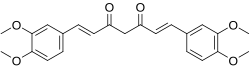
Dimethylcurcumin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ASC-J9; GO-Y025 |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| Drug class | Nonsteroidal antiandrogen; Selective androgen receptor degrader |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H24O6 |
| Molar mass | 396.439 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Dimethylcurcumin (development code ASC-J9) is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen and a synthetic curcuminoid which is under development by AndroScience Corporation as a topical medication for the treatment of acne vulgaris.[1][2] It has also been under investigation for the treatment of male pattern hair loss, spinal muscular atrophy, and wounds, but no development has been reported for these indications.[1] There has been interest in the drug for the potential treatment of prostate cancer as well.[2][3] As of 2017, it is in phase II clinical trials for acne vulgaris.[1]
Dimethylcurcumin is an androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor and shows strong and specific antiandrogenic activity in vitro (e.g., against LNCaP cell growth) at sufficiently high concentrations.[3] However, its mechanism of action and effects differ from those of conventional antiandrogens; it is not an antagonist of the AR and instead appears to act as a selective degradation enhancer (SARD) of certain subpopulations of the AR, for instance those present in the prostate gland.[1][3][2]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d "ASC-J9 (dimethylcurcumin)". AdisInsight.
- ^ a b c Shi Q, Shih CC, Lee KH (2009). "Novel anti-prostate cancer curcumin analogues that enhance androgen receptor degradation activity". Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 9 (8): 904–12. doi:10.2174/187152009789124655. PMID 19663790.
- ^ a b c Lai KP, Huang CK, Chang YJ, Chung CY, Yamashita S, Li L, Lee SO, Yeh S, Chang C (2013). "New therapeutic approach to suppress castration-resistant prostate cancer using ASC-J9 via targeting androgen receptor in selective prostate cells". Am. J. Pathol. 182 (2): 460–73. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.10.029. PMC 3562731. PMID 23219429.
