Golden Quadrilateral
| The Golden Quadrilateral | |
|---|---|
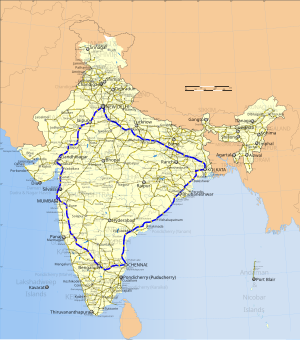 Highway map of India with the Golden Quadrilateral highlighted in solid blue colour | |
| Route information | |
| Maintained by NHAI | |
| Length | 5,846 km (3,633 mi) |
| Existed | July 2013–present |
| Kolkata – Delhi | |
| Length | 1,453 km (903 mi) |
| Major intersections | |
| Delhi – Mumbai | |
| Length | 1,419 km (882 mi) |
| Major intersections | |
| Mumbai – Chennai | |
| Length | 1,290 km (800 mi) |
| Major intersections | |
| Chennai – Kolkata | |
| Length | 1,684 km (1,046 mi) |
| Major intersections | |
| Location | |
| Country | India |
| Highway system | |





The Golden Quadrilateral (Hindi: स्वर्णिम चतुर्भुज, romanized: Svarnim Chaturbhuj; abbreviated GQ) is a national highway network connecting several major industrial, agricultural and cultural centres of India. It forms a quadrilateral with all the four major metro cities of India forming the vertices, viz., Delhi (north), Kolkata (east), Mumbai (west) and Chennai (south). Other major cities connected by this network include Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Vellore, Balasore, Bhadrak, Bhubaneswar, Bhilwara, Cuttack, Berhampur, Durgapur, Faridabad, Guntur, Gurugram, Jaipur, Kanpur, Pune, Kolhapur, Surat, Vijayawada, Eluru, Ajmer, Visakhapatnam, Bodhgaya, Varanasi, Prayagraj, Agra, Mathura, Dhanbad, Gandhinagar, Udaipur, and Vadodara. The main objective of these super highways is to reduce the travel time between the major cities of India, running roughly along the perimeter of the country. The North–South corridor linking Srinagar (Jammu and Kashmir) and Kanyakumari (Tamil Nadu), and East–West corridor linking Silchar (Assam) and Porbandar (Gujarat) are additional projects. These highway projects are implemented by the National Highway Authority Of India (NHAI). At 5,846 kilometres (3,633 mi), it is the largest highway project in India and the fifth longest in the world.[1] It is the first phase of the National Highways Development Project (NHDP), and consists of two, four, and six-lane express highways, built at a cost of ₹600 billion (US$7.2 billion).[2] The project was planned in 1999, launched in 2001, and was completed on 7 January 2012.[3]
The Golden Quadrilateral project is managed by the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) under the Ministry of Road, Transport and Highways. The vast majority of the system is not access controlled, although safety features such as guardrails, shoulders, and high-visibility signs are in use. The Mumbai–Pune Expressway, the first controlled-access toll road to be built in India, is a part of the GQ Project but not funded by NHAI, and is separate from the old Mumbai–Pune section of National Highway 48 (India). Infrastructure Leasing & Financial Services (IL&FS) has been one of the major contributors to the infrastructural development activity in the GQ project.[not verified in body]
History and costs
[edit]The Golden Quadrilateral Project (GQ Project) was intended to establish faster transport networks between major cities and ports, provide smaller towns better access to markets, reduce agricultural spoilage in transport, drive economical growth, and promote truck transport.[citation needed]
Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee laid the foundation stone for the project on 6 January 1999.[4] It was planned to be completed by 2006, but there were delays due to land acquisition constraints and disputes with contractors which had to be renegotiated.[5][6] In January 2012, India announced the four-lane GQ highway network as complete.[7][8]
India's government had initially estimated that the Golden Quadrilateral project would cost ₹600 billion (US$7.2 billion) at 1999 prices. However, the highway was built under-budget. As of August 2011, the cost incurred by the Indian government was about half of the initial estimate, at ₹308.58 billion (US$3.7 billion). The eight contracts in progress, as of August 2011, were worth ₹16.34 billion (US$200 million).[9][needs update]
In September 2009, it was announced that the existing four-laned highways would be converted into six-lane highways.[10] Sections of NH 2, NH 4, NH 5 and NH 8 were prioritized for widening to six lanes under DBFO (Design, Build, Finance, Operate) pattern and more sections would be six-laned in the future. On NH 8, six-lane work was completed from Vadodara to Surat.[when?][citation needed]
| No. | Segment | Length | Completed | Source[11][12] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Delhi–Kolkata | 1,453 km (903 mi) | 31 August 2011 | [5] Archived 1 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine |
| 2. | Chennai–Mumbai | 1,290 km (800 mi) | 31 August 2011 | [6] Archived 4 August 2009 at the Wayback Machine |
| 3. | Kolkata–Chennai | 1,684 km (1,046 mi) | 31 May 2013 | [7] Archived 23 July 2009 at the Wayback Machine |
| 4. | Mumbai–Delhi | 1,419 km (882 mi) | 31 August 2011 | [8] Archived 28 June 2009 at the Wayback Machine |
| Total | 5,846 km (3,633 mi) | 31 May 2013 | [9] Archived 29 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine |
Route
[edit]Only National Highways are used in the Golden Quadrilateral. The four legs use the following National Highways (new numbering system):
- Delhi – Kolkata: NH 44 from Delhi to Agra & NH 19 from Agra to Kolkata
- Delhi – Mumbai – Chennai: NH 48
- Kolkata – Chennai: NH 16
Connected cities
[edit]| Delhi–Kolkata | Kolkata–Chennai | Chennai–Mumbai | Mumbai–Delhi |
|---|---|---|---|
Length in each state
[edit]The completed Golden Quadrilateral passes through 12 states and a union territory:
- Andhra Pradesh – 1,014 km (630 mi)
- Uttar Pradesh – 756 km (470 mi)
- Rajasthan – 725 km (450 mi)
- Karnataka – 623 km (387 mi)
- Maharashtra – 487 km (303 mi)
- Gujarat – 485 km (301 mi)
- Odisha – 440 km (270 mi)
- West Bengal – 406 km (252 mi)
- Tamil Nadu – 342 km (213 mi)
- Bihar – 204 km (127 mi)
- Jharkhand – 192 km (119 mi)
- Haryana – 152 km (94 mi)
- Delhi – 25 km (16 mi)
- Total – 5,846 km (3,633 mi)
Corruption allegations
[edit]In August 2003, Jharkhand-based project director Satyendra Dubey, in a letter to the prime minister, outlined a list of bad faith (mala fide) actions in a segment of a highway in Bihar. Dubey's claims included that big contractors had inside information from NHAI officials,[13] that the contractors for this stretch were not executing the project themselves (as stipulated in the contract) but had been subcontracting the work to small builders who lacked technical expertise,[13] and that no follow-up was performed after awarding advances.[13] Dubey's name was leaked by the prime minister's office to the NHAI,[13] and he was transferred against his wishes to Gaya, Bihar, where he was murdered on 27 November.[13]
The NHAI eventually admitted that Dubey's allegations were substantiated, and implemented "radical reforms" in the selection and contract procedures.[14] After considerable Central Bureau of Investigation scrutiny, Mantu Kumar and three accomplices were arrested and charged with murder. Mantu escaped from court on 19 September 2005,[15] but was recaptured a month later. In 2010, Mantu and two others were convicted of murder and other offenses and sentenced to life in prison.[16]
See also
[edit]- Similar rail development
- Future of rail transport in India, rail development
- Dedicated freight corridors in India
- Similar roads development
- Bharatmala
- Diamond Quadrilateral, Subsumed in Bharatmala
- National Highways Development Project, Subsumed in Bharatmala
- North-South and East-West Corridor, Subsumed in Bharatmala
- India-China Border Roads, Subsumed in Bharatmala
- Expressways of India
- Setu Bharatam, river road bridge development in India
- Similar ports and river transport development
- Indian Rivers Inter-link
- List of National Waterways in India
- Sagar Mala project, national water port development connectivity scheme
- Similar air transport development
- Indian Human Spaceflight Programme
- UDAN, national airport development connectivity scheme
- Highways in India
- General
References
[edit]- ^ "World's 10 longest highways". Archived from the original on 23 January 2014. Retrieved 22 January 2014.
- ^ "Welcome to NHAI". Archived from the original on 14 April 2015. Retrieved 2013-07-23. Road network-Source-The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
- ^ Golden Quadrilateral Highway Network Archived 23 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine. Road Traffic Technology (2011-06-15). Retrieved on 2013-12-06.
- ^ "Building India's National Pride: The Golden Quadrilateral". Archived from the original on 17 July 2013. Retrieved 19 August 2012.
- ^ "Golden Quadrilateral still has miles to go". Financial Express. Archived from the original on 28 November 2005. Retrieved 26 August 2005.
- ^ R. N. Bhaskar. "Crossing the chasm". Forbes India. Archived from the original on 25 September 2009.
- ^ "Govt declares Golden Quadrilateral complete". The Indian Express. 7 January 2012. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ "National Highways Development Project Map". National Highways Institute of India. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 5 December 2005.
- ^ "Contractors take the sheen off Golden Quadrilateral". The Financial Express. 3 August 2011. Archived from the original on 31 July 2012.
- ^ Megha Bahree (21 September 2009). "Ambassador: Indian Economy Will Grow". Forbes. Archived from the original on 11 September 2018. Retrieved 29 August 2017.
- ^ "Govt. of India declares "Golden Quadrilateral" complete - Jan 7th 2012". Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 9 January 2012.
- ^ "NHAI - Current status". Archived from the original on 29 November 2009. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- ^ a b c d e [1] Archived 18 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine Bihar govt wakes up to IITian's murder-Source-Rediff News
- ^ [2] Archived 19 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine NHAI report to CBI proves Dubey right, contract rules being rewritten-Source-Indian Express
- ^ [3] Archived 16 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine Whistleblower in the 2004 National Highway Authority of India case escaped from police custody on Tuesday in Patna-Source-Rediff News
- ^ [4] Archived 10 May 2011 at the Wayback Machine Satyendranath Dubey killers get life imprisonment-Source-Oneindia. com
Further reading
[edit]- Fast Lane to the Future, Don Belt. National Geographic, October, 2008.
External links
[edit]- 'Mile by Mile, India Paves a Smoother Future' – extremely detailed New York Times article, dated 4 December 2005 (free registration required)
- "Golden Quadrilateral still has miles to go" – Financial Express article dated 26 August 2005
- Official website of the National Highways Authority of India
- Map of GQ progress on the NHAI website
- Ministry of Road Transport



