | 2025 |
| Church Fenton to York | 2025 |
| Stalybridge | 2024 |
| Leeds to Church Fenton | 2030 |
| Stalybridge to Marsden | 2032 |
| Huddersfield to Ravensthorpe | 2030 |
| Ravensthorpe to Leeds | 2030 |
See also
[edit]- 21st-century modernisation of the Great Western Main Line
- Felixstowe–Nuneaton railway upgrade
- History of rail transport in Great Britain 1995 to date
- List of proposed railway electrification routes in Great Britain
- Midland Main Line railway upgrade
- North West England electrification schemes
- Overhead line
- Railway electrification in Scotland
- West Coast Main Line route modernisation
References
[edit]- ^ "Coming soon Transpennine Railway Upgrade". Transpennine Route Upgrade. Archived from the original on 25 February 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ "Plans to improve the Manchester – Leeds – York route are advancing". Modern Railways. 20 May 2021. Archived from the original on 27 December 2021. Retrieved 27 December 2021.
- ^ "Government invests to transform journeys on Hope Valley line". GOV.UK. 11 March 2021. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ Abbott, James (20 May 2021). "Hope Valley Upgrade Third Express Path Per Hour". Modern Railways.
- ^ "Calder Valley rail route to keep Transpennine passengers moving this month". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 5 August 2022.
- ^ "Trans-Pennine Woodhead rail tunnels not to reopen". BBC News. 11 November 2013. Archived from the original on 2 January 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "The Skipton-Colne Rail Corridor: The New Transpennine Northern Link" (PDF). Skipton–East Lancashire Rail Action Partnership. November 2020. Retrieved 18 May 2022.
- ^ "Campaign to reopen railway between Colne and Skipton intensifies". Rail Insider. 28 May 2021.
- ^ "Transpennine upgrade". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d Department for Transport (18 November 2021). Integrated Rail Plan for the North and Midlands (PDF). Department for Transport. ISBN 978-1-5286-2947-8. Archived (PDF) from the original on 18 November 2021. Retrieved 18 November 2021.
- ^ Media, Insider. "Trans-Pennine Route Upgrade project moving to next phase". Insider Media Ltd. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "Northern Powerhouse Rail" (PDF). Parliament UK. 25 August 2022.
- ^ Abbott, James (February 2023). "2023: Key year for TRU". Modern Railways. No. 893. pp. 56–61.
- ^ "Freight RUS" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 16 May 2009.
- ^ "Rail Technology Magazine August September 2022 Page 78". mag.railtechnologymagazine.com. Retrieved 31 August 2022.
- ^ a b c Abbott 2023, pp. 56–61.
- ^ a b "The Transpennine Route Upgrade Programme – National Audit Office (NAO) Press release". National Audit Office. 19 July 2022. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ "NAO Transpennine Route Upgrade summary" (PDF). NAO UK government.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade, UK". Railway Technology. Retrieved 11 September 2024.
- ^ David Lawrance and James Hodge – Northern Programmes including Trans pennine Route Upgrade, 15 March 2017, archived from the original on 8 February 2021, retrieved 3 February 2022
- ^ Lawrance, David; Hodge, James (28 February 2017). "Northern Programmes". Permanent Way Institution. Archived from the original on 22 September 2018. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ a b c Trans Pennine route upgrade – Neil Kerry, The Permanent Way Institution, 26 October 2021, archived from the original on 11 January 2022, retrieved 11 January 2022
- ^ "Definition of 'Leeds'". Collins English Dictionary. Archived from the original on 15 December 2018. Retrieved 15 December 2018.
"Leeds Tourism". Planet Ware Travel Guide. Archived from the original on 5 May 2009. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
"Leeds stakes it claim to financial hub". The Yorkshire Post. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2009.
"About Leeds". www.bookinghime.com. Archived from the original on 9 May 2008. Retrieved 1 February 2009. - ^ "Regional economic activity by gross value added (balanced), UK: 1998 to 2017". Office for National Statistics. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ "Estimates of the population for the UK, England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland – Office for National Statistics". www.ons.gov.uk. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 29 January 2021.
- ^ "Greater Manchester Key Facts" (PDF). neweconomymanchester.com. January 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 March 2021. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- ^ Hodos, Jerome (December 2007). "Globalization and the Concept of the Second City". City & Community. 6 (4): 315–333. doi:10.1111/j.1540-6040.2007.00230.x. ISSN 1535-6841. S2CID 154848447. Archived from the original on 7 January 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ Rodger, James (11 January 2017). "More people think Manchester is UK's second city than Birmingham". BirminghamLive. Archived from the original on 7 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ "Why Manchester is definitely the UK's second city". The Manc. 10 June 2021. Archived from the original on 7 January 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ Name (7 October 2019). "Which is England's second city?". City Monitor. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 7 January 2022.
- ^ "England's second city: Birmingham". Britain Magazine. 24 May 2013. Archived from the original on 12 June 2018. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- ^ "An ode to Birmingham: how can the UK's second city fix its image problem?". The Guardian. 12 July 2014. Archived from the original on 14 February 2021. Retrieved 11 June 2018.
- ^ "York voted top city for tourists". BBC News Online. BBC. 14 June 2007. Archived from the original on 7 January 2009. Retrieved 28 July 2008.
- ^ a b Lancefield, Neil (23 March 2021). "MPs call for rolling programme of rail electrification projects to cut carbon". www.standard.co.uk. Archived from the original on 23 March 2021. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- ^ M62 junctions 18–29 route-based strategy (PDF) (Report). Highways England. March 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 22 December 2015. Retrieved 21 December 2015.
- ^ "M62 Junctions 24 to 27". In Depth: Traffic Congestion. 2003. Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 30 May 2007.
- ^ "Road traffic data tables". Road Statistics 2006: Traffic, Speeds and Congestion. Department for Transport. 26 July 2007. Archived from the original (Microsoft Excel spreadsheet) on 8 February 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2007.
- ^ Mode Shift Benefit Values: Technical Report (PDF). Department for Transport. April 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 10 February 2022.
- ^ "The north of England: the great divide". The Economist. Vol. 404, no. 8802. 15–21 September 2012. Archived from the original on 26 September 2017. Retrieved 6 February 2022.
- ^ "Transport spend per head is £2,700 for London but £5 per head in North East". IPPR North. 19 December 2011. Archived from the original on 9 March 2014. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ "Northern prosperity is national prosperity: A strategy for revitalising the UK economy". IPPR North, NEFC. 29 November 2012. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ Cordon, Gavin (18 September 2021). "Michael Gove heads rebranded 'Department for Levelling Up'". Evening Standard. London. Archived from the original on 15 October 2021. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
- ^ "Transport Committee: To hit its own decarbonisation deadline, Government must set out clear strategy for rail network – Committees – UK Parliament". committees.parliament.uk. Archived from the original on 23 March 2021. Retrieved 23 March 2021.
- ^ "Autumn Statement". UK Government national archives. 2011. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 April 2014. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ Northern Powerhouse Rail, Transport for the North, 202, archived from the original on 16 February 2022, retrieved 4 February 2022
- ^ "New report: Closer running and post-Brexit investment to transform the capacity of Britain's railways: News from Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMECHE)". www.pandct.com. Archived from the original on 5 August 2020. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ "HS2 suffers setback as legislation delayed by 12 months". www.railtechnologymagazine.com. Archived from the original on 15 April 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2022.
- ^ "HS2: North West and Yorkshire Routes Confirmed". BBC News. 15 November 2016. Archived from the original on 30 September 2018. Retrieved 15 November 2016.
- ^ "High Speed Two From Concept to Reality July 2017" (PDF). GOV.UK. Department for Transport. Archived (PDF) from the original on 1 December 2017. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ Smale, Katherine (28 June 2019). "HS2 fights for its future". Archived from the original on 30 June 2019. Retrieved 12 September 2020.
- ^ "Northern Powerhouse Rail". Transport for the North. Archived from the original on 4 April 2019. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "Northern Futures: improvements for northern road and rail". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 26 July 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Miles, Tony (September 2013). "North West Wiring". Modern Railways. No. 780. pp. 52–59.
- ^ Lomas, Hannah (7 June 2016). "Electrification. North of England programme" (PDF). Travelwatch-northwest. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 June 2021. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ^ "Rail Electrification briefing paper" (PDF). UK Government. 27 July 2017. p. 12. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 March 2017. Retrieved 3 January 2022.
- ^ "Easter rail upgrade is start of transformation of trans-Pennine route". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Two bridges in Tameside to be rebuilt as North West Electrification Programme continues". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 26 August 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Manchester to Stalybridge electrification one step closer as Ashton-under-Lyne bridge rebuild completes over three weeks early". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 7 December 2015. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Cox, Charlotte (12 January 2016). "Victoria Station to be closed every Sunday until mid-April for Ordsall Chord engineering works". Manchester Evening News. Archived from the original on 14 September 2016. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ jsimpo1990 (14 March 2017). "JVs win huge TransPennine rail upgrade deals". Construction News. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "West Yorkshire Transport update 2019" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Kirklees Council Rail updates" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Grayling: progress on Transpennine route upgrade and Crossrail 2 to advance in lockstep". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Huddersfield to Westtown (Dewsbury)". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Abbott 2023, p. 56.
- ^ "Compound on Queens Road, Miles Platting, Manchester". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Manchester to Stalybridge". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Work underway to deliver Trans-Pennine Route Upgrade". Rail Technology Magazine. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
- ^ "TransPennine £2.9bn rail upgrade will cause 'major disruption'". BBC News. 13 September 2018. Archived from the original on 4 November 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Manchester to Huddersfield passengers urged to plan Sunday journeys as railway upgrades continue". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "TWAO Huddersfield to Westtown document NR05" (PDF). March 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 May 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ "Manchester to Stalybridge". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 12 March 2021.
- ^ "Passengers to be kept on the move during major railway improvement works around Manchester". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 15 June 2021.
- ^ "Major 16-day railway overhaul completed in Manchester as part of the Transpennine Route Upgrade". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "Huddersfield to Westtown (Dewsbury)". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 7 October 2021.
- ^ "Government announces £317m in Transpennine Route Upgrade investment". Rail Technology Magazine. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ "£401 million investment into upgrades to deliver brighter rail future". GOV.UK. Archived from the original on 25 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ "TransPennine Upgrade moves forward with further funding | Railnews | Today's news for Tomorrow's railway". www.railnews.co.uk. Archived from the original on 26 May 2021. Retrieved 26 May 2021.
- ^ "York to Church Fenton Improvement Scheme". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ "Network Rail Piling notification York to Church Fenton".
- ^ "York to Church Fenton February 2021 update" (PDF). Network Rail. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 February 2021.
- ^ "York to Church Fenton improvement scheme project tracker" (PDF). Network Rail. May 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 28 May 2021.
- ^ "York to Church Fenton September 2021 Project Tracker" (PDF). Network Rail. August 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 August 2021. Retrieved 31 August 2021.
- ^ "£317M Pumped into crucial TransPennine route – NPH". Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 5 June 2021.
- ^ "Electrification works not funded, despite DfT pledge – The Transport Network". www.transport-network.co.uk. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ^ "York to Church Fenton Improvement Scheme". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 3 February 2021. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "Transpennine Upgrade Permanent Way Institution Lecture". Youtube and PWI. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021.
- ^ "Network Rail Overview upgrade map Huddersfield to Leeds". Archived from the original on 4 February 2021. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Network Rail planning £3.1bn TransPennine upgrade in CP6 – The Transport Network". www.transport-network.co.uk. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ^ "Detailed TransPennine £2.9bn rail upgrade plans unveiled". BBC News. 20 August 2019. Archived from the original on 14 October 2020. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "My vision for fully-electrified Transpennine rail will cost more than £2.9bn budget set by Chris Grayling, says Grant Shapps". www.yorkshirepost.co.uk. Archived from the original on 24 December 2020. Retrieved 22 February 2021.
- ^ "Restoring Standedge Tunnel – Huddersfield Narrow Canal". archive.is. 23 December 2013. Archived from the original on 23 December 2013. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Historic England. "Crawshaw Woods (Shippen House Farm) bridge, HUL4/20, Non Civil Parish (1419062)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Historic England. "Aberford Road Bridge, HUL4/18, Non Civil Parish (1419088)". National Heritage List for England. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ FIRSE, Paul Darlington CEng FIET (10 July 2023). "Transpennine Upgrade: still stepping ahead". Rail Engineer. Retrieved 11 July 2023.
- ^ "Huddersfield to Westtown (Dewsbury) improvements: Transport and Works Act Order" (PDF). UK Government Department of Transport.
- ^ "TransPennine Route Upgrade | Leaders Debate". Rail Technology Magazine. Retrieved 30 November 2022.
- ^ Ames, Chris (3 October 2022). "Truss makes Northern Powerhouse Rail U-turn". Transport Network. Hemming Media.
- ^ Artymiuk, Simon (4 November 2022). "British government changes course again on Northern Powerhouse Rail". International Railway Journal.
- ^ "The Northern Agenda Newsletter". The Northern Agenda. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ a b Abbott 2023, pp. 56–57.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade reveals plans to slash carbon emissions, generate thousands of jobs and deliver billions of pounds in social value in the North of England". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "On track to a better, more sustainable future" (PDF). Network Rail. 16 May 2023.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade reveals strategy for delivering on its sustainability and social value targets". Rail Technology Magazine. Retrieved 17 May 2023.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade reaches major regulatory milestone". Global Railway Review. Archived from the original on 2 April 2021. Retrieved 2 April 2021.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade – East of Leeds – Diversionary Routes [VEAT]". bidstats.uk. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2021.
- ^ "Transport Works Act Order application Huddersfield to Dewsbury document NR05" (PDF). Network Rail. April 2021. Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 May 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ Haigh, Philip (21 April 2021). "Trans-Pennine Route Upgrade takes shape". Rail Magazine. No. 929. p. 12.
- ^ "Trans-Pennine Route Upgrade takes shape", Modern Railways, 20 May 2021, archived from the original on 27 December 2021, retrieved 27 December 2021
- ^ Haigh, Philip (16 November 2022). "Trans-Pennine...transformative". Rail Magazine. No. 929. pp. 37–43.
- ^ "GRIP (Governance for Railway Investment Projects) process explained | Rail Engineer". Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ Abbott 2023, p. 60.
- ^ "MP visits site that will power the north's railway revolution". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 8 February 2021. Retrieved 4 February 2021.
- ^ Haigh, Philip (21 April 2021). "NR submits detailed plan for TransPennine Upgrade". Rail Magazine. No. 929. p. 13.
- ^ Sonagra, Radhika (1 August 2024). "Yorkshire day: The Transpennine Route Upgrade in numbers". Network Rail. Retrieved 1 August 2024.
- ^ "Manchester to Stalybridge". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "twitter – thegnrp/status/1500399284818255873". Twitter. Archived from the original on 7 March 2022. Retrieved 7 March 2022.
- ^ "Manchester rail upgrades continue for the multi-billion-pound Transpennine Route Upgrade". Network Rail Media Centre. Archived from the original on 22 February 2022. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ Smith, Roger (1 May 2022). "Watch: Bridges raised in Manchester as part of Transpennine Route Upgrade". RailAdvent. Archived from the original on 1 May 2022. Retrieved 2 May 2022.
- ^ Lavigueur, Nick (13 October 2020). "Huddersfield rail widening scheme will see 12 bridges demolished". YorkshireLive. Archived from the original on 25 June 2021. Retrieved 13 May 2021.
- ^ "A bridge to the future in Huddersfield". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 17 August 2022.
- ^ "Lady Anne level crossing". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 10 February 2021. Retrieved 10 February 2021.
- ^ "Rose Lane Level Crossing". Transpennine Route Upgrade. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 17 May 2022.
- ^ "Rose Lane Level Crossing". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 6 July 2021.
- ^ "Copmanthorpe Level Crossing". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "Barrowby Lane and Barrowby Foot level crossings". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "Proposed Rose Lance crossing order" (PDF). UK Government. 25 February 2022. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 May 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ Ross, Perri. "Church Fenton Level Crossing Reduction". Network Rail. Retrieved 28 July 2022.
- ^ "Leeds to Micklefield Upgrades". Network Rail. Retrieved 14 March 2023.
- ^ "Huddersfield to Westtown (Dewsbury)". Network Rail. Archived from the original on 1 February 2021. Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ Earnshaw, Tony (25 February 2022). "Huddersfield train station to close for months as revamp starts". YorkshireLive. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ "Strategic Planning Committee Kirklees Council" (PDF). Kirklees.gov. 24 February 2022. pp. 77–78. Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 February 2022. Retrieved 25 February 2022.
- ^ "Major 16-day railway overhaul completed in Manchester as part of the Transpennine Route Upgrade". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 16 August 2021.
- ^ "Revolutionary rail improvements in West Yorkshire given green light". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 30 June 2022.
- ^ "House of Commons Transpennine Route Upgrade funding". UK government.
- ^ "Transport update: Transpennine route upgrade". GOV.UK. Retrieved 20 July 2022.
- ^ "First wires installed to power faster, greener trains in Greater Manchester". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 9 November 2022.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade announces Managing Director ahead of pivotal year". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ^ "26 days of Stalybridge station upgrades to support the Transpennine Route Upgrade". Rail Technology Magazine. Retrieved 25 January 2023.
- ^ "Nine days of major upgrades in Morley – passengers should plan ahead". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ^ "26 days of major rail upgrades in Stalybridge – passengers urged to check before they travel". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 26 January 2023.
- ^ Abbott 2023, p. 61.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade thanks passengers after Morley station upgrade". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 13 February 2023.
- ^ "New Station for Morley". Modern Railways. No. 894. March 2023. p. 22.
- ^ "Rail Technology Magazine February / March 2023 Page 74". mag.railtechnologymagazine.com. Retrieved 7 March 2023.
- ^ "Stalybridge station reopens as Network Rail prepares for £88M Easter engineering programme". New Civil Engineer. 6 April 2023. Retrieved 6 April 2023.
- ^ "Transpennine Route Upgrade completes latest phase of work at Morley". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 26 June 2023.
- ^ "Leeds to Micklefield scheme: Transport and Works Act order". GOV.UK. 18 July 2023. Retrieved 18 July 2023.
- ^ "Leeds to Micklefield Upgrades". Network Rail. Retrieved 18 July 2023.
- ^ "Service announcement: £3.9 billion boost for more reliable train journeys in the North". GOV.UK. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ "Jake Berry on LinkedIn: #collaboration #ole #quality #construction #electrification". www.linkedin.com. Retrieved 13 March 2024.
- ^ "First electric train completes test run between Manchester and Stalybridge". Network Rail Media Centre. Retrieved 18 March 2024.
- ^ "Proposed Transport and Works Act Order for the Stalybridge to the eastern portal of Standedge Tunnel" (PDF). Gov.UK. 22 March 2024.
- ^ Broadbent, David; Wooddisse, Andrew (June 2024). "Transpennine Route Upgrade – East Infrastructure Challenges". Retrieved 11 June 2024.
- ^ "10-day closure of Huddersfield Railway Station completed". Huddersfield Hub. 9 April 2024. Retrieved 9 April 2024.
- ^ Broadbent & Wooddisse 2024.
- ^ "The Transpennine Route Upgrade (TRU) on LinkedIn: #transpenninerouteupgrade #tru #ontracktobetter". www.linkedin.com. Retrieved 10 July 2024.
- ^ "Network Rail appoints BAM to deliver the next phase of the Transpennine Route Upgrade". ukandireland.bam.com. 12 September 2024. Retrieved 12 September 2024.
- ^ "Major contract win on next phase of the Transpennine Route Upgrade". Amey. Retrieved 13 September 2024.
- ^ "TRANSPORT AND WORKS ACT 1992: APPLICATION FOR THE PROPOSED NETWORK RAIL (LEEDS TO MICKLEFIELD ENHANCEMENTS) ORDER AND DEEMED PLANNING PERMISSION" (PDF). UK Government. 1 October 2024.
- ^ "Government reaffirms commitment to TRU". Transpennine Route Upgrade. Retrieved 19 November 2024.
- ^ "State of Play for the North" (PDF). September 2024.
Further reading
[edit]- Keenor, Garry. Overhead Line Electrification for Railways 6th edition. also available as a free PDF download at www.ocs4rail.com
- "Network Rail A Guide to Overhead Electrification Revision 10" (PDF). Network Rail. February 2015.
- "On board with electrification". Permanent Way Institution Journal. 139 (1). January 2021. ISSN 2057-2425 – via PWI.
- Boocock, Colin (1991). East Coast Electrification. Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-1979-7.
- Nock, O.S. (1965). Britain's new railway: Electrification of the London-Midland main lines from Euston to Birmingham, Stoke-on-Trent, Crewe, Liverpool and Manchester. London: Ian Allan. OCLC 59003738.
- Nock, O.S. (1974). Electric Euston to Glasgow. Ian Allan. ISBN 978-0711005303.
- Semmens, P.W.B. (March 1991). Electrifying the East Coast Route: Making of Britain's First 140m.p.h. Railway. Patrick Stephens Ltd. ISBN 978-0850599299.
