Ahyi Seamount
| Ahyi Seamount | |
|---|---|
 Bathymetry map of Ahyi | |
 | |
| Summit depth | −75 m (−246 ft)[1] |
| Height | ~1,925 m (6,316 ft) |
| Location | |
| Range | Izu–Bonin–Mariana Arc |
| Coordinates | 20°25′12″N 145°01′48″E / 20.42000°N 145.03000°E[1] |
| Country | Northern Mariana Islands, United States |
| Geology | |
| Type | Stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | 2024 |
Ahyi Seamount is an active shallow submarine volcano in the Northern Mariana Islands, in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. It has erupted 5 times since the year 2000; in 2001, 2014, 2022–23, and twice in 2024.[1] Since 2009, it has been a part of Marianas Trench Marine National Monument of the United States.
Geography
[edit]
Ahyi is a submarine volcano which can be found in the northern portion of the Mariana Arc. The structure of the volcano consists of a 12 km (7 mi)-wide stratovolcanic cone that rises from around 2,000 m (6,562 ft) depth to 75 m (246 ft). It can be found 20 km (12 mi) southeast of Farallon de Pajaros.[2] Nearby seamounts include Makhahnas Seamount 19 km (12 mi) to the west and Supply Reef 33 km (21 mi) to the south.[3]
Geologic setting
[edit]The Ahyi Seamount can be found on the Mariana Arc, which is an arc of volcanoes of submarine origin which occurs as a result of subduction of the Pacific Plate lithosphere under the Philippine Sea Plate. The chain can be found west of the Mariana Trench where the Pacific Plate subducts through and east of the Mariana Trough, which is a back-arc basin.[4] Since the 1800s, 6 of the 9 volcanic islands in the Mariana Arc have had recorded activity. Other than islands, around 60 seamounts can be found in the arc and more than 20 of them have hydrothermal venting and 6 of them have had a recorded eruption.[3]
Petrology
[edit]During the 2014 eruption, several samples of plumes from Ahyi were collected. As a result, enriched concentrations of H2, 3He, CO2 and Fe were found in a laboratory analysis.[5][6]
Activity
[edit]Multiple occurrences of volcanic activity have been detected at the Ahyi-Supply Reef region since the 1960s. Most observations of activity have come from hydrophone recordings or seismograph recordings with very large location uncertainty which makes it unable to be assigned to a specific seamount. In other cases, observations came from direct observations at the location like discolored water on the sea surface.[1][3]
1960–70s activity
[edit]In 1969, seismic and hydrophone detections from far away of volcanic explosions from Ahyi were recorded; although the discolored water was seen a bit farther away from Ahyi, right in between Supply Reef and Ahyi. This activity in 1969 was described as similar to hydrophone recordings in the same region in 1967. In 1979, a fishing boat reported upwelling water and pumice with sulfur composition near Ahyi.[3]
2014 eruption
[edit]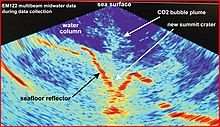
In late April 2014, Ahyi erupted, ending a 13-year dormancy period with an explosive eruption which lasted more than 2 weeks. At the time of the eruption, the remote location of the volcano and the presence of nearby volcanoes made it hard to understand the actual location of the eruption. The explosions were recorded by hydrophones in the region including in Wake Island and by seismographs including in Guam and Chichijima. Following May 8, acoustic waves from the events were observed until May 17. During the eruption, NOAA research divers and researchers on a ship near Farallon de Pajaros, around 20 km (12 mi) away from Ahyi, reported hearing explosions. In the same area, the NOAA crew observed orange-yellow bubbles covering parts of the sea surface. Despite these observations, satellite products did not show anything unusual throughout the whole eruption. During mid-May, an expedition on a NOAA ship which was planned to pass around the Ahyi eruption area was able to collect some samples and information about the eruption. Multibeam bathymetries were obtained at the same expedition. Comparison between 2003 and 2014 bathymetry proved that the summit depth of Ahyi had changed from 60 m (197 ft) in 2003 to 75 m (246 ft) in 2014. The bathymetry differences also revealed a new 95 m (312 ft) deep crater formed at the summit. South-southeast of the crater was a landslide trail towards the downslope with a deepest point of 2,300 m (7,546 ft). Plume particles were observed at three CTD casts of Ahyi.[7]
2022–23 eruption
[edit]The eruption had been occurring since November 18, 2022, until due to the lack of evidence of unrest, the aviation color code for Ahyi was reduced to unassigned in April 26, 2023 and the eruption was declared over. In May 23rd, Ahyi was declared erupting again, having its aviation color code increased to Yellow and volcano alert level to Advisory.[1]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e "Ahyi". Global Volcanism Program. Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved January 25, 2023.
- ^ Metz & Grevemeyer 2018, p. 11050.
- ^ a b c d Tepp et al. 2019, p. 3610.
- ^ Tepp et al. 2019, p. 3609.
- ^ Buck et al. 2018, p. 1668.
- ^ Neuholz et al. 2020, p. 21.
- ^ Haney et al. 2014, p. 1.
Sources
[edit]- Tepp, G.; Chadwick Jr., W. W.; Haney, M. M.; Lyons, J. J.; Dziak, R. P.; Merle, S. G.; Butterfield, D. A.; Young, C. W. (2019). "Hydroacoustic, Seismic, and Bathymetric Observations of the 2014 Submarine Eruption at Ahyi Seamount, Mariana Arc". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 20 (7): 3608–3627. Bibcode:2019GGG....20.3608T. doi:10.1029/2019GC008311. S2CID 198407967.
- Metz, D.; Grevemeyer, I. (2018). "Hydroacoustic Measurements of the 2014 Eruption at Ahyi Volcano, 20.4°N Mariana Arc". Geophysical Research Letters. 45 (20): 11, 050–11, 058. Bibcode:2018GeoRL..4511050M. doi:10.1029/2018GL079983. S2CID 134160489.
- Buck, N. J.; Resing, J. A.; Baker, E. T.; Lupton, J. E. (2018). "Chemical Fluxes From a Recently Erupted Shallow Submarine Volcano on the Mariana Arc". Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems. 19 (5): 1660–1673. Bibcode:2018GGG....19.1660B. doi:10.1029/2018GC007470. S2CID 134737270.
- Neuholz, R.; Kleint, C.; Schnetger, B.; Koschinsky, A.; Laan, P.; Middag, R.; Sander, S.; Thal, J.; Turke, A.; Walter, M.; Zitoun, R.; Brumsack, H-J. (2020). "Submarine Hydrothermal Discharge and Fluxes of Dissolved Fe and Mn, and He Isotopes at Brothers Volcano Based on Radium Isotopes". Minerals. 10 (11): 0–31. Bibcode:2020Mine...10..969N. doi:10.3390/min10110969.
- Haney, M. M.; Chadwick Jr., W. W.; Merle, S. G; Buck, N. J.; Butterfield, D. A.; Coombs, M. L.; Evers, L. G.; Heaney, K. D.; Lyons, J. J.; Searcy, C. K.; Walker, S. L.; Young, C.; Embley, R. W. (2014). "The 2014 Submarine eruption of Ahyi volcano, northern Mariana Islands". AGU Fall Meeting 2014. 1 (1). Bibcode:2014AGUFM.V11B4727H.
