15.ai
Type of site | Artificial intelligence, speech synthesis, generative artificial intelligence |
|---|---|
| Available in | English |
| Founder(s) | 15 |
| URL | 15 |
| Commercial | No |
| Registration | None |
| Launched | March 2020 |
| Current status | Inactive |
15.ai was a free non-commercial web application that used artificial intelligence to generate text-to-speech voices of fictional characters from popular media.[1] Created by an artificial intelligence researcher known as 15 during their time at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the application allowed users to make characters from video games, television shows, and movies speak custom text with emotional inflections faster than real-time.[a][2] The platform was notable for its ability to generate convincing voice output using minimal training data—the name "15.ai" referenced the creator's claim that a voice could be cloned with just 15 seconds of audio. It was an early example of an application of generative artificial intelligence during the initial stages of the AI boom.
Launched in March 2020,[3] 15.ai gained widespread attention in early 2021 when it went viral on social media platforms like YouTube and Twitter, and quickly became popular among Internet fandoms, including the My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic, Team Fortress 2, and SpongeBob SquarePants fandoms.[4][5] The service distinguished itself through its support for emotional context in speech generation through emojis and precise pronunciation control through phonetic transcriptions. 15.ai is credited as the first mainstream platform to popularize AI voice cloning (audio deepfakes) in memes and content creation.[6]
15.ai's approach to data-efficient voice synthesis and emotional expression was influential in subsequent developments in AI text-to-speech technology. In January 2022, Voiceverse NFT sparked controversy when it was discovered that the company, which had partnered with voice actor Troy Baker, had misappropriated 15.ai's work for their own platform. The service was ultimately taken offline in September 2022. Its shutdown led to the emergence of various commercial alternatives in subsequent years.
History
[edit]Background
[edit]
The field of artificial speech synthesis underwent a significant transformation with the introduction of deep learning approaches.[7] In 2016, DeepMind's publication of the seminal paper WaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio marked a pivotal shift toward neural network-based speech synthesis, demonstrating unprecedented audio quality through direct waveform modeling. WaveNet achieved this through dilated causal convolutions operating directly on raw audio waveforms at 16,000 samples per second, modeling the conditional probability distribution of each audio sample given all previous ones. Previously, concatenative synthesis–which worked by stitching together pre-recorded segments of human speech–was the predominant method for generating artificial speech, but it often produced robotic-sounding results with noticeable artifacts at the segment boundaries.[8]
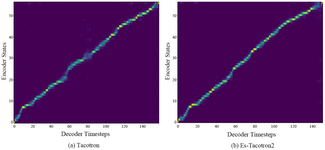
Two years later, this was followed by Google AI's Tacotron in 2018, which demonstrated that neural networks could produce highly natural speech synthesis but required substantial training data—typically tens of hours of audio—to achieve acceptable quality. Tacotron employed an encoder-decoder architecture with attention mechanisms to convert input text into mel-spectrograms, which were then converted to waveforms using a separate neural vocoder. When trained on smaller datasets, such as 2 hours of speech, the output quality degraded while still being able to maintain intelligible speech, and with just 24 minutes of training data, Tacotron failed to produce intelligible speech.[9]
In 2019, Microsoft Research introduced FastSpeech, which addressed speed limitations in autoregressive models like Tacotron.[10] FastSpeech utilized a non-autoregressive architecture that enabled parallel sequence generation, significantly reducing inference time while maintaining audio quality. Its feedforward transformer network with length regulation allowed for one-shot prediction of the full mel-spectrogram sequence, avoiding the sequential dependencies that bottlenecked previous approaches.[11] The same year saw the emergence of HiFi-GAN, a generative adversarial network (GAN)-based vocoder that improved the efficiency of waveform generation while producing high-fidelity speech.[12] This was followed by Glow-TTS, which introduced a flow-based approach that allowed for both fast inference and voice style transfer capabilities.[13]
Chinese tech companies also made significant contributions to the field.[14] Baidu and ByteDance developed proprietary text-to-speech frameworks that further advanced the state of the art, though specific technical details of their implementations remained largely undisclosed.[14]
Development, release, and operation
[edit][...] The website has multiple purposes. It serves as a proof of concept of a platform that allows anyone to create content, even if they can't hire someone to voice their projects.
It also demonstrates the progress of my research in a far more engaging manner - by being able to use the actual model, you can discover things about it that even I wasn't aware of (such as getting characters to make gasping noises or moans by placing commas in between certain phonemes).
It also doesn't let me get away with picking and choosing the best results and showing off only the ones that work [...] Being able to interact with the model with no filter allows the user to judge exactly how good the current work is at face value.
15.ai was conceived in 2016 as a research project in deep learning speech synthesis by a developer known as "15" (at the age of 18[16]) during their freshman year at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT)[17] as part of MIT's Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program (UROP).[18] The developer was inspired by DeepMind's WaveNet paper, with development continuing through their studies as Google AI released Tacotron the following year. By 2019, the developer had demonstrated at MIT their ability to replicate WaveNet and Tacotron's results using 75% less training data than previously required.[14] The name 15 is a reference to the creator's claim that a voice can be cloned with as little as 15 seconds of data.[19]
The developer had originally planned to pursue a doctorate based on their undergraduate research, but opted to work in the tech industry instead after their startup was accepted into the Y Combinator accelerator in 2019. After their departure in early 2020, the developer returned to their voice synthesis research, implementing it as a web application. According to the developer, instead of using conventional voice datasets like LJSpeech that contained simple, monotone recordings, they sought out more challenging voice samples that could demonstrate the model's ability to handle complex speech patterns and emotional undertones.[16] The Pony Preservation Project—a fan initiative originating from /mlp/,[14] 4chan's My Little Pony board, that had compiled voice clips from My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic—played a crucial role in the implementation. The project's contributors had manually trimmed, denoised, transcribed, and emotion-tagged every line from the show. This dataset provided ideal training material for 15.ai's deep learning model.[14][16]
15.ai was released in March 2020 with a limited selection of characters, including those from My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic and Team Fortress 2.[3][20] More voices were added to the website in the following months.[21] A significant technical advancement came in late 2020 with the implementation of a multi-speaker embedding in the deep neural network, enabling simultaneous training of multiple voices rather than requiring individual models for each character voice.[14] This not only allowed rapid expansion from eight to over fifty character voices,[16] but also let the model recognize common emotional patterns across characters, even when certain emotions were missing from some characters' training data.[22]
In early 2021, the application went viral on Twitter and YouTube, with people generating skits, memes, and fan content using voices from popular games and shows that have accumulated millions of views on social media.[23] Content creators, YouTubers, and TikTokers have also used 15.ai as part of their videos as voiceovers.[24][unreliable source?] At its peak, the platform incurred operational costs of US$12,000[14] per month from AWS infrastructure needed to handle millions of daily voice generations; despite receiving offers from companies to acquire 15.ai and its underlying technology, the website remained independent and was funded out of the personal previous startup earnings of the developer[14]—then aged 23 at the time.[16]
Voiceverse NFT controversy
[edit]
Troy Baker @TroyBakerVAI'm partnering with @VoiceverseNFT to explore ways where together we might bring new tools to new creators to make new things, and allow everyone a chance to own & invest in the IP's they create. We all have a story to tell. You can hate. Or you can create. What'll it be?
January 14, 2022[25]
On January 14, 2022, a controversy ensued after it was discovered that Voiceverse NFT, a company that video game and anime dub voice actor Troy Baker had announced his partnership with, had misappropriated voice lines generated from 15.ai as part of their marketing campaign.[26] This came shortly after 15.ai's developer had explicitly stated in December 2021 that they had no interest in incorporating NFTs into their work.[27] Log files showed that Voiceverse had generated audio of characters from My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic using 15.ai, pitched them up to make them sound unrecognizable from the original voices to market their own platform—in violation of 15.ai's terms of service.[28]
Voiceverse claimed that someone in their marketing team used the voice without properly crediting 15.ai; in response, 15 tweeted "Go fuck yourself,"[29] which went viral, amassing hundreds of thousands of retweets and likes on Twitter in support of the developer.[14] Following continued backlash and the plagiarism revelation, Baker acknowledged that his original announcement tweet ending with "You can hate. Or you can create. What'll it be?" may have been "antagonistic," and on January 31, 2022, announced he would discontinue his partnership with Voiceverse.[30]
Inactivity
[edit]In September 2022, 15.ai was taken offline[31] due to legal issues surrounding artificial intelligence and copyright.[14] The creator has suggested a potential future version that would better address copyright concerns from the outset, though the website remains inactive as of 2025.[14]
Features
[edit]The platform was non-commercial,[32] and operated without requiring user registration or accounts.[33] Users generated speech by inputting text and selecting a character voice, with optional parameters for emotional contextualizers and phonetic transcriptions. Each request produced three audio variations with distinct emotional deliveries sorted by confidence score.[34] Characters available included multiple characters from Team Fortress 2 and My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic; GLaDOS, Wheatley, and the Sentry Turret from the Portal series; SpongeBob SquarePants; Kyu Sugardust from HuniePop, Rise Kujikawa from Persona 4; Daria Morgendorffer and Jane Lane from Daria; Carl Brutananadilewski from Aqua Teen Hunger Force; Steven Universe from Steven Universe; Sans from Undertale; Madeline and multiple characters from Celeste; the Tenth Doctor Who; the Narrator from The Stanley Parable; and HAL 9000 from 2001: A Space Odyssey.[35] Out of the over fifty[16] voices available, thirty were of characters from My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic.[36] Certain "silent" characters like Chell and Gordon Freeman were able to be selected as a joke, and would emit silent audio files when any text was submitted.[37]
The deep learning model's nondeterministic properties produced variations in speech output, creating different intonations with each generation, similar to how voice actors produce different takes.[39] 15.ai introduced the concept of emotional contextualizers, which allowed users to specify the emotional tone of generated speech through guiding phrases.[14] The emotional contextualizer functionality utilized DeepMoji, a sentiment analysis neural network developed at the MIT Media Lab.[40] Introduced in 2017, DeepMoji processed emoji embeddings from 1.2 billion Twitter posts (from 2013 to 2017) to analyze emotional content. Testing showed the system could identify emotional elements, including sarcasm, more accurately than human evaluators.[41] If an input into 15.ai contained additional context (specified by a vertical bar), the additional context following the bar would be used as the emotional contextualizer.[18] For example, if the input was Today is a great day!|I'm very sad., the selected character would speak the sentence "Today is a great day!" in the emotion one would expect from someone saying the sentence "I'm very sad."[18]
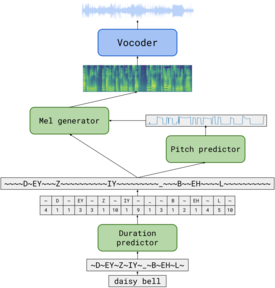
The application used pronunciation data from Oxford Dictionaries API, Wiktionary, and CMU Pronouncing Dictionary,[42] the last of which is based on ARPABET, a set of English phonetic transcriptions originally developed by the Advanced Research Projects Agency in the 1970s. For modern and Internet-specific terminology, the system incorporated pronunciation data from user-generated content websites, including Reddit, Urban Dictionary, 4chan, and Google.[42] Inputting ARPABET transcriptions was also supported, allowing users to correct mispronunciations or specify the desired pronunciation between heteronyms—words that have the same spelling but have different pronunciations. Users could invoke ARPABET transcriptions by enclosing the phoneme string in curly braces within the input box (for example, {AA1 R P AH0 B EH2 T} to specify the pronunciation of the word "ARPABET" (/ˈɑːrpəˌbɛt/ AR-pə-beht).[22] The interface displayed parsed words with color-coding to indicate pronunciation certainty: green for words found in the existing pronunciation lookup table, blue for manually entered ARPABET pronunciations, and red for words where the pronunciation had to be algorithmically predicted.[43]
Later versions of 15.ai introduced multi-speaker capabilities. Rather than training separate models for each voice, 15.ai used a unified model that learned multiple voices simultaneously through speaker embeddings–learned numerical representations that captured each character's unique vocal characteristics.[14][16] Along with the emotional context conferred by DeepMoji, this neural network architecture enabled the model to learn shared patterns across different characters' emotional expressions and speaking styles, even when individual characters lacked examples of certain emotional contexts in their training data.[22]
The interface included technical metrics and graphs,[38] which, according to the developer, served to highlight the research aspect of the website.[16] As of version v23, released in September 2021, the interface displayed comprehensive model analysis information, including word parsing results and emotional analysis data. The flow and generative adversarial network (GAN) hybrid vocoder and denoiser, introduced in an earlier version, was streamlined to remove manual parameter inputs.[38]
Reception
[edit]Critical reception
[edit]Critics described 15.ai as easy to use and generally able to convincingly replicate character voices, with occasional mixed results.[44] Natalie Clayton of PC Gamer wrote that SpongeBob SquarePants' voice was replicated well, but noted challenges in mimicking the Narrator from the The Stanley Parable: "the algorithm simply can't capture Kevan Brighting's whimsically droll intonation."[45] Zack Zwiezen of Kotaku reported that "[his] girlfriend was convinced it was a new voice line from GLaDOS' voice actor, Ellen McLain".[46] Rionaldi Chandraseta of AI newsletter Towards Data Science observed that "characters with large training data produce more natural dialogues with clearer inflections and pauses between words, especially for longer sentences."[18] Taiwanese newspaper United Daily News also highlighted 15.ai's ability to recreate GLaDOS's mechanical voice, alongside its diverse range of character voice options.[47] Yahoo! News Taiwan reported that "GLaDOS in Portal can pronounce lines nearly perfectly", but also criticized that "there are still many imperfections, such as word limit and tone control, which are still a little weird in some words."[48] Chris Button of AI newsletter Byteside called the ability to clone a voice with only 15 seconds of data "freaky" but also called tech behind it "impressive".[49] The platform's voice generation capabilities were regularly featured on Equestria Daily, a fandom news site dedicated to the show My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic and its other generations, with documented updates, fan creations, and additions of new character voices.[50] In a post introducing new character additions to 15.ai, Equestria Daily's founder Shaun Scotellaro—also known by his online moniker "Sethisto"—wrote that "some of [the voices] aren't great due to the lack of samples to draw from, but many are really impressive still anyway."[36]
Multiple other critics also found the word count limit, prosody options, and English-only nature of the application as not entirely satisfactory.[5][48] Peter Paltridge of anime and superhero news outlet Anime Superhero News opined that "voice synthesis has evolved to the point where the more expensive efforts are nearly indistinguishable from actual human speech," but also noted that "In some ways, SAM is still more advanced than this. It was possible to affect SAM’s inflections by using special characters, as well as change his pitch at will. With 15.ai, you’re at the mercy of whatever random inflections you get."[51] Conversely, Lauren Morton of Rock, Paper, Shotgun praised the depth of pronunciation control—"if you're willing to get into the nitty gritty of it".[52] Similarly, Eugenio Moto of Spanish news website Qore.com wrote that "the most experienced [users] can change parameters like the stress or the tone."[53] Takayuki Furushima of Den Fami Nico Gamer highlighted the "smooth pronunciations", and Yuki Kurosawa of AUTOMATON noted its "rich emotional expression" as a major feature; both Japanese authors noted the lack of Japanese-language support.[54][42] Renan do Prado of the Brazilian gaming news outlet Arkade and José Villalobos of Spanish gaming outlet LaPS4 pointed out that while users could create amusing results in Portuguese and Spanish respectively, the generation performed best in English.[55] Chinese gaming news outlet GamerSky called the app "interesting", but also criticized the word count limit of the text and the lack of intonations.[5] South Korean video game outlet Zuntata wrote that "the surprising thing about 15.ai is that [for some characters], there's only about 30 seconds of data, but it achieves pronunciation accuracy close to 100%".[56] Machine learning professor Yongqiang Li wrote in his blog that he was surprised to see that the application was free.[57]
Ethical concerns
[edit]Voice actors had mixed reactions to 15.ai's capabilities. While some industry professionals acknowledged the technical innovation, others raised concerns about the technology's implications for their profession.[58] When voice actor Troy Baker announced his partnership with Voiceverse NFT, which had misappropriated 15.ai's technology, it sparked widespread controversy within the voice acting industry.[59] Critics raised concerns about automated voice acting's potential reduction of employment opportunities for voice actors, risk of voice impersonation, and potential misuse in explicit content.[60] The controversy surrounding Voiceverse NFT and subsequent discussions highlighted broader industry concerns about AI voice synthesis technology.[61]
While 15.ai limited its scope to fictional characters and did not reproduce voices of real people or celebrities,[62] computer scientist Andrew Ng noted that similar technology could be used to do so, including for nefarious purposes.[3] In his 2020 assessment of 15.ai, he wrote:
"Voice cloning could be enormously productive. In Hollywood, it could revolutionize the use of virtual actors. In cartoons and audiobooks, it could enable voice actors to participate in many more productions. In online education, kids might pay more attention to lessons delivered by the voices of favorite personalities. And how many YouTube how-to video producers would love to have a synthetic Morgan Freeman narrate their scripts?
However, he also wrote:
"...but synthesizing a human actor's voice without consent is arguably unethical and possibly illegal. And this technology will be catnip for deepfakers, who could scrape recordings from social networks to impersonate private individuals."[3]
Legacy
[edit]15.ai was an early pioneer of audio deepfakes, leading to the emergence of AI speech synthesis-based memes during the initial stages of the AI boom in 2020.[63][64] 15.ai is credited as the first mainstream platform to popularize AI voice cloning in Internet memes and content creation, particularly through its ability to generate convincing character voices in real-time without requiring extensive technical expertise.[65] The platform's impact was especially notable in fan communities, including the My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic, Portal, Team Fortress 2, and SpongeBob SquarePants fandoms, where it enabled the creation of viral content that garnered millions of views across social media platforms like Twitter and YouTube.[66] Team Fortress 2 content creators also used the platform to produce both short-form memes and complex narrative animations using Source Filmmaker.[67] Fan creations included skits and new fan animations,[68] crossover content—such as Game Informer writer Liana Ruppert's demonstration combining Portal and Mass Effect dialogue in her coverage of the platform[69]—recreations of viral videos (including the infamous Big Bill Hell's Cars car dealership parody[70]), adaptations of fanfiction using AI-generated character voices,[71] music videos and new musical compositions—such as the explicit Pony Zone series[72]—and content where characters recited sea shanties.[73] Some fan creations gained mainstream attention, such as a viral edit replacing Donald Trump's cameo in Home Alone 2: Lost in New York with the Heavy Weapons Guy's AI-generated voice, which was featured on a daytime CNN segment in January 2021.[74][75] Some users integrated 15.ai's voice synthesis with VoiceAttack, a voice command software, to create personal assistants.[39]
Its influence has been noted in the years after it became defunct,[76] with several commercial alternatives emerging to fill the void, such as ElevenLabs[b] and Speechify.[31] Contemporary generative voice AI companies have acknowledged 15.ai's pioneering role. PlayHT called the debut of 15.ai "a breakthrough in the field of text-to-speech (TTS) and speech synthesis".[24] Cliff Weitzman, the founder and CEO of Speechify, credited 15.ai for "making AI voice cloning popular for content creation by being the first [...] to feature popular existing characters from fandoms".[78]
Prior to its shutdown, 15.ai established several technical precedents that influenced subsequent developments in AI voice synthesis. Its integration of DeepMoji for emotional analysis demonstrated the viability of incorporating sentiment-aware speech generation, while its support for ARPABET phonetic transcriptions set a standard for precise pronunciation control in public-facing voice synthesis tools.[14] The platform's unified multi-speaker model, which enabled simultaneous training of diverse character voices, proved particularly influential. This approach allowed the system to recognize emotional patterns across different voices even when certain emotions were absent from individual character training sets; for example, if one character had examples of joyful speech but no angry examples, while another had angry but no joyful samples, the system could learn to generate both emotions for both characters by understanding the common patterns of how emotions affect speech.[22]
15.ai also made a key contribution in reducing training data requirements for speech synthesis. Earlier systems like Google AI's Tacotron and Microsoft Research's FastSpeech required tens of hours of audio to produce acceptable results and failed to generate intelligible speech with less than 24 minutes of training data.[9][11] In contrast, 15.ai demonstrated the ability to generate speech with substantially less training data—specifically, the name "15.ai" refers to the creator's claim that a voice could be cloned with just 15 seconds of data.[79] This approach to data efficiency influenced subsequent developments in AI voice synthesis technology, as the 15-second benchmark became a reference point for subsequent voice synthesis systems. The original claim that only 15 seconds of data is required to clone a human's voice was corroborated by OpenAI in 2024.[80]
See also
[edit]- AI boom
- Character.ai
- Deepfake
- Ethics of artificial intelligence
- WaveNet
- My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic fandom
Explanatory footnotes
[edit]- ^ The term "faster than real-time" in speech synthesis means that the system can generate audio more quickly than the actual duration of the speech—for example, generating 10 seconds of speech in less than 10 seconds would be considered faster than real-time.
- ^ which uses "11.ai" as a legal byname for its web domain[77]
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ 遊戲 2021; Yoshiyuki 2021.
- ^ Kurosawa 2021; Ruppert 2021; Clayton 2021; Morton 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ a b c d Ng 2020.
- ^ Zwiezen 2021; Chandraseta 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ a b c GamerSky 2021.
- ^ Speechify 2024; Temitope 2024; Anirudh VK 2023; Wright 2023.
- ^ Barakat 2024.
- ^ van den Oord 2016.
- ^ a b Google 2018
- ^ Ren 2019; Temitope 2024.
- ^ a b Ren 2019.
- ^ Kong 2020.
- ^ Kim 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Temitope 2024.
- ^ Hacker News 2022
- ^ a b c d e f g h "The past and future of 15.ai". Twitter. Archived from the original on December 8, 2024. Retrieved December 19, 2024.
- ^ Chandraseta 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ a b c d Chandraseta 2021.
- ^ Chandraseta 2021; Button 2021.
- ^
- "About". fifteen.ai (Official website). February 19, 2020. Archived from the original on February 29, 2020. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
2020-02-19: The web app isn't fully ready just yet
- "About". fifteen.ai (Official website). March 2, 2020. Archived from the original on March 3, 2020. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- "About". fifteen.ai (Official website). February 19, 2020. Archived from the original on February 29, 2020. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- ^ Scotellaro 2020a; Scotellaro 2020b.
- ^ a b c d Kurosawa 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ Zwiezen 2021; Clayton 2021; Ruppert 2021; Morton 2021; Kurosawa 2021; Yoshiyuki 2021.
- ^ a b Play.ht 2024.
- ^ Baker, Troy [@TroyBakerVA] (January 14, 2022). "I'm partnering with @VoiceverseNFT to explore ways where together we might bring new tools to new creators to make new things, and allow everyone a chance to own & invest in the IP's they create. We all have a story to tell. You can hate. Or you can create. What'll it be? https://t.co/cfDGi4q0AZ" (Tweet). Archived from the original on September 16, 2022. Retrieved December 7, 2022 – via Twitter.
- ^ Lawrence 2022; Williams 2022; Wright 2022; Temitope 2024.
- ^ Lopez 2022.
- ^ Phillips 2022; Lopez 2022.
- ^ Wright 2022; Phillips 2022; fifteenai 2022.
- ^ Lawrence 2022; Williams 2022.
- ^ a b ElevenLabs 2024a; Play.ht 2024.
- ^ Williams 2022.
- ^ Phillips 2022.
- ^ Chandraseta 2021; Menor 2024.
- ^ Zwiezen 2021; Clayton 2021; Morton 2021; Ruppert 2021; Villalobos 2021; Yoshiyuki 2021; Kurosawa 2021.
- ^ a b Scotellaro 2020b.
- ^ Morton 2021; 遊戲 2021.
- ^ a b c www.equestriacn.com 2021.
- ^ a b Yoshiyuki 2021.
- ^ Kurosawa 2021; Chandraseta 2021.
- ^ Knight 2017.
- ^ a b c Kurosawa 2021.
- ^ www.equestriacn.com 2021; Kurosawa 2021.
- ^ Clayton 2021; Ruppert 2021; Moto 2021; Scotellaro 2020c; Villalobos 2021.
- ^ Clayton 2021.
- ^ Zwiezen 2021.
- ^ 遊戲 2021.
- ^ a b MrSun 2021.
- ^ Button 2021.
- ^ Scotellaro 2020a; Scotellaro 2020b; Scotellaro 2020c; Scotellaro 2020d; Scotellaro 2020e; Scotellaro 2020f.
- ^ Paltridge 2021.
- ^ Morton 2021.
- ^ Moto 2021.
- ^ Yoshiyuki 2021: 日本語入力には対応していないが、ローマ字入力でもなんとなくそれっぽい発音になる。; 15.aiはテキスト読み上げサービスだが、特筆すべきはそのなめらかな発音と、ゲームに登場するキャラクター音声を再現している点だ。 (transl. It does not support Japanese input, but even if you input using romaji, it will somehow give you a similar pronunciation.; 15.ai is a text-to-speech service, but what makes it particularly noteworthy is its smooth pronunciation and the fact that it reproduces the voices of characters that appear in games.)
- ^ do Prado 2021; Villalobos 2021.
- ^ zuntata.tistory.com 2021.
- ^ Li 2021.
- ^ Phillips 2022; Temitope 2024; Menor 2024.
- ^ Lawrence 2022; Phillips 2022; Wright 2022.
- ^ Phillips 2022; Menor 2024.
- ^ Phillips 2022; Lawrence 2022.
- ^ fifteenai 2020; Menor 2024.
- ^ MrSun 2021: 大家是否都曾經想像過,假如能讓自己喜歡的遊戲或是動畫角色說出自己想聽的話,不論是名字、惡搞或是經典名言,都是不少人的夢想吧。不過來到 2021 年,現在這種夢想不再是想想而已,因為有一個網站通過 AI 生成的技術,讓大家可以讓不少遊戲或是動畫角色,說出任何你想要他們講出的東西,而且相似度與音調都有相當高的準確度 (transl. Have you ever imagined what it would be like if your favorite game or anime characters could say exactly what you want to hear? Whether it's names, parodies, or classic quotes, this is a dream for many. However, as we enter 2021, this dream is no longer just a fantasy, because there is a website that uses AI-generated technology, allowing users to make various game and anime characters say anything they want with impressive accuracy in both similarity and tone).
- ^ Anirudh VK 2023.
- ^ Temitope 2024; Morton 2021.
- ^ Scotellaro 2020c; 遊戲 2021; Kurosawa 2021; Morton 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ Clayton 2021; Zweizen 2021; Morton 2021.
- ^ Morton 2021; Kurosawa 2021.
- ^ Ruppert 2021.
- ^ Zweizen 2021; Morton 2021.
- ^ Scotellaro 2020d.
- ^ Scotellaro 2020e.
- ^ Zweizen 2021; Ruppert 2021.
- ^ Clayton 2021; CNN 2021.
- ^ "The Heavy on CNN". Reddit. January 19, 2021. Retrieved December 31, 2024.
- ^ Wright 2023.
- ^ ElevenLabs 2024b.
- ^ Speechify 2024.
- ^ Chandraseta 2021; Button 2021; Temitope 2024.
- ^ OpenAI 2024; Temitope 2024.
Works cited
[edit]- Barakat, Huda; Turk, Oytun; Demiroglu, Cenk (2024). "Deep learning-based expressive speech synthesis: a systematic review of approaches, challenges, and resources". EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech, and Music Processing. 2024 (11).
- Button, Chris (January 19, 2021). "Make GLaDOS, SpongeBob and other friends say what you want with this AI text-to-speech tool". Byteside. Archived from the original on June 25, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Chandraseta, Rionaldi (January 21, 2021). "Generate Your Favourite Characters' Voice Lines using Machine Learning". Towards Data Science. Archived from the original on January 21, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Clayton, Natalie (January 19, 2021). "Make the cast of TF2 recite old memes with this AI text-to-speech tool". PC Gamer. Archived from the original on January 19, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- "CNN Newsroom". CNN. January 15, 2021.
- do Prado, Renan (January 19, 2021). "Faça GLaDOS, Bob Esponja e outros personagens falarem textos escritos por você!" [Make GLaDOS, SpongeBob and other characters speak texts written by you!]. Arkade (in Brazilian Portuguese). Archived from the original on August 19, 2022. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- "15.AI: Everything You Need to Know & Best Alternatives". ElevenLabs. 2024a. Archived from the original on December 25, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- "Can I publish the content I generate on the platform?". ElevenLabs (Official website). 2024b. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- "15.ai已经重新上线,版本更新至v23" [15.ai has been re-launched, version updated to v23]. EquestriaCN (in Chinese). October 1, 2021. Archived from the original on May 19, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- @fifteenai (January 14, 2022). "Go fuck yourself" (Tweet) – via Twitter.
- "这个网站可用AI生成语音 让ACG角色"说"出你输入的文本" [This Website Can Use AI to Generate Voice, Making ACG Characters "Say" the Text You Input]. GamerSky (in Chinese). January 18, 2021. Archived from the original on December 11, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- "Audio samples from "Semi-Supervised Training for Improving Data Efficiency in End-to-End Speech Synthesis"". August 30, 2018. Archived from the original on November 11, 2020. Retrieved June 5, 2022.
- "15.ai". Hacker News. June 12, 2022. Retrieved December 29, 2024.
- Kim, Jaehyeon (2020). "Glow-TTS: A Generative Flow for Text-to-Speech via Monotonic Alignment Search". arXiv:2005.11129 [eess.AS].
- Knight, Will (August 3, 2017). "An Algorithm Trained on Emoji Knows When You're Being Sarcastic on Twitter". MIT Technology Review. Archived from the original on June 2, 2022. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Kong, Jungil (2020). "HiFi-GAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Efficient and High Fidelity Speech Synthesis". arXiv:2010.05646 [cs.SD].
- Kurosawa, Yuki (January 19, 2021). "ゲームキャラ音声読み上げソフト「15.ai」公開中。『Undertale』や『Portal』のキャラに好きなセリフを言ってもらえる" [Game Character Voice Reading Software "15.ai" Now Available. Get Characters from Undertale and Portal to Say Your Desired Lines]. AUTOMATON (in Japanese). Archived from the original on January 19, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
英語版ボイスのみなので注意。;もうひとつ15.aiの大きな特徴として挙げられるのが、豊かな感情表現だ。
[Please note that only English voices are available.;Another major feature of 15.ai is its rich emotional expression.] - Lawrence, Briana (January 19, 2022). "Shonen Jump Scare Leads to Company Reassuring Fans That They Aren't Getting Into NFTs". The Mary Sue. Retrieved December 23, 2024.
- Li, Yongqiang (2021). "语音开源项目优选:免费配音网站15.ai" [Voice Open Source Project Selection: Free Voice Acting Website 15.ai]. Zhihu (in Chinese). Archived from the original on December 19, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Lopez, Ule (January 16, 2022). "Voiceverse NFT Service Reportedly Uses Stolen Technology from 15ai [UPDATE]". Wccftech. Archived from the original on January 16, 2022. Retrieved June 7, 2022.
- Menor, Deion (November 7, 2024). "15.ai – Natural and Emotional Text-to-Speech Using Neural Networks". HashDork. Retrieved January 3, 2025.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - Morton, Lauren (January 18, 2021). "Put words in game characters' mouths with this fascinating text to speech tool". Rock, Paper, Shotgun. Archived from the original on January 18, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Moto, Eugenio (January 20, 2021). "15.ai, el sitio que te permite usar voces de personajes populares para que digan lo que quieras". Qore (in Spanish). Archived from the original on December 28, 2024. Retrieved December 21, 2024.
Si bien los resultados ya son excepcionales, sin duda pueden mejorar más
[While the results are already exceptional, without a doubt they can improve even more] - MrSun (January 19, 2021). "讓你喜愛的ACG角色說出任何話! AI生成技術幫助你實現夢想" [Let your favorite ACG characters say anything! AI generation technology helps you realize your dreams]. Yahoo (in Chinese). Archived from the original on December 28, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- Ng, Andrew (April 1, 2020). "Voice Cloning for the Masses". DeepLearning.AI. Archived from the original on December 28, 2024. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- "Navigating the Challenges and Opportunities of Synthetic Voices". OpenAI. March 9, 2024. Archived from the original on November 25, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Ruppert, Liana (January 18, 2021). "Make Portal's GLaDOS And Other Beloved Characters Say The Weirdest Things With This App". Game Informer. Archived from the original on January 18, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Paltridge, Peter (January 18, 2021). "This Website Will Say Whatever You Type In Spongebob's Voice". Anime Superhero News. Archived from the original on October 17, 2021. Retrieved December 22, 2024.
- Phillips, Tom (January 14, 2022). "Video game voice actor Troy Baker is now promoting NFTs". Eurogamer. Retrieved December 31, 2024.
- Phillips, Tom (January 17, 2022). "Troy Baker-backed NFT firm admits using voice lines taken from another service without permission". Eurogamer. Archived from the original on January 17, 2022. Retrieved December 31, 2024.
- "Everything You Need to Know About 15.ai: The AI Voice Generator". Play.ht. September 12, 2024. Archived from the original on December 25, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Ren, Yi (2019). "FastSpeech: Fast, Robust and Controllable Text to Speech". arXiv:1905.09263 [cs.CL].
- "Free 15.ai Character Voice Cloning and Alternatives". Resemble.ai. October 17, 2024. Retrieved December 31, 2024.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020a). "Rainbow Dash Voice Added to 15.ai". Equestria Daily. Archived from the original on December 1, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020b). "15.ai Adds Tons of New Pony Voices". Equestria Daily. Archived from the original on December 26, 2024. Retrieved December 21, 2024.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020c). "Neat "Pony Preservation Project" Using Neural Networks to Create Pony Voices". Equestria Daily. Archived from the original on June 23, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020d). "Full Simple Animated Episode - The Tax Breaks (Twilight)". Equestria Daily. Retrieved January 1, 2025.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020e). "More Pony Music! We Shine Brighter Together!". Equestria Daily. Retrieved January 1, 2025.
- Scotellaro, Shaun (2020f). "New Among Us Animation Goes Viral... With Pony Voices". Equestria Daily. Retrieved January 1, 2025.
- Temitope, Yusuf (December 10, 2024). "15.ai Creator reveals journey from MIT Project to internet phenomenon". The Guardian. Archived from the original on December 28, 2024. Retrieved December 25, 2024.
- "게임 캐릭터 음성으로 영어를 읽어주는 소프트 15.ai 공개" [Software 15.ai Released That Reads English in Game Character Voices]. Tistory (in Korean). January 20, 2021. Archived from the original on December 20, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- 遊戲, 遊戲角落 (January 20, 2021). "這個AI語音可以模仿《傳送門》GLaDOS講出任何對白!連《Undertale》都可以學" [This AI Voice Can Imitate Portal's GLaDOS Saying Any Dialog! It Can Even Learn Undertale]. United Daily News (in Chinese (Taiwan)). Archived from the original on December 19, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- van den Oord, Aaron; Dieleman, Sander; Zen, Heiga; Simonyan, Karen; Vinyals, Oriol; Graves, Alex; Kalchbrenner, Nal; Senior, Andrew; Kavukcuoglu, Koray (September 12, 2016). "WaveNet: A Generative Model for Raw Audio". arXiv:1609.03499 [cs.SD].
- Villalobos, José (January 18, 2021). "Descubre 15.AI, un sitio web en el que podrás hacer que GlaDOS diga lo que quieras" [Discover 15.AI, a Website Where You Can Make GlaDOS Say What You Want]. LaPS4 (in Spanish). Archived from the original on January 18, 2021. Retrieved January 18, 2021.
La dirección es 15.AI y funciona tan fácil como parece.
[The address is 15.AI and it works as easy as it looks.] - Anirudh VK (March 18, 2023). "Deepfakes Are Elevating Meme Culture, But At What Cost?". Analytics India Magazine. Archived from the original on December 26, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
While AI voice memes have been around in some form since '15.ai' launched in 2020, [...]
- Weitzman, Cliff (November 19, 2023). "15.ai: All about 15.ai and the best alternative". Speechify. Retrieved December 31, 2024.
- Williams, Demi (January 18, 2022). "Voiceverse NFT admits to taking voice lines from non-commercial service". NME. Archived from the original on January 18, 2022. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Wright, Steve (January 17, 2022). "Troy Baker-backed NFT company admits to using content without permission". Stevivor. Archived from the original on January 17, 2022. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Wright, Steven (March 21, 2023). "Why Biden, Trump, and Obama Arguing Over Video Games Is YouTube's New Obsession". Inverse. Archived from the original on December 20, 2024. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
AI voice tools used to create "audio deepfakes" have existed for years in one form or another, with 15.ai being a notable example.
- Yoshiyuki, Furushima (January 18, 2021). "『Portal』のGLaDOSや『UNDERTALE』のサンズがテキストを読み上げてくれる。文章に込められた感情まで再現することを目指すサービス「15.ai」が話題に" [Portal's GLaDOS and UNDERTALE's Sans Will Read Text for You. "15.ai" Service Aims to Reproduce Even the Emotions in Text, Becomes Topic of Discussion]. Den Fami Nico Gamer (in Japanese). Archived from the original on January 18, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
- Zwiezen, Zack (January 18, 2021). "Website Lets You Make GLaDOS Say Whatever You Want". Kotaku. Archived from the original on January 17, 2021. Retrieved December 18, 2024.
External links
[edit]- Internet properties established in 2020
- Applications of artificial intelligence
- 2020 software
- 2020 in Internet culture
- 2020s in Internet culture
- 2020s fads and trends
- Web applications
- Speech synthesis
- Deep learning software applications
- Deepfakes
- Generative artificial intelligence
- My Little Pony: Friendship Is Magic fandom
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology software

