Quadrigula
Appearance
| Quadrigula | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Clade: | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Sphaeropleales |
| Family: | Selenastraceae |
| Genus: | Quadrigula Printz |
| Type species | |
| Quadrigula closterioides (Bohlin) Printz[1]
| |
| Species | |
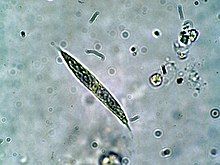
Quadrigula is a genus of green algae in the family Selenastraceae.[2] It is commonly found in freshwater habitats as phytoplankton.[3]
Description
[edit]Quadrigula forms colonies of two, four, or cells within a common mucilaginous envelope. Cells are cigar-shaped, 7 to 45 μm long and 1 to 8 μm wide. The cells are bundled such that the long axes of cells are parallel to each other. The tips of the cells are rounded or acutely pointed. Cells contain a single nucleus and one parietal chloroplast; the chloroplast may or may not contain a pyrenoid.[3][1]
Species identification relies on details of the cell size and shape.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Guiry, M.D.; Guiry, G.M. "Quadrigula". AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. Retrieved 2023-06-03.
- ^ See the NCBI webpage on Quadrigula. Data extracted from the "NCBI taxonomy resources". National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 2007-03-19.
- ^ a b Shubert, Elliot; Gärtner, Georg (2014). "Chapter 7. Nonmotile Coccoid and Colonial Green Algae". In Wehr, John D.; Sheath, Robert G.; Kociolek, J. Patrick (eds.). Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification (2 ed.). Elsevier Inc. ISBN 978-0-12-385876-4.
