From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Protein-coding gene in the species Homo sapiens
SIGLEC7 Identifiers Aliases SIGLEC7 External IDs OMIM : 604410 ; MGI : 1932475 ; HomoloGene : 130668 ; GeneCards : SIGLEC7 ; OMA :SIGLEC7 - orthologs Wikidata
Sialic acid-binding Ig-like lectin 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIGLEC7 gene .[ 5] [ 6] CD328 (cluster of differentiation 328).
^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000168995 – Ensembl , May 2017^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000030474 – Ensembl , May 2017^ "Human PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:" . National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine .^ Nicoll G, Ni J, Liu D, Klenerman P, Munday J, Dubock S, Mattei MG, Crocker PR (Dec 1999). "Identification and characterization of a novel siglec, siglec-7, expressed by human natural killer cells and monocytes" . J Biol Chem . 274 (48): 34089– 95. doi :10.1074/jbc.274.48.34089 PMID 10567377 . ^ "Entrez Gene: SIGLEC7 sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 7" .
Reif K, Buday L, Downward J, Cantrell DA (1994). "SH3 domains of the adapter molecule Grb2 complex with two proteins in T cells: the guanine nucleotide exchange protein Sos and a 75-kDa protein that is a substrate for T cell antigen receptor-activated tyrosine kinases" . J. Biol. Chem . 269 (19): 14081– 7. doi :10.1016/S0021-9258(17)36757-1 PMID 8188688 . Falco M, Biassoni R, Bottino C, et al. (1999). "Identification and molecular cloning of p75/AIRM1, a novel member of the sialoadhesin family that functions as an inhibitory receptor in human natural killer cells" . J. Exp. Med . 190 (6): 793– 802. doi :10.1084/jem.190.6.793 . PMC 2195632 PMID 10499918 . Ye X, Mehlen P, Rabizadeh S, et al. (1999). "TRAF family proteins interact with the common neurotrophin receptor and modulate apoptosis induction" . J. Biol. Chem . 274 (42): 30202– 8. doi :10.1074/jbc.274.42.30202 PMID 10514511 . Vitale C, Romagnani C, Falco M, et al. (2000). "Engagement of p75/AIRM1 or CD33 inhibits the proliferation of normal or leukemic myeloid cells" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 96 (26): 15091– 6. doi :10.1073/pnas.96.26.15091 PMC 24778 PMID 10611343 . Angata T, Varki A (2000). "Siglec-7: a sialic acid-binding lectin of the immunoglobulin superfamily" . Glycobiology . 10 (4): 431– 8. doi :10.1093/glycob/10.4.431 PMID 10764831 . Ito A, Handa K, Withers DA, et al. (2001). "Binding specificity of siglec7 to disialogangliosides of renal cell carcinoma: possible role of disialogangliosides in tumor progression" . FEBS Lett . 498 (1): 116– 20. doi :10.1016/S0014-5793(01)02476-0 PMID 11389909 . S2CID 6755832 . Mingari MC, Vitale C, Romagnani C, et al. (2001). "Regulation of myeloid cell proliferation and survival by p75/AIRM1 and CD33 surface receptors". Progress in Basic and Clinical Immunology . Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Vol. 495. pp. 55– 61. doi :10.1007/978-1-4615-0685-0_8 . ISBN 978-1-4613-5194-8 PMID 11774609 . Yousef GM, Ordon MH, Foussias G, Diamandis EP (2002). "Genomic organization of the siglec gene locus on chromosome 19q13.4 and cloning of two new siglec pseudogenes". Gene . 286 (2): 259– 70. doi :10.1016/S0378-1119(02)00432-8 . PMID 11943481 . Alphey MS, Attrill H, Crocker PR, van Aalten DM (2003). "High resolution crystal structures of Siglec-7. Insights into ligand specificity in the Siglec family" . J. Biol. Chem . 278 (5): 3372– 7. doi :10.1074/jbc.M210602200 PMID 12438315 . Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences" . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A . 99 (26): 16899– 903. Bibcode :2002PNAS...9916899M . doi :10.1073/pnas.242603899 PMC 139241 PMID 12477932 . Nicoll G, Avril T, Lock K, et al. (2003). "Ganglioside GD3 expression on target cells can modulate NK cell cytotoxicity via siglec-7-dependent and -independent mechanisms" . Eur. J. Immunol . 33 (6): 1642– 8. doi :10.1002/eji.200323693 PMID 12778482 . S2CID 7541832 . Dimasi N, Moretta A, Moretta L, et al. (2004). "Structure of the saccharide-binding domain of the human natural killer cell inhibitory receptor p75/AIRM1". Acta Crystallogr. D . 60 (Pt 2): 401– 3. doi :10.1107/S0907444903028439 . PMID 14747738 . Ikehara Y, Ikehara SK, Paulson JC (2004). "Negative regulation of T cell receptor signaling by Siglec-7 (p70/AIRM) and Siglec-9" . J. Biol. Chem . 279 (41): 43117– 25. doi :10.1074/jbc.M403538200 PMID 15292262 . Avril T, Floyd H, Lopez F, et al. (2005). "The membrane-proximal immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motif is critical for the inhibitory signaling mediated by Siglecs-7 and -9, CD33-related Siglecs expressed on human monocytes and NK cells" . J. Immunol . 173 (11): 6841– 9. doi :10.4049/jimmunol.173.11.6841 PMID 15557178 . Yamaji T, Mitsuki M, Teranishi T, Hashimoto Y (2005). "Characterization of inhibitory signaling motifs of the natural killer cell receptor Siglec-7: attenuated recruitment of phosphatases by the receptor is attributed to two amino acids in the motifs" . Glycobiology . 15 (7): 667– 76. doi :10.1093/glycob/cwi048 PMID 15703304 . Attrill H, Takazawa H, Witt S, et al. (2006). "The structure of siglec-7 in complex with sialosides: leads for rational structure-based inhibitor design" . Biochem. J . 397 (2): 271– 8. doi :10.1042/BJ20060103 . PMC 1513286 PMID 16623661 . Rapoport EM, Pazynina GV, Sablina MA, et al. (2006). "Probing sialic acid binding Ig-like lectins (siglecs) with sulfated oligosaccharides". Biochemistry Mosc . 71 (5): 496– 504. doi :10.1134/S0006297906050051 . PMID 16732727 . S2CID 11537303 . Biedermann B, Gil D, Bowen DT, Crocker PR (2007). "Analysis of the CD33-related siglec family reveals that Siglec-9 is an endocytic receptor expressed on subsets of acute myeloid leukemia cells and absent from normal hematopoietic progenitors". Leuk. Res . 31 (2): 211– 20. doi :10.1016/j.leukres.2006.05.026 . PMID 16828866 .
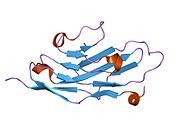
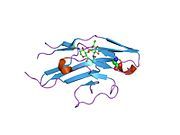
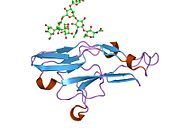
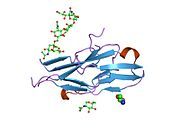
PDB gallery
1nko : Energetic and structural basis of sialylated oligosaccharide recognition by the natural killer cell inhibitory receptor p75/AIRM1 or Siglec-7
1o7s : HIGH RESOLUTION STRUCTURE OF SIGLEC-7
1o7v : HIGH RESOLUTION STRUCTURE OF SIGLEC-7
2df3 : The structure of Siglec-7 in complex with alpha(2,3)/alpha(2,6) disialyl lactotetraosyl 2-(trimethylsilyl)ethyl
2g5r : Crystal structure of Siglec-7 in complex with methyl-9-(aminooxalyl-amino)-9-deoxyNeu5Ac (oxamido-Neu5Ac)
2hrl : Siglec-7 in complex with GT1b
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine , which is in the public domain .
1–50 51–100 101–150 151–200 201–250 251–300 301–350