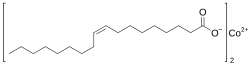
Cobalt oleate
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cobalt (Z)-octadec-9-enoate
| |
| Other names
Cobaltous oleate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.038.953 |
| EC Number |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C36H66CoO4 | |
| Molar mass | 621.853 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Purple powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in benzene, carbon tetrachloride, pyridine, chloroform, quinoline[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Warning | |
| H317, H411, H412 | |
| P261, P272, P273, P280, P302+P352, P321, P333+P313, P362+P364, P391, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other cations
|
Sodium oleate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Cobalt oleate is an organometallic compound with the formula Co(C18H33O2)2. When cobalt oleate is added to non-polar solvents, the viscosity rapidly increases, and then continues increasing over time. This unusual viscosity effect is caused by the formation of a weak coordination complex with the solvent molecules.[1]
Preparation
[edit]Cobalt oleate can be synthesized by heating a solution of sodium oleate and cobalt(II) chloride to 70 °C.[2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b Funakoshi, Hideo; Matuura, Ryohei (October 1964). "Peptizing Action of Some Polar Substances on the Benzene Solution of Cobalt Oleate". Nature. 204 (4954): 186. Bibcode:1964Natur.204..186F. doi:10.1038/204186a0. ISSN 0028-0836. S2CID 4198459.
- ^ An, Kwangjin; Lee, Nohyun; Park, Jongnam; Kim, Sung Chul; Hwang, Yosun; Park, Je-Geun; Kim, Jae-Young; Park, Jae-Hoon; Han, Myung Joon; Yu, Jaejun; Hyeon, Taeghwan (2006-08-01). "Synthesis, Characterization, and Self-Assembly of Pencil-Shaped CoO Nanorods". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 128 (30): 9753–9760. doi:10.1021/ja0608702. ISSN 0002-7863. PMID 16866531.

