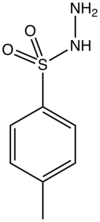
p-Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4-methylbenzenesulfonohydrazide
| |
| Other names
tosyl hydrazide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.917 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 108–110 °C (226–230 °F; 381–383 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    
| |
| Danger | |
| H242, H301, H302, H315, H317, H319, H341, H373, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P210, P220, P234, P260, P261, P264, P270, P272, P273, P280, P281, P301+P310, P301+P312, P302+P352, P305+P351+P338, P308+P313, P314, P321, P330, P332+P313, P333+P313, P337+P313, P362, P363, P370+P378, P391, P403+P235, P405, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
p-Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide is the organic compound with the formula CH3C6H4SO2NHNH2. It is a white solid that is soluble in many organic solvents but not water or alkanes. It is a reagent in organic synthesis.[1]
Synthesis
[edit]Toluenesulfonyl hydrazide is prepared by the reaction of a toluenesulfonyl chloride with hydrazine:[2]
Reactions
[edit]Tosylhydrazides can be installed by nucleophilic attack and later removed by base. It thus provides a way to convert C-Cl to C-H.[3]
With ketones and aldehydes, it condenses to give the hydrazones:
- CH3C6H4SO2NHNH2 + R2C=O → CH3C6H4SO2NHN=CR2 + H2O
Upon heating in solution, it degrades, releasing diimide (N2H2), a useful reducing agent. Triisopropylbenzenesulfonylhydrazide is far more useful for this reaction.
Use
[edit]The compound is an important reagent in organic synthesis, serving as a source of reactive diimide and its subsequent chemical reactions. It condenses with ketones and aldehydes to form hydrazones, which can be further transformed into reactive intermediates such as diazo compounds or carbenes. N-heterocycles can be synthesized through 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions. Ketone hydrazones are defunctionalized using mild reagents in a modified Wolff-Kishner reaction.[4] A notable commercial application of this compound is as a foaming reagent for polymers.[5]
References
[edit]- ^ Chamberlin, A. Richard; Sheppeck, James E.; Goess, Brian; Lee, Chulbom (2007). "P-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt137.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ^ Friedman, Lester; Litle, Robert L.; Reichle, Walter R. (1960). "p-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide". Org. Synth. 40: 93. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.040.0093.
- ^ W. L. F. Armarego (1967). "Halogenoquinazolines". In W. L. F. Armarego (ed.). Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. pp. 11–38. doi:10.1002/9780470186916.ch7. ISBN 9780470186916.
- ^ Chamberlin, A. Richard; Sheppeck, James E.; Goess, Brian; Lee, Chulbom (2007). "P-Toluenesulfonylhydrazide". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rt137.pub2. ISBN 978-0471936237.
- ^ Baoming, X.; Huan, H.; Yangyang, H.; Jie, Z.; Zhishan P.; Qiang, T.: Research progress on the synthesis and application of the sulfonyl hydrazides blowing agent in Chemistry World 56 (2015) 125–128.


