Toll-like receptor 3
Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) also known as CD283 (cluster of differentiation 283) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TLR3 gene.[5] TLR3 is a member of the toll-like receptor family of pattern recognition receptors of the innate immune system. TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA in endosomes, which is a common feature of viral genomes internalised by macrophages and dendritic cells.
Function
[edit]TLR3 is a member of the toll-like receptor (TLR) family which plays a fundamental role in pathogen recognition and activation of innate immunity. TLRs are highly conserved from Drosophila to humans and share structural and functional similarities. They recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that are expressed on infectious agents, and mediate the production of cytokines necessary for the development of effective immunity. The various TLRs exhibit different patterns of expression. This receptor is most abundantly expressed in placenta and pancreas, and is restricted to the dendritic subpopulation of the leukocytes. It recognizes dsRNA associated with viral infection, and induces the activation of IRF3 and NF-κB.[6] Unlike other TLRs, TLR3 uses TRIF as the sole adaptor.[6] IRF3 ultimately induces the production of type I interferons. It may thus play a role in host defense against viruses.[7]
TLR3 recognizes double-stranded RNA, a form of genetic information carried by some viruses such as reoviruses. Additionally, an ephemeral form of double-stranded RNA exists as a replicative intermediate during virus replication.[8] Upon recognition, TLR3 induces the activation of IRF3 to increase production of type I interferons which signal other cells to increase their antiviral defenses. Double-stranded RNA is also recognised by the cytoplasmic receptors RIG-I and MDA-5.[9]
TLR3 displays a protective role in mouse models of atherosclerosis,[10] and activation of TLR3 signaling is associated with ischemic preconditioning-induced protection against brain ischemia and attenuation of reactive astrogliosis.[11][12] Furthermore, TLR3 activation has been shown to promote hair follicle regeneration in skin wound healing.[13] In addition, TLR3 activators show effects on human vascular cells.[10]
Structure
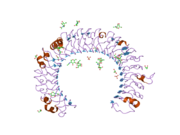
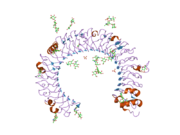
[edit]The structure of TLR3 was reported in June 2005 by researchers at The Scripps Research Institute.[14] TLR3 forms a large horseshoe shape that contacts with a neighboring horseshoe, forming a "dimer" of two horseshoes. Much of the TLR3 protein surface is covered with sugar molecules, making it a glycoprotein, but on one face (including the proposed interface between the two horseshoes), there is a large sugar-free surface. This surface also contains two distinct patches rich in positively charged amino acids, which may be a binding site for negatively charged double-stranded RNA.
Despite being a glycoprotein, TLR3 crystallises readily – a prerequisite for structural analysis by x-ray crystallography.
Ligands
[edit]- Antagonists
References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000164342 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000031639 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Rock FL, Hardiman G, Timans JC, Kastelein RA, Bazan JF (January 1998). "A family of human receptors structurally related to Drosophila Toll". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 95 (2): 588–593. Bibcode:1998PNAS...95..588R. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.2.588. PMC 18464. PMID 9435236.
- ^ a b Kawai T, Akira S (November 2007). "Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors". Trends in Molecular Medicine. 13 (11): 460–469. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2007.09.002. PMID 18029230.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: toll-like receptor 3".
- ^ Norval M (2012). "Virus–Cell Interactions". In Greenwood D, Slack RC, Barer MR, Irving WL (eds.). Medical Microbiology (18th ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone. p. 88. ISBN 978-0-7020-4089-4.
- ^ Alexopoulou L, Holt AC, Medzhitov R, Flavell RA (October 2001). "Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptor 3". Nature. 413 (6857): 732–738. Bibcode:2001Natur.413..732A. doi:10.1038/35099560. PMID 11607032. S2CID 4346537.
- ^ a b Cole JE, Navin TJ, Cross AJ, Goddard ME, Alexopoulou L, Mitra AT, et al. (February 2011). "Unexpected protective role for Toll-like receptor 3 in the arterial wall". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 108 (6): 2372–2377. doi:10.1073/pnas.1018515108. PMC 3038746. PMID 21220319.
- ^ Pan LN, Zhu W, Li Y, Xu XL, Guo LJ, Lu Q, et al. (2014). "Astrocytic Toll-like receptor 3 is associated with ischemic preconditioning-induced protection against brain ischemia in rodents". PLOS ONE. 9 (6): e99526. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...999526P. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099526. PMC 4051824. PMID 24914679.
- ^ Li Y, Xu XL, Zhao D, Pan LN, Huang CW, Guo LJ, et al. (November 2015). "TLR3 ligand Poly IC Attenuates Reactive Astrogliosis and Improves Recovery of Rats after Focal Cerebral Ischemia". CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 21 (11): 905–913. doi:10.1111/cns.12469. PMC 4638223. PMID 26494128.
- ^ Nelson AM, Reddy SK, Ratliff TS, Hossain MZ, Katseff AS, Zhu AS, et al. (August 2015). "dsRNA Released by Tissue Damage Activates TLR3 to Drive Skin Regeneration". Cell Stem Cell. 17 (2): 139–151. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2015.07.008. PMC 4529957. PMID 26253200.
- ^ Choe J, Kelker MS, Wilson IA (July 2005). "Crystal structure of human toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ectodomain". Science. 309 (5734): 581–585. Bibcode:2005Sci...309..581C. doi:10.1126/science.1115253. PMID 15961631. S2CID 4962727.
Further reading
[edit]- Lien E, Ingalls RR (January 2002). "Toll-like receptors". Critical Care Medicine. 30 (1 Suppl): S1-11. doi:10.1097/00003246-200201001-00001. PMID 11782555.
- Wang PF, Fang H, Chen J, Lin S, Liu Y, Xiong XY, et al. (May 2014). "Polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid has therapeutic effects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through the downregulation of TLR4 signaling via TLR3". Journal of Immunology. 192 (10): 4783–4794. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1303108. PMC 4009499. PMID 24729619.
- Li Y, Xu XL, Zhao D, Pan LN, Huang CW, Guo LJ, et al. (November 2015). "TLR3 ligand Poly IC Attenuates Reactive Astrogliosis and Improves Recovery of Rats after Focal Cerebral Ischemia". CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics. 21 (11): 905–913. doi:10.1111/cns.12469. PMC 4638223. PMID 26494128.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.