Portal:United Kingdom
The United Kingdom Portal
 |
 |
| |
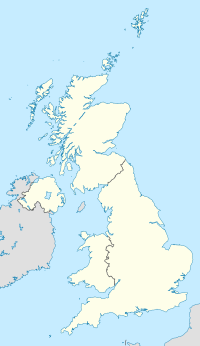
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. The UK includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and most of the smaller islands within the British Isles, making up a total area of 94,354 square miles (244,376 km2). Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea, and the Irish Sea. The United Kingdom had an estimated population of over 68.2 million people in 2023. The capital and largest city of both England and the United Kingdom is London, whose wider metropolitan area is the largest in Western Europe, with a population of 14.9 million. The cities of Edinburgh, Cardiff, and Belfast are the national capitals of Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland, respectively.
The lands of the UK have been inhabited continuously since the Neolithic. In AD 43, the Roman conquest of Britain began; the Roman departure was followed by Anglo-Saxon settlement. In 1066, the Normans conquered England. With the end of the Wars of the Roses, the English state stabilised and began to grow in power, resulting by the 16th century in the annexation of Wales, and the establishment of the British Empire. Over the course of the 17th century, the role of the British monarchy was reduced, particularly as a result of the English Civil War. In 1707, the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of Scotland united under the Treaty of Union to create the Kingdom of Great Britain. The Acts of Union 1800 incorporated the Kingdom of Ireland to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland in 1801. Most of Ireland seceded from the UK in 1922 as the Irish Free State, and the Royal and Parliamentary Titles Act 1927 created the present United Kingdom.
The UK became the first industrialised country and was the world's foremost power for the majority of the 19th and early 20th centuries, particularly during the Pax Britannica between 1815 and 1914. The British Empire was the leading economic power for most of the 19th century, a position supported by its agricultural prosperity, its role as a dominant trading nation, a massive industrial capacity, significant technological achievements, and the rise of 19th-century London as the world's principal financial centre. At its height in the 1920s, the British Empire encompassed almost a quarter of the world's landmass and population, and was the largest empire in history. However, its involvement in the First World War and the Second World War damaged Britain's economic power and a global wave of decolonisation led to the independence of most British colonies. (Full article...)
Featured article
Ashford v Thornton was an 1818 English legal case in the Court of King's Bench that upheld the right of the defendant, on a private appeal from an acquittal for murder, to trial by battle. In 1817, Abraham Thornton (pictured) was charged with the murder of Mary Ashford. Thornton met Ashford at a dance, and walked with her from the event. The next morning, Ashford was found drowned in a pit, with little outward signs of violence. Although public opinion was heavily against Thornton, the jury quickly acquitted him, and also found him not guilty of rape. Mary's brother, William Ashford, launched an appeal, and Thornton was rearrested. Thornton claimed the right to trial by battle, a medieval usage which had never been repealed by Parliament. Ashford argued that the evidence against Thornton was overwhelming, and that he was thus ineligible to wager battle. The court decided that the evidence against Thornton was not overwhelming, and that trial by battle was a permissible option under law; thus Thornton was granted trial by battle. Ashford declined the offer of battle and Thornton was freed from custody. Appeals such as Ashford's were abolished by statute the following year, and with them the right to trial by battle. Thornton emigrated to the United States, where he died about 1860. (Full article...)
Featured biography
John Michael Wright (May 1617 – July 1694) was an English painter, mainly of portraits in the Baroque style. Born and raised in London, Wright trained in Edinburgh under the Scots painter George Jamesone, and sometimes described himself as Scottish in documents. He acquired a considerable reputation as an artist and scholar during a long sojourn in Rome. There he was admitted to the Accademia di San Luca and was associated with some of the leading artists of his generation. He was engaged by Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria, the governor of the Spanish Netherlands, to acquire artworks in Oliver Cromwell's England in 1655.
He took up permanent residence in England from 1656 and served as court painter before and after the English Restoration. A convert to Roman Catholicism, he was a favourite of the restored Stuart court, a client of both Charles II and James II, and was a witness to many of the political manoeuvrings of the era. In the final years of the Stuart monarchy he returned to Rome as part of an embassy to Pope Innocent XI.
After a period of critical neglect, Wright is now rated as one of the leading indigenous British painters of his generation, largely for the distinctive realism in his portraiture. Perhaps due to the unusually cosmopolitan nature of his experience, he was favoured by patrons at the highest level of society in an age in which foreign artists were usually preferred. Wright's paintings of royalty and aristocracy are included amongst the collections of many leading galleries today. (Full article...)
General images -
Subportals
WikiProjects
Things you can do
- Visit the British Wikipedians' notice board.
- The noticeboard is the central forum for information and discussion on editing related to the United Kingdom.
- Comment at the British deletion sorting page.
- This page lists deletion discussions on topics relating to the United Kingdom.
Featured pictures
Did you know -

- ... that when Westminster City Council in London agreed to use "global majority" as a more inclusive term than BAME or "ethnic minority", a Conservative MP called it "deeply sinister"?
- ... that Phil Fletcher as Hacker T. Dog caused Lauren Layfield to make the "most famous snort" in the United Kingdom in 2016?
- ... that, before same-sex unions were legally recognised in the UK, the London Partnership Register allowed nearly 1,000 couples to celebrate their relationships?
- ... that booing heard after the United Kingdom's entry at the Eurovision Song Contest 1984 was reportedly either a response to past football hooliganism, claims of lip syncing, or alleged plagiarism of the Supremes?
- ... that Sting wrote "We Work the Black Seam" because he felt that "the case for coal was never put to the nation" during the 1984–85 British miners' strike, which began 40 years ago today?
- ... that Graham Fraser pioneered cochlear implantation in the United Kingdom?
In the news
- 18 January 2025 – Israel–Hamas war protests
- Israel–Hamas war protests in the United Kingdom
- More than 70 people are arrested at a pro-Palestine protest in London, England, United Kingdom for violating protest regulations. (BBC News)
- 18 January 2025 – Protests against Donald Trump
- In Washington, D.C., the Women's March holds a protest rebranded as the People's March against U.S. President-elect Donald Trump ahead of his inauguration on Monday. Women's March protests are also held in several cities in the United Kingdom. (Reuters) (WRC-TV) (BBC News)
- 17 January 2025 –
- British oil and gas company BP announces that it will lay off 4,700 employees and 3,000 contractors globally to reduce costs. (AP)
- 16 January 2025 – Ukraine–United Kingdom relations
- British Prime Minister Keir Starmer visits Kyiv, Ukraine, to sign a 100-year agreement with Ukraine that will formalize British economic and military support for Ukraine. (Sky News) (BBC News)
- 14 January 2025 –
- British Treasury Economic Secretary Tulip Siddiq resigns amid an anti-corruption investigation in Bangladesh involving her family. (BBC News)
Categories
Other UK-connected Wikipedias
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus