Gaboxadol
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | THIP; OV101; OV-101 |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.059.039 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
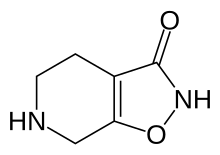
| Formula | C6H8N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 140.142 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Gaboxadol, also known as 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo(5,4-c)pyridin-3-ol (THIP), is a conformationally constrained derivative of the alkaloid muscimol that was first synthesized in 1977 by the Danish chemist Poul Krogsgaard-Larsen.[1] In the early 1980s gaboxadol was the subject of a series of pilot studies that tested its efficacy as an analgesic and anxiolytic, as well as a treatment for tardive dyskinesia, Huntington's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and spasticity.[1] It was not until 1996 that researchers attempted to harness gaboxadol's frequently reported sedative "adverse effect" for the treatment of insomnia, resulting in a series of clinical trials sponsored by Lundbeck and Merck.[1][2] In March, 2007, Merck and Lundbeck cancelled work on the drug, citing safety concerns and the failure of an efficacy trial. It acts on the GABA system, but in a different way from benzodiazepines, Z-Drugs, and barbiturates. Lundbeck states that gaboxadol also increases deep sleep (stage 4). Unlike benzodiazepines, gaboxadol does not demonstrate reinforcement in mice or baboons despite activation of dopaminergic neurons in the ventral tegmental area.[3]
In 2015, Lundbeck sold its rights to the molecule to Ovid Therapeutics, whose plan is to develop it for FXS and Angelman syndrome.[4] It is known internally in Ovid as OV101.
Pharmacology
[edit]Gaboxadol is a supra-maximal agonist at α4β3δ, low-potency agonist at α1β3γ2, partial agonist at α4β3γ, and antagonist at ρ1 GABAA receptors.[5][6][7] Its affinity for extrasynaptic α4β3δ GABAA receptors is 10-fold greater than other subtypes.[8] Gaboxadol has a unique affinity for extrasynaptic α4β3δ GABAA receptors, which mediate tonic inhibition and are typically activated by ambient, low levels of GABA in the extrasynaptic space.[9]
Compared to muscimol, gaboxadol binds less potently to α4β3δ GABAA receptors (EC50 .2μM vs 13μM), but is capable of evoking a greater maximum response (Emax 120% vs 224%).[7] The supra-maximial efficacy of gabaxadol at α4β3δ GABAA receptors has been attributed to an increase in the duration and frequency of channel openings relative to the endogenous agonist GABA.[7]
Clinical studies
[edit]Gaboxadol produced effects in clinical studies including sedation, euphoria, and dissociation or perceptual changes.[10][11] It showed less euphoria and misuse potential, more negative and dissociative effects, and fewer sedative effects than zolpidem at the assessed doses.[11]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Morris H (August 2013). "Gaboxadol". Harper's Magazine. Retrieved 2014-11-20.
- ^ US 4278676, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, "Heterocyclic compounds", issued 14 July 1981, assigned to H Lundbeck AS
- ^ Vashchinkina E, Panhelainen A, Vekovischeva OY, Aitta-aho T, Ebert B, Ator NA, et al. (April 2012). "GABA site agonist gaboxadol induces addiction-predicting persistent changes in ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons but is not rewarding in mice or baboons". The Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (15): 5310–20. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4697-11.2012. PMC 6622081. PMID 22496576.
- ^ Tirrell M (16 April 2015). "Former Teva CEO's new gig at Ovid Therapeutics". CNBC. Retrieved 2015-05-06.
- ^ Brown N, Kerby J, Bonnert TP, Whiting PJ, Wafford KA (August 2002). "Pharmacological characterization of a novel cell line expressing human alpha(4)beta(3)delta GABA(A) receptors". British Journal of Pharmacology. 136 (7): 965–974. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704795. PMC 1573424. PMID 12145096.
- ^ Orser BA (2006-04-15). "Extrasynaptic GABAA Receptors Are Critical Targets for Sedative-Hypnotic Drugs". Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine. 02 (2). doi:10.5664/jcsm.26526. ISSN 1550-9389.
- ^ a b c Johnston GA (October 2014). "Muscimol as an ionotropic GABA receptor agonist". Neurochemical Research. 39 (10): 1942–1947. doi:10.1007/s11064-014-1245-y. PMID 24473816.
- ^ Rudolph U, Knoflach F (July 2011). "Beyond classical benzodiazepines: novel therapeutic potential of GABAA receptor subtypes". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 10 (9): 685–697. doi:10.1038/nrd3502. PMC 3375401. PMID 21799515.
- ^ Mortensen M, Ebert B, Wafford K, Smart TG (April 2010). "Distinct activities of GABA agonists at synaptic- and extrasynaptic-type GABAA receptors". The Journal of Physiology. 588 (Pt 8): 1251–1268. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2009.182444. PMC 2872731. PMID 20176630.
- ^ Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Frølund B, Liljefors T (2006). "GABA(A) agonists and partial agonists: THIP (Gaboxadol) as a non-opioid analgesic and a novel type of hypnotic". Adv Pharmacol. 54: 53–71. doi:10.1016/s1054-3589(06)54003-7. PMID 17175810.
In cancer patients and also in patients with chronic anxiety (Hoehn‐Saric, 1983) the desired effects of Gaboxadol were accompanied by side effects, notably sedation, nausea, and in a few cases euphoria. The side effects of Gaboxadol have, however, been described as mild and similar in quality to those of other GABA‐mimetics (Hoehn‐Saric, 1983). This combination of analgesic and anxiolytic effects of THIP obviously has therapeutic prospects.
- ^ a b Schoedel KA, Rosen LB, Alexander R, Wang J, Snavely D, Murphy MG, et al. (16 January 2009). "Poster Session I (PI 1-89): PI-44: A single-dose randomized, double-blind, crossover abuse liability study to evaluate the subjective and objective effects of gaboxadol and zolpidem in recreational drug users". Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics. 85 (S1 [Supplement: Abstracts of the 2009 Annual Meeting of the American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. National Harbor, Maryland, USA. March 18‐21, 2009]): S9–S36 (S22–S22). doi:10.1038/sj.clpt.2008.283. ISSN 0009-9236.
External links
[edit]- 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo(5,4-c)pyridin-3-ol at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- H. Lundbeck Website
- Medical News Today article
- Report of cancellation of development.
- Gaboxadol
