Portal:Central America
The Central America Portal

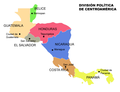
Central America is a subregion of North America. Its political boundaries are defined as bordering Mexico to the north, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the southwest. Central America is usually defined as consisting of seven countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from southern Mexico to southeastern Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes, which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage.
In the pre-Columbian era, Central America was inhabited by the Indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica to the north and west and the Isthmo-Colombian peoples to the south and east. Following the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' voyages to the Americas, Spain began to colonize the Americas. From 1609 to 1821, the majority of Central American territories (except for what would become Belize and Panama, and including the modern Mexican state of Chiapas) were governed by the viceroyalty of New Spain from Mexico City as the Captaincy General of Guatemala. On 24 August 1821, Spanish Viceroy Juan de O'Donojú signed the Treaty of Córdoba, which established New Spain's independence from Spain. On 15 September 1821, the Act of Independence of Central America was enacted to announce Central America's separation from the Spanish Empire and provide for the establishment of a new Central American state. Some of New Spain's provinces in the Central American region (i.e. what would become Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua and Costa Rica) were annexed to the First Mexican Empire; however in 1823 they seceded from Mexico to form the Federal Republic of Central America until 1838. (Full article...)
Selected article
The final offensive of 1981 (Spanish: ofensiva final de 1981), also known as the general offensive of 1981 (Spanish: ofensiva general de 1981), was the unsuccessful first military offensive conducted by the Farabundo Martí National Liberation Front (FMLN) during the Salvadoran Civil War. The objective of the offensive was to initiate a popular revolution to overthrow the Revolutionary Government Junta (JRG), which had been ruling the country since the 1979 Salvadoran coup d'état. The FMLN hoped that the government would be overthrown by 20 January 1981; the date Ronald Reagan was to be inaugurated as president of the United States.
During the first phase of the offensive from 10 to 17 January, the FMLN carried out attacks across northern and western El Salvador, incited a general strike across the nation, a military mutiny in the second largest city, Santa Ana, and secured several important cities and villages. During the second phase from 18 to 26 January, the FMLN began, what they termed, a "temporary tactical retreat" as government forces began to recapture previously lost territory. The offensive ended in a military defeat for the FMLN, but it solidified the group as an effective fighting force. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that Alfredo Frohlich formed an award-winning collection of Panamanian postal history that included items from as early as 1777?
- ... that the government of El Salvador, the Catholic Church, and street gangs negotiated a truce to reduce homicides from 2012 to 2014?
- ... that the 7th Macho de Monte Infantry Company of the Panama Defense Forces was named after a tapir?
- ... that the Nicaraguan nun Dorotea Wilson joined a guerrilla group, renounced her vows, and became a women's rights activist and politician?
- ... that footballer Alexandra Pinell scored the Costa Rica U20 team's only goal at the FIFA tournament hosted by their country?
- ... that Panama cross-banded tree frog males synchronize their mating calls to confuse predators that locate them by sound?
- ... that Swedish naval officer Axel Lagerbielke was imprisoned in Lima for over a year, held in Callao and eventually escaped from Panama on an English packet boat to Jamaica?
- ... that composer Gonzalo Brenes was a politician in the National Assembly of Panama and served for seven years as Panama's secretary of culture?
Related portals
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Central America-related articles, see WikiProject Central America.
Need help?
Do you have a question about Central America that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
General images
In the news
- 20 January 2025 – Second presidency of Donald Trump
- Anti-Trump protests are held in cities across the United States, as well as in other countries, such as Mexico, Panama, and the United Kingdom. (The Guardian)
- 7 January 2025 – Denmark–United States relations, Proposals for the United States to purchase Greenland, Panama–United States relations
- U.S. president-elect Donald Trump refuses to rule out using military force to take control of Greenland and the Panama Canal, declaring U.S. control of both to be "vital to American national security". (AP)
- Trump's son Donald Trump Jr. makes a personal visit to Greenland weeks after Trump announced that "ownership and control of Greenland is an absolute necessity". In response to the visit, Danish prime minister Mette Frederiksen states that "Greenland belongs to the Greenlanders". (BBC News)
- Panamanian foreign minister Javier Martínez-Acha asserts that only Panamanians operate the Panama Canal and that its sovereignty is non-negotiable, dismissing Trump's claims that China operates the canal and his suggestion of potential U.S. military action to regain control. (DW)
- 6 January 2025 –
- Davivienda, of Colombia, and Scotiabank, of Canada, announced a merger where Davivienda absorbs Scotiabank operations in Colombia, Costa Rica and Panama, and, in turn, Scotiabank acquires 20% of the stakes in Davivienda. (Scotiabank)
- 4 January 2025 – Haitian crisis, Guatemala–Haiti relations
- Gang war in Haiti
Subcategories
Topics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus





































![Image 39Mesoamerica and Central America in the 16th century before Spanish arrival [according to whom?] (from Mesoamerica)](/uploads/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/06/Mesoam%C3%A9rica_y_Centroamerica_prehispanica_siglo_XVI.svg/120px-Mesoam%C3%A9rica_y_Centroamerica_prehispanica_siglo_XVI.svg.png?auto=webp)