Racepinefrine
Appearance
(Redirected from Racepinephrine)
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | AsthmaNefrin, Dey-Dose, Micronefrin, Nephron, S-2 Inhalant, Vaponefrin, Vaponephrin |
| Other names | Racepinephrine; Racemic epinephrine; Racemic adrenaline; DL-Epinephrine; DL-Adrenaline; dl-Epinephrine; dl-Adrenaline; (±)-Epinephrine; (±)-Adrenaline |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
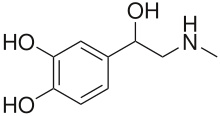
| Formula | C9H13NO3 |
| Molar mass | 183.207 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Racepinefrine (INN, USAN), or racepinephrine, sold under the brand name Vaponefrin among others, is a sympathomimetic medication described as a vasoconstrictor, bronchodilator, cardiostimulant, mydriatic, and antiglaucoma agent.[1][2][3][4][5] It is the racemic form of epinephrine (adrenaline) and is also known as dl-epinephrine and (±)-epinephrine.[1][2][3] The drug is used pharmaceutically as the hydrochloride salt.[3][2] It has been marketed in the United States and Canada.[3]
References
[edit]- ^ a b Elks, J. (2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer US. p. 1-PA247. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- ^ a b c Buckingham, J. (1993). Dictionary of Natural Products. Taylor & Francis. p. 87. ISBN 978-0-412-46620-5. Retrieved 2024-09-01.
- ^ a b c d Schweizerischer Apotheker-Verein (2000). Index Nominum 2000: International Drug Directory. Index nominum. Medpharm Scientific Publishers. p. 909. ISBN 978-3-88763-075-1. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- ^ Publishing, W.A.W.A. (2013). Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Encyclopedia. Volumes 1-4. Elsevier Science. pp. 1448–1449. ISBN 978-0-8155-1856-3. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- ^ Milne, G.W.A. (2018). Drugs: Synonyms and Properties. Routledge Revivals. Taylor & Francis. p. 513. ISBN 978-1-351-78990-5. Retrieved 1 September 2024.
