Wheat allergy
| Wheat allergy | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Wheat | |
| Specialty | Immunology |
Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat that typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Wheat allergy may be immunoglobulin E mediated or not[1] and may involve mast cell response.[2] Wheat allergy is rare. Prevalence in adults was estimated to be 0.21% in a 2012 study in Japan.[3]
Wheat allergy may be a misnomer. There are many allergenic components in wheat (for example: serine protease inhibitors, glutelins and prolamins) and different responses are often attributed to different proteins. Twenty-seven potential wheat allergens have been successfully identified.[4]
Typically, the allergy is limited to the seed storage proteins of wheat. Some reactions are restricted to wheat proteins, while others can occur across many varieties of seeds and other plant tissues. The most severe response is exercise/aspirin-induced anaphylaxis attributed to one omega gliadin that is a relative of the protein that causes celiac disease.[5] Other more common symptoms include nausea, urticaria, and atopy.[6]
Gluten sensitivity and Coeliac disease are two different diseases, however the management is similar.[7] Management of wheat allergy consists of complete withdrawal of any food containing wheat or other gluten-containing cereals.
Types of allergens
[edit]Most wheat allergens are proteins,[4] including seed storage proteins. There are four major classes of seed storage proteins: albumins, globulins, prolamins and glutelins.
Gluten allergy
[edit]Within wheat, prolamins are called gliadins. Gliadins and glutenins form the classic glutens. While gluten is also the causative agent of celiac disease (CD), celiac disease can be contrasted to gluten allergy by the involvement of different immune cells and antibody types (See Comparative pathophysiology of gluten sensitivities).
Prolamin allergies
[edit]Prolamins, called gliadins, are associated with the more severe disease than glutenins.[citation needed] A proteomics based study found a γ-gliadin isoform gene.[5]
Glutelin allergies
[edit]Glutenin (wheat glutelin) is a predominant allergen in wheat.[5] Nine subunits of LMW-glutenin have been found to be in connection with wheat allergies.[clarification needed]
Albumin and globulin allergy
[edit]At present many of the allergens of wheat have not been characterized; however, the early studies found many to be in the albumin class.[8] A recent study in Europe confirmed the increased presence of allergies to amylase/trypsin inhibitors (serpins)[5][9] and lipid transfer protein (LPT),[10] but less reactivity to the globulin fraction.[11] The allergies tend to differ between populations (Italian, Japanese, Danish or Swiss),[citation needed] indicating a potential genetic component to these reactivities.
Other allergies
[edit]Wheat pollen and grass allergies
[edit]Respiratory allergies are an occupational disease that develop in food service workers. Previous studies detected 40 allergens from wheat; some cross-reacted with rye proteins and a few cross-reacted with grass pollens.[12] A later study showed that baker's allergy extend over a broad range of cereal grasses (wheat, durum wheat, triticale, cereal rye, barley, rye grass, oats, canary grass, rice, maize, sorghum and Johnson grass) though the greatest similarities were seen between wheat and rye,[13] and that these allergies show cross reactivity between seed proteins and pollen proteins,[14] including a prominent crossreactivity between the common environment rye pollen and wheat gluten.[15][16]
Derivative allergies
[edit]Proteins are made of a chain of dehydrated amino acids. When enzymes cut proteins into pieces they add water back to the site at which they cut. This process is called enzymatic hydrolysis, or in the case of proteins it is called proteolysis. The initial products of this hydrolysis are polypeptides, and smaller products are called simply peptides; these are called wheat protein hydrolysates. These hydrolysates can create allergens out of wheat proteins that previously did not exist by the exposure of buried antigenic sites in the proteins.[citation needed]
When proteins are cut into polypeptides, buried regions are exposed to the surface, and these buried regions may possibly be antigenic. Such hydrolyzed wheat protein is used as an additive in foods and cosmetics. The peptides are often 1 kD in size (9 amino acid residues in length) and may increase the allergic response.[17] These wheat polypeptides can cause immediate contact urticaria in susceptible people.[18]
Signs and symptoms
[edit]Wheat allergies are not altogether different from other food allergies or respiratory allergies. However two conditions, exercise/aspirin induced anaphylaxis and urticaria, occur more frequently with wheat allergies.[citation needed]
Common symptoms of a wheat allergy include eczema (atopic dermatitis), hives (urticaria), asthma, "hay fever" (allergic rhinitis), angioedema (tissue swelling due to fluid leakage from blood vessels), abdominal cramps, nausea, and vomiting.[19] Rarer symptoms include [citation needed] anaphylactic shock, anxiety, arthritis, bloated stomach, chest pains, depression or mood swings, diarrhea, dizziness, headache, joint and muscle aches and pains (may be associated with progressive arthritis), palpitations, psoriasis, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), swollen throat or tongue, tiredness and lethargy, and unexplained cough.
Reactions may become more severe with repeated exposure.[citation needed]
Asthma, anaphylaxis, nasal allergies
[edit]Exercise-induced anaphylaxis
[edit]Wheat gliadins and potentially oat avenins are associated with another disease, known as wheat-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA) which is similar to baker's allergy as both are mediated by IgE responses.[1] In WDEIA, however, the ω-gliadins or a high molecular weight glutenin subunit, and similar proteins in other Triticeae genera, enter the blood stream during exercise where they cause acute asthmatic or allergic reaction.[1] Wheat may specifically induce WDEIA and certain chronic urticaria because the anti-gliadin IgE detects ω5-gliadins expressed by most of the Gli-B1 alleles, but prolamins extracted from rye or wheat/rye translocates invoke almost no responses.[1] The Gli-B1 gene in wheat, Triticum aestivum, comes from the progenitor species Aegilops speltoides. This indicates that nascent mutations on the B genome of wheat are from a small number of cultivated Triticeae species.[20]
Baker's allergy
[edit]Baker's allergy has a ω-gliadin component and thioredoxin hB component.[21] In addition, a gluten-extrinsic allergen has been identified as aspergillus amylase, added to flour to increase its baking properties.[citation needed]
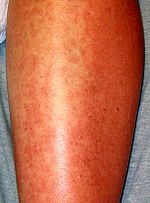
Urticaria, atopy, eczema
[edit]Contact sensitivity,[22] atopic dermatitis,[23] eczema, and urticaria appear to be related phenomena, the cause of which is generally believed to be the hydrophobic prolamin components of certain Triticeae, Aveneae cultivars. In wheat one of these proteins is ω-gliadin (Gli-B1 gene product). A study of mothers and infants on an allergen-free diet demonstrated that these conditions can be avoided if wheat sensitive cohort in the population avoid wheat in the first year of life.[24] As with exercise induced anaphylaxis, aspirin (also: tartrazine, sodium benzoate, sodium glutamate (MSG), sodium metabisulfite, tyramine) may be sensitizing factors for reactivity.[25] Studies of the wheat-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis demonstrate that atopy and EIA can be triggered from the ingestion wheat proteins into the blood, where IgE reacts within allergens in the dermal tissues. Some individuals may be so sensitive that low dose aspirin therapy can increase risk for both atopy and WDEIA.[citation needed]
Wheat allergies were also common with contact dermatitis. A primary cause was the donning agent used for latex gloves prior to the 1990s, however most gloves now use protein free starch as a donning agent.[citation needed]
Rheumatoid arthritis
[edit]There appears to be an association of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) both with gluten sensitive enteropathy (GSE) and gluten allergies.[26] RA in GSE/CD may be secondary to tissue transglutaminase (tTG) autoimmunity. In a recent study in Turkey, 8 of 20 RA patients had wheat reactivities on the radioallergosorbent test (RAST). When this allergic food and all other patient specific RAST+ foods were removed half of the patients had improved RA by serological markers. In patients with wheat allergies, rye was effectively substituted.[27] This may indicate that some proportion of RA in GSE/CD is due to downstream effects of allergic responses. In addition, cross-reactive anti-beef-collagen antibodies (IgG) may explain some rheumatoid arthritis (RA) incidences.[spelling?][28]
Neuropathies
[edit]Migraines. In the late 1970s it was reported that people with migraines had reactions to food allergens, like RA, the most common reaction was to wheat (78%), orange, eggs, tea, coffee, chocolate, milk, beef, corn, cane sugar, and yeast. When 10 foods causing the most reactions were removed migraines fell precipitously, hypertension declined.[29] Some specific instances are attributed to wheat.[30]
Autism. Parents of children with autism often ascribe the children's gastrointestinal symptoms to allergies to wheat and other foods. The published data on this approach are sparse, with the only double-blind study reporting negative results.[31]
Diagnosis
[edit]This section needs additional citations for verification. (May 2021) |
Diagnoses of wheat allergy may deserve special consideration.[1] Omega-5 gliadin, the most potent wheat allergen, cannot be detected in whole wheat preparations; it must be extracted and partially digested (similar to how it degrades in the intestine) to reach full activity. Other studies show that digestion of wheat proteins to about 10 amino acids can increase the allergic response 10 fold. Certain allergy tests may not be suitable to detect all wheat allergies, resulting in cryptic allergies. Because many of the symptoms associated with wheat allergies, such as eczema and asthma, may be related or unrelated to a wheat allergy, medical deduction can be an effective way of determining the cause. If symptoms are alleviated by immunosuppressant drugs, such as prednisone, an allergy-related cause is likely. If multiple symptoms associated with wheat allergies are present in the absence of immunosuppressants then a wheat allergy is probable.[1]
Prevention
[edit]Management of wheat allergy consists of complete withdrawal of any food containing wheat and other gluten-containing cereals (gluten-free diet).[32][33] However, some patients can tolerate barley, rye or oats.[34]
In people with less severe forms of wheat-dependent exercise induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA), avoiding wheat consumption before exercise and other cofactors that trigger disease symptoms, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and alcohol, can be sufficient to avoid an allergy.[33]
Wheat is often a cryptic contaminant of many foods; more obvious items are bread crumbs, maltodextrin, bran, cereal extract, couscous, cracker meal, enriched flour, gluten, high-gluten flour, high-protein flour, seitan, semolina wheat, vital gluten, wheat bran, wheat germ, wheat gluten, wheat malt, wheat starch or whole wheat flour. Less obvious sources of wheat could be gelatinized starch, hydrolyzed vegetable protein, modified food starch, modified starch, natural flavoring, soy sauce, soy bean paste, hoisin sauce, starch, vegetable gum, specifically beta-glucan, vegetable starch.[citation needed]
Alternative cereals
[edit]Triticeae gluten-free oats (free of wheat, rye or barley) may be a useful source of cereal fiber. Some wheat allergies allow the use of rye bread as a substitute. Rice flour is a commonly used alternative for those allergic to wheat. Wheat-free millet flour, buckwheat, flax seed meal, corn meal, quinoa flour, chia seed flour, tapioca starch or flour, and others can be used as substitutes.
Treatment
[edit]
Treatment for accidental ingestion of wheat products by allergic individuals varies depending on the sensitivity of the person. An antihistamine such as diphenhydramine may be prescribed. Sometimes prednisone will be prescribed to prevent a possible late phase Type I hypersensitivity reaction.[35] Severe allergic reactions (anaphalaxis) may require treatment with an epinephrine pen, which is an injection device designed to be used by a non-healthcare professional when emergency treatment is warranted.[36]
See also
[edit]- Allergy (has diagrams showing involvement of different types of white blood cells)
- Food allergy (has images of hives, skin prick test and patch test)
- Gluten immunochemistry
- List of allergens (food and non-food)
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f Cianferoni, Antonella (29 January 2016). "Wheat allergy: diagnosis and management". Journal of Asthma and Allergy. 9: 13–25. doi:10.2147/jaa.s81550. ISSN 1178-6965. PMC 4743586. PMID 26889090.
- ^ Sutton, Brian J.; Davies, Anna M.; Bax, Heather J.; Karagiannis, Sophia N. (22 Feb 2019). "IgE Antibodies: From Structure to Function and Clinical Translation". Antibodies. 8 (1): 19. doi:10.3390/antib8010019. PMC 6640697. PMID 31544825.
- ^ Morita E, Chinuki Y, Takahashi H, Nabika T, Yamasaki M, Shiwaku K (March 2012). "Prevalence of wheat allergy in Japanese adults". Allergol Int. 61 (1): 101–5. doi:10.2332/allergolint.11-OA-0345. PMID 22377522.
- ^ a b Sotkovský P, Sklenář J, Halada P, Cinová J, Setinová I, Kainarová A, Goliáš J, Pavlásková K, Honzová S, Tučková L (July 2011). "A new approach to the isolation and characterization of wheat flour allergens". Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 41 (7): 1031–43. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.2011.03766.x. PMID 21623965. S2CID 21906042.
- ^ a b c d Akagawa M, Handoyo T, Ishii T, Kumazawa S, Morita N, Suyama K (2007). "Proteomic analysis of wheat flour allergens". J. Agric. Food Chem. 55 (17): 6863–70. doi:10.1021/jf070843a. PMID 17655322.
- ^ Perr HA (2006). "Novel foods to treat food allergy and gastrointestinal infection". Current Allergy and Asthma Reports. 6 (2): 153–9. doi:10.1007/s11882-006-0054-z. PMC 7088959. PMID 16566866.
- ^ Costantino, A., Aversano, G., Lasagni, G., Smania, V., Doneda, L., Vecchi, M., ... & Elli, L. (2022). Diagnostic management of patients reporting symptoms after wheat ingestion. Frontiers in Nutrition, 9.
- ^ Sutton R, Hill DJ, Baldo BA, Wrigley CW (1982). "Immunoglobulin E antibodies to ingested cereal flour components: studies with sera from subjects with asthma and eczema". Clinical & Experimental Allergy. 12 (1): 63–74. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1982.tb03127.x. PMID 7067068. S2CID 13263808.
- ^ Armentia A, Sanchez-Monge R, Gomez L, Barber D, Salcedo G (1993). "In vivo allergenic activities of eleven purified members of a major allergen family from wheat and barley flour". Clin. Exp. Allergy. 23 (5): 410–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1993.tb00347.x. PMID 8334538. S2CID 6752902.
- ^ Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Conti A, et al. (2007). "Wheat IgE-mediated food allergy in European patients: alpha-amylase inhibitors, lipid transfer proteins and low-molecular-weight glutenins. Allergenic molecules recognized by double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge". Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 144 (1): 10–22. doi:10.1159/000102609. PMID 17496422. S2CID 202644198.
- ^ Walsh BJ, Wrigley CW, Musk AW, Baldo BA (1985). "A comparison of the binding of IgE in the sera of patients with bakers' asthma to soluble and insoluble wheat-grain proteins". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 76 (1): 23–8. doi:10.1016/0091-6749(85)90799-7. PMID 3839248.
- ^ Blands J, Diamant B, Kallós P, Kallós-Deffner L, Lowenstein H (1976). "Flour allergy in bakers. I. Identification of allergenic fractions in flour and comparison of diagnostic methods". Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 52 (1–4): 392–406. doi:10.1159/000231706. PMID 65335.
- ^ Baldo BA, Krilis S, Wrigley CW (1980). "Hypersensitivity to inhaled flour allergens. Comparison between cereals". Allergy. 35 (1): 45–56. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01716.x. PMID 6154431. S2CID 10966071.
- ^ Valero Santiago A, Amat Par P, Sanosa Valls J, Sierra Martínez P, Malet Casajuana A, García Calderón PA (1988). "Hypersensitivity to wheat flour in bakers". Allergologia et Immunopathologia. 16 (5): 309–14. PMID 3228051.
- ^ Donovan GR, Baldo BA (1990). "Crossreactivity of IgE antibodies from sera of subjects allergic to both ryegrass pollen and wheat endosperm proteins: evidence for common allergenic determinants". Clin. Exp. Allergy. 20 (5): 501–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1990.tb03142.x. PMID 2253081. S2CID 24293429.
- ^ Yazicioglu M, Oner N, Celtik C, Okutan O, Pala O (2004). "Sensitization to common allergens, especially pollens, among children with respiratory allergy in the Trakya region of Turkey". Asian Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 22 (4): 183–90. PMID 15783130..
- ^ Akiyama H, Sakata K, Yoshioka Y, et al. (2006). "Profile analysis and immunoglobulin E reactivity of wheat protein hydrolysates". Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 140 (1): 36–42. doi:10.1159/000092000. PMID 16534217. S2CID 37040078.
- ^ Laurière M, Pecquet C, Bouchez-Mahiout I, et al. (2006). "Hydrolysed wheat proteins present in cosmetics can induce immediate hypersensitivities". Contact Derm. 54 (5): 283–9. doi:10.1111/j.0105-1873.2006.00830.x. PMID 16689814. S2CID 23991489.
- ^ "Allergy Society of South Africa – Wheat Allergy". Archived from the original on 2008-04-24. Retrieved 2008-10-20.
- ^ Denery-Papini S, Lauriére M, Branlard G, et al. (2007). "Influence of the allelic variants encoded at the Gli-B1 locus, responsible for a major allergen of wheat, on IgE reactivity for patients suffering from food allergy to wheat". J. Agric. Food Chem. 55 (3): 799–805. doi:10.1021/jf062749k. PMID 17263477.
- ^ Weichel M, Glaser AG, Ballmer-Weber BK, Schmid-Grendelmeier P, Crameri R (2006). "Wheat and maize thioredoxins: a novel cross-reactive cereal allergen family related to baker's asthma". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 117 (3): 676–81. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2005.11.040. PMID 16522470.
- ^ Langeland T, Nyrud M (1982). "Contact urticaria to wheat bran bath: a case report". Acta Derm. Venereol. 62 (1): 82–3. doi:10.2340/00015555628283. PMID 6175150. S2CID 33018967.
- ^ Barnetson RS, Wright AL, Benton EC (1989). "IgE-mediated allergy in adults with severe atopic eczema". Clin. Exp. Allergy. 19 (3): 321–5. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2222.1989.tb02390.x. PMID 2736432. S2CID 24637855.
- ^ Zeiger RS, Heller S, Mellon MH, et al. (1989). "Effect of combined maternal and infant food-allergen avoidance on development of atopy in early infancy: a randomized study". J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 84 (1): 72–89. doi:10.1016/0091-6749(89)90181-4. PMID 2754147.
- ^ Van Bever HP, Docx M, Stevens WJ (1989). "Food and food additives in severe atopic dermatitis". Allergy. 44 (8): 588–94. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.1989.tb04205.x. PMID 2610332. S2CID 24402326.
- ^ Hvatum M, Kanerud L, Hällgren R, Brandtzaeg P (2006). "The gut–joint axis: cross reactive food antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis". Gut. 55 (9): 1240–7. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.076901. PMC 1860040. PMID 16484508.
- ^ Karatay S, Erdem T, Kiziltunc A, et al. (2006). "General or personal diet: the individualized model for diet challenges in patients with rheumatoid arthritis". Rheumatol. Int. 26 (6): 556–60. doi:10.1007/s00296-005-0018-y. PMID 16025333. S2CID 33308142.
- ^ Dieterich W, Esslinger B, Trapp D, Hahn E, Huff T, Seilmeier W, Wieser H, Schuppan D (2006). "Cross linking to tissue transglutaminase and collagen favours gliadin toxicity in coeliac disease". Gut. 55 (4): 478–84. doi:10.1136/gut.2005.069385. PMC 1856150. PMID 16188922.
- ^ Grant EC (1979). "Food allergies and migraine". Lancet. 1 (8123): 966–9. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(79)91735-5. PMID 87628. S2CID 6965185.
- ^ Pascual J, Leno C (2005). "A woman with daily headaches". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (2): 91–2. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0158-1. PMC 3452314. PMID 16362649.
- ^ Elder JH (2008). "The gluten-free, casein-free diet in autism: an overview with clinical implications". Nutr Clin Pract. 23 (6): 583–8. doi:10.1177/0884533608326061. PMID 19033217.
- ^ Hischenhuber C, Crevel R, Jarry B, Mäki M, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Romano A, Troncone R, Ward R (Mar 1, 2006). "Review article: safe amounts of gluten for patients with wheat allergy or coeliac disease". Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 23 (5): 559–75. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2036.2006.02768.x. PMID 16480395.
For both wheat allergy and coeliac disease the dietary avoidance of wheat and other gluten-containing cereals is the only effective treatment.
- ^ a b Scherf KA, Brockow K, Biedermann T, Koehler P, Wieser H (Sep 18, 2015). "Wheat-Dependent Exercise-Induced Anaphylaxis". Clin Exp Allergy. 46 (1): 10–20. doi:10.1111/cea.12640. PMID 26381478. S2CID 25066563.
Wheat-dependent exercise-induced anaphylaxis (WDEIA) is a rare, but potentially severe food allergy exclusively occurring when wheat ingestion is accompanied by augmenting cofactors. (...) The most reliable prophylaxis of WDEIA is a gluten-free diet. In less severe cases, a strict limitation of wheat ingestion before exercise and avoidance of other cofactors may be sufficient.
- ^ Pietzak M (Jan 2012). "Celiac disease, wheat allergy, and gluten sensitivity: when gluten free is not a fad". JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 36 (1 Suppl): 68S–75S. doi:10.1177/0148607111426276. PMID 22237879.
- ^ Tang AW (October 2003). "A practical guide to anaphylaxis". Am Fam Physician. 68 (7): 1325–32. PMID 14567487.
- ^ The EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines Group (August 2014). "Anaphylaxis: guidelines from the European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology". Allergy. 69 (8): 1026–45. doi:10.1111/all.12437. PMID 24909803. S2CID 11054771.
