Lenacil
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
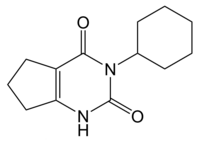
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-cyclohexyl-1,5,6,7-tetrahydrocyclopenta[d]pyrimidine-2,4-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.818 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H18N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 234.299 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H351, H410 | |
| P203, P273, P280, P318, P391, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Lenacil is a uracil-derived chemical herbicide used to control dicotyledons. Its formula is C13H18N2O2.
Production and synthesis
[edit]Lenacil was first patented and manufactured by DuPont[1][2] in the 1960s.[3]
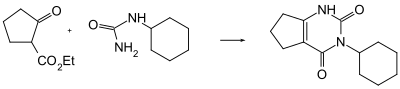
The compound can be produced via a condensation reaction between ethyl-2-oxocyclopentanecarboxylate and cyclohexylurea under an environment of phosphoric acid:[4][5]
Uses
[edit]Lenacil is used in the agricultural industry as a selective herbicide to protect sugar and fodder beets.[6]
Toxicity
[edit]Lenacil is noted as a potential endocrine disrupting compound.[7] It is not acutely toxic or genotoxic to mammals, though there is limited evidence the compound is carcinogenic. Lenacil is noted as particularly damaging to algae and aquatic plants, which is a concern if the compound leaches into groundwater when used as a pesticide.[6]
References
[edit]- ^ Bahadir M, Parlar H, Spiteller M (2000). Springer Umweltlexikon (in German). Springer. p. 702. ISBN 978-3-540-63561-1.
- ^ Roberts TR, Hutson DH (1999). Metabolic pathways of agrochemicals. Vol. 2. Royal Soc of Chemistry. p. 699. ISBN 978-0-85404-499-3.
- ^ U.S. Patent 3235360, "Control of undesirable vegetation" van 15 februari 1966 aan E.I. Du Pont de Nemours and Company. Gearchiveerd op 9 september 2023.
- ^ Ullmann's Agrochemicals. Vol. 1. Wiley-VCH. 2007. p. 809ff. ISBN 978-3-527-31604-5.[dead link]
- ^ Unger TA (1996). Pesticide synthesis handbook. p. 569. ISBN 978-0-81551401-5.
- ^ a b "Peer review of the pesticide risk assessment of the active substance lenacil | EFSA". www.efsa.europa.eu. October 7, 2009. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1326. Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- ^ Andres S, Dulio V (2024). "List of 7074 potential endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) by PARC T4.2 (NORMAN-SLE-S109.0.1.0) [Data set]". Zenodo. doi:10.5281/zenodo.10944199.
