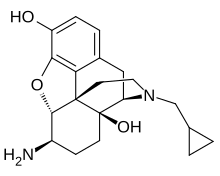
β-Naltrexamine
Appearance
(Redirected from Draft:Naltrexamine)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | β-Naltrexamine; 6β-Aminonaltrexol; 6β-Amino-17-(cyclopropylmethyl)-4,5α-epoxymorphinan-3,14-diol |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H26N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 342.439 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
β-Naltrexamine, or 6β-naltrexamine, is an opioid receptor antagonist related to naltrexol and naltrexone.[1][2][3] It has served as a parent pharmacophore for irreversible antagonists of the μ-opioid receptor (MOR) such as β-chlornaltrexamine (β-CNA) and β-funaltrexamine (β-FNA).[1][2] Naltrexamine itself is a neutral antagonist of the MOR and the δ-opioid receptor (DOR) with similarly high affinity for both receptors.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Fulton BS (2014). Drug Discovery for the Treatment of Addiction: Medicinal Chemistry Strategies. Wiley. p. 220. ISBN 978-1-118-88957-2. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ^ a b Testa B (2013). Advances in Drug Research. ISSN. Elsevier Science. p. 184. ISBN 978-1-4832-8798-0. Retrieved 14 September 2024.
- ^ a b Wang D, Raehal KM, Bilsky EJ, Sadée W (June 2001). "Inverse agonists and neutral antagonists at mu opioid receptor (MOR): possible role of basal receptor signaling in narcotic dependence". J Neurochem. 77 (6): 1590–1600. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2001.00362.x. PMID 11413242.
