List of sovereign states and dependent territories in Europe
The list below includes all entities falling even partially under any of the various common definitions of Europe, geographical or political. Fifty generally recognised sovereign states, Kosovo with limited, but substantial, international recognition, and four largely unrecognised de facto states with limited to no recognition have territory in Europe and/or membership in international European organisations. There are eight entities that are not integral parts of a European state or have special political arrangements.
Boundary of Europe
[edit]Geographical
[edit]Under the commonly used geographic definition, the boundary between the continents of Asia and Europe stretches along the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, and the Caspian Sea in the east, the Greater Caucasus range,[1] and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and the Dardanelles, in the south.[2][3] Based on such a commonly used division of the continents, the transcontinental countries of Azerbaijan, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Turkey have territory in both Asia and Europe.
The island of Cyprus in Western Asia is close to Anatolia (or Asia Minor) but is often considered to be a part of Europe and is a member of the European Union. Like Cyprus, Armenia is also entirely in Western Asia but is a member of several European organisations.[4]
Although the Mediterranean Sea provides a clearer divide between Africa and Europe, some traditionally European islands such as Malta, Pantelleria, the Pelagie Islands, and Sicily are actually located on the African Plate.[5] The island of Iceland is part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, straddling the Eurasian Plate and the North American Plate.[6]
Some territories which are geographically outside of Europe have strong connections with European states. Greenland, for example, has socio-political connections with Europe and is part of the Kingdom of Denmark but is located closer to the continent of North America and is usually grouped with that continent.[7]
Other territories are part of European countries but are geographically located on other continents, such as the French overseas regions,[8] the Spanish autonomous cities of Ceuta and Melilla on the coast of Africa,[9] and the Dutch BES islands of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius, and Saba in the Caribbean.[10]
Political
[edit]The political boundaries of Europe vary with the definition of Europe that is used by different political organizations. For instance, the Council of Europe and the European Court of Human Rights include 46 countries in their definition of Europe. The European Higher Education Area includes 48 countries, and the European Cultural Convention and the European Olympic Committees include 50 countries in their definitions.
Sovereign states
[edit]
A sovereign state is a political association with effective sovereignty over a population for whom it makes decisions in the national interest.[11] According to the Montevideo Convention, a state must have a permanent population, a defined territory, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other states.[12]
UN member states and UNGA non-member observer state
[edit]There are 50 sovereign states with territory located within the common definition of Europe and/or membership in international European organisations that are almost universally recognized internationally. All are either member states of the United Nations or non-member observer states at the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA),[13] and all except Belarus, Kazakhstan, Russia, and Vatican City are members of the Council of Europe.[14] 44 countries have their capital city located within Europe, and (as of 2022) 27 of those countries are member states of the European Union, which means that they are highly integrated with one another and share their sovereignty through EU institutions.
Each entry in the list below has a map of its location in Europe. Territory in Europe is shown in dark-green; territory not geographically in Europe is shown in a lighter shade of green. The lightest shade of green represents other states in the EU and is shown on the maps of all territories within the EU.
| * | = Member of the EU[15] |
| Flag | Map | English short, formal names, and ISO [16][17][18][19] |
Domestic short and formal name(s) [16][17][18] |
Capital [19][20][21] |
Population 2021 [22][23] |
Area [a][24] |
Currency [19] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
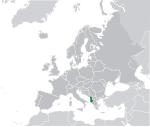 |
Albania[b] Republic of Albania ALB |
Albanian: Shqipëri / Shqipëria – Republika e Shqipërisë | Tirana Albanian: Tiranë |
2,854,710 | 28,748 km2 (11,100 sq mi) | Albanian lek |
 |
 |
Andorra Principality of Andorra AND |
Catalan: Andorra – Principat d'Andorra | Andorra la Vella Catalan: Andorra la Vella |
79,034 | 468 km2 (181 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
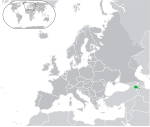 |
Armenia[c] Republic of Armenia ARM |
Armenian: Հայաստան – Հայաստանի Հանրապետություն (Hayastan – Hayastani Hanrapetut'yun) | Yerevan Armenian: Երևան (Yerevan) |
2,790,974 | 29,743 km2 (11,484 sq mi) | Armenian dram |
 |
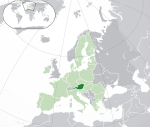 |
Austria* Republic of Austria AUT |
German: Österreich – Republik Österreich | Vienna German: Wien |
8,922,082 | 83,871 km2 (32,383 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
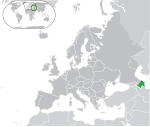 |
Azerbaijan[c] Republic of Azerbaijan AZE |
Azerbaijani: Azǝrbaycan – Azǝrbaycan Respublikası | Baku Azerbaijani: Bakı |
10,312,992 | 86,600 km2 (33,436 sq mi) | Azerbaijani manat |
 |
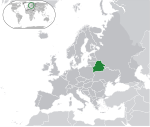 |
Belarus Republic of Belarus BLR |
Belarusian: Беларусь – Рэспубліка Беларусь (Bielaruś – Respublika Bielaruś) Russian: Беларусь – Республика Беларусь (Belarus' — Respublika Belarus') |
Minsk Belarusian: Мінск (Minsk) Russian: Минск (Minsk) |
9,578,167 | 207,600 km2 (80,155 sq mi) | Belarusian rouble |
 |
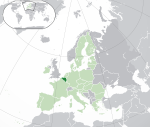 |
Belgium* Kingdom of Belgium BEL |
Dutch: België – Koninkrijk België French: Belgique – Royaume de Belgique German: Belgien – Königreich Belgien |
Brussels Dutch: Brussel French: Bruxelles German: Brüssel |
11,611,419 | 30,528 km2 (11,787 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
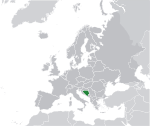 |
Bosnia and Herzegovina BIH |
Bosnian: Bosna i Hercegovina Croatian: Bosna i Hercegovina Serbian: Босна и Херцеговина |
Sarajevo Bosnian: Sarajevo Croatian: Sarajevo Serbian: Сарајево |
3,270,943 | 51,197 km2 (19,767 sq mi) | Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark |
 |
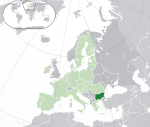 |
Bulgaria* Republic of Bulgaria BGR |
Bulgarian: България – Република България (Bulgaria – Republika Bulgaria) | Sofia Bulgarian: София (Sofia) |
6,885,868 | 110,879 km2 (42,811 sq mi) | Bulgarian lev |
 |
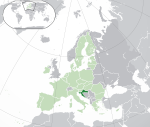 |
Croatia* Republic of Croatia HRV |
Croatian: Hrvatska – Republika Hrvatska | Zagreb Croatian: Zagreb |
4,060,135 | 56,594 km2 (21,851 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
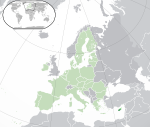 |
Cyprus*[d] Republic of Cyprus CYP |
Greek: Κύπρος – Κυπριακή Δημοκρατία (Kýpros – Kypriakí Dimokratía) Turkish: Kıbrıs – Kıbrıs Cumhuriyeti |
Nicosia Greek: Λευκωσία (Lefkosía) Turkish: Lefkoşa |
1,244,188 | 9,251 km2 (3,572 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
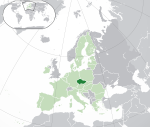 |
Czechia*[e] Czech Republic CZE |
Czech: Česko – Česká republika | Prague Czech: Praha |
10,510,751 | 78,867 km2 (30,451 sq mi) | Czech koruna |
 |
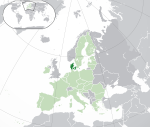 |
Denmark*[f] Kingdom of Denmark DNK |
Danish: Danmark – Kongeriget Danmark | Copenhagen Danish: København |
5,854,240 | 42,933 km2 (16,577 sq mi) | Danish krone |
 |
 |
Estonia* Republic of Estonia EST |
Estonian: Eesti – Eesti Vabariik | Tallinn Estonian: Tallinn |
1,328,701 | 45,228 km2 (17,463 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
Finland* Republic of Finland FIN |
Finnish: Suomi – Suomen tasavalta Swedish: Finland – Republiken Finland |
Helsinki Finnish: Helsinki Swedish: Helsingfors |
5,535,992 | 338,145 km2 (130,559 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
France* French Republic FRA |
French: France – République française | Paris French: Paris |
64,531,444 | 643,427 km2 (248,429 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
Georgia[c] GEO |
Georgian: საქართველო (Sakartvelo) | Tbilisi / T'bilisi Georgian: თბილისი (T'bilisi) |
3,757,980 | 69,700 km2 (26,911 sq mi) | Georgian lari |
 |
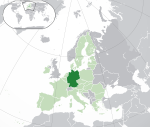 |
Germany* Federal Republic of Germany DEU |
German: Deutschland – Bundesrepublik Deutschland | Berlin German: Berlin |
83,408,554 | 357,022 km2 (137,847 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
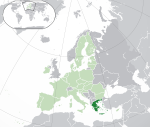 |
Greece* Hellenic Republic GRC |
Greek: Ελλάδα – Ελληνική Δημοκρατία (Elláda – Ellinikí Dimokratía) | Athens Greek: Αθήνα (Athína) |
10,445,365 | 131,957 km2 (50,949 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
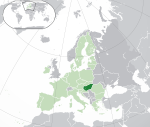 |
Hungary* HUN |
Hungarian: Magyarország | Budapest Hungarian: Budapest |
9,709,786 | 93,028 km2 (35,918 sq mi) | Hungarian forint |
 |
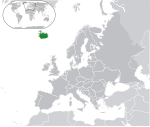 |
Iceland ISL |
Icelandic: Ísland – Lýðveldið Ísland | Reykjavík Icelandic: Reykjavík |
370,335 | 103,000 km2 (39,769 sq mi) | Icelandic króna |
 |
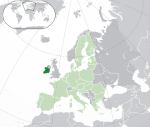 |
Ireland*[25][g] IRL |
English: Ireland Irish: Éire |
Dublin Irish: Baile Átha Cliath |
4,986,526 | 70,273 km2 (27,133 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
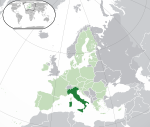 |
Italy* Italian Republic ITA |
Italian: Italia – Repubblica Italiana | Rome Italian: Roma |
59,240,329 | 301,340 km2 (116,348 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
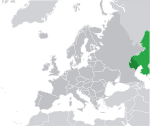 |
Kazakhstan[h] Republic of Kazakhstan KAZ |
Kazakh: Қазақстан – Қазақстан Республикасы (Qazaqstan – Qazaqstan Respūblīkasy) Russian: Казахстан – Республика Казахстан (Kazakhstan – Respublika Kazakhstan) |
Astana Kazakh: Астана (Astana) Russian: Астана (Astana) |
19,196,465 | 2,724,900 km2 (1,052,090 sq mi) | Kazakhstani tenge |
 |
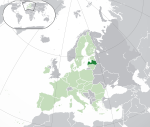 |
Latvia* Republic of Latvia LVA |
Latvian: Latvija – Latvijas Republika | Riga Latvian: Rīga |
1,873,919 | 64,589 km2 (24,938 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
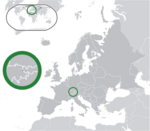 |
Liechtenstein Principality of Liechtenstein LIE |
German: Liechtenstein – Fürstentum Liechtenstein | Vaduz German: Vaduz |
39,039 | 160 km2 (62 sq mi) | Liechtenstein franc |
 |
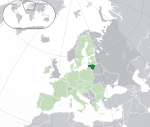 |
Lithuania* Republic of Lithuania LTU |
Lithuanian: Lietuva – Lietuvos Respublika | Vilnius Lithuanian: Vilnius |
2,786,651 | 65,300 km2 (25,212 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
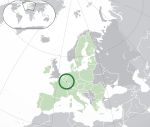 |
Luxembourg* Grand Duchy of Luxembourg LUX |
German: Luxemburg – Großherzogtum Luxemburg French: Luxembourg – Grand-Duché de Luxembourg Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg - Groussherzogtum Lëtzebuerg |
Luxembourg German: Luxemburg French: Luxembourg Luxembourgish: Lëtzebuerg |
639,321 | 2,586 km2 (998 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
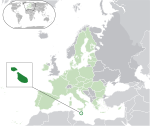 |
Malta* Republic of Malta MLT |
English: Malta – Republic of Malta Maltese: Malta – Repubblika ta' Malta |
Valletta Maltese: Valletta |
526,748 | 316 km2 (122 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
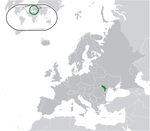 |
Moldova[b] Republic of Moldova MDA |
Romanian: Moldova – Republica Moldova | Chișinău Romanian: Chișinău |
3,061,506 | 33,851 km2 (13,070 sq mi) | Moldovan leu |
 |
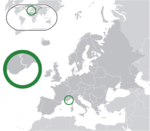 |
Monaco Principality of Monaco MCO |
French: Monaco – Principauté de Monaco | Monaco French: Monaco |
36,686 | 2 km2 (0.8 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
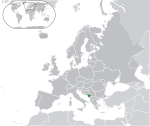 |
Montenegro[b] MNE |
Montenegrin: Црна Гора (Crna Gora) | Podgorica Montenegrin: Подгорица (Podgorica) |
627,859 | 13,812 km2 (5,333 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
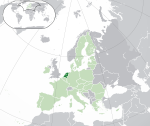 |
Netherlands*[f][i][10] Kingdom of the Netherlands NLD |
Dutch: Nederland – Koninkrijk der Nederlanden | Amsterdam (capital) Dutch: Amsterdam The Hague (seat of government) Dutch: 's-Gravenhage / Den Haag |
17,501,696 | 41,543 km2 (16,040 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
North Macedonia[b] Republic of North Macedonia MKD |
Macedonian: Северна Македонија – Република Северна Македонија (Severna Makedonija – Republika Severna Makedonija) | Skopje Macedonian: Скопје (Skopje) |
2,103,330 | 25,713 km2 (9,928 sq mi) | Macedonian denar |
 |
 |
Norway Kingdom of Norway NOR |
Bokmål: Norge – Kongeriket Norge Nynorsk: Noreg – Kongeriket Noreg |
Oslo Norwegian: Oslo |
5,403,021 | 323,802 km2 (125,021 sq mi) | Norwegian krone |
 |
 |
Poland* Republic of Poland POL |
Polish: Polska – Rzeczpospolita Polska | Warsaw Polish: Warszawa |
38,307,726 | 312,685 km2 (120,728 sq mi) | Polish złoty |
 |
 |
Portugal* Portuguese Republic PRT |
Portuguese: Portugal – República Portuguesa | Lisbon Portuguese: Lisboa |
10,290,103 | 92,090 km2 (35,556 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
Romania* ROU |
Romanian: România | Bucharest Romanian: București |
19,328,560 | 238,391 km2 (92,043 sq mi) | Romanian leu |
 |
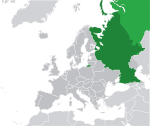 |
Russia[j] Russian Federation RUS |
Russian: Россия – Российская Федерация (Rossija – Rossijskaja Federacija) | Moscow Russian: Москва (Moskva) |
145,102,755 | 17,098,242 km2 (6,601,668 sq mi) | Russian rouble |
 |
 |
San Marino Republic of San Marino SMR |
Italian: San Marino – Repubblica di San Marino | San Marino Italian: San Marino |
33,745 | 61 km2 (24 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
Serbia[b] Republic of Serbia SRB |
Serbian: Србија – Република Србија (Srbija – Republika Srbija) | Belgrade Serbian: Београд (Beograd) |
7,296,769 | 88,361 km2 (34,116 sq mi) | Serbian dinar |
 |
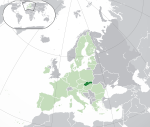 |
Slovakia* Slovak Republic SVK |
Slovak: Slovensko – Slovenská republika | Bratislava Slovak: Bratislava |
5,447,622 | 49,035 km2 (18,933 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
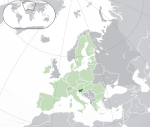 |
Slovenia* Republic of Slovenia SVN |
Slovene: Slovenija – Republika Slovenija | Ljubljana Slovene: Ljubljana |
2,119,410 | 20,273 km2 (7,827 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
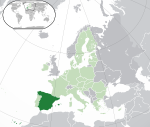 |
Spain* Kingdom of Spain ESP |
Spanish: España – Reino de España | Madrid Spanish: Madrid |
47,486,935 | 505,370 km2 (195,124 sq mi) | Euro |
 |
 |
Sweden* Kingdom of Sweden SWE |
Swedish: Sverige – Konungariket Sverige | Stockholm Swedish: Stockholm |
10,467,097 | 450,295 km2 (173,860 sq mi) | Swedish krona |
 |
 |
Switzerland Swiss Confederation CHE |
German: Schweiz – Schweizerische Eidgenossenschaft French: Suisse – Confédération suisse Italian: Svizzera – Confederazione Svizzera Romansh: Svizra – Confederaziun svizra |
Bern / Berne German: Bern French: Berne Italian and Romansh: Berna |
8,691,406 | 41,277 km2 (15,937 sq mi) | Swiss franc |
 |
 |
Turkey[h][b] Republic of Turkey TUR |
Turkish: Türkiye – Türkiye Cumhuriyeti | Ankara Turkish: Ankara |
84,775,404 | 783,562 km2 (302,535 sq mi) | Turkish lira |
 |
 |
Ukraine[b] UKR |
Ukrainian: Украïна (Ukraïna) |
Kyiv Ukrainian: Київ (Kyiv) |
43,531,422 | 603,550 km2 (233,032 sq mi) | Ukrainian hryvnia |
 |
 |
United Kingdom[k] United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland GBR |
English: United Kingdom – United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland | London | 67,281,039 | 243,610 km2 (94,058 sq mi) | Sterling |
 |
 |
Vatican City Vatican City State VAT |
Italian: Città del Vaticano – Stato della Città del Vaticano Latin: Status Civitatis Vaticanae[26] |
Vatican City Italian: Città del Vaticano |
511 | 0.49 km2 (0.19 sq mi) | Euro |
De facto states
[edit]The following five entities in Europe have partial diplomatic recognition by one or more UN member states (and therefore are defined as states by the constitutive theory of statehood) or have no diplomatic recognition by any UN member state but are defined as states by the declarative theory of statehood. None are members of the UN, Council of Europe or EU.
| Flag | Map | English common and formal names | Status | Domestic common and formal names | Capital | Population[a] | Area[a] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Abkhazia[c] Republic of Abkhazia |
Claimed as an autonomous republic of Georgia. Recognised by five UN member states.[27] | Abkhaz: Аҧсны - Аԥсны Аҳәынҭқарра (Apsny - Apsny Ahwyntqarra) Russian: Абхазия - Республика Абхазия (Abhaziya - Respublika Abkhaziya) |
Sukhumi Abkhaz: Аҟəа (Akwa) Russian: Суху́м(и) (Sukhum(i)) |
250,000[28] | 8,660 km2 (3,344 sq mi)[29] |
 |
 |
Kosovo Republic of Kosovo[16] |
Claimed by Serbia. Has been recognized as sovereign by 104 UN member states.[30] | Albanian: Kosova / Kosovë – Republika e Kosovës Serbian: Косово – Република Косово (Kosovo – Republika Kosovo) |
Pristina[20] Albanian: Prishtina, Prishtinë Serbian: Приштина (Priština) |
1,836,529[31] | 10,887 km2 (4,203 sq mi)[24] |
 |
 |
Northern Cyprus[d] Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus |
Claimed as part of the Republic of Cyprus. Recognised by Turkey.[32] | Turkish: Kuzey Kıbrıs – Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti | North Nicosia Turkish: Lefkoşa |
294,906[33] | 3,355 km2 (1,295 sq mi)[24] |
 |
 |
South Ossetia[c] Republic of South Ossetia |
Claimed as part of Georgia. Recognised by five UN member states.[27] | Ossetian: Хуссар Ирыстон – Республикӕ Хуссар Ирыстон (Khussar Iryston – Respublikæ Khussar Iryston) Russian: Южная Осетия – Республика Южная Осетия (Yuzhnaya Osetiya – Respublika Yuzhnaya Osetiya) |
Tskhinvali Ossetian: Цхинвал or Чъреба (Chreba) Russian: Цхинва́л(и) (Tskhinvál(i)) |
56,000[34] | 3,900 km2 (1,506 sq mi)[35] |
 |
 |
Transnistria / Trans-Dniester Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic |
Claimed as a territorial unit of Moldova. De facto independent state,[36] recognised by two non-UN states. | Romanian: Transnistria – Republica Moldovenească Nistreană Russian: Приднестровье – Приднестровская Молдавская Республика (Pridnestrov'ye – Pridnestrovskaya Moldavskaya Respublika) Ukrainian: Придністров'я – Придністровська Молдавська Республіка (Prydnistrovia – Pridnistrovska Moldavska Respublika) |
Tiraspol Romanian: Tiraspol Russian: Тираcполь (Tiraspol') Ukrainian: Тирасполь (Tyraspol) |
347,251[37] | 3,500 km2 (1,351 sq mi)[38] |
Non-sovereign territories
[edit]Dependent territories
[edit]The following six European entities are dependent territories.[39]
| Flag | Map | English common and formal names[16][19] | Legal status | Domestic common and formal names | Capital[20] | Population[31] | Area[24] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Akrotiri and Dhekelia[d] Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia |
British Overseas Territory | English: Akrotiri and Dhekelia – Sovereign Base Areas of Akrotiri and Dhekelia Greek: Ακρωτήρι και Δεκέλεια – Περιοχές Κυρίαρχων Βάσεων Ακρωτηρίου και Δεκέλειας (Akrotíri ke Dekélia – Periochés Kyríarchon Váseon Akrotiríou ke Dekélias) |
Episkopi Cantonment Greek: Φρουρά Επισκοπής (Frourá Episkopís) |
15,700 | 254 km2 (98 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Faroe Islands / Faeroe Islands | Constituent country of the Kingdom of Denmark | Faroese: Føroyar Danish: Færøerne |
Tórshavn Faroese: Tórshavn Danish: Thorshavn |
54,000 | 1,393 km2 (538 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Gibraltar[40] | British Overseas Territory | English: Gibraltar | Gibraltar | 29,185 | 6.5 km2 (2.5 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Guernsey[k] Bailiwick of Guernsey |
Crown Dependency in right of Guernsey[41][42][43] | English: Guernsey – Bailiwick of Guernsey French: Guernesey – Bailliage de Guernesey Guernésiais: Guernési – Bailliage de Guernési |
Saint Peter Port French: Saint Pierre Port Guernésiais: Saint Pierre Port |
65,849 | 78 km2 (30 sq mi) |
 |
 |
Isle of Man[k] | Crown Dependency in right of Man[43][44][45] | English: Isle of Man Manx: Mannin – Ellan Vannin |
Douglas Manx: Doolish |
86,866 | 572 km2 (221 sq mi) |
 |
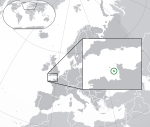 |
Jersey[k] Bailiwick of Jersey |
Crown Dependency in right of Jersey[41][42][43] | English: Jersey – Bailiwick of Jersey French: Jersey – Bailliage de Jersey Jèrriais: Jèrri – Bailliage de Jèrri |
Saint Helier French: Saint-Hélier Jèrriais: Saint Hélyi |
96,513 | 118 km2 (46 sq mi) |
Areas of special sovereignty
[edit]The following places are considered integral parts of their sovereign state, but have a political arrangement that was decided through an international agreement.
| * | = A part of the EU, although there may be some special arrangements. |
| Flag | Map | English common and formal names | Legal status | Domestic common and formal names | Capital | Population | Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Åland*[46] Åland Islands[19] |
Self-governing area of Finland, significant autonomy as the result of the Åland crisis[47] | Swedish: Åland – Landskapet Åland | Mariehamn[19] Swedish: Mariehamn |
27,500[48] | 6,787 km2 (2,620 sq mi)[48] |
 |
 |
Northern Ireland | Part of the United Kingdom, devolved government determined by the Good Friday Agreement[49] | English: Northern Ireland Irish: Tuaisceart Éireann Scots: Norlin Airlann |
Belfast[50] | 1,810,863[51] | 14,130 km2 (5,456 sq mi)[50] |
 |
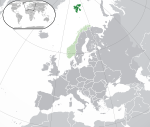 |
Svalbard[16] | Special territory of Norway, determined by the Svalbard Treaty[52] | Norwegian: Svalbard | Longyearbyen[19][20] Norwegian: Longyearbyen |
2,019[31] | 62,045 km2 (23,956 sq mi)[24] |
See also
[edit]- International organisations in Europe
- Lists of European countries:
- List of former sovereign states in Europe
- Predecessors of sovereign states in Europe
- Regions of Europe
Notes
[edit]- ^ Jump up to: a b c Area and population numbers include integral areas located outside of Europe. The area and population of states with separatist regions includes that of the separatist regions.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g EU candidate country.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e Part of the South Caucasus, at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. Physiographically, Armenia falls entirely in Western Asia, while Georgia and Azerbaijan are mostly in Asia with small portions north of the Caucasus Mountains divide in Europe.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c The island of Cyprus is located on the Cyprian arc on the edge of the Anatolian Plate and is physiographically associated with Asia, but it is part of European organisations such as the EU.
- ^ A simpler official short name has been encouraged by the Czech government, "Czechia". By 2017, this variant remains uncommon. Nevertheless, this term has been adopted by several companies and organisations, including Google Maps, instead of the term "Czech Republic". See Name of the Czech Republic.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Denmark and the Netherlands are constituent countries of the Kingdom of Denmark and the Kingdom of the Netherlands respectively. Both are members of the EU; however, the other constituent countries of their kingdoms are not. In international organisations, the terms Denmark and the Netherlands are often used as short names for their respective kingdoms as a whole.
- ^ The terms Republic of Ireland and Poblacht na hÉireann are official descriptions but are not official names.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Kazakhstan and Turkey both have territory in both Europe (dark green) and Asia (light green).
- ^ The Netherlands is also known as "Holland", but this name properly refers only to a region of the country. See Netherlands (terminology).
- ^ Russia is a transcontinental country located in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia, with the vast majority of its population (78%) living within its European part.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d The United Kingdom consists of the countries of England, Northern Ireland, Scotland and Wales. The UK is responsible for the foreign relations and ultimate good governance of the Crown Dependencies of Guernsey, the Isle of Man and Jersey, which are otherwise separate. England, Scotland and Wales make up the island of Great Britain (or simply Britain), which is sometimes used synonymously with the United Kingdom.
References
[edit]- ^ Lewis, Martin W.; Wigen, Kären (11 August 1997). The Myth of Continents. University of California Press. p. 28. ISBN 9780520207431.
- ^ Charles T. Evans (1 July 2009). "Black Sea". Novaonline.nvcc.edu. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopaedia 2007. Europe. Archived from the original on 28 October 2009. Retrieved 27 December 2007.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "Council of Europe in Brief". Coe.int. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Geological Development of the Sicilian-Tunisian Platform held in Italy (University of Urbino) on November 4, 5, 6, 1992". Oai.dtic.mil. 6 November 1992. Archived from the original on 22 July 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Understanding plate motions [This Dynamic Earth, USGS]". Pubs.usgs.gov. 9 June 1994. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Richard Connor (11 January 2010). "French overseas territories vote to remain close to Paris". Dw-world.de. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Regions and territories: Ceuta, Melilla". BBC News. 6 October 2010. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Netherlands". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Untying the Sovereign State: A Double Reading of the Anarchy Problematique". Mil.sagepub.com. 1 June 1988. Archived from the original on 11 December 2019. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States". Council on Foreign Relations. Archived from the original on 28 June 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "Member States of the United Nations". United Nations. Archived from the original on 28 February 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "47 countries, 1 Europe". Council of Europe. Archived from the original on 19 March 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Member States". Europa. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Field Listing :: Names". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 30 September 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "UNGEGN List of Country Names" (PDF). United Nations Statistics Division. 2007. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "UNGEGN List of Country Names" (PDF). United Nations Statistics Division. 2019. Retrieved 6 April 2021.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e f g "List of countries, territories and currencies". Europa. 9 August 2011. Retrieved 10 August 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d "Field Listing :: Capital". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "UNGEGN World Geographical Names". United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names. 13 September 2010. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022". United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ "World Population Prospects 2022: Demographic indicators by region, subregion and country, annually for 1950-2100" (XSLX) ("Total Population, as of 1 July (thousands)"). United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. Retrieved 17 July 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c d e "Field Listing :: Area". Central Intelligence Agency. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ "Republic of Ireland Act, 1948". No. 22/1948. 1948. Retrieved 16 December 2008.
- ^ "Holy See (Vatican City)". Central Intelligence Agency. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Tuvalu Retracts Recognition of Abkhazia, South Ossetia". Radio Free Europe/Radio Liberty. 31 March 2014.
- ^ "Regions and territories: Abkhazia". BBC News. 8 February 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Abkhazia (autonomous republic, Georgia)". Britannica.com. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ "Najčešća pitanja - Kancelarija za Kosovo i Metohiju, Vlada Republike Srbije". www.kim.gov.rs. Retrieved 22 February 2022.
- ^ Jump up to: a b c "Country Comparison :: Population". Central Intelligence Agency. July 2014. Archived from the original on 27 September 2011. Retrieved 17 October 2014.
- ^ "Cyprus". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ "Turkish Cyprus announces population as 294,906". World Bulletin. 9 December 2011. Retrieved 9 January 2014.
- ^ "Regions and territories: South Ossetia". BBC News. 8 February 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "South Ossetia". Hartford-hwp.com. Retrieved 9 March 2011.
- ^ Ker-Lindsay, James (2012). The Foreign Policy of Counter Secession: Preventing the Recognition of Contested States. Oxford University Press. p. 53. ISBN 9780199698394.
...there are three other territories that have unilaterally declared independence and are generally regarded as having met the Montevideo criteria for statehood but have not been recognised by any states: Transnistria, Nagorny Karabakh, and Somaliland.
. - ^ Перепись населения ПМР [Population census of PMR]. newspmr.com (in Russian). 9 March 2017. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ "Transdniestria (separatist enclave, Moldova)". Britannica.com. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ "CIA - The World Factbook - Field Listing :: Dependency status". Central Intelligence Agency. 9 February 1920. Archived from the original on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Mark Oliver; Sally Bolton; Jon Dennis; Matthew Tempest (4 August 2004). "Gibraltar; Politics". The Guardian. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Supreme Court decision" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ Jump up to: a b Queen and Crown dependencies page of the official website of the British Monarchy Archived 21 September 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Jump up to: a b c Ministry of Justice's fact sheet on the UK's relationship with the Crown Dependencies
- ^ "Supreme Court decision "The Channel Islands, like the Isle of Man (although it has a rather different history), are not part of the United Kingdom. Nor have they ever been British colonies, or British Overseas Territories as the few remaining colonies are now termed. They are Crown Dependencies, enjoying a unique relationship with the United Kingdom and the rest of the British Commonwealth through the Crown, in the person of the Sovereign."" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 October 2016. Retrieved 16 March 2016.
- ^ Queen and Crown dependencies page of the official website of the British Monarchy
- ^ European Commission for Democracy through Law (1996). Local self-government, territorial integrity, and protection of minorities: proceedings of the UniDem Seminar organised in Lausanne on 25–27 April 1996, in co-operation with the Swiss Institute of Comparative Law. Strasbourg: Council of Europe. pp. 32–35. ISBN 92-871-3173-2.
- ^ "Independence". Visitaland.com. Archived from the original on 7 January 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "Åland Official Tourist Gateway - Facts". Visitaland.com. Archived from the original on 10 February 2011. Retrieved 17 February 2011.
- ^ "Good Friday Agreement". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ Jump up to: a b "The Countries of the UK". Office for National Statistics (United Kingdom). Retrieved 7 July 2015.
- ^ Northern Ireland Statistics & Research Agency (December 2012). "Census 2011 Key Statistics for Northern Ireland" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 24 December 2012. Retrieved 14 January 2013.
- ^ "The Svalbard Treaty". Governor of Svalbard. 9 April 2008. Archived from the original on 6 May 2012. Retrieved 3 March 2011.
