Neocortex
| Neocortex | |
|---|---|
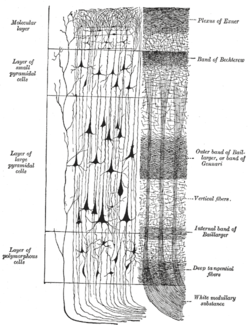 A representative column of neocortex. Cell body layers are labeled on the left, and fiber layers are labeled on the right. | |
| Identifiers | |
| MeSH | D019579 |
| NeuroNames | 2314 |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_2547 |
| TA98 | A14.1.09.304 A14.1.09.307 |
| TA2 | 5532 |
| FMA | 62429 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands,[1] spatial reasoning and language.[2] The neocortex is further subdivided into the true isocortex and the proisocortex.[3]
In the human brain, the cerebral cortex consists of the larger neocortex and the smaller allocortex, respectively taking up 90% and 10%.[4] The neocortex is made up of six layers, labelled from the outermost inwards, I to VI.
Etymology
[edit]The term is from cortex, Latin, "bark" or "rind", combined with neo-, Greek, "new". Neopallium is a similar hybrid, from Latin pallium, "cloak". Isocortex and allocortex are hybrids with Greek isos, "same", and allos, "other".
Anatomy
[edit]The neocortex is the most developed in its organisation and number of layers, of the cerebral tissues.[5] The neocortex consists of the grey matter, or neuronal cell bodies and unmyelinated fibers, surrounding the deeper white matter (myelinated axons) in the cerebrum. This is a very thin layer though, about 2–4 mm thick.[6] There are two types of cortex in the neocortex, the proisocortex and the true isocortex. The pro-isocortex is a transitional area between the true isocortex and the periallocortex (part of the allocortex). It is found in the cingulate cortex (part of the limbic system), in Brodmann's areas 24, 25, 30 and 32, the insula and the parahippocampal gyrus.
Of all the mammals studied to date (including humans), a species of oceanic dolphin known as the long-finned pilot whale has been found to have the most neocortical neurons.[7]
Geometry
[edit]The neocortex is smooth in rodents and other small mammals, whereas in elephants, dolphins and primates and other larger mammals it has deep grooves (sulci) and ridges (gyri). These folds allow the surface area of the neocortex to be greatly increased. All human brains have the same overall pattern of main gyri and sulci, although they differ in detail from one person to another.[8] The mechanism by which the gyri form during embryogenesis is not entirely clear, and there are several competing hypotheses that explain gyrification, such as axonal tension,[9] cortical buckling[10] or differences in cellular proliferation rates in different areas of the cortex.[11]
Layers
[edit]
The neocortex contains both excitatory (~80%) and inhibitory (~20%) neurons, named for their effect on other neurons.[12] The human neocortex consists of hundreds of different types of cells.[13] The structure of the neocortex is relatively uniform (hence the alternative names "iso-" and "homotypic" cortex), consisting of six horizontal layers segregated principally by cell type and neuronal connections.[14] However, there are many exceptions to this uniformity; for example, layer IV is small or missing in the primary motor cortex. There is some canonical circuitry within the cortex; for example, pyramidal neurons in the upper layers II and III project their axons to other areas of neocortex, while those in the deeper layers V and VI often project out of the cortex, e.g. to the thalamus, brainstem, and spinal cord. Neurons in layer IV receive the majority of the synaptic connections from outside the cortex (mostly from thalamus), and themselves make short-range, local connections to other cortical layers.[12] Thus, layer IV is the main recipient of incoming sensory information and distributes it to the other layers for further processing.
Cortical columns
[edit]
The neocortex is often described as being arranged in vertical structures called cortical columns, patches of neocortex with a diameter of roughly 0.5 mm (and a depth of 2 mm, i.e., spanning all six layers). These columns are often thought of as the basic repeating functional units of the neocortex, but their many definitions, in terms of anatomy, size, or function, are generally not consistent with each other, leading to a lack of consensus regarding their structure or function or even whether it makes sense to try to understand the neocortex in terms of columns.[15]
Function
[edit]The neocortex is derived embryonically from the dorsal telencephalon, which is the rostral part of the forebrain. The neocortex is divided into regions demarcated by the cranial sutures in the skull above, into frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal lobes, which perform different functions. For example, the occipital lobe contains the primary visual cortex, and the temporal lobe contains the primary auditory cortex. Further subdivisions or areas of neocortex are responsible for more specific cognitive processes. In humans, the frontal lobe contains areas devoted to abilities that are enhanced in or unique to our species, such as complex language processing localized to the ventrolateral prefrontal cortex (Broca's area).[12] In humans and other primates, social and emotional processing is localized to the orbitofrontal cortex.
The neocortex has also been shown to play an influential role in sleep, memory and learning processes. Semantic memories appear to be stored in the neocortex, specifically the anterolateral temporal lobe of the neocortex.[16] It is also involved in instrumental conditioning; responsible for transmitting sensory information and information about plans for movement to the basal ganglia.[16] The firing rate of neurons in the neocortex also has an effect on slow-wave sleep. When the neurons are at rest and are hyperpolarizing, a period of inhibition occurs during a slow oscillation, called the down state. When the neurons of the neocortex are in the excitatory depolarizing phase and are firing briefly at a high rate, a period of excitation occurs during a slow oscillation, called the up state.[16]
Clinical significance
[edit]Lesions that develop in neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, interrupt the transfer of information from the sensory neocortex to the prefrontal neocortex. This disruption of sensory information contributes to the progressive symptoms seen in neurodegenerative disorders such as changes in personality, decline in cognitive abilities, and dementia.[17] Damage to the neocortex of the anterolateral temporal lobe results in semantic dementia, which is the loss of memory of factual information (semantic memories). These symptoms can also be replicated by transcranial magnetic stimulation of this area. If damage is sustained to this area, patients do not develop anterograde amnesia and are able to recall episodic information.[18]
Evolution
[edit]The neocortex is the newest part of the cerebral cortex to evolve (hence the prefix neo meaning new); the other part of the cerebral cortex is the allocortex. The cellular organization of the allocortex is different from the six-layered neocortex. In humans, 90% of the cerebral cortex and 76% of the entire brain is neocortex.[12]
For a species to develop a larger neocortex, the brain must evolve in size so that it is large enough to support the region. Body size, basal metabolic rate and life history are factors affecting brain evolution and the coevolution of neocortex size and group size.[19] The neocortex increased in size in response to pressures for greater cooperation and competition in early ancestors. With the size increase, there was greater voluntary inhibitory control of social behaviors resulting in increased social harmony.[20]
The six-layer cortex appears to be a distinguishing feature of mammals; it has been found in the brains of all mammals, but not in any other animals.[2] There is some debate,[21][22] however, as to the cross-species nomenclature for neocortex. In avians, for instance, there are clear examples of cognitive processes that are thought to be neocortical in nature, despite the lack of the distinctive six-layer neocortical structure.[23] Evidence suggest the avian pallium to be broadly equivalent to the mammalian neocortex.[24][25][26] In a similar manner, reptiles, such as turtles, have primary sensory cortices. A consistent, alternative name has yet to be agreed upon.
Neocortex ratio
[edit]The neocortex ratio of a species is the ratio of the size of the neocortex to the rest of the brain. A high neocortex ratio is thought to correlate with a number of social variables such as group size and the complexity of social mating behaviors.[27] Humans have a large neocortex as a percentage of total brain matter when compared with other mammals. For example, there is only a 30:1 ratio of neocortical gray matter to the size of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem of chimpanzees, while the ratio is 60:1 in humans.[28]
See also
[edit]- List of regions in the human brain
- Blue Brain, a project to produce a computer simulation of a neocortical column and eventually a whole neocortex
- Memory-prediction framework, a theory of the neocortex function by Jeff Hawkins and related software models
- Claustrum
References
[edit]- ^ Lodato S, Arlotta P (2015-11-13). "Generating neuronal diversity in the mammalian cerebral cortex". Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology. 31 (1): 699–720. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100814-125353. PMC 4778709. PMID 26359774.
The neocortex is the part of the brain responsible for execution of higher-order brain functions, including cognition, sensory perception, and sophisticated motor control.
- ^ a b Lui JH, Hansen DV, Kriegstein AR (July 2011). "Development and evolution of the human neocortex". Cell. 146 (1): 18–36. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.030. PMC 3610574. PMID 21729779.
- ^ "BrainInfo". braininfo.rprc.washington.edu.
- ^ Saladin, K (2012). Anatomy & physiology : the unity of form and function (6th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill. p. 417. ISBN 9780073378251.
- ^ Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary (32nd ed.). Elsevier Saunders. 2012. p. 1238. ISBN 978-1-4160-6257-8.
- ^ Kandel E (2006). Principles of neural science (5th ed.). Appleton and Lange: McGraw Hill. ISBN 978-0071390118.
- ^ Mortensen HS, Pakkenberg B, Dam M, Dietz R, Sonne C, Mikkelsen B, Eriksen N (2014). "Quantitative relationships in delphinid neocortex". Frontiers in Neuroanatomy. 8: 132. doi:10.3389/fnana.2014.00132. PMC 4244864. PMID 25505387.
- ^ Moerel M, De Martino F, Formisano E (2006). "An anatomical and functional topography of human auditory cortical areas". Front. Neurosci. 8 (225): 225. doi:10.3389/fnins.2014.00225. PMC 4114190. PMID 25120426.
For example, in the human brain, the auditory cortex presents an expansion of cortical surface, with additional gyri and with a much larger inter-individual variability...
- ^ Van Essen DC (January 1997). "A tension-based theory of morphogenesis and compact wiring in the central nervous system" (PDF). Nature. 385 (6614): 313–8. doi:10.1038/385313a0. PMID 9002514. S2CID 4355025.
- ^ Richman DP, Stewart RM, Hutchinson JW, Caviness VS (July 1975). "Mechanical model of brain convolutional development". Science. 189 (4196): 18–21. doi:10.1126/science.1135626. PMID 1135626.
- ^ Ronan L, Voets N, Rua C, Alexander-Bloch A, Hough M, Mackay C, Crow TJ, James A, Giedd JN, Fletcher PC (August 2014). "Differential tangential expansion as a mechanism for cortical gyrification". Cerebral Cortex. 24 (8): 2219–28. doi:10.1093/cercor/bht082. PMC 4089386. PMID 23542881.
- ^ a b c d Noback CR, Strominger NL, Demarest RJ, Ruggiero DA (2005). The Human Nervous System: Structure and Function (Sixth ed.). Totowa, NJ: Humana Press. ISBN 1-59259-730-0.
- ^ Berg, Jim; Sorensen, Staci A.; Ting, Jonathan T.; Miller, Jeremy A.; Chartrand, Thomas; Buchin, Anatoly; Bakken, Trygve E.; Budzillo, Agata; Dee, Nick; Ding, Song-Lin; Gouwens, Nathan W.; Hodge, Rebecca D.; Kalmbach, Brian; Lee, Changkyu; Lee, Brian R. (October 2021). "Human neocortical expansion involves glutamatergic neuron diversification". Nature. 598 (7879): 151–158. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03813-8. ISSN 1476-4687. PMC 8494638. PMID 34616067.
- ^ Kurzweil R (2012). How to Create a Mind: The Secret of Human Thought Revealed. New York: Viking Penguin. p. 36. ISBN 978-0670025299.
- ^ Horton JC, Adams DL (April 2005). "The cortical column: a structure without a function". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 360 (1456): 837–62. doi:10.1098/rstb.2005.1623. PMC 1569491. PMID 15937015.
- ^ a b c Carlson N (2013). Physiology of Psychology (Eleventh ed.). Pearson. ISBN 978-0-205-239481.
- ^ Braak H, Del-Tredici K, Bohl J, Bratzke H, Braak E (2000). Annals of the New York academy of sciences, Vol. 911. New York, NY, US: New York Academy of Sciences. ISBN 1-57331-263-0.
- ^ Carlson N (2013). Physiology of Behavior. Pearson. ISBN 978-0-205-23948-1.
- ^ Dunbar RI, Shultz S (April 2007). "Understanding primate brain evolution". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences. 362 (1480): 649–58. doi:10.1098/rstb.2006.2001. PMC 2346523. PMID 17301028.
- ^ Bjorklund D, Kipp K (2002). Social cognition, inhibition, and theory of mind: The evolution of human intelligence. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associate Publishers. ISBN 0-8058-3267-X.
- ^ Jarvis ED, Güntürkün O, Bruce L, Csillag A, Karten H, Kuenzel W, et al. (February 2005). "Avian brains and a new understanding of vertebrate brain evolution". Nature Reviews. Neuroscience. 6 (2): 151–9. doi:10.1038/nrn1606. PMC 2507884. PMID 15685220.
- ^ Reiner A, Perkel DJ, Bruce LL, Butler AB, Csillag A, Kuenzel W, et al. (May 2004). "Revised nomenclature for avian telencephalon and some related brainstem nuclei". The Journal of Comparative Neurology. 473 (3): 377–414. doi:10.1002/cne.20118. PMC 2518311. PMID 15116397.
- ^ Prior H, Schwarz A, Güntürkün O (August 2008). De Waal F (ed.). "Mirror-induced behavior in the magpie (Pica pica): evidence of self-recognition". PLOS Biology. 6 (8): e202. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.0060202. PMC 2517622. PMID 18715117.
- Alison Motluk (19 August 2008). "Mirror test shows magpies aren't so bird-brained". New Scientist.
- ^ Stacho, Martin; Herold, Christina; Rook, Noemi; Wagner, Hermann; Axer, Markus; Amunts, Katrin; Güntürkün, Onur (2020-09-25). "A cortex-like canonical circuit in the avian forebrain". Science. 369 (6511). doi:10.1126/science.abc5534. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32973004.
- ^ Nieder, Andreas; Wagener, Lysann; Rinnert, Paul (September 25, 2020). "A neural correlate of sensory consciousness in a corvid bird". Science. 369 (6511): 1626–1629. Bibcode:2020Sci...369.1626N. doi:10.1126/science.abb1447. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32973028.
- ^ Herculano-Houzel, Suzana (September 25, 2020). "Birds do have a brain cortex—and think". Science. 369 (6511): 1567–1568. Bibcode:2020Sci...369.1567H. doi:10.1126/science.abe0536. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 32973020.
- ^ Dunbar RI (1995). "Neocortex size and group size in primates: A test of the hypothesis". Journal of Human Evolution. 28 (3): 287–96. doi:10.1006/jhev.1995.1021.
- ^ Semendeferi K, Lu A, Schenker N, Damasio H (March 2002). "Humans and great apes share a large frontal cortex". Nature Neuroscience. 5 (3): 272–6. doi:10.1038/nn814. PMID 11850633. S2CID 5921065.
External links
[edit]- Comparative Neuroscience at Wikiversity
- "Model of the neocortex". Brain Engineering Laboratory. Dartmouth College.
- "Proisocortex". Brain Info. University of Washington. Archived from the original on 2006-10-23. Retrieved 2014-06-17.
