User:Subseaven/sandbox
List of graphical symbols commonly used in circuit diagrams for hydraulic machinery
Graphical symbols in circuit diagrams for hydraulic machinery
[edit]The graphical symbols for circuit diagrams of hydraulic machinery are a subset of symbols used in fluid power systems. All symbols for fluid power systems using hydraulics, pneumatics and the like are standardized in ISO 1219:2012.
Direction of fluid flows
[edit]The direction of fluid flows in hydraulics is generally indicated by arrows in the corresponding fluid elements, pipes, and valves, respectively.
Hydraulic accumulators and reservoirs
[edit]Hydraulic accumulators and reservoirs are fluid containers that may have the following purpose:
- collecting excess fluid escaping from the circuit in a predefined manner, e.g. by means of a pressure relief valve
- adding fluid from the accumulator to the circuit in a predefined manner, e.g. by means of a hydraulic pump
- removing dirt from the hydraulic fluid as dirt particals will eventually sink to the bottom of the reservoir
| Liquid reservoir Connected to atmosphere | |
| Liquid reservoir Connected to atmosphere; fitting above the fluid level | |
| Liquid reservoir Connected to atmosphere; fitting below the fluid level |
Hydraulic pumps
[edit]| Hydraulic pump The arrow inside the circle shows the fitting where the fluid leaves the pump. | |

|
Hydraulic pump with fixed direction of rotation. The arrow inside the circle facing outward indicates the fitting where the fluid leaves the pump. The arrow on the stylized axis of rotation indicates the direction of rotation (clockwise or anticlockwise). |
Hydraulic motors
[edit]| Hydraulic motor The arrows inside the circle facing inward indicate that the motor can run both clockwise and anticlockwise. |
Filter
[edit]| Filter | |

|
Filter with clogging indicator |
Valves
[edit]Valves regulate the flow of a hydraulic fluid between at least two ports in the valve body. Different types have different tasks in a hydraulic circuit.
Directional control valves
[edit]A directional control valves (DCV) can redirect the flow paths between its ports or simply block one or more ports. Also called a selector valve.
| DCV with two positions General symbol | |
| DCV with three positions General symbol | |

|
DCV with three positions and four ways General symbol |

|
DCV with intermediate positions and two end positions. Also called proportional valve. General symbol |
| One fluid flow path (the ports are connected and the fluid can flow through the valve body) | |
| Closed position (the ports are closed, the fluid cannot flow through) | |
| File:Symbol Two flow paths.svg |
Two flow paths |
| Two flow paths and one closed port | |
| Two flow paths with a connection | |
| Tandem center: one flow path in shunt connection |
Check valves
[edit]A check valve lets the fluid pass only in one direction between its two ports. The opposite flow direction is blocked by the valve. Thus it is the mechanical analogue of an electronic diode.
| Check valve | |
| Check valve Spring tensioned | |

|
Pilot line operated check valve Prevents closing when actuated |

|
Pilot line check valve Prevents opening when actuated |
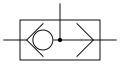
|
Shuttle valve Works as a logical OR gate in a hydraulic circuit |

|
Two pressure valve Works as a logical AND gate in a hydraulic circuit |
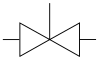
|
Stop valve |
Pressure control valves
[edit]A pressure control valve (PCV) allows to limit or reduce the pressure inside a hydraulic circuit to certain value behind the valve. The pressure limit can be fixed or adjustable.

|
Pressure relief valve (PRV) Adjustable |

|
Pressure sequence valve Adjustable |

|
Pressure sequence valve With drain line |

|
Pressure control valve Adjustable |

|
Pressure control valve Adjustable, with drain line |
| Drosselventil Querschnitt konstant | |
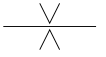
|
Blendenventil Querschnitt konstant |

|
Messblende Querschnitt einstellbar |

|
Drosselventil Querschnitt einstellbar |

|
Drosselventil Querschnitt durch Handbetätigung einstellbar |

|
Drosselrückschlagventil |
Betätigungsarten (von Ventilen)
[edit]| Muskelkraftbetätigung (allgemein) | |
| Muskelkraftbetätigung mit Druck- und Zugknopf | |
| Muskelkraftbetätigung mit Druckknopf | |
| Muskelkraftbetätigung mit Zugknopf | |
| Hebel | |
| Pedal | |
| Pedal mit zwei Betätigungsrichtungen | |
| Elektrische Betätigung mit magnetischer Spule. Bei Spannung an der Spule rückt der Ventilblock in Richtung des oberen Endes des Schrägstrichs, der die Spule symbolisiert, und die Durchleitung des in die Mitte gerückten Quadrats wird aktiv. Hier rückt der Block nach rechts und die Durchleitung des linken Quadrates wäre aktiv. | |

|
Elektrische Betätigung mit Elektromotor |
| Druckbetätigung direkt; allgemein | |
| Druckbetätigung direkt; durch Druckluft | |
| Druckbetätigung direkt; durch Flüssigkeit | |
| Stößel | |
| Rollenstößel | |

|
Rollenhebel |
| Feder | |
| Druckbetätigung indirekt mit pneumatisch betätigter Vorstufe | |

|
Parallelbetätigung z. B. Betätigung durch Druckknopf oder pneumatischer Vorstufe |
| Serienbetätigung z. B. elektrischer Magnet betätigt Druckventil, welches das Hauptventil betätigt |
Aktoren / Zylinder (Arbeitsglieder)
[edit]| Zylinder einfach wirkend mit Rückhub-Feder | |
| Zylinder doppelt wirkend | |
| Zylinder doppelt wirkend, vereinfachte Darstellung | |
| Zylinder (Gleichlaufzylinder) doppelt wirkend mit zweiseitiger Kolbenstange | |
| Zylinder doppelt wirkend mit kolbenseitiger Dämpfung | |
| Zylinder doppelt wirkend mit kolbenseitiger einstellbarer Dämpfung | |
| Zylinder doppelt wirkend mit beidseitiger Dämpfung | |
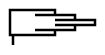
|
Teleskopzylinder einfach wirkend |
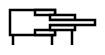
|
Teleskopzylinder doppelt wirkend |
Mess- und Anzeigegeräte (Messglieder)
[edit]| Manometer, Druckmessgerät | |
| Differenzdruckmessgerät | |
| Temperaturmesser (Thermometer) | |
| Flüssigkeitsniveaumesser | |
| Volumenstrommessgerät | |
| Volumenstromanzeiger | |
| Drehzahlmessgerät | |
| Drehmomentmessgerät |
Siehe auch
[edit]Weblinks
[edit]- D&C Scheme Editor – kostenloses Programm zur Schaltplanerstellung und Wartung der Bauelemente

