Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle
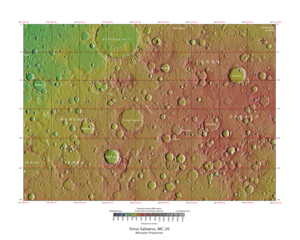 Map of Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle from Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) data. The highest elevations are red and the lowest are blue. | |
| Coordinates | 15°00′S 337°30′W / 15°S 337.5°W |
|---|---|

The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. It is also referred to as MC-20 (Mars Chart-20).[1] The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle covers the area from 315° to 360° west longitude and 0° to 30° degrees south latitude on Mars. It contains Schiaparelli, a large, easily visible crater that sits close to the equator. The Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle contains parts of Noachis Terra and Terra Sabaea.
The name comes from an incense-rich location south of the Arabian peninsula (the Gulf of Aden).[2]
Layers
[edit]Wislicenus Crater and the Schiaparelli basin crater contains layers, also called strata. Many places on Mars show rocks arranged in layers.[3] Sometimes the layers are of different colors. Light-toned rocks on Mars have been associated with hydrated minerals like sulfates. The Mars rover Opportunity examined such layers close-up with several instruments. Some layers are probably made up of fine particles because they seem to break up into fine dust. Other layers break up into large boulders so they are probably much harder. Basalt, a volcanic rock, is thought to in the layers that form boulders. Basalt has been identified on Mars in many places. Instruments on orbiting spacecraft have detected clay (also called phyllosilicates) in some layers. Scientists are excited about finding hydrated minerals such as sulfates and clays on Mars because they are usually formed in the presence of water.[4] Places that contain clays and/or other hydrated minerals would be good places to look for evidence of life.[5]
Rock can form layers in a variety of ways. Volcanoes, wind, or water can produce layers.[6] Layers can be hardened by the action of groundwater. Martian ground water probably moved hundreds of kilometers, and in the process it dissolved many minerals from the rock it passed through. When ground water surfaces in low areas containing sediments, water evaporates in the thin atmosphere and leaves behind minerals as deposits and/or cementing agents. Consequently, layers of dust could not later easily erode away since they were cemented together. On Earth, mineral-rich waters often evaporate forming large deposits of various types of salts and other minerals. Sometimes water flows through Earth's aquifers, and then evaporates at the surface just as is hypothesized for Mars. One location this occurs on Earth is the Great Artesian Basin of Australia.[7] On Earth the hardness of many sedimentary rocks, like sandstone, is largely due to the cement that was put in place as water passed through.
Schiaparelli Crater
[edit]
Schiaparelli is an impact crater on Mars located near Mars's equator. It is 461 kilometers (286 mi) in diameter and located at latitude 3° south and longitude 344°. Some places within Schiaparelli show many layers that may have formed by the wind, volcanoes, or deposition under water.
Other craters
[edit]When a comet or asteroid collides at a high speed interplanetary with the surface of Mars it creates a primary impact crater. The primary impact may also eject significant numbers of rocks which eventually fall back to make secondary craters.[8] The secondary craters may be arranged in clusters. All of the craters in the cluster would appear to be equally eroded; indicating that they would all are of the same age. If these secondary craters formed from a single, large, nearby impact, then they would have formed at roughly the same instant in time. The image below of Denning Crater shows a cluster of secondary craters.
Impact craters generally have a rim with ejecta around them, in contrast volcanic craters usually do not have a rim or ejecta deposits. As craters get larger (greater than 10 km in diameter) they usually have a central peak.[9] The peak is caused by a rebound of the crater floor following the impact.[10] If one measures the diameter of a crater, the original depth can be estimated with various ratios. Because of this relationship, researchers have found that many Martian craters contain a great deal of material; much of it is believed to be ice deposited when the climate was different.[11] Sometimes craters expose layers that were buried. Rocks from deep underground are tossed onto the surface. Hence, craters can show us what lies deep under the surface.
White rock in Pollack crater
[edit]
Within the region is Pollack crater, which has light-toned rock deposits. Mars has an old surface compared to Earth. While much of Earth's land surface is just a few hundred million years old, large areas of Mars are billions of years old. Some surface areas have been formed, eroded away, then covered over with new layers of rocks. The Mariner 9 spacecraft in the 1970s photographed a feature that was called "White Rock". Newer images revealed that the rock is not really white, but that the area close by is so dark that the white rock looks really white.[3] It was thought that this feature could have been a salt deposit, but information from the instruments on Mars Global Surveyor demonstrated rather that it was probably volcanic ash or dust. Today, it is believed that White Rock represents an old rock layer that once filled the whole crater that it is in, but today it has since been mostly eroded away. The picture below shows white rock with a spot of the same rock some distance from the main deposit, so it is thought that the white material once covered a far larger area.[12]
Channels in Sinus Sabaeus quadrangle
[edit]There is enormous evidence that water once flowed in river valleys on Mars.[13][14] Images of curved channels have been seen in images from Mars spacecraft dating back to the early 1970s with the Mariner 9 orbiter.[15][16][17][18] Indeed, a study published in June 2017, calculated that the volume of water needed to carve all the channels on Mars was even larger than the proposed ocean that the planet may have had. Water was probably recycled many times from the ocean to rainfall around Mars.[19][20]
Other Mars quadrangles
[edit]Interactive Mars map
[edit]
 Interactive image map of the global topography of Mars. Hover your mouse over the image to see the names of over 60 prominent geographic features, and click to link to them. Coloring of the base map indicates relative elevations, based on data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor. Whites and browns indicate the highest elevations (+12 to +8 km); followed by pinks and reds (+8 to +3 km); yellow is 0 km; greens and blues are lower elevations (down to −8 km). Axes are latitude and longitude; Polar regions are noted.
Interactive image map of the global topography of Mars. Hover your mouse over the image to see the names of over 60 prominent geographic features, and click to link to them. Coloring of the base map indicates relative elevations, based on data from the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter on NASA's Mars Global Surveyor. Whites and browns indicate the highest elevations (+12 to +8 km); followed by pinks and reds (+8 to +3 km); yellow is 0 km; greens and blues are lower elevations (down to −8 km). Axes are latitude and longitude; Polar regions are noted.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Davies, M.E.; Batson, R.M.; Wu, S.S.C. “Geodesy and Cartography” in Kieffer, H.H.; Jakosky, B.M.; Snyder, C.W.; Matthews, M.S., Eds. Mars. University of Arizona Press: Tucson, 1992.
- ^ Blunck, J. 1982. Mars and its Satellites. Exposition Press. Smithtown, N.Y.
- ^ a b Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.) 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM
- ^ "Target Zone: Nilosyrtis? | Mars Odyssey Mission THEMIS".
- ^ "HiRISE | Craters and Valleys in the Elysium Fossae (PSP_004046_2080)".
- ^ "HiRISE | High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment". hirise.lpl.arizona.edu.
- ^ Habermehl, M. A. (1980) The Great Artesian Basin, Australia. J. Austr. Geol. Geophys. 5, 9–38.
- ^ "HiRISE | Science Themes: Impact Processes".
- ^ "Stones, Wind, and Ice: A Guide to Martian Impact Craters".
- ^ Hugh H. Kieffer (1992). Mars. University of Arizona Press. ISBN 978-0-8165-1257-7. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
- ^ Garvin, J., et al. 2002. Global geometric properities of martian impact craters. Lunar Planet Sci. 33. Abstract @1255.
- ^ "Mars: What We Know About the Red Planet". Space.com. October 2021.
- ^ Baker, V., et al. 2015. Fluvial geomorphology on Earth-like planetary surfaces: a review. Geomorphology. 245, 149–182.
- ^ Carr, M. 1996. in Water on Mars. Oxford Univ. Press.
- ^ Baker, V. 1982. The Channels of Mars. Univ. of Tex. Press, Austin, TX
- ^ Baker, V., R. Strom, R., V. Gulick, J. Kargel, G. Komatsu, V. Kale. 1991. Ancient oceans, ice sheets and the hydrological cycle on Mars. Nature 352, 589–594.
- ^ Carr, M. 1979. Formation of Martian flood features by release of water from confined aquifers. J. Geophys. Res. 84, 2995–300.
- ^ Komar, P. 1979. Comparisons of the hydraulics of water flows in Martian outflow channels with flows of similar scale on Earth. Icarus 37, 156–181.
- ^ "How Much Water Was Needed to Carve Valleys on Mars? - SpaceRef". 5 June 2017.
- ^ Luo, W., et al. 2017. New Martian valley network volume estimate consistent with ancient ocean and warm and wet climate. Nature Communications 8. Article number: 15766 (2017). doi:10.1038/ncomms15766
- ^ Morton, Oliver (2002). Mapping Mars: Science, Imagination, and the Birth of a World. New York: Picador USA. p. 98. ISBN 0-312-24551-3.
- ^ "Online Atlas of Mars". Ralphaeschliman.com. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ^ "PIA03467: The MGS MOC Wide Angle Map of Mars". Photojournal. NASA / Jet Propulsion Laboratory. February 16, 2002. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
Further reading
[edit]- Grotzinger, J. and R. Milliken (eds.). 2012. Sedimentary Geology of Mars. SEPM.

