Cyclooctadiene iridium methoxide dimer
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
bis[(cyclooctadiene]di-μ-methoxydiiridium
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.156.683 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H30Ir2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 662.870 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow solid |
| Density | 2.552 g/cm3 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
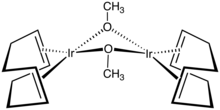
Cyclooctadiene iridium methoxide dimer is an organoiridium compound with the formula Ir2(OCH3)2(C8H12)2, where C8H12 is the diene 1,5-cyclooctadiene. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. The complex is used as a precursor to other iridium complexes, some of which are used in homogeneous catalysis.[1]
The compound is prepared by treating cyclooctadiene iridium chloride dimer with sodium methoxide.[2] In terms of its molecular structure, the iridium centers are square planar as is typical for a d8 complex. The Ir2O2 core is folded.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ Li, Hongbo; Colacot, Thomas J. (2010). "Di-μ-methoxobis(1,5-cyclooctadiene)diiridium(I)". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01167. ISBN 978-0471936237..
- ^ Uson, R.; Oro, L. A.; Cabeza, J. A. (1985). "Dinuclear Methoxy, Cyclooctadiene, and Barrelene Complexes of Rhodium(I) and Iridium(I)". Inorganic Syntheses. Vol. 23. pp. 126–130. doi:10.1002/9780470132548.ch25. ISBN 9780470132548.
- ^ Carlton, Laurence; Nyoni, Michelle S.; Fernandes, Manuel A. (2016). "Triazenide complexes of iridium. Evidence for [Ir(η1-N3Ph2)(HN3Ph2)(1,5-cod)], Structures of [Ir2(μ-OMe)2(1,5-cod)2], [Ir2(μ-N3Ph2)2(1,5-cod)2], [Ir(η2-N3Ph2)(H)(SiPh3)(1,5-cod)], [Ir(η2-N3Ph2)(H)(SnPh3)(1,5-cod)] and [Ir(η2-N3Ph2)(SC6F5)2(1,5-cod)]". Polyhedron. 119: 194–201. doi:10.1016/j.poly.2016.03.022.
