STK19
| STK19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | STK19, D6S60, D6S60E, G11, HLA-RP1, RP1, serine/threonine kinase 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | OMIM: 604977; MGI: 1860085; HomoloGene: 10449; GeneCards: STK19; OMA:STK19 - orthologs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Serine/threonine-protein kinase 19 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the STK19 gene[5][6][7] and is involved in DNA repair, specifically the Transcription Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair Pathway (TC-NER). [8][9]
The name is misleading — although STK19 was initially identified as a serine/threonine kinase, analysis of the crystal structure revealed absence of the kinase domain [10] and it does not seem to possess any kinase activity. [11]
This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6 and expresses two transcript variants.[7]
Structure
[edit]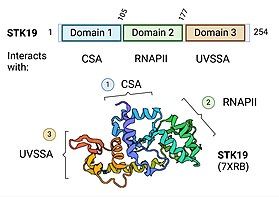
STK19 contains 3 different protein-interaction domains, which are essential to its function in DNA repair: the CSA interacting domain, RNA Polymerase II (RNAPII) interacting domain, and UVSSA interacting domain. [9] These domains allow STK19 to incorporate into the Transcription-Coupled DNA Repair (TCR) complex, which is recruited to RNA Polymerase II stalled at DNA lesions. [9]
Part of the UVSAA binding domain may also interact with XPD, a protein in the TFIIH (transcription factor IIH) complex. This complex is recruited to the TCR and is involved in excising the damaged DNA. STK19 binding to XPD is theorized to help optimally position the TFIIH ATPase subunits XPD and XPB onto the DNA in front of the lesion. [9]
Role in Transcription Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair
[edit]STK19 is involved in Transcription Coupled Nucleotide Excision Repair (TC-NER), a DNA repair pathway that preferentially detects and removes DNA damage in portions of the genome that are being actively transcribed (copied from DNA into RNA). (By contrast, the non-transcribed strand and portions of the genome not under active transcription are repaired more slowly, using Global Genome Nucleotide Excision Repair or GG-NER). [8]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c ENSG00000206342, ENSG00000236250, ENSG00000226033, ENSG00000204344, ENSG00000234947 GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000226257, ENSG00000206342, ENSG00000236250, ENSG00000226033, ENSG00000204344, ENSG00000234947 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000061207 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Sargent CA, Anderson MJ, Hsieh SL, Kendall E, Gomez-Escobar N, Campbell RD (Jul 1994). "Characterisation of the novel gene G11 lying adjacent to the complement C4A gene in the human major histocompatibility complex". Hum Mol Genet. 3 (3): 481–8. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.3.481. PMID 8012361.
- ^ Gomez-Escobar N, Chou CF, Lin WW, Hsieh SL, Campbell RD (Dec 1998). "The G11 gene located in the major histocompatibility complex encodes a novel nuclear serine/threonine protein kinase". J Biol Chem. 273 (47): 30954–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.47.30954. PMID 9812991.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: STK19 serine/threonine kinase 19".
- ^ a b Mevissen, Tycho E. T.; Kümmecke, Maximilian; Schmid, Ernst W.; Farnung, Lucas; Walter, Johannes C. (2024-12-12). "STK19 positions TFIIH for cell-free transcription-coupled DNA repair". Cell. 187 (25): 7091–7106.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.020. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 11645862. PMID 39547228.
- ^ a b c d e Heuvel, Diana van den; Rodríguez-Martínez, Marta; Meer, Paula J. van der; Moreno, Nicolas Nieto; Park, Jiyoung; Kim, Hyun-Suk; Schie, Janne J. M. van; Wondergem, Annelotte P.; D'Souza, Areetha; Yakoub, George; Herlihy, Anna E.; Kashyap, Krushanka; Boissière, Thierry; Walker, Jane; Mitter, Richard (2024-12-12). "STK19 facilitates the clearance of lesion-stalled RNAPII during transcription-coupled DNA repair". Cell. 187 (25): 7107–7125.e25. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.018. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 39547229.
- ^ Li, Yuling; Gong, Yanqiu; Zhou, Yue; Xiao, Yuzhou; Huang, Wenxin; Zhou, Qiao; Tu, Yingfeng; Zhao, Yinglan; Zhang, Shuyu; Dai, Lunzhi; Sun, Qingxiang (2024-01-22). "STK19 is a DNA/RNA-binding protein critical for DNA damage repair and cell proliferation". Journal of Cell Biology. 223 (2): e202301090. doi:10.1083/jcb.202301090. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 10806857. PMID 38252411.
- ^ Rodríguez-Martínez, Marta; Boissiére, Thierry; Gonzalez, Melvin Noe; Litchfield, Kevin; Mitter, Richard; Walker, Jane; Kjœr, Svend; Ismail, Mohamed; Downward, Julian; Swanton, Charles; Svejstrup, Jesper Q. (2020-06-11). "Evidence That STK19 Is Not an NRAS-dependent Melanoma Driver". Cell. 181 (6): 1395–1405.e11. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.014. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 7298618. PMID 32531245.
- ^ Sun, Q.; Li, Y. (2023-06-07). "human STK19 dimer". www.wwpdb.org. doi:10.2210/pdb7xrb/pdb. Retrieved 2024-12-13.
- ^ Sipes, Jared (12 December 2024). "Domains of STK19". Biorender.com.
Further reading
[edit]- Yu CY (1991). "The complete exon-intron structure of a human complement component C4A gene. DNA sequences, polymorphism, and linkage to the 21-hydroxylase gene". J. Immunol. 146 (3): 1057–66. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.146.3.1057. PMID 1988494.
- Shen L, Wu LC, Sanlioglu S, et al. (1994). "Structure and genetics of the partially duplicated gene RP located immediately upstream of the complement C4A and the C4B genes in the HLA class III region. Molecular cloning, exon-intron structure, composite retroposon, and breakpoint of gene duplication". J. Biol. Chem. 269 (11): 8466–76. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)37217-4. PMID 8132574.
- Ulgiati D, Townend DC, Christiansen FT, et al. (1996). "Complete sequence of the complement C4 gene from the HLA-A1, B8, C4AQ0, C4B1, DR3 haplotype". Immunogenetics. 43 (4): 250–2. doi:10.1007/BF00587313. PMID 8575831.
- Yang Z, Shen L, Dangel AW, et al. (1998). "Four ubiquitously expressed genes, RD (D6S45)-SKI2W (SKIV2L)-DOM3Z-RP1 (D6S60E), are present between complement component genes factor B and C4 in the class III region of the HLA". Genomics. 53 (3): 338–47. doi:10.1006/geno.1998.5499. PMID 9799600.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
- Mungall AJ, Palmer SA, Sims SK, et al. (2003). "The DNA sequence and analysis of human chromosome 6". Nature. 425 (6960): 805–11. Bibcode:2003Natur.425..805M. doi:10.1038/nature02055. PMID 14574404.
- Xie T, Rowen L, Aguado B, et al. (2004). "Analysis of the gene-dense major histocompatibility complex class III region and its comparison to mouse". Genome Res. 13 (12): 2621–36. doi:10.1101/gr.1736803. PMC 403804. PMID 14656967.
- Lehner B, Semple JI, Brown SE, et al. (2004). "Analysis of a high-throughput yeast two-hybrid system and its use to predict the function of intracellular proteins encoded within the human MHC class III region". Genomics. 83 (1): 153–67. doi:10.1016/S0888-7543(03)00235-0. PMID 14667819.
- Wadle A, Mischo A, Henrich PP, et al. (2005). "Characterization of Hap/BAG-1 variants as RP1 binding proteins with antiapoptotic activity". Int. J. Cancer. 117 (6): 896–904. doi:10.1002/ijc.21259. PMID 15986447. S2CID 36464436.
STK19 involvement in DNA repair
- Mevissen, Tycho E. T.; Kümmecke, Maximilian; Schmid, Ernst W.; Farnung, Lucas; Walter, Johannes C. (2024-12-12). "STK19 positions TFIIH for cell-free transcription-coupled DNA repair". Cell. 187 (25): 7091–7106.e24. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.020. ISSN 0092-8674. PMC 11645862. PMID 39547228.
- Heuvel, Diana van den; Rodríguez-Martínez, Marta; Meer, Paula J. van der; Moreno, Nicolas Nieto; Park, Jiyoung; Kim, Hyun-Suk; Schie, Janne J. M. van; Wondergem, Annelotte P.; D'Souza, Areetha; Yakoub, George; Herlihy, Anna E.; Kashyap, Krushanka; Boissière, Thierry; Walker, Jane; Mitter, Richard (2024-12-12). "STK19 facilitates the clearance of lesion-stalled RNAPII during transcription-coupled DNA repair". Cell. 187 (25): 7107–7125.e25. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.10.018. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 39547229.






