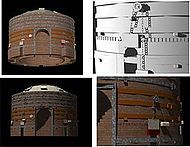
Kiln





A kiln is a thermally insulated chamber, a type of oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete some process, such as hardening, drying, or chemical changes. Kilns have been used for millennia to turn objects made from clay into pottery, tiles and bricks. Various industries use rotary kilns for pyroprocessing (to calcinate ores, such as limestone to lime for cement) and to transform many other materials.
Etymology
[edit]According to the Oxford English Dictionary, kiln was derived from the words cyline, cylene, cyln(e) in Old English, in turn derived from Latin culina ("kitchen"). In Middle English, the word is attested as kulne, kyllne, kilne, kiln, kylle, kyll, kil, kill, keele, kiele.[1][2] In Greek the word καίειν, kaiein, means 'to burn'.
Pronunciation
[edit]The word "kiln" was originally pronounced "kil" with the "n" silent, as is referenced in Webster's Dictionary of 1828 [3] and in English Words as Spoken and Written for Upper Grades by James A. Bowen 1900: "The digraph ln, n silent, occurs in kiln. A fall down the kiln can kill you."[4] Bowen was noting that "kill" and "kiln" are homophones.[5]
Uses of kilns
[edit]Pit fired pottery was produced for thousands of years before the earliest known kiln, which dates to around 6000 BCE, and was found at the Yarim Tepe site in modern Iraq.[6] Neolithic kilns were able to produce temperatures greater than 900 °C (1652 °F).[7] Uses include:
- Annealing, fusing and deforming glass, or fusing metallic oxide paints to the surface of glass
- Heat treatment for metallic workpieces
- Ceramics
- Brickworks
- Melting metal for casting
- Calcination of ore in a rotary kiln prior to smelting
- Pyrolysis of chemical materials
- Heating limestone with clay in the manufacture of Portland cement, the cement kiln
- Heating limestone to make quicklime or calcium oxide, the lime kiln
- Heating gypsum to make plaster of Paris
- For cremation (at high temperature)
- Drying of tobacco leaves
- Drying malted barley for brewing and other fermentations
- Drying hops for brewing (known as a hop kiln or oast house)
- Drying corn (grain) before grinding or storage, sometimes called a corn kiln, corn drying kiln[8]
- Drying green lumber so it can be used immediately
- Drying wood for use as firewood
- Heating wood to the point of pyrolysis to produce charcoal
- Extracting pine tar from pine tree logs or roots
Ceramic kilns
[edit]Kilns are an essential part of the manufacture of almost all types of ceramics. Ceramics require high temperatures so chemical and physical reactions will occur to permanently alter the unfired body. In the case of pottery, clay materials are shaped, dried and then fired in a kiln. The final characteristics are determined by the composition and preparation of the clay body and the temperature at which it is fired. After a first firing, glazes may be used and the ware is fired a second time to fuse the glaze into the body. A third firing at a lower temperature may be required to fix overglaze decoration. Modern kilns often have sophisticated electronic control systems, although pyrometric devices are often also used.
Clay consists of fine-grained particles that are relatively weak and porous. Clay is combined with other minerals to create a workable clay body. The firing process includes sintering. This heats the clay until the particles partially melt and flow together, creating a strong, single mass, composed of a glassy phase interspersed with pores and crystalline material. Through firing, the pores are reduced in size, causing the material to shrink slightly.
In the broadest terms, there are two types of kilns: intermittent and continuous, both being an insulated box with a controlled inner temperature and atmosphere.
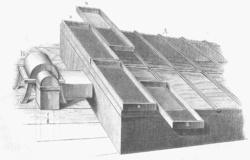
A continuous kiln, sometimes called a tunnel kiln, is long with only the central portion directly heated. From the cool entrance, ware is slowly moved through the kiln, and its temperature is increased steadily as it approaches the central, hottest part of the kiln. As it continues through the kiln, the temperature is reduced until the ware exits the kiln nearly at room temperature. A continuous kiln is energy-efficient, because heat given off during cooling is recycled to pre-heat the incoming ware. In some designs, the ware is left in one place, while the heating zone moves across it. Kilns in this type include:
- Hoffmann kiln
- Bull's Trench kiln
- Habla (Zig-Zag) kiln
- Roller kiln: A special type of kiln, common in tableware and tile manufacture, is the roller-hearth kiln, in which wares placed on bats are carried through the kiln on rollers.
In the intermittent kiln, the ware is placed inside the kiln, the kiln is closed, and the internal temperature is increased according to a schedule. After the firing is completed, both the kiln and the ware are cooled. The ware is removed, the kiln is cleaned and the next cycle begins. Kilns in this type include:[9]
- Clamp kiln
- Skove kiln
- Scotch kiln
- Down-draft kiln
- Shuttle kilns: this is a car-bottom kiln with a door on one or both ends. Burners are positioned top and bottom on each side, creating a turbulent circular air flow. This type of kiln is generally a multi-car design and is used for processing whitewares, technical ceramics and refractories in batches. Depending upon the size of ware, shuttle kilns may be equipped with car-moving devices to transfer fired and unfired ware in and out of the kiln. Shuttle kilns can be either updraft or downdraft. A shuttle kiln derives its name from the fact that kiln cars can enter a shuttle kiln from either end of the kiln, whereas a tunnel kiln has flow in only one direction.
Kiln technology is very old. Kilns developed from a simple earthen trench filled with pots and fuel pit firing, to modern methods. One improvement was to build a firing chamber around pots with baffles and a stoking hole. This conserved heat. A chimney stack improved the air flow or draw of the kiln, thus burning the fuel more completely.
Chinese kiln technology has always been a key factor in the development of Chinese pottery, and until recent centuries was the most advanced in the world. The Chinese developed kilns capable of firing at around 1,000 °C before 2000 BCE. These were updraft kilns, often built below ground. Two main types of kiln were developed by about 200 AD and remained in use until modern times. These are the dragon kiln of hilly southern China, usually fuelled by wood, long and thin and running up a slope, and the horseshoe-shaped mantou kiln of the north Chinese plains, smaller and more compact. Both could reliably produce the temperatures of up to 1300 °C or more needed for porcelain. In the late Ming, the egg-shaped kiln or zhenyao was developed at Jingdezhen and mainly used there. This was something of a compromise between the other types, and offered locations in the firing chamber with a range of firing conditions.[10]
Both Ancient Roman pottery and medieval Chinese pottery could be fired in industrial quantities, with tens of thousands of pieces in a single firing.[11] Early examples of simpler kilns found in Britain include those that made roof-tiles during the Roman occupation. These kilns were built up the side of a slope, such that a fire could be lit at the bottom and the heat would rise up into the kiln.
Traditional kilns include:
- Dragon kiln of south China: thin and long, climbing up a hillside. This type spread to the rest of East Asia giving the Japanese anagama kiln, arriving via Korea in the 5th century. This kiln usually consists of one long firing chamber, pierced with smaller ware stacking ports on one side, with a firebox at one end and a flue at the other. Firing time can vary from one day to several weeks. Traditional anagama kilns are also built on a slope to allow for a better draft. The Japanese noborigama kiln is an evolution from anagama design as a multi-chamber kiln where wood is stacked from the front firebox at first, then only through the side-stoking holes with the benefit of having air heated up to 600 °C (1,100 °F) from the front firebox, enabling more efficient firings.

- Khmer Kiln: quite similar to the anagama kiln; however, traditional Khmer Kilns had a flat roof. Chinese, Korean or Japanese kilns have an arch roof. These types of kiln vary in size and can measure in the tens of meters. The firing time also varies and can last several days.
- Bottle kiln: a type of intermittent kiln, usually coal-fired, formerly used in the firing of pottery; such a kiln was surrounded by a tall brick hovel or cone, of typical bottle shape. The tableware was enclosed in sealed fireclay saggars; as the heat and smoke from the fires passed through the oven it would be fired at temperatures up to 1,400 °C (2,600 °F).
- Biscuit kiln: The first firing would take place in the biscuit kiln.
- Glost kiln: The biscuit-ware was glazed and given a second glost firing in glost kilns.
- Mantou kiln of north China, smaller and more compact than the dragon kiln
- Muffle kiln: This was used to fire over-glaze decoration, at a temperature under 800 °C (1,500 °F). In these cool kilns the smoke from the fires passed through flues outside the oven.
- Catenary arch kiln: Typically used for the firing of pottery using salt, these by their form (a catenary arch) tend to retain their shape over repeated heating and cooling cycles, whereas other types require extensive metalwork supports.
- Sèvres kiln: invented in Sèvres, France, it efficiently generated high-temperatures 1,240 °C (2,260 °F) to produce waterproof ceramic bodies and easy-to-obtain glazes. It features a down-draft design that produces high temperature in shorter time, even with wood-firing.
- Bourry box kiln, similar to previous one
Modern kilns
[edit]
With the industrial age, kilns were designed to use electricity and more refined fuels, including natural gas and propane. Many large industrial pottery kilns use natural gas, as it is generally clean, efficient and easy to control. Modern kilns can be fitted with computerized controls allowing for fine adjustments during the firing. A user may choose to control the rate of temperature climb or ramp, hold or soak the temperature at any given point, or control the rate of cooling. Both electric and gas kilns are common for smaller scale production in industry and craft, handmade and sculptural work.
Modern kilns include:
- Retort kiln: a type of kiln which can reach temperatures around 1,500 °C (2,700 °F) for extended periods of time. Typically, these kilns are used in industrial purposes, and feature movable charging cars which make up the bottom and door of the kiln.
- Electric kilns: kilns operated by electricity were developed in the 20th century, primarily for smaller scale use such as in schools, universities, and hobby centers. The atmosphere in most designs of electric kiln is rich in oxygen, as there is no open flame to consume oxygen molecules. However, reducing conditions can be created with appropriate gas input, or by using saggars in a particular way.
- Feller kiln: brought contemporary design to wood firing by re-using unburnt gas from the chimney to heat intake air before it enters the firebox. This leads to an even shorter firing cycle and less wood consumption. This design requires external ventilation to prevent the in-chimney radiator from melting, being typically in metal. The result is a very efficient wood kiln firing one cubic metre of ceramics with one cubic meter of wood.[citation needed]
- Microwave assisted firing: this technique combines microwave energy with more conventional energy sources, such as radiant gas or electric heating, to process ceramic materials to the required high temperatures. Microwave-assisted firing offers significant economic benefits.
- Microwave kiln: These small kilns are designed to be placed inside a standard microwave oven. The kiln body is made from a porous ceramic material lined with a coating that absorbs microwave energy. The microwave kiln is placed inside a microwave oven and heated to the desired temperature. The heating process is much less controlled than most modern electric kilns, as there is no built-in temperature monitoring. The user must monitor the process closely to achieve the desired results, adjusting time and power levels programmed on the microwave oven. A small hole in the lid of the kiln can be used to estimate the interior temperature visually, as hot materials will glow. Microwave kilns are designed to reach internal temperatures of over 1,400 °C (2,600 °F), hot enough to work some types of glass, metals, and ceramics, while the outside of the kiln remains cool enough to handle with hot pads or tongs. After firing, the kiln should be removed from the microwave oven and placed on heat-proof surface while it is allowed to cool. Microwave kilns are limited in size, usually no more than 20 centimetres (8 in) in diameter.[12]
- Top-hat kiln: an intermittent kiln of a type sometimes used to fire pottery. The ware is set on a refractory hearth, or plinth, over which a box-shaped cover is lowered.
Wood-drying kiln
[edit]Green wood coming straight from the felled tree has far too high a moisture content to be commercially useful and will rot, warp and split. Both hardwoods and softwood must be left to dry out until the moisture content is between 18% and 8%. This can be a long process unless accelerated by use of a kiln. A variety of kiln technologies exist today: conventional, dehumidification, solar, vacuum and radio frequency.
Conventional wood dry kilns[13] are either package-type (side-loader) or track-type (tram) construction. Most hardwood lumber kilns are side-loader kilns in which fork trucks are used to load lumber packages into the kiln. Most softwood kilns are track types in which the timber is loaded on kiln/track cars for loading the kiln. Modern high-temperature, high-air-velocity conventional kilns can typically dry 25-millimetre-thick (1 in) green wood in 10 hours down to a moisture content of 18%. However, 25-mm-thick green red oak requires about 28 days to dry down to a moisture content of 8%.[citation needed]
Heat is typically introduced via steam running through fin/tube heat exchangers controlled by on/off pneumatic valves. Humidity is removed by a system of vents, the specific layout of which are usually particular to a given manufacturer. In general, cool dry air is introduced at one end of the kiln while warm moist air is expelled at the other. Hardwood conventional kilns also require the introduction of humidity via either steam spray or cold water misting systems to keep the relative humidity inside the kiln from dropping too low during the drying cycle. Fan directions are typically reversed periodically to ensure even drying of larger kiln charges.[citation needed]
Most softwood kilns operate below 115 °C (240 °F) temperature. Hardwood kiln drying schedules typically keep the dry bulb temperature below 80 °C (180 °F). Difficult-to-dry species might not exceed 60 °C (140 °F).
Dehumidification kilns are similar to other kilns in basic construction and drying times are usually comparable. Heat comes primarily from an integral dehumidification unit that also removes humidity. Auxiliary heat is often provided early in the schedule to supplement the dehumidifier.
Solar kilns are conventional kilns, typically built by hobbyists to keep initial investment costs low. Heat is provided via solar radiation, while internal air circulation is typically passive.
Vacuum and radio frequency kilns reduce the air pressure to attempt to speed up the drying process. A variety of these vacuum technologies exist, varying primarily in the method heat is introduced into the wood charge. Hot water platten vacuum kilns use aluminum heating plates with the water circulating within as the heat source, and typically operate at significantly reduced absolute pressure. Discontinuous and SSV (super-heated steam) use atmosphere pressure to introduce heat into the kiln charge. The entire kiln charge comes up to full atmospheric pressure, the air in the chamber is then heated and finally a vacuum is pulled as the charge cools. SSV run at partial-atmospheres, typically around 1/3 of full atmospheric pressure, in a hybrid of vacuum and conventional kiln technology (SSV kilns are significantly more popular in Europe where the locally harvested wood is easier to dry than the North American woods.) RF/V (radio frequency + vacuum) kilns use microwave radiation to heat the kiln charge, and typically have the highest operating cost due to the heat of vaporization being provided by electricity rather than local fossil fuel or waste wood sources.[citation needed]
The economics of different wood drying technologies are based on the total energy, capital, insurance/risk, environmental impacts, labor, maintenance, and product degradation costs. These costs, which can be a significant part of plant costs, involve the differential impact of the presence of drying equipment in a specific plant. Every piece of equipment from the green trimmer to the infeed system at the planer mill is part of the "drying system". The true costs of the drying system can only be determined when comparing the total plant costs and risks with and without drying.[citation needed]
Kiln dried firewood was pioneered during the 1980s, and was later adopted extensively in Europe due to the economic and practical benefits of selling wood with a lower moisture content (with optimal moisture levels of under 20% being much easier to achieve).[14][15][16][17][18]
The total (harmful) air emissions produced by wood kilns, including their heat source, can be significant. Typically, the higher the temperature at which the kiln operates, the larger the quantity of emissions that are produced (per mass unit of water removed). This is especially true in the drying of thin veneers and high-temperature drying of softwoods.[citation needed]
Gallery
[edit]-
Brickmaking kilns, Mekong Delta. The cargo boat in the foreground is carrying the rice chaff used as fuel for the firing.
-
A wood fired pottery kiln in Hội An, Vietnam.
-
Rice chaff being put to a brickmaking kiln in Mekong delta
-
A catenary arch kiln used for firing high temperature electron tube grade aluminium oxide ceramics
-
A two-story porcelain kiln with furnaces á alandier in Sèvres, France circa 1880
-
CAD representation of a beehive kiln
-
CAD representation of a tunnel kiln
-
A kiln yard with multiple kilns
See also
[edit]- Forge – Workshops of blacksmith, who is an ironsmith who makes iron into tools or other objects
- Industrial furnace – Device used for providing heat in industrial applications
- Limepit – Old method of calcining limestone
- List of ovens
- Top-lit updraft gasifier
- Kiln furniture
Notes
[edit]- ^ "Home: Oxford English Dictionary".
- ^ "Definition of KILN". 18 May 2023.
- ^ "Websters Dictionary 1828 - Webster's Dictionary 1828 - Kiln".
- ^ Bowen, James A. (1915). "English Words as Spoken and Written, for Upper Grades: Designed to Teach the Powers of Letters and the Construction and Use of Syllables".
- ^ "Kill, kiln at Homophone".
- ^ Piotr Bienkowski; Alan Millard (15 April 2010). Dictionary of the Ancient Near East. University of Pennsylvania Press. p. 233. ISBN 978-0-8122-2115-2.
- ^ James E. McClellan III; Harold Dorn. Science and Technology in World History: An Introduction. JHU Press; 14 April 2006. ISBN 978-0-8018-8360-6. p. 21.
- ^ Conran, Sheelagh; et al. (2011). Past Times, Changing Fortunes. Proceedings of a public seminar on archaeological discoveries on national road schemes. ARCHAEOLOGY AND THE NATIONAL ROADS AUTHORITY, Monograph Series No.8. Dublin: Transport Infrastructure Ireland. pp. 73–84. ISBN 9780956418050.
- ^ "Small Scale Brickmaking". Archived from the original on 2013-12-31. Retrieved 2013-03-20.
- ^ Rawson, 364, 369-370; Vainker, 222-223; JP Hayes article from the Grove Dictionary of Art
- ^ Vainker, 222-223; JP Hayes article from the Grove Dictionary of Art
- ^ "Microwave Kilns".
- ^ Rasmussen 1988.
- ^ Maviglio, S. 1986. From stump to stove in three days. Yankee. 50(12): 95-96 (December).
- ^ fpl.fs.fed.us
- ^ "Important information and facts about our firewood". www.certainlywood.co.uk. Retrieved 2016-10-27.
- ^ "Efficient Kiln-Dried Firewood Heating". Lekto Woodfuels. 2021-12-06. Retrieved 2022-02-11.
- ^ Firewood.co.uk. "Wet Firewood Ban - Ready to Burn | Not Sure What This Means, or Why it Matters?".
References
[edit]- Hamer, Frank and Janet. The Potter's Dictionary of Materials and Techniques. A & C Black Publishers, Limited, London, England, Third Edition 1991. ISBN 0-8122-3112-0.
- Smith, Ed. Dry Kiln Design Manual. J.E. Smith Engineering and Consulting, Blooming Grove, Texas. Available for purchase from author J.E. Smith Archived 2006-08-29 at the Wayback Machine
- M. Kornmann and CTTB, "Clay bricks and roof tiles, manufacturing and properties", Soc. industrie minérale, Paris, (2007) ISBN 2-9517765-6-X
- Rasmussen, E.F. (1988). Forest Products Laboratory, U.S. Department of Agriculture. (ed.). Dry Kiln Operators Manual. Hardwood Research Council.
External links
[edit]- Kilns and Firing Structures entry in the UCLA Encyclopedia of Egyptology
- Information about the history of bottle ovens (kilns) from Gladstone Pottery Museum in Stoke-on-Trent, UK.
- How the Bottle kiln works