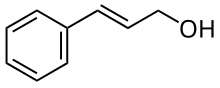
Cinnamyl alcohol
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2E)-3-Phenylprop-2-en-1-ol | |
| Other names | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.216.224 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H10O | |
| Molar mass | 134.178 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.0397 g/cm3 at 35 °C |
| Melting point | 33 °C (91 °F; 306 K) |
| Boiling point | 250 °C (482 °F; 523 K) |
| Slightly | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, acetone, dichloromethane |
| -87.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P261, P272, P280, P302+P352, P321, P333+P313, P363, P501 | |
| Flash point | 126°C |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Cinnamic acid; Cinnamaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
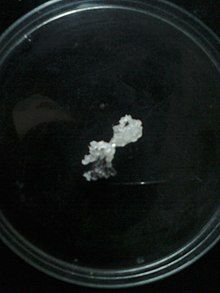
Cinnamyl alcohol or styron[2] is an organic compound that is found in esterified form in storax, Balsam of Peru, and cinnamon leaves. It forms a white crystalline solid when pure, or a yellow oil when even slightly impure. It can be produced by the hydrolysis of storax.
Cinnamyl alcohol occurs naturally only in small quantities, so its industrial demand is usually fulfilled by chemical synthesis starting from cinnamaldehyde.[3]
Properties
[edit]The compound is a solid at room temperature, forming colorless crystals that melt upon gentle heating. As is typical of most higher-molecular weight alcohols, it is sparingly soluble in water at room temperature, but highly soluble in most common organic solvents.
Uses
[edit]Cinnamyl alcohol has a distinctive odor described as "sweet, balsam, hyacinth, spicy, green, powdery, cinnamic" and is used in perfumery[4] and as a deodorant.
Cinnamyl alcohol is the starting material used in the synthesis of reboxetine.[5]
Safety
[edit]Cinnamyl alcohol has been found to have a sensitizing effect on some people[6][7] and as a result is the subject of a Restricted Standard issued by IFRA (International Fragrance Association).
Glycosides
[edit]Rosarin and rosavin are cinnamyl alcohol glycosides isolated from Rhodiola rosea.
References
[edit]- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 2305
- ^ a b Chemical News and Journal of Industrial Science, Volumes 27-28, Sir William Crookes, page 126
- ^ Zucca, P; Littarru, M; Rescigno, A; Sanjust, E (May 2009). "Cofactor recycling for selective enzymatic biotransformation of cinnamaldehyde to cinnamyl alcohol". Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 73 (5): 1224–6. doi:10.1271/bbb.90025. PMID 19420690. S2CID 28741979.
- ^ "cinnamyl alcohol 104-54-1". thegoodscentscompany.com. Retrieved 26 July 2015.
- ^ "Reboxetine mesilate".
- ^ "Food and Chemical Toxicology" (PDF). RIFM. 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2021-01-12. Retrieved 2012-04-05.
- ^ Survey and health assessment of chemical substances in massage oils Archived 2007-06-28 at the Wayback Machine
