Immunoradiometric assay
| Immunoradiometric assay | |
|---|---|
 |
Immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) is an assay that uses radiolabeled antibodies. It differs from conventional radioimmunoassay (RIA) in that the compound to be measured combines immediately with the radiolabeled antibodies, rather than displacing another antigen by degrees over some period.
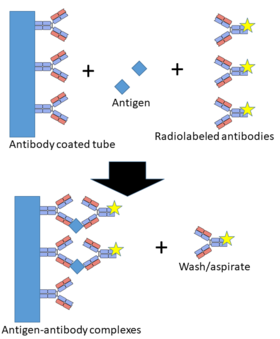
Principle:- A noncompetitive assay in which analyte to be measured sandwich btw two Antibodies
Introduction
[edit]Fluorescent and radioactive antibodies have been used to locate or measure solid-phase antigens for many years. However, only recently has the labeled antibody been applied to measurement of antigen to sample. The method converts the unknown antigen into a traceable radioactive product. Immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) was first introduced by "Miles and Hales" in 1968, who proposed certain theoretical advantages of the method with regard to improving the sensitivity and precision of immunoassays.
Principle
[edit]In IRMA, the antibodies are labeled with radioisotopes which are used to bind antigens present in the specimen. When a positive sample is added to the tubes, radioactively labeled (labeled with I125 or I131 radioisotopes) antibodies bind to the free epitopes of antigens and form an antigen-antibody complex. Unbound labeled antibodies are removed by a second reaction with a solid phase antigen. The amount of radioactive remaining in the solution is direct function of the antigen concentration.
References
[edit]
