Geotrygon
| Geotrygon | |
|---|---|

| |
| Key West quail-dove | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Columbiformes |
| Family: | Columbidae |
| Subfamily: | Columbinae |
| Genus: | Geotrygon Gosse, 1847 |
| Type species | |
| Columba cristata[1] = Geotrygon versicolor Temminck, 1809
| |
| Species | |
|
see text | |
Geotrygon is a bird genus in the pigeon and dove family (Columbidae). Its members are called quail-doves, and all live in the Neotropics. The species of this genus have ranges from southern Mexico and Central America to the West Indies and South America, with 2 species recorded as occasional vagrants reported in Texas and Florida in the United States. Quail-doves are ground-dwelling pigeons that live, nest, and feed in dense forests. They are remarkable for their vivid coloration with light-and-dark facial markings.
Taxonomy
[edit]The genus Geotrygon was introduced in 1847 by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse.[2] The name combines the Ancient Greek geō- meaning "ground-" and trygōn meaning "turtledove".[3] The type species was subsequently designated as the crested quail-dove (Geotrygon versicolor).[4]
Species
[edit]The genus contains nine species:[5]
| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grey-fronted quail-dove | Geotrygon caniceps (Gundlach, 1852) |
Cuba
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
VU
|
| Key West quail-dove | Geotrygon chrysia Bonaparte, 1855 |
Bahamas. southern Florida, Greater Antilles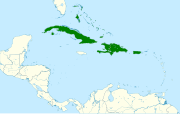
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| White-fronted quail-dove or Hispaniolan quail-dove | Geotrygon leucometopia (Chapman, 1917) |
Dominican Republic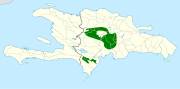
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
| Ruddy quail-dove | Geotrygon montana (Linnaeus, 1758) Two subspecies
|
the West Indies, Central America, and tropical South America
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Bridled quail-dove | Geotrygon mystacea (Temminck, 1811) |
Saint Lucia in the Lesser Antilles north and west to Puerto Rico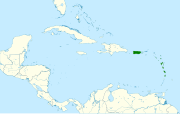
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Purple quail-dove | Geotrygon purpurata (Salvin, 1878) |
Colombia and Ecuador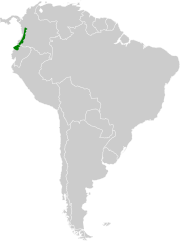
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
EN
|
| Sapphire quail-dove | Geotrygon saphirina Bonaparte, 1855 |
Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, and Peru.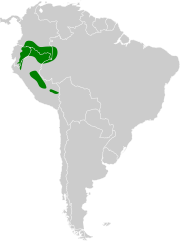
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
| Crested quail-dove | Geotrygon versicolor (Lafresnaye, 1846) |
Jamaica
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
NT
|
| Violaceous quail-dove | Geotrygon violacea (Temminck, 1809) Two subspecies
|
Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Costa Rica, Guyana, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela.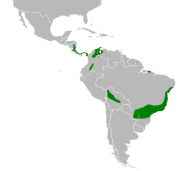
|
Size: Habitat: Diet: |
LC
|
- Fossils
- †Puerto Rican quail-dove, Geotrygon larva - prehistoric
Members of the genera Zentrygon and Leptotrygon are also known as quail-doves, and were formerly included in Geotrygon. The Cuban species Starnoenas cyanocephala was previously referred to as a quail-dove, though this English name is no longer used.[6]
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| Cladogram showing the position of genera in the tribe Zenaidini.[7][8] |
References
[edit]- ^ "Columbidae". aviansystematics.org. The Trust for Avian Systematics. Retrieved 2023-08-05.
- ^ Gosse, Philip Henry (1847). The Birds of Jamaica. London: J. Van Voorst. p. 316.
- ^ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London: Christopher Helm. p. 172. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4.
- ^ Peters, James Lee, ed. (1937). Check-List of Birds of the World. Vol. 3. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 132.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (2020). "Pigeons". IOC World Bird List Version 10.1. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 14 March 2020.
- ^ Olson, Storrs L.; Wiley, James W. (2016). "The Blue-headed Quail-Dove (Starnoenas cyanocephala): An Australasian dove marooned in Cuba". The Wilson Journal of Ornithology. 128: 1–21. doi:10.1676/1559-4491-128.1.1.
- ^ Banks, R.C.; Weckstein, J.D.; Remsen Jr, J.V.; Johnson, K.P. (2013). "Classification of a clade of New World doves (Columbidae: Zenaidini)". Zootaxa. 3669 (2): 184–188. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3669.2.11.
- ^ Johnson, K.P.; Weckstein, J.D. (2011). "The Central American land bridge as an engine of diversification in New World doves". Journal of Biogeography. 38: 1069–1076. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2011.02501.x.
- Gibbs, David; Barnes, Eustace; Cox, John (2001). Pigeons and Doves: A Guide to the Pigeons and Doves of the World. Yale University Press. pp. 370–390. ISBN 0-300-07886-2.










