Mesoniviridae
| Alphamesonivirus | |
|---|---|
| |
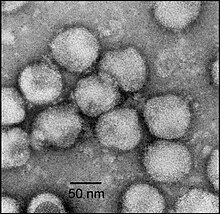
| Electron micrograph of negatively stained Nam Dinh virus (NDiV) virions | |
| |
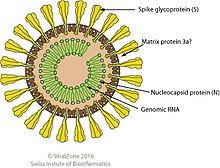
| Mesonivirus virion | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Orthornavirae |
| Phylum: | Pisuviricota |
| Class: | Pisoniviricetes |
| Order: | Nidovirales |
| Suborder: | Mesnidovirineae |
| Family: | Mesoniviridae |
| Subfamily: | Hexponivirinae |
| Genus: | Alphamesonivirus |
Mesoniviridae is a family of enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses in the order Nidovirales which infect mosquitoes. The family is named after the size of the genomes relative to other nidoviruses, with meso- coming from the Greek word mesos, which means medium, and -ni being an abbreviation of nido.[1][2][3]
History
[edit]The family is relatively new, having only been discovered in 2011. The first virus, which was named Nam Dinh virus, was found in the Vietnamese province of Nam Định.[2] The second virus, named Cavally virus, was then found in Côte d'Ivoire.[4] These two viruses were later found to be of the same species. A third member of this first species, named Dak Nong virus, was later found in Culex tritaeniorhynchus populations in Vietnam.[5] In 2013, four more mesoniviruses were discovered in mosquito populations, all within Côte d'Ivoire,[6] and in 2014 four mesoniviruses were discovered in mosquito populations in Australia,[7] Indonesia, and Thailand.[3]
Virology
[edit]Structure
[edit]Members of this family are enveloped, spherical in shape and 60–80 nm in diameter with club-shaped surface spikes. There are eight major structural proteins, including a nucleocapsid protein (25 kDa in weight), four differentially glycosylated forms of the membrane protein (20, 19, 18 and 17 kDa) and the spike (S) protein (77 kDa), which is cleaved to produce two S protein subunits (23 and 57 kDa).[6][4]
Genome
[edit]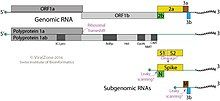
The genomes are linear, positive-sense, polycistronic, single-stranded RNA, and are about 20,000 nucleotides in length, with a 3' poly(A) tail and seven major open reading frames (ORFs). Two overlapping ORFs, together known as ORF1ab, are at the 5'-end, encoding the major non-structural proteins and are expressed as a fusion protein by ribosomal frameshift. ORFs 1a and 1b contain six replicase domains, as well as the 3'-5' exoribonuclease (ExoN) that controls RNA replication fidelity and a 2'-O-methyltransferase, both of which are found in larger nidoviruses. ORF 1b also encodes an N7-methyltransferase.[2][4]
Taxonomy
[edit]
Mesoniviridae is a member of the order Nidovirales, an order of +ssRNA viruses with animal hosts. The family has only one subfamily, Hexponivirinae, which contains only one genus, Alphamesonivirus. There are 8 subgenera and 10 species in Alphamesonivirus:[8]
The discovery and phylogenetic analysis of four additional mesoniviruses in 2013, named Hana virus, Méno virus, Nsé virus and Moumo virus, has suggested that they represent at least three new species of mesoniviruses.[6] Additionally, in 2014 four potentially new species were discovered in Australia, Indonesia, and Thailand, named Casuarina virus, Karang Sari virus, Bontag Baru virus, and Kamphaeng Phet virus, respectively.[3][7]
References
[edit]- ^ Lauber, C.; Ziebuhr, J.; Junglen, S.; Drosten, C.; Zirkel, F.; Nga, P. T.; Morita, K.; Snijder, E. J.; Gorbalenya, A. E. (2012). "Mesoniviridae: A proposed new family in the order Nidovirales formed by a single species of mosquito-borne viruses". Archives of Virology. 157 (8): 1623–1628. doi:10.1007/s00705-012-1295-x. PMC 3407358. PMID 22527862.
- ^ a b c Nga, P. T.; Parquet Mdel, M. D. C.; Lauber, C.; Parida, M.; Nabeshima, T.; Yu, F.; Thuy, N. T.; Inoue, S.; Ito, T.; Okamoto, K.; Ichinose, A.; Snijder, E. J.; Morita, K.; Gorbalenya, A. E. (2011). Baric, Ralph S (ed.). "Discovery of the First Insect Nidovirus, a Missing Evolutionary Link in the Emergence of the Largest RNA Virus Genomes". PLOS Pathogens. 7 (9): e1002215. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1002215. PMC 3169540. PMID 21931546.
- ^ a b c Vasilakis, N; Guzman, H; Firth, C; Forrester, N. L.; Widen, S. G.; Wood, T. G.; Rossi, S. L.; Ghedin, E; Popov, V; Blasdell, K. R.; Walker, P. J.; Tesh, R. B. (2014). "Mesoniviruses are mosquito-specific viruses with extensive geographic distribution and host range". Virology Journal. 11: 97. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-11-97. PMC 4038087. PMID 24884700.
- ^ a b c Zirkel, F.; Kurth, A.; Quan, P. -L.; Briese, T.; Ellerbrok, H.; Pauli, G.; Leendertz, F. H.; Lipkin, W. I.; Ziebuhr, J.; Drosten, C.; Junglen, S. (2011). "An Insect Nidovirus Emerging from a Primary Tropical Rainforest". mBio. 2 (3): e00077 – e00011. doi:10.1128/mBio.00077-11. PMC 3111606. PMID 21673192.
- ^ Kuwata, R.; Satho, T.; Isawa, H.; Yen, N. T.; Phong, T. V.; Nga, P. T.; Kurashige, T.; Hiramatsu, Y.; Fukumitsu, Y.; Hoshino, K.; Sasaki, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Mizutani, T.; Sawabe, K. (2013). "Characterization of Dak Nong virus, an insect nidovirus isolated from Culex mosquitoes in Vietnam". Archives of Virology. 158 (11): 2273–2284. doi:10.1007/s00705-013-1741-4. PMC 7087109. PMID 23728735.
- ^ a b c Zirkel, F.; Roth, H.; Kurth, A.; Drosten, C.; Ziebuhr, J.; Junglen, S. (2013). "Identification and Characterization of Genetically Divergent Members of the Newly Established Family Mesoniviridae". Journal of Virology. 87 (11): 6346–6358. doi:10.1128/JVI.00416-13. PMC 3648093. PMID 23536661.
- ^ a b Warrilow, D; Watterson, D; Hall, R. A.; Davis, S. S.; Weir, R; Kurucz, N; Whelan, P; Allcock, R; Hall-Mendelin, S; O'Brien, C. A.; Hobson-Peters, J (2014). "A new species of mesonivirus from the Northern Territory, Australia". PLOS ONE. 9 (3): e91103. Bibcode:2014PLoSO...991103W. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0091103. PMC 3966781. PMID 24670468.
- ^ "International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV)".

