Iron condor
This article needs additional citations for verification. (August 2022) |
The iron condor is an options trading strategy utilizing two vertical spreads – a put spread and a call spread with the same expiration and four different strikes. A long iron condor is essentially selling both sides of the underlying instrument by simultaneously shorting the same number of calls and puts, then covering each position with the purchase of further out of the money call(s) and put(s) respectively. The converse produces a short iron condor.
The position is so named because of the shape of the profit/loss graph, which replicates that of a condor but with a different combination of options. Traders often refer to the inner options collectively as the "body" and the outer options as the "wings". The word iron in the name of this position indicates that, like an iron butterfly, this position is constructed using both calls and puts, by combining a bull put spread with a bear call spread. The combination of these two credit spreads makes the long iron condor (and the long iron butterfly) a credit spread, despite the fact that it is "long." This distinguishes the position from a plain Condor position (and the plain Butterfly), which would be constructed with all calls or all puts, by combining either a bull call spread with a bear call spread or a bull put spread with a bear put spread. Because the long, plain Condor (and Butterfly) combine a debit spread with a credit spread, that overall position is instead entered at a net debit (though usually small).[1]
One of the practical advantages of an iron condor over a single vertical spread (a put spread or call spread), is that the initial and maintenance margin requirements[2] for the iron condor are often the same as the margin requirements for a single vertical spread, yet the iron condor offers the profit potential of two net credit premiums instead of only one. This can significantly improve the potential rate of return on capital risked when the trader doesn't expect the underlying instrument's spot price to change significantly.
Another practical advantage of the iron condor is that if the spot price of the underlying is between the inner strikes towards the end of the option contract, the trader can avoid additional transaction charges by simply letting some or all of the options contracts expire. If the trader is uncomfortable, however, with the proximity of the underlying's spot price to one of the inner strikes and/or is concerned about pin risk, then the trader can close one or both sides of the position by first re-purchasing the written options and then selling the purchased options.
Short iron condor
[edit]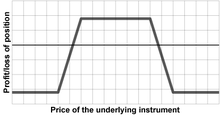
To SELL or "go short" an iron condor, the trader will SELL options contracts for the inner strikes using an out-of-the-money put and out-of-the-money call options. The trader will then also BUY the options contracts for the outer strikes.
A short iron condor comprises two credit spreads, a bull put spread and a bear call spread. The difference between the put contract strikes will generally be the same as the distance between the call contract strikes.
A short iron condor is a net credit transaction because the premium earned on the sales of the written contracts is greater than the premium paid on the purchased contracts. This net credit represents the maximum profit potential for an iron condor.
The potential loss of a short iron condor is the difference between the strikes on either the call spread or the put spread (whichever is greater if it is not balanced) multiplied by the contract size (typically 100 or 1000 shares of the underlying instrument), less the net credit received.
A trader who sells an iron condor speculates that the spot price of the underlying instrument will be between the short strikes when the options expire where the position is the most profitable. Thus, the short iron condor is an options strategy considered when the trader has a neutral outlook for the stock.
The short iron condor is an effective strategy for capturing any perceived excessive volatility risk premium,[3] which is the difference between the realized volatility of the underlying instrument and the volatility implied by options prices.
Related strategies
[edit]An option trader who considers a short iron condor is one who expects the price of the underlying instrument to change very little for a significant duration of time. This trader might also consider one or more of the following strategies.
- A short strangle is effectively a short iron condor, but without the wings. It is constructed by writing an out-of-the-money put and an out-of-the money call. A short strangle with the same short strikes as an iron condor is generally more profitable, but unlike a short iron condor, the short strangle offers no protection to limit losses should the underlying instrument's spot price change dramatically.
- A short iron butterfly is very similar to a short iron condor, except that the inner, short strikes are at the same strike. The iron butterfly requires the underlying instrument's spot price to remain virtually unchanged over the life of the contract in order to retain the full net credit, but the trade is potentially more profitable (larger net credit) than an Iron Condor.
- A short straddle is effectively a short iron butterfly without the wings and is constructed simply by writing an at-the-money call and an at-the-money put. Similar to a short strangle, the short straddle offers no protection to limit losses and similar to a short iron butterfly, the straddle requires the underlying instrument's spot price to remain virtually unchanged over the life of the contract in order to retain the full net credit.
- A bull put spread is simply the lower side of a short iron condor and has virtually identical initial and maintenance margin requirements. It allows the trader to realize maximum profit when the underling is above the short strike on expiration. This strategy is alternatively called a put credit spread.
- A bear call spread is simply the upper side of a short iron condor and has virtually identical initial and maintenance margin requirements. It allows the trader to realize maximum profit when the underlying is below the short strike on expiration. This strategy is alternatively called a call credit spread.
Long iron condor
[edit]
To BUY or "go long" an iron condor, the trader will BUY (long) options contracts for the inner strikes using an out-of-the-money put and out-of-the-money call options. The trader will then also SELL or write (short) the options contracts for the outer strikes.
Because the premium earned on the sales of the written contracts is less than the premium paid for the purchased contracts, a long iron condor is typically a net debit transaction. This debit represents the maximum potential loss for the long iron condor.
The potential profit for a long iron condor is the difference between the strikes on either the call spread or the put spread (whichever is greater if it is not balanced) multiplied by the size of each contract (typically 100 or 1000 shares of the underlying instrument) less the net debit paid.
A trader who sells a long iron condor speculates that the spot price of the underlying instrument will not be between the long strikes when the options expire. If the spot price of the underlying is less than the outer put strike, or greater than the outer call strike at expiration, then the long iron condor trader will realise the maximum profit potential.
Related strategies
[edit]An option trader who considers a long iron condor strategy is one who expects the price of the underlying to change greatly, but isn't certain of the direction of the change. This trader might also consider one or more of the following strategies.
- A strangle is effectively a long iron condor, but without the wings. It is constructed by purchasing an out-of-the-money put and an out-of-the money call. The strangle is a more expensive trade (higher net debit to be paid due to the absence of the outer strikes that typically reduce the net debit), but the Strangle does not restrict profit potential in the case of a dramatic change in the spot price of the underlying instrument.
- A long iron butterfly is very similar to a long iron condor, except that the inner, long strikes are at the same strike. The resulting position requires the underlying's spot price to change less before there is a profit, but the trade is typically more expensive (larger net debit) than a long iron condor. Likewise, a long iron butterfly almost never allows the trader to realize that maximum profit potential, as this would require the stock to expire exactly at the strike price on expiration. This contrasts with the iron condor, which offers a wider space in between the long strikes. The iron butterfly is alternatively called an ironfly.
- A straddle is effectively a long iron butterfly without the wings and is constructed simply by purchasing an at-the-money call and an at-the-money put. Similar to the strangle, the straddle offers a greater profit potential at the expense of a greater net debit.
- A bear put spread is simply the lower side of a long iron condor and has virtually identical initial and maintenance margin requirements. This spread is alternatively called a put debit spread.
- A bull call spread is simply the upper side of a long iron condor and has virtually identical initial and maintenance margin requirements. This spread is alternatively called a call debit spread.
References
[edit]- ^ Cohen, Guy. (2005). The Bible of Options Strategies. New Jersey : Pearson Education, Inc. ISBN 0-13-171066-4.
- ^ "Chicago Board Options Exchange - Margin Manual" (PDF).
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-09-19. Retrieved 2009-11-10.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
