Austroasiatic languages
| Austroasiatic | |
|---|---|
| Austro-Asiatic | |
| Geographic distribution | Southeast, South and East Asia |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Austroasiatic |
| Subdivisions | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-5 | aav |
| Glottolog | aust1305 (Austroasiatic) |
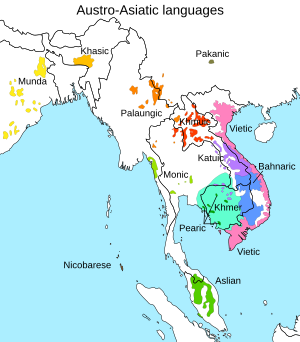 | |
The Austroasiatic languages[note 1] (/ˌɒstroʊ.eɪʒiˈætɪk, ˌɔː-/ OSS-troh-ay-zhee-AT-ik, AWSS-) are a large language family spoken throughout Mainland Southeast Asia, South Asia and East Asia. These languages are natively spoken by the majority of the population in Vietnam and Cambodia, and by minority populations scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China. Approximately 117 million people speak an Austroasiatic language, of which more than two-thirds are Vietnamese speakers.[1] Of the Austroasiatic languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have lengthy, established presences in the historical record. Only two are presently considered to be the national languages of sovereign states: Vietnamese in Vietnam, and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand, while the Wa language is a "recognized national language" in the de facto autonomous Wa State within Myanmar. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The remainder of the family's languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status.
Ethnologue identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly attested, as a fourteenth), which have traditionally been grouped into two, as Mon–Khmer,[2] and Munda. However, one recent classification posits three groups (Munda, Mon-Khmer, and Khasi–Khmuic),[3] while another has abandoned Mon–Khmer as a taxon altogether, making it synonymous with the larger family.[4]
Austroasiatic languages appear to be the extant autochthonous languages in mainland Southeast Asia, with the neighboring Kra–Dai, Hmong-Mien, Austronesian, and Sino-Tibetan languages having arrived via later migrations.[5]
Etymology
[edit]The name Austroasiatic was coined by Wilhelm Schmidt (German: austroasiatisch) based on auster, the Latin word for "South" (but idiosyncratically used by Schmidt to refer to the southeast), and "Asia".[6] Despite the literal meaning of its name, only three Austroasiatic branches are actually spoken in South Asia: Khasic, Munda, and Nicobarese.
Typology
[edit]Regarding word structure, Austroasiatic languages are well known for having an iambic "sesquisyllabic" pattern, with basic nouns and verbs consisting of an initial, unstressed, reduced minor syllable followed by a stressed, full syllable.[7] This reduction of presyllables has led to a variety of phonological shapes of the same original Proto-Austroasiatic prefixes, such as the causative prefix, ranging from CVC syllables to consonant clusters to single consonants among the modern languages.[8] As for word formation, most Austroasiatic languages have a variety of derivational prefixes, many have infixes, but suffixes are almost completely non-existent in most branches except Munda, and a few specialized exceptions in other Austroasiatic branches.[9]
The Austroasiatic languages are further characterized as having unusually large vowel inventories and employing some sort of register contrast, either between modal (normal) voice and breathy (lax) voice or between modal voice and creaky voice.[10] Languages in the Pearic branch and some in the Vietic branch can have a three- or even four-way voicing contrast.
However, some Austroasiatic languages have lost the register contrast by evolving more diphthongs or in a few cases, such as Vietnamese, tonogenesis. Vietnamese has been so heavily influenced by Chinese that its original Austroasiatic phonological quality is obscured and now resembles that of South Chinese languages, whereas Khmer, which had more influence from Sanskrit, has retained a more typically Austroasiatic structure.
Proto-language
[edit]Much work has been done on the reconstruction of Proto-Mon–Khmer in Harry L. Shorto's Mon–Khmer Comparative Dictionary. Little work has been done on the Munda languages, which are not well documented. With their demotion from a primary branch, Proto-Mon–Khmer becomes synonymous with Proto-Austroasiatic. Paul Sidwell (2005) reconstructs the consonant inventory of Proto-Mon–Khmer as follows:[11]
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | voiceless | *p | *t | *c | *k | *ʔ |
| voiced | *b | *d | *ɟ | *ɡ | ||
| implosive | *ɓ | *ɗ | *ʄ | |||
| Nasal | *m | *n | *ɲ | *ŋ | ||
| Liquid | *w | *l, *r | *j | |||
| Fricative | *s | *h | ||||
This is identical to earlier reconstructions except for *ʄ. *ʄ is better preserved in the Katuic languages, which Sidwell has specialized in.
Internal classification
[edit]Linguists traditionally recognize two primary divisions of Austroasiatic: the Mon–Khmer languages of Southeast Asia, Northeast India and the Nicobar Islands, and the Munda languages of East and Central India and parts of Bangladesh and Nepal. However, no evidence for this classification has ever been published.
Each of the families that is written in boldface type below is accepted as a valid clade.[clarification needed] By contrast, the relationships between these families within Austroasiatic are debated. In addition to the traditional classification, two recent proposals are given, neither of which accepts traditional "Mon–Khmer" as a valid unit. However, little of the data used for competing classifications has ever been published, and therefore cannot be evaluated by peer review.
In addition, there are suggestions that additional branches of Austroasiatic might be preserved in substrata of Acehnese in Sumatra (Diffloth), the Chamic languages of Vietnam, and the Land Dayak languages of Borneo (Adelaar 1995).[12]
Diffloth (1974)
[edit]Diffloth's widely cited original classification, now abandoned by Diffloth himself, is used in Encyclopædia Britannica and—except for the breakup of Southern Mon–Khmer—in Ethnologue.
- Austro‑Asiatic
Peiros (2004)
[edit]Peiros is a lexicostatistic classification, based on percentages of shared vocabulary. This means that languages can appear to be more distantly related than they actually are due to language contact. Indeed, when Sidwell (2009) replicated Peiros's study with languages known well enough to account for loans, he did not find the internal (branching) structure below.
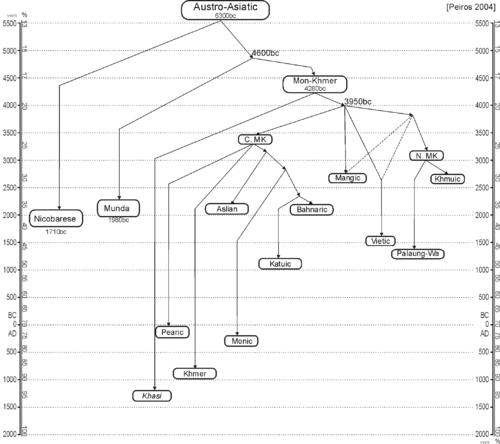
- Austro‑Asiatic
Diffloth (2005)
[edit]Diffloth compares reconstructions of various clades, and attempts to classify them based on shared innovations, though like other classifications the evidence has not been published. As a schematic, we have:
| Austro‑Asiatic | |
Or in more detail,
- Austro‑Asiatic
- Munda languages (India)
- Koraput: 7 languages
- Core Munda languages
- Kharian–Juang: 2 languages
- North Munda languages
- Korku
- Kherwarian: 12 languages
- Khasi–Khmuic languages (Northern Mon–Khmer)
- Khasian: 3 languages of north eastern India and adjacent region of Bangladesh
- Palaungo-Khmuic languages
- Nuclear Mon–Khmer languages
- Khmero-Vietic languages (Eastern Mon–Khmer)
- Vieto-Katuic languages ?[13]
- Vietic: 10 languages of Vietnam and Laos, including Muong and Vietnamese, which has the most speakers of any Austroasiatic language.
- Katuic: 19 languages of Laos, Vietnam, and Thailand.
- Khmero-Bahnaric languages
- Vieto-Katuic languages ?[13]
- Nico-Monic languages (Southern Mon–Khmer)
- Nicobarese: 6 languages of the Nicobar Islands, a territory of India.
- Asli-Monic languages
- Aslian: 19 languages of peninsular Malaysia and Thailand.
- Monic: 2 languages, the Mon language of Burma and the Nyahkur language of Thailand.
- Khmero-Vietic languages (Eastern Mon–Khmer)
- Munda languages (India)
Sidwell (2009–2015)
[edit]
Paul Sidwell (2009), in a lexicostatistical comparison of 36 languages which are well known enough to exclude loanwords, finds little evidence for internal branching, though he did find an area of increased contact between the Bahnaric and Katuic languages, such that languages of all branches apart from the geographically distant Munda and Nicobarese show greater similarity to Bahnaric and Katuic the closer they are to those branches, without any noticeable innovations common to Bahnaric and Katuic.
He therefore takes the conservative view that the thirteen branches of Austroasiatic should be treated as equidistant on current evidence. Sidwell & Blench (2011) discuss this proposal in more detail, and note that there is good evidence for a Khasi–Palaungic node, which could also possibly be closely related to Khmuic.[5]
If this would the case, Sidwell & Blench suggest that Khasic may have been an early offshoot of Palaungic that had spread westward. Sidwell & Blench (2011) suggest Shompen as an additional branch, and believe that a Vieto-Katuic connection is worth investigating. In general, however, the family is thought to have diversified too quickly for a deeply nested structure to have developed, since Proto-Austroasiatic speakers are believed by Sidwell to have radiated out from the central Mekong river valley relatively quickly.
Subsequently, Sidwell (2015a: 179)[14] proposed that Nicobarese subgroups with Aslian, just as how Khasian and Palaungic subgroup with each other.
Austroasiatic: Mon–Khmer
|
|
A subsequent computational phylogenetic analysis (Sidwell 2015b)[15] suggests that Austroasiatic branches may have a loosely nested structure rather than a completely rake-like structure, with an east–west division (consisting of Munda, Khasic, Palaungic, and Khmuic forming a western group as opposed to all of the other branches) occurring possibly as early as 7,000 years before present. However, he still considers the subbranching dubious.
Integrating computational phylogenetic linguistics with recent archaeological findings, Paul Sidwell (2015c)[16] further expanded his Mekong riverine hypothesis by proposing that Austroasiatic had ultimately expanded into Indochina from the Lingnan area of southern China, with the subsequent Mekong riverine dispersal taking place after the initial arrival of Neolithic farmers from southern China.
Sidwell (2015c) tentatively suggests that Austroasiatic may have begun to split up 5,000 years B.P. during the Neolithic transition era of mainland Southeast Asia, with all the major branches of Austroasiatic formed by 4,000 B.P. Austroasiatic would have had two possible dispersal routes from the western periphery of the Pearl River watershed of Lingnan, which would have been either a coastal route down the coast of Vietnam, or downstream through the Mekong River via Yunnan.[16] Both the reconstructed lexicon of Proto-Austroasiatic and the archaeological record clearly show that early Austroasiatic speakers around 4,000 B.P. cultivated rice and millet, kept livestock such as dogs, pigs, and chickens, and thrived mostly in estuarine rather than coastal environments.[16]
At 4,500 B.P., this "Neolithic package" suddenly arrived in Indochina from the Lingnan area without cereal grains and displaced the earlier pre-Neolithic hunter-gatherer cultures, with grain husks found in northern Indochina by 4,100 B.P. and in southern Indochina by 3,800 B.P.[16] However, Sidwell (2015c) found that iron is not reconstructable in Proto-Austroasiatic, since each Austroasiatic branch has different terms for iron that had been borrowed relatively lately from Tai, Chinese, Tibetan, Malay, and other languages.
During the Iron Age about 2,500 B.P., relatively young Austroasiatic branches in Indochina such as Vietic, Katuic, Pearic, and Khmer were formed, while the more internally diverse Bahnaric branch (dating to about 3,000 B.P.) underwent more extensive internal diversification.[16] By the Iron Age, all of the Austroasiatic branches were more or less in their present-day locations, with most of the diversification within Austroasiatic taking place during the Iron Age.[16]
Paul Sidwell (2018)[17] considers the Austroasiatic language family to have rapidly diversified around 4,000 years B.P. during the arrival of rice agriculture in Indochina, but notes that the origin of Proto-Austroasiatic itself is older than that date. The lexicon of Proto-Austroasiatic can be divided into an early and late stratum. The early stratum consists of basic lexicon including body parts, animal names, natural features, and pronouns, while the names of cultural items (agriculture terms and words for cultural artifacts, which are reconstructible in Proto-Austroasiatic) form part of the later stratum.
Roger Blench (2017)[18] suggests that vocabulary related to aquatic subsistence strategies (such as boats, waterways, river fauna, and fish capture techniques) can be reconstructed for Proto-Austroasiatic. Blench (2017) finds widespread Austroasiatic roots for 'river, valley', 'boat', 'fish', 'catfish sp.', 'eel', 'prawn', 'shrimp' (Central Austroasiatic), 'crab', 'tortoise', 'turtle', 'otter', 'crocodile', 'heron, fishing bird', and 'fish trap'. Archaeological evidence for the presence of agriculture in northern Indochina (northern Vietnam, Laos, and other nearby areas) dates back to only about 4,000 years ago (2,000 BC), with agriculture ultimately being introduced from further up to the north in the Yangtze valley where it has been dated to 6,000 B.P.[18]
Sidwell (2022)[19][20] proposes that the locus of Proto-Austroasiatic was in the Red River Delta area about 4,000-4,500 years before present, instead of the Middle Mekong as he had previously proposed. Austroasiatic dispersed coastal maritime routes and also upstream through river valleys. Khmuic, Palaungic, and Khasic resulted from a westward dispersal that ultimately came from the Red Valley valley. Based on their current distributions, about half of all Austroasiatic branches (including Nicobaric and Munda) can be traced to coastal maritime dispersals.
Hence, this points to a relatively late riverine dispersal of Austroasiatic as compared to Sino-Tibetan, whose speakers had a distinct non-riverine culture. In addition to living an aquatic-based lifestyle, early Austroasiatic speakers would have also had access to livestock, crops, and newer types of watercraft. As early Austroasiatic speakers dispersed rapidly via waterways, they would have encountered speakers of older language families who were already settled in the area, such as Sino-Tibetan.[18]
Sidwell (2018)
[edit]Sidwell (2018)[21] (quoted in Sidwell 2021[22]) gives a more nested classification of Austroasiatic branches as suggested by his computational phylogenetic analysis of Austroasiatic languages using a 200-word list. Many of the tentative groupings are likely linkages. Pakanic and Shompen were not included.
| Austroasiatic | |
Possible extinct branches
[edit]Roger Blench (2009)[23] also proposes that there might have been other primary branches of Austroasiatic that are now extinct, based on substrate evidence in modern-day languages.
- Pre-Chamic languages (the languages of coastal Vietnam before the Chamic migrations). Chamic has various Austroasiatic loanwords that cannot be clearly traced to existing Austroasiatic branches (Sidwell 2006, 2007).[24][25] Larish (1999)[26] also notes that Moklenic languages contain many Austroasiatic loanwords, some of which are similar to the ones found in Chamic.
- Acehnese substratum (Sidwell 2006).[24] Acehnese has many basic words that are of Austroasiatic origin, suggesting that either Austronesian speakers have absorbed earlier Austroasiatic residents in northern Sumatra, or that words might have been borrowed from Austroasiatic languages in southern Vietnam – or perhaps a combination of both. Sidwell (2006) argues that Acehnese and Chamic had often borrowed Austroasiatic words independently of each other, while some Austroasiatic words can be traced back to Proto-Aceh-Chamic. Sidwell (2006) accepts that Acehnese and Chamic are related, but that they had separated from each other before Chamic had borrowed most of its Austroasiatic lexicon.
- Bornean substrate languages (Blench 2010).[27] Blench cites Austroasiatic-origin words in modern-day Bornean branches such as Land Dayak (Bidayuh, Dayak Bakatiq, etc.), Dusunic (Central Dusun, Visayan, etc.), Kayan, and Kenyah, noting especially resemblances with Aslian. As further evidence for his proposal, Blench also cites ethnographic evidence such as musical instruments in Borneo shared in common with Austroasiatic-speaking groups in mainland Southeast Asia. Adelaar (1995)[28] has also noticed phonological and lexical similarities between Land Dayak and Aslian. Kaufman (2018) presents dozens of lexical comparisons showing similarities between various Bornean and Austroasiatic languages.[29]
- Lepcha substratum ("Rongic").[30] Many words of Austroasiatic origin have been noticed in Lepcha, suggesting a Sino-Tibetan superstrate laid over an Austroasiatic substrate. Blench (2013) calls this branch "Rongic" based on the Lepcha autonym Róng.
Other languages with proposed Austroasiatic substrata are:
- Jiamao, based on evidence from the register system of Jiamao, a Hlai language (Thurgood 1992).[31] Jiamao is known for its highly aberrant vocabulary in relation to other Hlai languages.
- Kerinci: van Reijn (1974)[32] notes that Kerinci, a Malayic language of central Sumatra, shares many phonological similarities with Austroasiatic languages, such as sesquisyllabic word structure and vowel inventory.
John Peterson (2017)[33] suggests that "pre-Munda" (early languages related to Proto-Munda) languages may have once dominated the eastern Indo-Gangetic Plain, and were then absorbed by Indo-Aryan languages at an early date as Indo-Aryan spread east. Peterson notes that eastern Indo-Aryan languages display many morphosyntactic features similar to those of Munda languages, while western Indo-Aryan languages do not.
Writing systems
[edit]Other than Latin-based alphabets, many Austroasiatic languages are written with the Khmer, Thai, Lao, and Burmese alphabets. Vietnamese divergently had an indigenous script based on Chinese logographic writing. This has since been supplanted by the Latin alphabet in the 20th century. The following are examples of past-used alphabets or current alphabets of Austroasiatic languages.
- Chữ Nôm[34]
- Khmer alphabet[35]
- Khom script (used for a short period in the early 20th century for indigenous languages in Laos)
- Old Mon script
- Mon script
- Pahawh Hmong was once used to write Khmu, under the name "Pahawh Khmu"
- Tai Le (Palaung, Blang)
- Tai Tham (Blang)
- Ol Chiki alphabet (Santali alphabet)[36]
- Mundari Bani (Mundari alphabet)
- Warang Citi (Ho alphabet)[37]
- Ol Onal (Bhumij alphabet)
- Sorang Sompeng alphabet (Sora alphabet)[38]
External relations
[edit]Austric languages
[edit]Austroasiatic is an integral part of the controversial Austric hypothesis, which also includes the Austronesian languages, and in some proposals also the Kra–Dai languages and the Hmong–Mien languages.[39]
Hmong-Mien
[edit]Several lexical resemblances are found between the Hmong-Mien and Austroasiatic language families (Ratliff 2010), some of which had earlier been proposed by Haudricourt (1951). This could imply a relation or early language contact along the Yangtze.[40]
According to Cai (et al. 2011), Hmong–Mien people are genetically related to Austroasiatic speakers, and their languages were heavily influenced by Sino-Tibetan, especially Tibeto-Burman languages.[41]
Indo-Aryan languages
[edit]It is suggested that the Austroasiatic languages have some influence on Indo-Aryan languages including Sanskrit and middle Indo-Aryan languages. Indian linguist Suniti Kumar Chatterji pointed that a specific number of substantives in languages such as Hindi, Punjabi and Bengali were borrowed from Munda languages. Additionally, French linguist Jean Przyluski suggested a similarity between the tales from the Austroasiatic realm and the Indian mythological stories of Matsyagandha (Satyavati from Mahabharata) and the Nāgas.[42]
Austroasiatic migrations and archaeogenetics
[edit]Mitsuru Sakitani suggests that Haplogroup O1b1, which is common in Austroasiatic people and some other ethnic groups in southern China, and haplogroup O1b2, which is common in today's Japanese and Koreans, are the carriers of early rice agriculture from southern China.[43] Another study suggests that the haplogroup O1b1 is the major Austroasiatic paternal lineage and O1b2 the "para-Austroasiatic" lineage of the Koreans and Yayoi people.[44]


A full genomic study by Lipson et al. (2018) identified a characteristic lineage that can be associated with the spread of Austroasiatic languages in Southeast Asia and which can be traced back to remains of Neolithic farmers from Mán Bạc (c. 2000 BCE) in the Red River Delta in northern Vietnam, and to closely related Ban Chiang and Vat Komnou remains in Thailand and Cambodia respectively. This Austroasiatic lineage can be modeled as a sister group of the Austronesian peoples with significant admixture (ca. 30%) from a deeply diverging eastern Eurasian source (modeled by the authors as sharing some genetic drift with the Onge, a modern Andamanese hunter-gatherer group) and which is ancestral to modern Austroasiatic-speaking groups of Southeast Asia such as the Mlabri and the Nicobarese, and partially to the Austroasiatic Munda-speaking groups of South Asia (e.g. the Juang). Significant levels of Austroasiatic ancestry were also found in Austronesian-speaking groups of Sumatra, Java, and Borneo.[45][note 3] Austroasiatic-speaking groups in southern China (such as the Wa and Blang in Yunnan) predominatly carry the same Mainland Southeast Asian Neolithic farmer ancestry, but with additional geneflow from northern and southern East Asian lineages that can be associated with the spread of Tibeto-Burman and Kra-Dai languages, respectively.[47]
Migration into India
[edit]According to Chaubey et al., "Austro-Asiatic speakers in India today are derived from dispersal from Southeast Asia, followed by extensive sex-specific admixture with local Indian populations."[48] According to Riccio et al., the Munda peoples are likely descended from Austroasiatic migrants from Southeast Asia.[49]
According to Zhang et al., Austroasiatic migrations from Southeast Asia into India took place after the Last Glacial Maximum, circa 10,000 years ago.[50] Arunkumar et al., suggest Austroasiatic migrations from Southeast Asia occurred into Northeast India 5.2 ± 0.6 kya and into East India 4.3 ± 0.2 kya.[51]
According to Tagore et al., the ancestors of present-day Austroasiatic peoples lived in diverse territories, from central India to mainland Southeast Asia. Austroasiatic Indians and Malaysians also shared common ancestry until about 10.5 kya. Around 7 kya, East Asian farmers migrated to mainland Southeast Asia and intermixed with local Austroasiatic hunter-gatherers. Continuous migration eventually led to the fragmentation and isolation of the latter. East Asian ancestry was not introduced in Austroasiatic Indians, who intermixed with locals with Ancestral South Indian ancestry.[52]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Sometimes also Austro-Asiatic or Austroasian
- ^ Earlier classifications by Sidwell had lumped Mang and Pakanic together into a Mangic subgroup, but Sidwell currently considers Mang and Pakanic to each be independent branches of Austroasiatic.
- ^ Austroasiatic-related ancestry had been detected before also in other ethnic groups of the Sunda Islands (e.g. Javanese, Sundanese, and Manggarai).[46]
References
[edit]- ^ "Austroasiatic". www.languagesgulper.com. Archived from the original on 29 March 2019. Retrieved 15 October 2017.
- ^ Bradley (2012) notes, MK in the wider sense including the Munda languages of eastern South Asia is also known as Austroasiatic.
- ^ Diffloth 2005
- ^ Sidwell 2009
- ^ a b Sidwell, Paul, and Roger Blench. 2011. "The Austroasiatic Urheimat: the Southeastern Riverine Hypothesis Archived 18 November 2017 at the Wayback Machine." Enfield, NJ (ed.) Dynamics of Human Diversity, 317–345. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics.
- ^ Schmidt, Wilhelm (1906). "Die Mon–Khmer-Völker, ein Bindeglied zwischen Völkern Zentralasiens und Austronesiens ('[The Mon–Khmer Peoples, a Link between the Peoples of Central Asia and Austronesia')". Archiv für Anthropologie. 5: 59–109.
- ^ Alves 2014, p. 524.
- ^ Alves 2014, p. 526.
- ^ Alves 2014, 2015
- ^ Diffloth, Gérard (1989). "Proto-Austroasiatic creaky voice." Archived 25 August 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sidwell (2005), p. 196.
- ^ Roger Blench, 2009. Are there four additional unrecognised branches of Austroasiatic? Presentation at ICAAL-4, Bangkok, 29–30 October. Summarized in Sidwell and Blench (2011).
- ^ a b Sidwell (2005) casts doubt on Diffloth's Vieto-Katuic hypothesis, saying that the evidence is ambiguous, and that it is not clear where Katuic belongs in the family.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2015a. "Austroasiatic classification." In Jenny, Mathias and Paul Sidwell, eds (2015). The Handbook of Austroasiatic Languages. Leiden: Brill.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2015b. A comprehensive phylogenetic analysis of the Austroasiatic languages Archived 15 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Presented at Diversity Linguistics: Retrospect and Prospect, 1–3 May 2015 (Leipzig, Germany), Closing conference of the Department of Linguistics at the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology.
- ^ a b c d e f Sidwell, Paul. 2015c. Phylogeny, innovations, and correlations in the prehistory of Austroasiatic. Paper presented at the workshop Integrating inferences about our past: new findings and current issues in the peopling of the Pacific and South East Asia, 22–23 June 2015, Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Jena, Germany.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2018. Austroasiatic deep chronology and the problem of cultural lexicon. Paper presented at the 28th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, held 17–19 May 2018 in Kaohsiung, Taiwan.
- ^ a b c Blench, Roger. 2017. Waterworld: lexical evidence for aquatic subsistence strategies in Austroasiatic Archived 14 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Presented at ICAAL 7, Kiel, Germany.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul (28 January 2022). Alves, Mark; Sidwell, Paul (eds.). "Austroasiatic Dispersal: the AA "Water-World" Extended". Journal of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society: Papers from the 30th Conference of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society (2021). 15 (3): 95–111. doi:10.5281/zenodo.5773247. ISSN 1836-6821. Archived from the original on 30 January 2022. Retrieved 14 February 2022.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2021. Austroasiatic Dispersal: the AA "Water-World" Extended Archived 17 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine. SEALS 2021 Archived 16 December 2021 at the Wayback Machine. (Video) Archived 17 February 2022 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2018. Austroasiatic deep chronology and the problem of cultural lexicon Archived 31 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine. Paper presented at the 28th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society. Kaohsiung, Taiwan. (accessed 16 December 2020).
- ^ Sidwell, Paul (9 August 2021). "Classification of MSEA Austroasiatic languages". The Languages and Linguistics of Mainland Southeast Asia. De Gruyter. pp. 179–206. doi:10.1515/9783110558142-011. ISBN 9783110558142. S2CID 242599355.
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2009. "Are there four additional unrecognised branches of Austroasiatic? Archived 3 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine."
- ^ a b Sidwell, Paul. 2006. "Dating the Separation of Acehnese and Chamic By Etymological Analysis of the Aceh-Chamic Lexicon Archived 8 November 2014 at the Wayback Machine." In The Mon-Khmer Studies, 36: 187–206.
- ^ Sidwell, Paul. 2007. "The Mon-Khmer Substrate in Chamic: Chamic, Bahnaric and Katuic Contact Archived 16 June 2015 at the Wayback Machine." In SEALS XII Papers from the 12th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society 2002, edited by Ratree Wayland et al.. Canberra, Australia, 113-128. Pacific Linguistics, Research School of Pacific and Asian Studies, The Australian National University.
- ^ Larish, Michael David. 1999. The Position of Moken and Moklen Within the Austronesian Language Family. Doctoral dissertation, University of Hawai'i at Mānoa.
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2010. "Was there an Austroasiatic Presence in Island Southeast Asia prior to the Austronesian Expansion? Archived 31 March 2023 at the Wayback Machine" In Bulletin of the Indo-Pacific Prehistory Association, Vol. 30.
- ^ Adelaar, K.A. 1995. Borneo as a cross-roads for comparative Austronesian linguistics Archived 3 July 2018 at the Wayback Machine. In P. Bellwood, J.J. Fox and D. Tryon (eds.), The Austronesians, pp. 81-102. Canberra: Australian National University.
- ^ Kaufman, Daniel. 2018. Between mainland and island Southeast Asia: Evidence for a Mon-Khmer presence in Borneo. Ronald and Janette Gatty Lecture Series. Kahin Center for Advanced Research on Southeast Asia, Cornell University. (handout Archived 18 February 2023 at the Wayback Machine / slides Archived 18 February 2023 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ Blench, Roger. 2013. Rongic: a vanished branch of Austroasiatic Archived 9 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. m.s.
- ^ Thurgood, Graham. 1992. "The aberrancy of the Jiamao dialect of Hlai: speculation on its origins and history Archived 30 January 2018 at the Wayback Machine". In Ratliff, Martha S. and Schiller, E. (eds.), Papers from the First Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society, 417–433. Arizona State University, Program for Southeast Asian Studies.
- ^ van Reijn, E. O. (1974). "Some Remarks on the Dialects of North Kerintji: A link with Mon-Khmer Languages." Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society, 31, 2: 130–138. JSTOR 41492089.
- ^ Peterson, John (2017). "The prehistorical spread of Austro-Asiatic in South Asia Archived 11 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine". Presented at ICAAL 7, Kiel, Germany.
- ^ "Vietnamese Chu Nom script". Omniglot.com. Archived from the original on 2 February 2012. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- ^ "Khmer/Cambodian alphabet, pronunciation and language". Omniglot.com. Archived from the original on 13 February 2012. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- ^ "Santali alphabet, pronunciation and language". Omniglot.com. Archived from the original on 5 November 2010. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- ^ Everson, Michael (19 April 2012). "N4259: Final proposal for encoding the Warang Citi script in the SMP of the UCS" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 20 August 2016.
- ^ "Sorang Sompeng script". Omniglot.com. 18 June 1936. Archived from the original on 27 April 2021. Retrieved 11 March 2012.
- ^ Reid, Lawrence A. (2009). "Austric Hypothesis". In Brown, Keith; Ogilvie, Sarah (eds.). Concise Encyclopaedia of Languages of the World. Oxford: Elsevier. pp. 92–94.
- ^ Haudricourt, André-Georges. 1951. Introduction à la phonologie historique des langues miao-yao Archived 22 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine [An introduction to the historical phonology of the Miao-Yao languages]. Bulletin de l'École Française d'Extrême-Orient 44(2). 555–576.
- ^ Consortium, the Genographic; Li, Hui; Jin, Li; Huang, Xingqiu; Li, Shilin; Wang, Chuanchao; Wei, Lanhai; Lu, Yan; Wang, Yi (31 August 2011). "Human Migration through Bottlenecks from Southeast Asia into East Asia during Last Glacial Maximum Revealed by Y Chromosomes". PLOS ONE. 6 (8): e24282. Bibcode:2011PLoSO...624282C. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0024282. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3164178. PMID 21904623.
- ^ Lévi, Sylvain; Przyluski, Jean; Bloch, Jules (1993). Pre-Aryan and Pre-Dravidian in India. Asian Educational Services. p. 4,15. ISBN 9788120607729. Archived from the original on 26 March 2023. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ 崎谷満『DNA・考古・言語の学際研究が示す新・日本列島史』(勉誠出版 2009年)
- ^ Robbeets, Martine; Savelyev, Alexander (21 December 2017). Language Dispersal Beyond Farming. John Benjamins Publishing Company. ISBN 9789027264640. Archived from the original on 31 March 2023. Retrieved 15 October 2020.
- ^ Lipson M, Cheronet O, Mallick S, Rohland N, Oxenham M, Pietrusewsky M, et al. (2018). "Ancient genomes document multiple waves of migration in Southeast Asian prehistory". Science. 361 (6397): 92–95. Bibcode:2018Sci...361...92L. doi:10.1126/science.aat3188. PMC 6476732. PMID 29773666.
- ^ Lipson, Mark; Loh, Po-Ru; Patterson, Nick; Moorjani, Priya; Ko, Ying-Chin; Stoneking, Mark; Berger, Bonnie; Reich, David (19 August 2014). "Reconstructing Austronesian population history in Island Southeast Asia". Nature Communications. 5: 4689. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5.4689L. doi:10.1038/ncomms5689. PMC 4143916. PMID 25137359.
- ^ Guo, Jianxin; Wang, Weitao; Zhao, Kai; Li, Guangxing; He, Guanglin; Zhao, Jing; Yang, Xiaomin; Chen, Jinwen; Zhu, Kongyang; Wang, Rui; Ma, Hao (2022). "Genomic insights into Neolithic farming-related migrations in the junction of east and southeast Asia". American Journal of Biological Anthropology. 177 (2): 328–342. doi:10.1002/ajpa.24434. ISSN 2692-7691. S2CID 244155341. Archived from the original on 5 January 2022. Retrieved 5 January 2022.
In our study, we found the sharing of a large amount of ancestry (>50%) among the Vietnam Late Neolithic ancients, Wa_L and Blang_X, indicating the Yunnan Austroasiatic populations had been influenced both linguistically and genetically by the expansion of Austroasiatic groups from mainland SEA.
- ^ Chaubey et al. 2010, p. 1013.
- ^ Riccio, M. E.; et al. (2011). "The Austroasiatic Munda population from India and Its enigmatic origin: a HLA diversity study". Human Biology. 83 (3): 405–435. doi:10.3378/027.083.0306. JSTOR 41466748. PMID 21740156. S2CID 39428816.
- ^ Zhang 2015.
- ^ Arunkumar, G.; et al. (2015). "A late Neolithic expansion of Y chromosomal haplogroup O2a1-M95 from east to west". Journal of Systematics and Evolution. 53 (6): 546–560. doi:10.1111/jse.12147. S2CID 83103649.
- ^ Tagore, Debashree; Aghakhanian, Farhang; Naidu, Rakesh; Phipps, Maude E.; Basu, Analabha (2021). "Insights into the demographic history of Asia from common ancestry and admixture in the genomic landscape of present-day Austroasiatic speakers". BMC Biology. 19 (61) – via BMC.
Sources
[edit]- Adams, K. L. (1989). Systems of numeral classification in the Mon–Khmer, Nicobarese and Aslian subfamilies of Austroasiatic. Canberra, A.C.T., Australia: Dept. of Linguistics, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0-85883-373-5
- Alves, Mark J. (2014). "Mon-Khmer". In Rochelle Lieber; Pavel Stekauer (eds.). The Oxford Handbook of Derivational Morphology. Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 520–544.
- Alves, Mark J. (2015). Morphological functions among Mon-Khmer languages: beyond the basics. In N. J. Enfield & Bernard Comrie (eds.), Languages of Mainland Southeast Asia: the state of the art. Berlin: de Gruyter Mouton, 531–557.
- Bradley, David (2012). "Languages and Language Families in China Archived 30 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine", in Rint Sybesma (ed.), Encyclopedia of Chinese Language and Linguistics.
- Chakrabarti, Byomkes. (1994). A Comparative Study of Santali and Bengali.
- Chaubey, G.; et al. (2010). "Population Genetic Structure in Indian Austroasiatic Speakers: The Role of Landscape Barriers and Sex-Specific Admixture". Mol Biol Evol. 28 (2): 1013–1024. doi:10.1093/molbev/msq288. PMC 3355372. PMID 20978040.
- Diffloth, Gérard. (2005). "The contribution of linguistic palaeontology and Austro-Asiatic". in Laurent Sagart, Roger Blench and Alicia Sanchez-Mazas, eds. The Peopling of East Asia: Putting Together Archaeology, Linguistics and Genetics. 77–80. London: Routledge Curzon. ISBN 0-415-32242-1
- Filbeck, D. (1978). T'in: a historical study. Pacific linguistics, no. 49. Canberra: Dept. of Linguistics, Research School of Pacific Studies, Australian National University. ISBN 0-85883-172-4
- Hemeling, K. (1907). Die Nanking Kuanhua. (German language)
- Jenny, Mathias and Paul Sidwell, eds (2015). The Handbook of Austroasiatic Languages Archived 5 March 2015 at the Wayback Machine. Leiden: Brill.
- Peck, B. M., Comp. (1988). An Enumerative Bibliography of South Asian Language Dictionaries.
- Peiros, Ilia. 1998. Comparative Linguistics in Southeast Asia. Pacific Linguistics Series C, No. 142. Canberra: Australian National University.
- Shorto, Harry L. edited by Sidwell, Paul, Cooper, Doug and Bauer, Christian (2006). A Mon–Khmer comparative dictionary Archived 9 August 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Canberra: Australian National University. Pacific Linguistics. ISBN 0-85883-570-3
- Shorto, H. L. Bibliographies of Mon–Khmer and Tai Linguistics. London oriental bibliographies, v. 2. London: Oxford University Press, 1963.
- Sidwell, Paul (2005). "Proto-Katuic Phonology and the Sub-grouping of Mon–Khmer Languages" (PDF). In Paul Sidwell (ed.). SEALSXV: papers from the 15th meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistic Society. Canberra: Pacific Linguistics. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022. Retrieved 11 March 2020.
- Sidwell, Paul (2009). Classifying the Austroasiatic languages: history and state of the art. LINCOM studies in Asian linguistics. Vol. 76. Munich: Lincom Europa. ISBN 978-3-929075-67-0.[permanent dead link]
- Sidwell, Paul (2010). "The Austroasiatic central riverine hypothesis" (PDF). Journal of Language Relationship. 4: 117–134. Archived (PDF) from the original on 30 January 2022. Retrieved 28 October 2011.
- van Driem, George. (2007). Austroasiatic phylogeny and the Austroasiatic homeland in light of recent population genetic studies. Mon-Khmer Studies, 37, 1–14.
- Zide, Norman H., and Milton E. Barker. (1966) Studies in Comparative Austroasiatic Linguistics, The Hague: Mouton (Indo-Iranian monographs, v. 5.).
- Zhang; et al. (2015). "Y-chromosome diversity suggests southern origin and Paleolithic backwave migration of Austro-Asiatic speakers from eastern Asia to the Indian subcontinent". Scientific Reports. 5: 1548. Bibcode:2015NatSR...515486Z. doi:10.1038/srep15486. PMC 4611482. PMID 26482917.
Further reading
[edit]- Sidwell, Paul; Jenny, Mathias, eds. (2021). The Languages and Linguistics of Mainland Southeast Asia (PDF). De Gruyter. doi:10.1515/9783110558142. hdl:2262/97064. ISBN 978-3-11-055814-2. S2CID 242359233. Archived (PDF) from the original on 9 October 2022.
- Mann, Noel, Wendy Smith and Eva Ujlakyova. 2009. Linguistic clusters of Mainland Southeast Asia: an overview of the language families. Archived 24 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine Chiang Mai: Payap University.
- Mason, Francis (1854). "The Talaing Language". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 4: 277, 279–288. JSTOR 592280.
- Sidwell, Paul (2013). "Issues in Austroasiatic Classification". Language and Linguistics Compass. 7 (8): 437–457. doi:10.1111/lnc3.12038.
- Sidwell, Paul. 2016. Bibliography of Austroasiatic linguistics and related resources Archived 24 March 2019 at the Wayback Machine.
- E. K. Brown (ed.) Encyclopedia of Languages and Linguistics. Oxford: Elsevier Press.
- Gregory D. S. Anderson and Norman H. Zide. 2002. Issues in Proto-Munda and Proto-Austroasiatic Nominal Derivation: The Bimoraic Constraint. In Marlys A. Macken (ed.) Papers from the 10th Annual Meeting of the Southeast Asian Linguistics Society. Tempe, AZ: Arizona State University, South East Asian Studies Program, Monograph Series Press. pp. 55–74.
External links
[edit]- Swadesh lists for Austro-Asiatic languages (from Wiktionary's Swadesh-list appendix)
- Mon–Khmer.com Lectures by Paul Sidwell
- Mon–Khmer Languages Project at SEAlang
- Munda Languages Project at SEAlang
- RWAAI (Repository and Workspace for Austroasiatic Intangible Heritage)
- RWAAI Digital Archive
- Michel Ferlus's recordings of Mon-Khmer (Austroasiatic) languages Archived 9 February 2019 at the Wayback Machine (CNRS)
