Dyspropterin
Appearance
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2022) |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
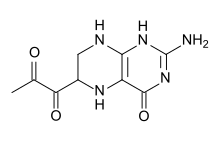
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2-Amino-4-oxo-5,6,7,8-tetrahydro-1H-pteridin-6-yl)propane-1,2-dione | |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1-(2-Amino-4-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl)propane-1,2-dione | |
| Other names
6-Pyruvoyltetrahydropterin; 6-PTHB
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | 6-PTHB |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Dyspropterin |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H11N5O3 | |
| Molar mass | 237.219 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dyspropterin (6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin, 6-PTHB) is an intermediate in tetrahydrobiopterin biosynthesis. It is the product of the enzyme 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase and the substrate of two enzymes, 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin 2'-reductase and sepiapterin reductase.
Dyspropterin exists in all living organisms, ranging from bacteria to humans.[1] Dyspropterin has been detected, but not quantified in, a few different foods, such as ducks (Anatidae), chickens (Gallus gallus), and domestic pigs (Sus scrofa domestica).[2] This could make dyspropterin a potential biomarker for the consumption of these foods.[3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Showing Compound Dyspropterin (FDB022481) - FooDB". foodb.ca. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
- ^ "Showing Compound Dyspropterin (FDB022481) - FooDB". foodb.ca. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
- ^ "Showing Compound Dyspropterin (FDB022481) - FooDB". foodb.ca. Retrieved 2022-03-30.
