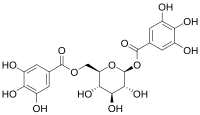
1,6-Digalloylglucose
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
β-D-Glucopyranose 1,6-bis(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate)
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-{[(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy]methyl}oxan-2-yl 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate | |
| Other names
Digalloyl glucose
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H20O14 | |
| Molar mass | 484.366 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
1,6-Digalloylglucose, or more specifically 1,6-di-O-galloyl-β-D-glucose, is a gallotannin. It can be found in some oak species.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ Mämmelä, Pirjo; Savolainen, Heikki; Lindroos, Lasse; Kangas, Juhani; Vartiainen, Terttu (2000). "Analysis of oak tannins by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionisation mass spectrometry". Journal of Chromatography A. 891 (1): 75–83. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)00624-5. PMID 10999626.
