Pashalik of Scutari
Pashalik of Scutari Pashallëku i Shkodrës | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1757–1831 | |||||||||||
|
Flag during the reign of Kara Mahmud Bushati | |||||||||||
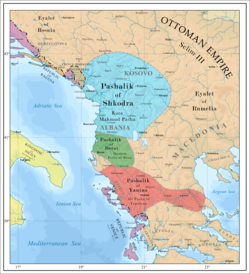 Albanian pashaliks in 1790-1795. The Pashalik of Shkodra is colored in blue. | |||||||||||
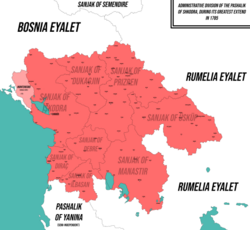 Pashalik of Scutari in 1785 | |||||||||||
| Status | Autonomous province of the Ottoman Empire; de facto independent[1] | ||||||||||
| Capital | Shkodër | ||||||||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam Roman Catholicism Eastern Orthodoxy | ||||||||||
| Government | Pashalik | ||||||||||
| Pasha | |||||||||||
• 1757–1774 | Mehmed Bushati | ||||||||||
• 1774–1778 | Mustafa Bushati | ||||||||||
• 1778–1796 | Kara Mahmud Bushati | ||||||||||
• 1796–1810 | Ibrahim Bushati | ||||||||||
• 1810–1831 | Mustafa Sherifi Bushati | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Early modern period | ||||||||||
• Established | 1757 | ||||||||||
• Disestablished | 1831 | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||
The Pashalik of Scutari (1757–1831), also known as the Bushati Pashalik,[2] was an Albanian pashalik within the Ottoman Empire that was ruled by the Bushati family. Its capital was Shkodër and ruled areas in modern-day Albania and large majority of modern-day Montenegro.[1]
At its peak, during the reign of Kara Mahmud Bushati, the pashalik encompassed much of Albania and Kosovo, western Macedonia, southeastern Serbia, and most of Montenegro. Up to 1830, the Pashalik of Shkodra controlled most of the aforementioned lands (including southern Montenegro).[3][4]
Background
[edit]The weakening of Ottoman central authority and the timar system of land ownership brought anarchy to the Albanian-populated region of the Ottoman empire. In the late eighteenth century, two Albanian centers of power emerged: Shkodër, under the Bushati family; and Janina, under Ali Pasha of Tepelenë. Both regions cooperated with and defied the Sublime Porte as their interests required.[5]
History
[edit]The influence of the Bushati was established between 1757 and 1775 by Mehmed Bushati,[6] known as Bushatli Mehmed Pasha Plaku[7] (Albanian: plaku, 'the elder'). In 1757, Mehmed, having eliminated two rival families[8] and heading the Tabak esnaf of Shkodra as their spiritual Sheikh proclaimed himself pasha of Shkodër. Mehmet Bushati transformed the Sanjak of Scutari, created in 1479, into a semi-autonomous Pashalik of Shkodra. He was praised by Istanbul for ending the Arab and Berber pirates' reign of terror over the Venetian ships in the Adriatic.[citation needed] Mehmet expanded his area of control to the northeast, enlarged his political authority and refused to pay taxes to the Sublime Porte.[6]
Mehmed Bushati's son and third successor, Kara Mahmud Bushati, pursued a policy of military expansion and established his control over northern Albania up to the Toskëria and Kosovo. He launched two attacks on Montenegro (1785, 1796) and against Venice in revenge for the Bey of Tunis[clarification needed]. He defeated several Ottoman expeditions dispatched to subdue him for his uncontrolled behavior. Kara Mahmud subdued Montenegrin tribes and forced the Venetians to pay him a tribute (haraç). He courted both the Austrian and Russian empires, receiving a promise from Vienna that they would recognise him as lord of all Albania in return for an alliance against the Sublime Porte. However, after taking money from the Austrians he decapited the Viennese emissaries, sent their heads to Istanbul and pledged loyalty to the sultan.[9] In response, the Ottomans ex post facto pardoned Kara Mahmud for his attacks against Venice and reappointed him governor of Shkodër.

In 1796, the Montenegrin tribes of Piperi and Bjelopavlići defeated an expedition launched against them by the Shkodran Muslims in the Battle of Krusi and decapitated Kara Mahmud Bushati.[9] His death signalled a decline in autonomy for the pashalik.[1] Kara Mahmud's successor Ibrahim Bushati cooperated with the Ottoman empire until his own death (1810). He was appointed Beylerbey of Rumelia and subdued the Serbs during his military expeditions against Belgrade.[9]
When the Russo-Turkish War (1828–1829) broke out the territories of the Pahsalik of Scutari were further extended by Mustafa Pasha Bushati. Sultan Mahmud II required Mustafa Pasha Bushati's aid in raising troops. In return for the Pasha's support the sultan put more than half of Albania under Bushati's administration, but Mustafa requested more territory and power. After the Russo-Turkish War, fearing Albanian disobedience and consequent independence, the sultan commanded Bushati to transfer his territories to the Grand Vizier and to agree to the placement of an Ottoman garrison in Shkodra. However Bushati refused the sultan's order, consequently Ottoman troops were sent against him. The Albanian and Ottoman armies clashed in Macedonia, where Mustafa Bushati lost three battles and was obliged to retreat to Shkodra.[6]
The Bushati dynasty's rule came to an end when an Ottoman army under Mehmed Reshid Pasha laid siege to the Rozafa castle at Shkodër in 1831 and forced the surrender of the last pasha Mustafa Bushati who had rebelled against the sultan whom they accused as Kaurr – infidel.[9] This defeat not only ended a planned alliance between the Albanians and the Bosnians, who were similarly seeking autonomy,[9] but also brought about the dissolution of the pashalik.
Aftermath
[edit]In 1867, the Sanjak of Scutari merged with the Sanjak of Üsküb (Skopje), forming the Scutari Vilayet. The vilayet was subsequently divided into three sanjaks: İșkodra (Scutari), Prizren and Dibra. In 1877, the Sanjak of Prizren was transferred to the Kosovo Vilayet, and the Sanjak of Dibra was transferred to the Monastir Vilayet. Following the territorial transfers, the Sanjak of Scutari was subsequently divided into two sanjaks: Sanjak of Scutari and Sanjak of Draç (Durrës).
Pashas
[edit]- Mehmed Bushati (1757–1774)
- Mustafa Bushati (1774–1778)
- Kara Mahmud Bushati (1778–1796)
- Ibrahim Bushati (1796–1810)
- Mustafa Sherifi[10] (1810-1831)
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Elsie 2005, p. 65.
- ^ Brisku, Adrian (2013-08-01). Bittersweet Europe: Albanian and Georgian Discourses on Europe, 1878-2008. Berghahn Books. ISBN 978-0-85745-985-5.
- ^ Vickers 1999, p. 18.
- ^ Iseni 2008, p. 120.
- ^ Zickel & Iwaskiw 1994, p. 19.
- ^ a b c Dauti 2018, p. 32.
- ^ Kiel 1990, p. 231.
- ^ Castellan 2002, p. 37: ayant éliminé deux familles rivales
- ^ a b c d e Jazexhi 2002, p. 48.
- ^ Elsie 2012, p. [page needed].
Bibliography
[edit]- Bahl, Taru; Syed, M. H. (2003). Encyclopaedia of Muslim World. New Delhi: Anmol Publications Pvt. Ltd. ISBN 978-81-261-1419-1.[permanent dead link]
- Castellan, Georges (2002). Histoire de l'Albanie et des albanais. N.p.: Editions Armeline. ISBN 978-2-910878-20-7.
- Dauti, Daut (30 January 2018). Britain, the Albanian Question and the Demise of the Ottoman Empire 1876-1914 (phd). University of Leeds.
- Elsie, Robert (2005). Albanian literature: a short history. London: I. B. Tauris in association with The Centre for Albanian Studies. ISBN 978-1-84511-031-4.
- Elsie, Robert (2012). A Biographical Dictionary of Albanian History. London / New York: I.B. Tauris in association with The Centre of Albanian Studies. ISBN 978-1-78076-431-3.
- Iseni, Bashkim (2008). La question nationale en Europe du Sud-Est: genèse, émergence et développement de l'identité nationale albanaise au Kosovo et en Macédoine. Peter Lang. ISBN 9783039113200. Retrieved 5 March 2013.
- Jazexhi, Olsi (2002). The Albanian Pashalik of Shkodra under Bushatlis 1757 – 1831. Kuala Lumpur: IIUM. Archived from the original on 2015-06-27.
- Jelavich, Barbara (1999) [1983]. History of the Balkans: Eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-27458-6.
Kiel, Machiel (1990). Ottoman architecture in Albania, 1385-1912. Research Centre for Islamic History, Art and Culture. ISBN 978-92-9063-330-3.
- Vickers, Miranda (1999). The Albanians: A Modern History. New York: I. B. Tauris. ISBN 978-1-86064-541-9.
- Zickel, Raymond; Iwaskiw, Walter R. (1994). Albania: A Country Study. Washington, D.C.: GPO for Library of Congress.

