Cheungkongella
| Cheungkongella Temporal range: Cambrian Stage 3,
| |
|---|---|

| |
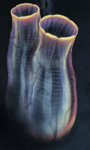
| Restoration of C. ancestralis. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Subphylum: | Tunicata |
| Class: | Ascidiacea |
| Genus: | †Cheungkongella Shu et al., 2001 |
| Type species | |
| †Cheungkongella ancestralis Shu et al., 2001
| |
| Species | |
| |
Cheungkongella is a fossil organism from the lower Cambrian Chengjiang lagerstatte, the affinity of which has been the subject of debate. It was announced as a "probable" tunicate while noting the lack of definitive Cambrian fossils from that group.[2] However, this affinity was later disputed in a paper announcing the discovery of Shankouclava, also from Chengjiang, as the oldest known tunicate.[3] Cheungkongella has been accepted as a distinct taxon and possible tunicate by multiple workers not involved in its discovery,[4][5][6][7] but the dispute remains unresolved.[3][8]
Etymology
[edit]"Cheungkong" is "a metaphor of China" and honors the Cheungkong Scholars Programme's support for the work leading to the fossil's discovery. "Ancestralis" refers to the fossil's possible primitive taxonomic position.[2]
Description
[edit]Cheungkongella has a club-shaped body similar to the extant ascidian Styela, with a bucket-shaped main body with thick, tapering stem beneath it. A large oral siphon with short tentacles at the top of the animal leads to a pharynx occupying two-thirds of the main body, with a structure presumed to ben an alimentary canal beneath it. A small cloacal siphon emerges from the side above the transition to the stem.[9]
Classification
[edit]Cheungkongella was placed in the class Ascidiacea based on its resemblance Styela.[2] This classification was initially accepted by other workers.[10]
Proposal to synonomize with Phlogites
[edit]
(BT: branching tentacles; CIS: Complex internal organs; Os: Oral siphon; S: Stem; Sp: Simple pharynx; St: Stomach)
A 2003 paper announcing Shankouclava as the oldest known tunicate both disputed Cheungkongella's affinities and proposed that it is a junior synonym of Phlogites, which was though to be a lophophorate at the time[11]
The paper stated that Cheungkongella is "indistinguishable" from Phlogites, but proceeded to note several differences, most notably the lack of any "obvious" arms in Cheungkongella despite acknowledging that three or five such arms are a prominent feature of Phlogites. The paper speculated that this is "perhaps because its arms broke off or are covered by rock." The lack of a coiled gut in Cheunkongella was dismissed by noting that not all specimens of Phlogites display one.[11]
The original description of Cheungkongella noted light dots in the area interpreted as a pharynx that could be gill slits, but stated that the interpretation required confirmation. The Shankouclava paper suggested that these dots are taphonomic artifacts due to their irregular pattern. However, the paper's other arguments against tunicate affinities were based on newly discovered specimens of Phlogites.[11] Phlogites is now known to be a cambroernid, and has never been assigned to the tunicates except as a result of Cheungkongella being considered a synonym.[12][13]
A responding paper disputing the synonymization with Phlogites provided the image shown on this page in response to criticisms of poor image quality in past publications.[14]
A paper on the affinities of Phlogites accepted the synonymization, but did not discuss the Cheungkongella fossil except to note a similar thickness of stem between it and a subset of the new Phlogites specimens.[15] The similarity of the lower section has also been noted by workers who consider the two taxa to be separate.[9][16]
The resemblance between Cheunkongella and Phlogites has been dismissed as "superficial" by a researcher not involved with the discoveries of either of those taxa or of Shankcouklava.[4] Other sources not directly involved in the dispute have recognized both Cheungkongella (as distinct from Phlogites) and Shankouclava as possible (if debatable) tunicates,[5][6] or recognize Cheungkongella as a tunicate and Shankouclava as chordate.[7]
The dispute remains unresolved, as has been noted by sources that accept or tentatively accept the synonymization.[3][8]
References
[edit]- ^ Yang et al. 2018
- ^ a b c Shu et al. 2001
- ^ a b c Gee 2018, p. 99
- ^ a b Conway Morris 2006, p. 1076
- ^ a b Northcutt 2012, p. 10628
- ^ a b Janvier 2015, p. 484
- ^ a b Kimmig, Meyer & Lieberman 2019, p. 172
- ^ a b Hou et al. 2017, p. 256
- ^ a b Shu 2008, p. 230–231
- ^ Chen et al. 2003, p. 285
- ^ a b c Chen et al. 2003, p. 8316
- ^ Giribet & Edgecombe 2020, p. 105
- ^ Hou et al. 2017, p. 252
- ^ Shu 2005, p. 2352
- ^ Hou et al. 2006, p. 47–49
- ^ Caron et al. 2010, p. 2
Works cited
[edit]- Caron, J.; Conway Morris, S.; Shu, D.; Soares, D. (2010). Soares, Daphne (ed.). "Tentaculate fossils from the Cambrian of Canada (British Columbia) and China (Yunnan) interpreted as primitive deuterostomes". PLOS ONE. 5 (3): e9586. Bibcode:2010PLoSO...5.9586C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009586. PMC 2833208. PMID 20221405.
- Chen, Ailin; Feng, Hongzhen; Zhu, Maoyan; Ma, Dongsheng; Li, Ming (September 2003). "A New Vetulicolian from the Early Cambrian Chengjiang Fauna in Yunnan of China". Acta Geologica Sinica. 77 (3): 281–287. Bibcode:2003AcGlS..77..281C. doi:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2003.tb00742.x.
- Chen, Jun-Yuan; Huang, Di-Ying; Peng, Qing-Qing; Chi, Hui-Mei; Wang, Xiu-Qiang; Feng, Man (2003). "The first tunicate from the Early Cambrian of South China". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 100 (14): 8314–8318. Bibcode:2003PNAS..100.8314C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1431177100. PMC 166226. PMID 12835415.
- Conway Morris, Simon (2006). "Darwin's dilemma: the realities of the Cambrian 'explosion'". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B. 361 (1470): 1069–1083. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.1846. PMC 1578734. PMID 16754615.
- Gee, Henry (July 4, 2018). "Tunicates". Across the Bridge: Understanding the Origin of Vertebrates. University of Chicago Press. pp. 85–99. ISBN 978-0226402864.
- Giribet, Gonzalo; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (March 3, 2020). "Deuterostomia". The Invertebrate Tree of Life. Princeton University Press. pp. 102–107. ISBN 978-0691170251.
- Hou, Xian-Guang; Bergström, Jan; Ma, Xiao-Ya; Zhao, Jie (2006). "The Lower Cambrian Phlogites Luo & Hu Re-Considered". GFF. 128 (1): 47–51. Bibcode:2006GFF...128...47X. doi:10.1080/11035890601281047.
- Hou, Xian-guang; Siveter, David J.; Siveter, Derek J.; Aldridge, Richard J.; Cong, Pei-yun; Gabbott, Sarah; Ma, Xiao-ya; Purnell, Mark A.; Williams, Mark (2017). "Vetulicolians". The Cambrian Fossils of Chengjiang, China: The Flowering of Early Animal Life (2 ed.). pp. 272–281. doi:10.1002/9781118896372.ch25.
- Janvier, Philippe (April 23, 2015). "Facts and fancies about early fossil chordates and vertebrates". Nature. 520 (7548): 483–89. Bibcode:2015Natur.520..483J. doi:10.1038/nature14437. PMID 25903630.
- Kimmig, Julien; Meyer, Ronald C.; Lieberman, Bruce S. (2019). "Herpetogaster from the early Cambrian of Nevada (Series 2, Stage 4) and its implications for the evolution of deuterostomes". Geological Magazine. 156 (1): 172–178. Bibcode:2019GeoM..156..172K. doi:10.1017/S0016756818000389. ISSN 1469-5081. S2CID 134642027.
- Nanglu, Karma; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Weaver, James C.; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2023). "A mid-Cambrian tunicate and the deep origin of the ascidiacean body plan". Nature Communications. 14 (1): 3832. Bibcode:2023NatCo..14.3832N. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39012-4. PMC 10325964. PMID 37414759.
- Northcutt, R. Glenn (June 26, 2012). "Evolution of centralized nervous systems: Two schools of evolutionary thought". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 109 (Supplement 1: In the Light of Evolution VI: Brain and Behavior): 10626–10633. Bibcode:2012PNAS..10910626N. doi:10.1073/pnas.1201889109. JSTOR 41601648. PMC 3386872. PMID 22723354.
- Shu, Degan (October 2005). "On the Phylum Vetulicolia". Chinese Science Bulletin. 50 (20): 2342–2354. Bibcode:2005ChSBu..50.2342S. doi:10.1007/BF03183746. Retrieved 1 October 2024.
- Shu, D. (2008). "Cambrian explosion: Birth of tree of animals". Gondwana Research. 14 (1–2): 219–240. Bibcode:2008GondR..14..219S. doi:10.1016/j.gr.2007.08.004.
- Shu, D.-G.; Chen, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, X.-L. (May 24, 2001). "An Early Cambrian tunicate from China". Nature. 411 (6836): 472–473. Bibcode:2001Natur.411..472S. doi:10.1038/35078069. PMID 11373678.
- Shu, D.-G.; Conway Morris, S.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Han, J. (2010). "The earliest history of the deuterostomes: The importance of the Chengjiang Fossil-Lagerstätte". Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. 277 (1679): 165–174. doi:10.1098/rspb.2009.0646. PMC 2842668. PMID 19439437.
- Yang, C.; Li, X.-H.; Zhu, M.; Condon, D. J.; Chen, J. (2018). "Geochronological constraint on the Cambrian Chengjiang biota, South China" (PDF). Journal of the Geological Society. 175 (4): 659–666. Bibcode:2018JGSoc.175..659Y. doi:10.1144/jgs2017-103. ISSN 0016-7649. S2CID 135091168.