DPH-362
Tools
Actions
General
Print/export
In other projects
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
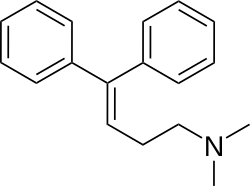
DPH-362 is a simplified chemical analog of amitriptyline.
Pharmaceutical compound
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | PD129167 |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H21N |
| Molar mass | 251.373 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
DPH-362 is a simplified amitriptyline analog created by omission of the two-carbon dibenzosuberane bridge (the seven membered ring). The resulting compound still had activity in a test to explore TCA sodium channel blockers with analgesic properties.[1][2]
It is based on previous structures such as Spasmolytic A29 (one of the active ingredients in Ketogan)[3][4] and SKF-89976A.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Bölcskei H, Tarnawa I, Kocsis P (June 2008). "Voltage-gated sodium channel blockers, 2001-2006: An overview". Medicinal Chemistry Research. 17 (2–7): 356–368. doi:10.1007/s00044-007-9071-2.
- ^ Hudgens DP, Taylor C, Batts TW, Patel MK, Brown ML (December 2006). "Discovery of diphenyl amine based sodium channel blockers, effective against hNav1.2". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 14 (24): 8366–8378. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.09.010. PMC 2756728. PMID 17035036.
- ^ Petersen PV (1951). "Studies on a new spasmolytic compound 1,1-diphenyl-3-dimethylaminobutene-1 (A29), related to methadone, and on the combined use of this compound and a potent analgesic, ketobemidone (A21)". Acta Pharmacologica et Toxicologica. 7 (1): 51–64. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.1951.tb02849.x. PMID 14829296.
- ^ Ebert B, Thorkildsen C, Andersen S, Christrup LL, Hjeds H (September 1998). "Opioid analgesics as noncompetitive N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) antagonists". Biochemical Pharmacology. 56 (5): 553–559. doi:10.1016/s0006-2952(98)00088-4. PMID 9783723.
| Esters by acid |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amides | |||||||
| Combinations | |||||||
| |||||||
| Opioids |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paracetamol-type | |||||||||||||||||
| NSAIDs |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cannabinoids | |||||||||||||||||
| Ion channel modulators |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Myorelaxants | |||||||||||||||||
| Others | |||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| GABAergics |
| ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Channel modulators |
| ||||||
| Others |
| ||||||
| |||||||
Retrieved from "https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=DPH-362&oldid=1266671693"
Hidden categories:
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugs missing an ATC code
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All stub articles
