Help talk:IPA/English/Archive 13
| This is an archive of past discussions about Help talk:IPA/English. Do not edit the contents of this page. If you wish to start a new discussion or revive an old one, please do so on the current talk page. |
| Archive 10 | Archive 11 | Archive 12 | Archive 13 | Archive 14 | Archive 15 | → | Archive 20 |
Key
I am not sure wheher this article is aimed at helping Wikipedia readers to understand IPA symbolization, or helping writers to use the symbols properly. But the Key section seems to me very disorganized. The vowels and consonants are listed in what seems like random order, compared with the tidy layout seen in the article on English phonology, and this makes it very difficult to check what is there (where is the NURSE vowel, for example?). Some sections in the Key just don't work - the syllabification section has a lot of errors. Readers may well find it hard to understand (as I do) why the vowel section of the key has a separate section for vowels combined with /r/, with some vowels corresponding to those in the other vowels column and others (e.g. some triphthongs) not corresponding. Can this be overhauled? Peter Roach. RoachPeter (talk) 17:44, 11 March 2012 (UTC)
- This page is aimed at helping both readers and editors understand how IPA is used for English at Wikipedia. The symbols are in quasi-alphabetical order, but of course for symbols that aren't part of the normal Latin alphabet we have to improvise, e.g. by listing θ as if it were a variety of O. The NURSE vowel is in the r-colored vowel column after ʌr; apparently whoever put it there considers it the heterosyllabic realization of ʌ + r. Personally, I'd put it between the SQUARE vowel and the mirror/Sirius vowel, leaving the non-r-colored side empty. As for the syllabification section, I don't see any flat-out errors, though I do see some implicit claims that may be controversial. (AFAIK there's very little consensus in the literature about where syllable breaks fall in English.) As for why there is a "vowels followed by /r/" section, it's because the key is trying to accommodate as many accents as possible (cf. International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects). So for example, most North American speakers using this key have to plot the symbol "ɒ" onto their /ɑ/ phoneme in words like lot, but they have to plot "ɒr" onto /ɔr/ in words like moral, so we list plain "ɒ" and "ɒr" separately. Which triphthongs are missing? Angr (talk) 07:23, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
- OK, let's start with smaller matters. Regarding syllabification, the IPA dot symbol is used to show where syllables are divided. There is quite a good consensus on where English syllable breaks fall, and the English phonology article says a bit about it under Phonotactics. Both major British pronunciation dictionaries show syllable divisions in all polysyllabic words, and explain their criteria for doing so in their Introductions (see the Longman Pronunciation Dictionary edited by J.C.Wells and the Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary which I edit). Now the examples in the present article show sensible use of this convention for 'hire', 'higher', 'moai'. The syllable division is supposed to help readers see that 'Windhoek' does not have two syllables in the part following 'Wind-", if I have understood correctly, so here it the ABSENCE of the dot which is supposed to be helpful. In 'Vancouvieria' it seems again that the absence of a dot is supposed to tell us something, but it makes it look as if everything after the stress mark is just one syllable. As for 'Myki' and 'Mikey', I simply cannot see how they could be syllabified differently. Regarding triphthongs, the usual presentation for British English (RP/BBC) is to take the set of diphthongs in FACE, PRICE, CHOICE, GOAT, MOUTH and add a schwa on the end. It is not normal to regard triphthongs as unit phonemes. Whether you get triphthongs followed by /r/ in the same syllable varies from one accent to another. While on smaller matters, the table of Reduced Vowels contains some things that need fixing, for example the statement that a vowel is frequently dropped in 'nasturtium'.
- For the presentation of the vowels and consonant symbols, the usual way is to group them under phonetic criteria. For vowels this usually means one block for short or lax vowels, one block for long or tense vowels and one for diphthongs. Since this presentation is apparently meant to be used for most major varieties of English pronunciation, it does not seem to me to be sensible to present a restricted list of combinations of vowel symbols with /r/. All the vowels and diphthongs may in principle be combined with /r/ , so there is no point in having a separate table, except perhaps to give some helpful examples.
- For consonants, again it would be better to use phonetic criteria, starting with plosives /p, t, k, b, d, g/, going on to fricatives, affricates, nasals and so on. There is no need to have a separate entry for the nasal plus /g/ in 'finger'. This is a simple combination of two phonemes. Peter Roach. RoachPeter (talk) 09:58, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
The ⟨.⟩ is only used where there might be some confusion. Windhoek and Vancouver might be misread as having th and ng sounds in them if we didn't use the dot. "Myki" and "Mikey" might be obvious to you, but the point of a transcription is for when the reader doesn't know the pronunciation.
Wells is hardly universally accepted. I suspect that MW and the OED would disagree in many many cases. And experience has shown that if we do indicate syllable boundaries, people will "correct" them, then correct the corrections, and soon we'll have a fight over who does or does not understand English.
Aren't your triphthongs just the vowels in our rhotic column?
The reason we need a rhotic column is that there is no regular correspondence between /V./ and /Vr./. We do not use a phonemic transcription because RP speakers balked at it being too American. It was one of the compromises we made to get an English IPA convention, rather than listing multiple dialects for each transcription.
Consonants should not be grouped by phonetic principals, IMO. If you know those, you won't need the key. There is a need for /ŋɡ/, due to the confusion from orthography. — kwami (talk) 10:31, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
- (edit conflict)I think the point of the syllable break in Windhoek is not to show that there is only syllable after the "Wind-", it's to prevent nonspecialists from interpreting the "th" of /vɪnthʊk/ as /θ/, while in Vancouveria it's there to show the absence of nasal assimilation of /n/ to /ŋ/. I cannot agree with you that there is quite a good consensus on where English syllable breaks fall. Even in a comparatively simple word like happy, there's considerable disagreement as to whether it's [hæ.pi], [hæp.i] or [hæpi] with an ambisyllabic [p]. (And there's no way to use the '.' to mark ambisyllabicity without creating the illusion of a geminate consonsant, e.g. [hæp.pi].) I'm not familiar with the word "Myki", but as it seems to be derived from "my key", I think the point is that in "Mikey" the /k/ belongs (partly or wholly) to the first syllable while in "Myki" it's entirely in the second syllable, which depending on accent could have an effect on both the quality and the duration of the diphthong in the first syllable. You say "all the vowels and diphthongs may in principle be combined with /r/", but in most varieties of North American English the selection of vowels that may occur before /r/ is quite restricted, regardless of whether the /r/ is syllable-final or followed by another vowel. Thus an American for whom /æ/ can never be followed by /r/ will find out from this page that when he sees /ær/ in a transcription, he is to interpret that as the sound of marry or barrow (i.e. [ɛr] for him). Grouping the symbols by phonetic criteria is useful for linguists who are already familiar with the phonetic criteria, but users who come here looking for the meaning of a symbol will probably have better luck finding it if the symbols are in alphabetical order or a reasonable approximation of it. Angr (talk) 10:55, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
- Now that you're familiar with some of the issues at play with the key, Peter, would you be interested in putting up what you have in mind as a sandbox subpage? It wouldn't be a good idea to mess with such a high-profile page (any time someone has a question about an English word's IPA, they go here), but your experience in writing introductory textbooks might prompt us to see how to modify the presentation of our transcription system in a more helpful way to our readers.
- When you've done it, you can let us know and we can discuss it and incorporate any things that people like. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 14:31, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
- Since you're relatively new to Wikipedia and might not know what a "sandbox subpage" is, you can create it by clicking here: Wikipedia:IPA for English/Sandbox. Angr (talk) 14:45, 12 March 2012 (UTC)
- thanks, I would be happy to have a go at doing that in a way that does not overwrite what is there aleady. I will delay doing it until I am back in UK and able to use a proper computer instead of pecking away at an iPad on holiday! Peter Roach RoachPeter (talk) 16:59, 13 March 2012 (UTC)
In the rightmost column, 15th entry, I think there's a typo. The phonetic symbols spell out 'yure' whereas the example word is 'cure.' Add a k-like symbol before the j-like symbol (or potentially a kx-combo, since the aspirated stop 'k' creates friction as the tongue progresses to 'y'), and it'll match.Tdbostick (talk) 08:18, 29 May 2012 (UTC)
- The C is not bolded, so jʊər is intended to be the pronunciation of the URE only. ― A. di M. 10:16, 29 May 2012 (UTC)
- Nothing is bolded in CURE. Suggest making URE truly boldface, and the problem will be solved 134.176.158.20 (talk) 10:44, 11 July 2012 (UTC)tdbostick
- Upon closer inspection by zooming in the page, URE is bolded, however this is impossible to see at a normal zoom factor because the font and/or size of the text doesn't match similar nearby entries. 134.176.158.20 (talk) 10:44, 11 July 2012 (UTC)tdbostick
- The capital letters mark lexical sets, so we may want to simply add another example. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 12:32, 11 July 2012 (UTC)
- How about replacing the boldfacing with underlining? A. di M. (talk) 14:38, 11 July 2012 (UTC)
- According to this IPA template discussion underline obscures some IPA characters. -- Q Chris (talk) 07:57, 12 July 2012 (UTC)
- I think he's talking about the bold in the example words and lexical sets, not the IPA. Underlining would be fine with me. We could even do both underling and bolding. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 11:58, 12 July 2012 (UTC)
- Ah, in that case it's fine with me too -- Q Chris (talk) 12:33, 12 July 2012 (UTC)
- I think he's talking about the bold in the example words and lexical sets, not the IPA. Underlining would be fine with me. We could even do both underling and bolding. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 11:58, 12 July 2012 (UTC)
- According to this IPA template discussion underline obscures some IPA characters. -- Q Chris (talk) 07:57, 12 July 2012 (UTC)
- How about replacing the boldfacing with underlining? A. di M. (talk) 14:38, 11 July 2012 (UTC)
- The capital letters mark lexical sets, so we may want to simply add another example. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 12:32, 11 July 2012 (UTC)
- Upon closer inspection by zooming in the page, URE is bolded, however this is impossible to see at a normal zoom factor because the font and/or size of the text doesn't match similar nearby entries. 134.176.158.20 (talk) 10:44, 11 July 2012 (UTC)tdbostick
- Nothing is bolded in CURE. Suggest making URE truly boldface, and the problem will be solved 134.176.158.20 (talk) 10:44, 11 July 2012 (UTC)tdbostick
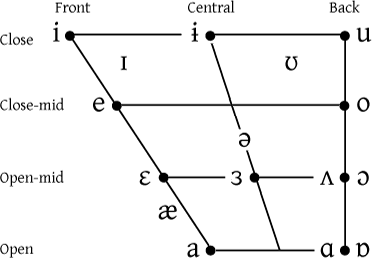
The current alphabetical list of vowels and consonants is easier to use than Peter's suggestion of grouping them according to phonetic principles, but a good compromise would be to add general English vowel and consonant chart(s) showing place of articulation and also links to charts for at least UK and US English, e.g. the chart shown at the right and the ones here. Such charts would also be much easier to use by non-native speakers than the current alphabetical list, and not only due to its unnecessarily difficult and exotic words (minimal pairs chosen to please the linguists who wrote this and the IPAc-en template despite being totally unhelpful and confusing for most non-native and many native speakers). --Espoo (talk) 14:15, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
- As I've argued in the past, this help guide is not about teaching phonetics to readers, it is a quick and dirty guide to help them understand the relationship between our transcription scheme and their own pronunciation. A formant chart won't accomplish that. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 14:25, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
- I meant adding the charts with each symbol as a clickable link to the entry in the current list, not as explanations of the sounds, though the charts' info won't hurt. For most users, the current list is very hard to navigate and looks like a hopelessly chaotic list of often exotic symbols. The problem is augmented by the fact that most users can't even use their browser's search function because they can't enter the symbol and don't remember the option of copy-pasting or don't know how to do that with the IPA code that takes them here when they try to copy it. --Espoo (talk) 14:48, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
- Cluttering the page with additional charts would make it seem even more chaotic. I also don't think it's technically feasible to provide links to a specific part of a table... if that's what your suggesting. We can't provide links to specific phone pages because these are diaphonemes; in many cases, there is not one phone or even one phoneme being represented. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 16:12, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
- I meant adding the charts with each symbol as a clickable link to the entry in the current list, not as explanations of the sounds, though the charts' info won't hurt. For most users, the current list is very hard to navigate and looks like a hopelessly chaotic list of often exotic symbols. The problem is augmented by the fact that most users can't even use their browser's search function because they can't enter the symbol and don't remember the option of copy-pasting or don't know how to do that with the IPA code that takes them here when they try to copy it. --Espoo (talk) 14:48, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
Also Key
It says that ɨ can be pronounced as either ɪ or ə, using the examples roses and emission, with the explanation that it differs between dialect. I can understand that different dialects pronounce a word differently, but aren't IPA characters supposed to be the 'atoms' of linguistics, the things that you can't break down? Or does IPA have homophones after all? Could somebody expand on this? — Preceding unsigned comment added by 81.71.110.7 (talk) 20:50, 24 June 2012 (UTC)
- This page uses the symbol ɨ like an algebraic symbol to stand for "ɪ or ə depending on accent", not in its IPA role of "high central unrounded vowel". Angr (talk) 21:05, 24 June 2012 (UTC)
- Right, and this means that the use of the "barred i" symbol as noted here is not IPA practice. RoachPeter (talk) 17:43, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- The IPA, a phonetic alphabet, has commonly been used for phonemes. Phonemes themselves are abstract groupings of phones. The diaphonemic approach here furthers the abstraction to cross-dialectal correspondences. It's not a common practice to use the IPA explicitly in this way, but it's useful for our purposes. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 18:00, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- I don't think it's really that rare to use IPA symbols diaphonemically and cross-dialectally, though it is rare to try to represent both RP and GenAm using a single set of symbols. But using a single set of symbols to represent all the accents of Southern England, say, or even Southern England plus the Southern Hemisphere, is actually fairly common. And in other languages, it's common enough to use a single symbol to represent a range of dialectal realizations; for example Duden uses /r/ to stand for all realizations of the German r-sound, whether [r], [ʀ], [ʁ], or [ɐ̯] (in coda position after a short vowel; it does use /ɐ̯/ in coda position after a long vowel). Angr (talk) 18:11, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- Yeah, it's pretty common to pick a character to represent a phoneme that has different dialectal variants. It's also common enough to have one transcription system for phonetically distinct varieties that share the same phoneme inventory. It's less common to combine two or more varieties that have divergent phonemic systems or even, in the case above, to use a single character to represent systematic differences in incidence. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 18:52, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- I don't think it's really that rare to use IPA symbols diaphonemically and cross-dialectally, though it is rare to try to represent both RP and GenAm using a single set of symbols. But using a single set of symbols to represent all the accents of Southern England, say, or even Southern England plus the Southern Hemisphere, is actually fairly common. And in other languages, it's common enough to use a single symbol to represent a range of dialectal realizations; for example Duden uses /r/ to stand for all realizations of the German r-sound, whether [r], [ʀ], [ʁ], or [ɐ̯] (in coda position after a short vowel; it does use /ɐ̯/ in coda position after a long vowel). Angr (talk) 18:11, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- The IPA, a phonetic alphabet, has commonly been used for phonemes. Phonemes themselves are abstract groupings of phones. The diaphonemic approach here furthers the abstraction to cross-dialectal correspondences. It's not a common practice to use the IPA explicitly in this way, but it's useful for our purposes. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 18:00, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
- Right, and this means that the use of the "barred i" symbol as noted here is not IPA practice. RoachPeter (talk) 17:43, 25 June 2012 (UTC)
English placenames
I just went through a few dozen Englishcommonwealth placenames and put in/restored postvocalic r's in the IPA transcriptions. For some reason, I thought that that was something that would be more closely monitored. Is there a walled-garden thing going on? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 17:37, 4 July 2012 (UTC)
- There has been in the past. I haven't been keeping up recently. But in Melbourne I think a note about the local pronunciation is useful. Yes, it's covered by the generic one, but we may have readers who are interested by don't know the local dialect to be able to predict it. (But s.t. like Bathurst is so obvious that IMO it doesn't need mentioning.) — kwami (talk) 19:50, 4 July 2012 (UTC)
- I made the change to Melbourne before looking in the talk page archives. I've re-added the local pronunciation and made its presentation a little clearer. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 20:28, 4 July 2012 (UTC)
Suggestions
[i] is not a reduced vowel. The long markings should be removed from the other vowels because there aren’t short long contrasts in English, compare to say Hungarian or Japanese. I’d consider this inappropriate for the purposes of a general overview that gets linked to as a general pronunciation guide on the other pages. I keep seeing in the notes “we’re doing this and leaving it unspecified.” If you’re not trying to specify it on some level, what is the purpose of this article?
Also, one of the first rules to writing a phonetics paper is the define each symbol you are using by place/manner/etc on the IPA chart, this is especially crucial if you’re choosing phonemic symbols that do not quite match the sound you are describing. I also *strongly* advise against using a glaringly different symbol as it creates confusion. You can’t expect someone referring to the IPA guide on wikipedia to have studied linguistics enough to understand that this or that person is known to use an inaccurate symbol phonemically. If you don't want to write out the description, perhaps link to it?
Mordrynne (talk) 22:22, 7 July 2012 (UTC)Mordrynne
- While [i] may not be reduced (and this is arguable), it only appears in unstressed vowels. I'm not sure what a better term would be.
- English does indeed have short-long contrasts, though the distinction is enhanced by qualitative differences, which differs from e.g. Japanese, which makes contrasts purely on length (Hungarian is like English in this regard).
- I'm not sure what "we're doing this and leaving it unspecified" means. Can you point to an example?
- The problem with a number of the entries here is that there is no one specific phonetic value, only a range of them. For example, the PRICE vowel can be [ɑe], [aɪ], [ʌi], [ɔɪ], [əi], [aː], or [ai], depending on dialect. That's one of the reasons we've been emphasizing lexical sets, here and in the usage of {{IPAc-en}}. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 23:09, 7 July 2012 (UTC)
- there aren’t short long contrasts in English -- depends on what variety you are talking about. There are in mine. Grover cleveland (talk)
Example word for ər (perform, perfume)
I appreciate Aeusoes1's change or the example from perform, which confused me, but I don't think that the "er" in "perfume" has the same sound. I personally pronounce the 'er' as "ɜr" fitting the wictionary /ˈpɜːfjuːm/, which is contrasts with the wictionary for perform /pə.ˈfɔːm/. I think ideally we could do with a different example, but failing that perhaps we should revert to "perform". -- Q Chris (talk) 13:00, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- Oh, gosh. I'd assumed everybody pronounced it like I did, with stress on the second syllable. Perhaps perhaps would do. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:17, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- I think I have /ɜr/ in "perhaps". Either syllable could be stressed. — kwami (talk) 13:29, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- This is more difficult than I thought! Perhaps would certainly do for my pronunciation, and the Wiktionary transcription as /pəˈhæps/ for RP and /pɚˈhæps/ implies it is also correct for both RP and General American, but from Kwamikagami's comments this might not be universal. -- Q Chris (talk) 13:33, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- It works in connected speech, but as an interjection it's more variable. — kwami (talk) 13:40, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- Perceive? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:45, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- Again fine the way I pronounce it, and Wiktionary confirms it as OK for RP and GA. -- Q Chris (talk) 16:35, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- Works for me. — kwami (talk) 00:49, 11 July 2012 (UTC)
- Again fine the way I pronounce it, and Wiktionary confirms it as OK for RP and GA. -- Q Chris (talk) 16:35, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- Perceive? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:45, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- It works in connected speech, but as an interjection it's more variable. — kwami (talk) 13:40, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- This is more difficult than I thought! Perhaps would certainly do for my pronunciation, and the Wiktionary transcription as /pəˈhæps/ for RP and /pɚˈhæps/ implies it is also correct for both RP and General American, but from Kwamikagami's comments this might not be universal. -- Q Chris (talk) 13:33, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
- I think I have /ɜr/ in "perhaps". Either syllable could be stressed. — kwami (talk) 13:29, 10 July 2012 (UTC)
ju
Why is ju listed as a full vowel Wikipedia:IPA_for_English#Key. It doesn't seem to be a vowel at all. ju is a yoo sound. We write words starting with the ju sounds like a university rather then an university because the yoo is not a vowel sound but a "y" consonant sound. Regards, Sun Creator(talk) 01:25, 25 August 2012 (UTC)
- Okay, never mind. U is not a vowel sound, that's where it gets confusing. Regards, Sun Creator(talk) 01:37, 25 August 2012 (UTC)
Raw-ther!
Forgive me if this has been discussed before, but I'm wondering about a certain vowel phoneme -- I don't know a name for it -- that has marked difference between "American" dialects (AD) and "British" dialects (BD). In AD, it is indistinguishable from what is commonly called "short A", as in "bat", so the two phonemes are really just one; but in BD, this phoneme is commonly more like the A in "father". To Americans, a stereo-typical example is the word "rather", to them having the same A sound as in "bat"; but the British pronunciation seems to them as if the word were spelled "rawther". This creates a question of whether this phoneme should use the IPA symbol used for "father", or the one for "trap". 141.158.64.119 (talk) 07:32, 15 September 2012 (UTC)
- This phenomenon is discussed at Phonological history of English short A#Trap–bath split. We don't use a single character to cover these sounds. Rather, we would write something like: "Rather (English pronunciation: /ˈræðɚ/; English pronunciation: /ˈrɑːðə/)" to cover it. (It's a little misleading since it is not the case either that everyone in the US says /ˈræðɚ/ or that everyone in the UK says /ˈrɑːðə/, but Wiktionary rather than Wikipedia is the place for comprehensive lists of pronunciations.) Angr (talk) 10:01, 15 September 2012 (UTC)
- (edit conflict) That's known as the BATH lexical set. I once proposed to introduce a symbol for that, but the consensus was that it wouldn't be worth bothering and that for those words both pronunciations should be given separately. — A. di M. 10:04, 15 September 2012 (UTC)
- Thanks awfully, you know! 141.158.64.119 (talk) 00:19, 16 September 2012 (UTC)
External Link to ASCII codes?
I'd love it if someone could link to a Wikipedia page on how to write these weird symbols. I'm not having much luck finding one and I'd like to add a pronunciation to a Wikipedia page. Molasseskat (talk) 16:13, 30 September 2012 (UTC)
It took me forever but I finally found this: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Manual_of_Style/Pronunciation#Entering_IPA_characters — Preceding unsigned comment added by Molasseskat (talk • contribs) 17:54, 30 September 2012 (UTC)
request for clarification of /hw/
See the conversation here http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wikipedia:Reference_desk/Language#IPA, Auesoues. μηδείς (talk) 03:43, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- I see that, but I still don't understand how it's helpful for our target audience. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 12:33, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- We should decide what our aims for the target audience are. I would suggest that it is unrealistic to hope that we can teach someone who's accent does not have the "hw" sound how it is pronounced. Similarly I don't think we can help them decide whether a word should be transcribed with "w" or "hw". All we can do is explain to them why some words will have the "hw" transcription and others the "w" - i.e. they belong to different lexical sets that are not differentiated in their own accent. I think the explanation does this reasonably well. -- Q Chris (talk) 12:44, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- There is a lot of confusion about /hw/ and /hj/, as exemplified in the discussion referred to above. It might help to look at the notes following the Consonants section in English phonology, especially Note 3. RoachPeter (talk) 15:42, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- I am not set on any particular wording, but the fact that it is not pronounced as the spelling indicates, but comes historically from an hw sequence is clear and enlightening to the layman. The notion that we must accept that this cannot be clarified is an odd one for an encyclopedia. I remember being taught as a child to pronounce the /h/, that people say it, and complaining to my teachers that no one says /wəhət/ for "what". Had they explained it was really like /hwət/, I'd've understood them. Indeed, it was after studying Old English that I learned the history, and finally recognized it when I came across it in others. Giving that simple fact, that the sound comes from /hw/ historically can hardly be objectionable. μηδείς (talk) 18:19, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- What exactly are we supposed to be clarifying? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 18:36, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- I think it's essential to get it clear that the "voiceless w" is not a /h/ followed by a /w/, nor a /w/ followed by a /h/. It is not a sequence at all. It is a single sound, a voiceless w, but it's conventional to represent it with a pair of characters. All the confusion shown in discussions about it stem from misunderstanding this transcription convention. RoachPeter (talk) 18:51, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- That's not always the case. The unaspirated voiceless w is one allophone. There are speakers who do prefix an h. The issue can be avoided by pointing out that historically it derives from hw, which no one denies. Layman will get a lot more out of making the analogy sack:swack::thack:thwack::hack:hwack(i.e., "whack") than they will being told this is a voiceless bilabial approximant. Given the request for clarification on this matter by Language Ref Desk rather well-educated volunteers with, in most cases, experiences in many languages, I am confused by the opposition here to expanding one footnote on this page to help clarify the topic. μηδείς (talk) 19:25, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- The opposition comes partly from the implicit claim that we should be teaching people how to pronounce the sound in question when all we should be saying is that, if they pronounce w and wh the same, then they can ignore the difference between /w/ and /hw/ in our transcriptions and that, if they do distinguish them, then /hw/ is the sound of 'why.'"
- Even if we were trying to teach the sound to our readers, telling them how it was spelled in Old English seems pretty indirect. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:48, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- That is how it was spellt in Old English, a much more rational spelling that still reflects how some do pronounce it. The point of clarifying is that there is absolutely no point in telling people that some English speakers distinguish between thingumajiggies and whatchmacallits if they have no idea what those things are. The original note might as well be written in Klingon or deleted entirely if 99% of our readers will be unable to parse it. The bottom line is, is the clarification true, which it is; and is the clarification problematic, which it is not. μηδείς (talk) 20:10, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- If that's a problem, then it's not isolated to the w/wh distinction. Every vowel contrast ("If you pronounce cot and caught the same, then you may simply ignore the difference between the symbols /ɒ/ and /ɔː/") and phonotactic constraint that differs between dialects but that we encode for is treated the same way. I'd have thought that wh/hw would be comparatively clear in that regard, considering the IPA transcription is so close to how the sound is spelled. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 20:50, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- That is how it was spellt in Old English, a much more rational spelling that still reflects how some do pronounce it. The point of clarifying is that there is absolutely no point in telling people that some English speakers distinguish between thingumajiggies and whatchmacallits if they have no idea what those things are. The original note might as well be written in Klingon or deleted entirely if 99% of our readers will be unable to parse it. The bottom line is, is the clarification true, which it is; and is the clarification problematic, which it is not. μηδείς (talk) 20:10, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- That's not always the case. The unaspirated voiceless w is one allophone. There are speakers who do prefix an h. The issue can be avoided by pointing out that historically it derives from hw, which no one denies. Layman will get a lot more out of making the analogy sack:swack::thack:thwack::hack:hwack(i.e., "whack") than they will being told this is a voiceless bilabial approximant. Given the request for clarification on this matter by Language Ref Desk rather well-educated volunteers with, in most cases, experiences in many languages, I am confused by the opposition here to expanding one footnote on this page to help clarify the topic. μηδείς (talk) 19:25, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- I think it's essential to get it clear that the "voiceless w" is not a /h/ followed by a /w/, nor a /w/ followed by a /h/. It is not a sequence at all. It is a single sound, a voiceless w, but it's conventional to represent it with a pair of characters. All the confusion shown in discussions about it stem from misunderstanding this transcription convention. RoachPeter (talk) 18:51, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- What exactly are we supposed to be clarifying? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 18:36, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- I am not set on any particular wording, but the fact that it is not pronounced as the spelling indicates, but comes historically from an hw sequence is clear and enlightening to the layman. The notion that we must accept that this cannot be clarified is an odd one for an encyclopedia. I remember being taught as a child to pronounce the /h/, that people say it, and complaining to my teachers that no one says /wəhət/ for "what". Had they explained it was really like /hwət/, I'd've understood them. Indeed, it was after studying Old English that I learned the history, and finally recognized it when I came across it in others. Giving that simple fact, that the sound comes from /hw/ historically can hardly be objectionable. μηδείς (talk) 18:19, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- There is a lot of confusion about /hw/ and /hj/, as exemplified in the discussion referred to above. It might help to look at the notes following the Consonants section in English phonology, especially Note 3. RoachPeter (talk) 15:42, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
- We should decide what our aims for the target audience are. I would suggest that it is unrealistic to hope that we can teach someone who's accent does not have the "hw" sound how it is pronounced. Similarly I don't think we can help them decide whether a word should be transcribed with "w" or "hw". All we can do is explain to them why some words will have the "hw" transcription and others the "w" - i.e. they belong to different lexical sets that are not differentiated in their own accent. I think the explanation does this reasonably well. -- Q Chris (talk) 12:44, 24 October 2012 (UTC)
Medeis, per this edit summary, maybe you didn't understand my previous comment. I have refuted your claim that the clarification on wh is needed. If you disagree, you'll need to convince myself and others why we should be telling our readers how to pronounce things they don't pronounce, rather than telling them to ignore contrasts they don't make. You're the only one who's made the case here that the note should be there. Until you get consensus to add the note, we should keep it off. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:26, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- Sorry, but this has already been discussed here and at the ref desk. You are the only editor opposing the edit or some version of it. And telling me to get consensus first is a clear violation of WP:OWNERSHIP. μηδείς (talk) 19:43, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- I think it's pretty clear that Q Chris also argued against it as well. What you're proposing would require a fairly drastic shift in what we are attempting to do here. If you disagree with that assessment, you should respond to my arguments, not make silly warnings on my talk page or trumped up accusations of bad faith editing. Citing policy should be corrective, not a means to avoid discussing a topic. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:55, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- He and RoachPeter seemed to be agreeing the subject merited discussion--neither reverted the edit when it was made two months back. Can you not think of a compromise, something like "earlier spelt hw"? μηδείς (talk) 20:01, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- The point of the note is to help people understand how it's pronounced, correct? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 20:06, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- I've been waiting a month for a response. Since you won't answer, I will. The answer is that, yes the note is intended to help people understand how /hw/ pronounced. That is not the role of this help page, nor should it be. As the help page says, "the following tables list the relevant transcription for various English diaphonemes." It does not say anything about describing the phonetic details of particular sounds in English.
- It's understandable if you or others in the refdesk don't understand the precise role of the help page, since it is a subtle distinction. Its subtlety belies its importance. Let me reiterate, we are not teaching people how to pronounce sounds at this help page. Those who believe otherwise, including those at the refdesk, are wrong in believing that that is in any way its role. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 03:00, 10 January 2013 (UTC)
- I'm sorry I missed your earlier edit, I watch a lot of pages. I don't think what's at issue here is really any matter of understanding of ref desk editors. The half a sentence mentioning the /hw/ origin is accurate and helpful and reflects exactly what is explained at length in the whine-wine merger article. There's not really any need to mention Old English as such in the footnote, we could simply say that historically the sound developed from the /hw/ sequence, although people might wonder when in Modern English words were spelled that way, and pointing them to Old English in a very small part of a very large footnote section hardly seems problematic. If saying something like "historically, this sound, now written "wh", developed from an hw cluster" is acceptable, let me know. Otherwise an RfC whether the comment should be removed would be the next step, because I do oppose removing the accurate historical explanation for what appears to me an aesthetic objection. μηδείς (talk) 03:41, 10 January 2013 (UTC)
- While the comment may be accurate, I disagree that it is helpful. Again, the point of this help page is to tell readers how we are using IPA, so going into historical development on a particular sound is tangential. An RfC may be in order unless some other editors watching this page want to chime in. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 04:25, 10 January 2013 (UTC)
- I'm sorry I missed your earlier edit, I watch a lot of pages. I don't think what's at issue here is really any matter of understanding of ref desk editors. The half a sentence mentioning the /hw/ origin is accurate and helpful and reflects exactly what is explained at length in the whine-wine merger article. There's not really any need to mention Old English as such in the footnote, we could simply say that historically the sound developed from the /hw/ sequence, although people might wonder when in Modern English words were spelled that way, and pointing them to Old English in a very small part of a very large footnote section hardly seems problematic. If saying something like "historically, this sound, now written "wh", developed from an hw cluster" is acceptable, let me know. Otherwise an RfC whether the comment should be removed would be the next step, because I do oppose removing the accurate historical explanation for what appears to me an aesthetic objection. μηδείς (talk) 03:41, 10 January 2013 (UTC)
- The point of the note is to help people understand how it's pronounced, correct? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 20:06, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- He and RoachPeter seemed to be agreeing the subject merited discussion--neither reverted the edit when it was made two months back. Can you not think of a compromise, something like "earlier spelt hw"? μηδείς (talk) 20:01, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
- I think it's pretty clear that Q Chris also argued against it as well. What you're proposing would require a fairly drastic shift in what we are attempting to do here. If you disagree with that assessment, you should respond to my arguments, not make silly warnings on my talk page or trumped up accusations of bad faith editing. Citing policy should be corrective, not a means to avoid discussing a topic. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:55, 9 December 2012 (UTC)
John Fashanu
Something weird has happened with the IPA at John Fashanu. It displays as /ˈfəʃ[unsupported input][unsupported input]/ which clearly isn't right. Sorry, but I don't know much about the IPA code - can someone here fix it? Thanks, Bazonka (talk) 18:50, 29 December 2012 (UTC)
 Fixed. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:27, 29 December 2012 (UTC)
Fixed. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 19:27, 29 December 2012 (UTC)
- Thanks. Bazonka (talk) 20:29, 29 December 2012 (UTC)
making the key helpful
The purpose of this article and IPAc-en's mouseover help is to help, not confuse users by using difficult and rare words. So we need to replace all difficult words with easy ones, such as those used in all printed dictionaries, none of which use words such as "nigh" or "phi". There is absolutely no need to produce a list of minimal pairs. See also this discussion. --Espoo (talk) 14:37, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
And where should already discussed or bold changes be made, or is that a bad idea, considering the wide use of the template? Here, at H:IPA, or IPAc-en? And/or where should these changes be discussed? Some changes were already accepted in this discussion. --Espoo (talk) 15:11, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
- That seems like a reasonable proposal. I'm not sure the best place to propose such things; I'd recommend starting it in one and then, if you don't get a sufficient response, put a simple notification in the others. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 16:03, 3 February 2013 (UTC)
Superscript "marginal" consonants
Do we really want to use superscript letters to indicate sounds that aren't always pronounced? I'd be in favor of using parentheses instead. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:31, 24 April 2013 (UTC)
- Yeah, I think that would be more intuitive. Superscript letters are used to indicate 2ndary articulation characteristics in the IPA, so there's also potential to confuse. — Lfdder (talk) 13:42, 24 April 2013 (UTC)
- Before we even get there, do we really want to open this can of worms? It won't be long at all before we're using it for every nonprevocalic /(r)/, every /(h)w/, every /d(j), n(j), s(j), t(j), (h)(j).../, instances of /n(t)s/ and the like, /(d)ʒ/ in loanwords, and on and on. — ˈzɪzɨvə (talk) 15:49, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- We should limit it to those items that have variable pronunciations unrelated to the regional variation we already deal with in our transcription system. That would exclude all of those except for a handful of instances of /(d)ʒ/. Is there a way to clearly articulate that? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 16:14, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- Also, parentheses are probably obvious enough that we can get away without putting this in the key (so that maybe it won't be abused). — Lfdder (talk) 16:20, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- Alternatively, how many sounds actually vary in this way? It's a pretty small list, isn't it? Couldn't we simply add /ts/ to the list of marginal consonants, or possibly a list of non-native sounds (like at the German key), with a note that many speakers use /s/ instead? — ˈzɪzɨvə (talk) 17:00, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- I don't think English /ts/ is ever treated as an affricate so I don't think that's necessary (or even appropriate). — Lfdder (talk) 17:19, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- We do seem to shy away from putting consonant sequences in these guides. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 23:57, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- I don't think English /ts/ is ever treated as an affricate so I don't think that's necessary (or even appropriate). — Lfdder (talk) 17:19, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- Alternatively, how many sounds actually vary in this way? It's a pretty small list, isn't it? Couldn't we simply add /ts/ to the list of marginal consonants, or possibly a list of non-native sounds (like at the German key), with a note that many speakers use /s/ instead? — ˈzɪzɨvə (talk) 17:00, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- Also, parentheses are probably obvious enough that we can get away without putting this in the key (so that maybe it won't be abused). — Lfdder (talk) 16:20, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- We should limit it to those items that have variable pronunciations unrelated to the regional variation we already deal with in our transcription system. That would exclude all of those except for a handful of instances of /(d)ʒ/. Is there a way to clearly articulate that? — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 16:14, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
- Before we even get there, do we really want to open this can of worms? It won't be long at all before we're using it for every nonprevocalic /(r)/, every /(h)w/, every /d(j), n(j), s(j), t(j), (h)(j).../, instances of /n(t)s/ and the like, /(d)ʒ/ in loanwords, and on and on. — ˈzɪzɨvə (talk) 15:49, 27 April 2013 (UTC)
Problem with /oʊ/
I've seen this come up in almost every instance of the sound /əʊ/ - the way in which I see it written so often (that is /oʊ/) is not at all a common sound in any dialect of English. It's a really widespread thing. Gitgo567 (talk) 07:09, 28 April 2013 (UTC)
- /oʊ/ is the usual pronunciation in North American English. We use it here as a pandialectal symbol for the GOAT vowel because the fact that it contains the letter "o" makes it easy to associate with words containing the sound, almost all of which are spelled with the letter "o" too. Angr (talk) 08:06, 28 April 2013 (UTC)
- Almost all of the vowel symbols we use, although representing both American and British pronunciations in our transcriptions, more accurately reflect the pronunciation of Received Pronunciation; this is sort of a compromise/balance thing, as having post-vocalic r (a necessity) makes the transcriptions look much more American. The most notable exception is /oʊ/; in addition to the ease of understanding issue that Angr brings up, /oʊ/ is also the most common way of transcribing the GOAT vowel in American English (even though it's not quite accurate). — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:37, 28 April 2013 (UTC)
- /oʊ/ is most definitely not the pronunciation of GOAT diphthong in American English - it would more accurately be /. What I don't understand is the whole 'ease of understanding' thing - the IPA is about accuracy not ease of use. 'The purpose of IPA is to provide a standard set of symbols that are used to represent sounds so that the same symbols always represent the sounds, even to people from different language backgrounds.' said this guy who I admit I did just find through Google - nonetheless, he's right. One letter means one sound, even in broad transcription. Gitgo567 (talk) 16:27, 30 April 2013 (UTC)
- More accurately be what? Anyway, I'm American and I pronounce it /oʊ/, but I'm from Texas so maybe my pronunciation isn't typical. And that description is far more idealistic than reality. Every use of the IPA requires certain language-specific conventions for interpretation or we'd never get anywhere, and broad transcriptions even more so than narrow ones. The English word house and the German word Haus don't sound identical, but both are correctly transcribed /haʊs/. Or English toot and French toute—they don't sound the same, but they're both /tut/. The IPA is about accuracy, but it isn't always about precision, and /oʊ/ is perfectly accurate, even if it isn't precise for all English speakers (though it certainly is for some of us). Angr (talk) 21:25, 30 April 2013 (UTC)
- Oh geez, I messed up - somewhere I went wrong thinking that /o/ represented the 'o' in 'not' in RP and Australian English. Sorry for the trouble! Gitgo567 (talk) 13:42, 1 May 2013 (UTC)
- More accurately be what? Anyway, I'm American and I pronounce it /oʊ/, but I'm from Texas so maybe my pronunciation isn't typical. And that description is far more idealistic than reality. Every use of the IPA requires certain language-specific conventions for interpretation or we'd never get anywhere, and broad transcriptions even more so than narrow ones. The English word house and the German word Haus don't sound identical, but both are correctly transcribed /haʊs/. Or English toot and French toute—they don't sound the same, but they're both /tut/. The IPA is about accuracy, but it isn't always about precision, and /oʊ/ is perfectly accurate, even if it isn't precise for all English speakers (though it certainly is for some of us). Angr (talk) 21:25, 30 April 2013 (UTC)
- /oʊ/ is most definitely not the pronunciation of GOAT diphthong in American English - it would more accurately be /. What I don't understand is the whole 'ease of understanding' thing - the IPA is about accuracy not ease of use. 'The purpose of IPA is to provide a standard set of symbols that are used to represent sounds so that the same symbols always represent the sounds, even to people from different language backgrounds.' said this guy who I admit I did just find through Google - nonetheless, he's right. One letter means one sound, even in broad transcription. Gitgo567 (talk) 16:27, 30 April 2013 (UTC)
- Almost all of the vowel symbols we use, although representing both American and British pronunciations in our transcriptions, more accurately reflect the pronunciation of Received Pronunciation; this is sort of a compromise/balance thing, as having post-vocalic r (a necessity) makes the transcriptions look much more American. The most notable exception is /oʊ/; in addition to the ease of understanding issue that Angr brings up, /oʊ/ is also the most common way of transcribing the GOAT vowel in American English (even though it's not quite accurate). — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:37, 28 April 2013 (UTC)
Marginal consonants -- gloss needed
Could someone add a clarifying note about the precise sense of "marginal" here (and to other such pages), please? It's just about clear from context if one actually knows the phonology of language concerned, but if it's a standard linguistic terms it's one I'm not familiar with, and didn't get much on via googling. 84.203.43.181 (talk) 00:41, 30 April 2013 (UTC)
- It just means that they're rare here. — Lfdder (talk) 17:19, 1 May 2013 (UTC)
- I thought the precise connotation was that they might not occur in some ideolects at all. (Unless I'm falsely generalising from the examples here, of course.) But either way... I mean, gloss in the page, not the talk! 84.203.43.181 (talk) 02:23, 2 May 2013 (UTC)
serious–Sirius merger
In the sections for the vowels /ɪr/ and /ɪər/, it should be mentioned that many speakers, including me, merge them, hence the serious–Sirius merger.--Solomonfromfinland (talk) 08:31, 16 May 2013 (UTC)
- Done. (I'm surprised that the Mary-merry merger was mentioned but this one wasn't.) — A. di M. 13:11, 16 May 2013 (UTC)
ŋɡ
In the list of consonants, why does /ŋɡ/ need its own entry? Isn't it just a sequence of consonants, and not an affricate like /t͡ʃ/ or /d͡ʒ/?--Solomonfromfinland (talk) 08:25, 16 May 2013 (UTC)
- It's a sequence of two consonants, but I suppose it's listed for the sake of those who might otherwise not notice the difference between the ng in singer and the ng in finger. Angr (talk) 19:29, 16 May 2013 (UTC)
Ian Ziering
On earlier versions of the Ian Ziering page, I noticed the IPA key regarding the pronunciation of his first name was parsed as /'ajn/. But when I revisited that same page more recently, it was corrected to the proper /'aɪən/. Therefore, /'ajn/ is improper use of IPA. WikiPro1981X (talk) 05:43, 20 May 2013 (UTC)
Marginal consonant ʔ
Can someone with access please restore the Hawai'i example in the "Marginal consonant ʔ" section? This was a really good example of the use of this marginal consonant. Now the IPA guide has only one example of ʔ, so it's not a great guide: anyone who can't figure out what sound is being made in uh-oh won't know what sound is being made.
For reference, thye example, before it was removed, was:
Hawai‘i /həˈwaɪʔiː/<ref>Most people pronounce the English word Hawaii without the /ʔ/ (glottal stop) that occurs in the Hawaiian word Hawai‘i.</ref>
72.165.10.254 (talk) 01:10, 5 April 2013 (UTC)
- How many non-Hawaiian, non-pedantic native English speakers do actually use a glottal stop in there? — A. di M. 08:49, 5 April 2013 (UTC)
- I heard Bill Kurtis pronounce it that way, though it sounded like he was pronouncing it /həˈwʌʔiː/. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:31, 5 April 2013 (UTC)
- I pronounce it the same way as Bill Kurtis. It's not a pendantic prounciation because I know that it should be pronounced /hɐˈvɐiʔi/ for full demonstration of one's erudition, I just don't care. I'll note that our Hawaii article also has /həˈwaɪʔiː/ as an acceptable pronunciation, so I'm sure Bill Curtis and I aren't the only ones. I imagine that the pronunciation stems from the glottal stop being the most salient part of the native pronunciation of "Hawai'i". You hear it once, notice it, and "correct" your pronunciation of that one feature from then on out. —Quintucket (talk) 15:48, 28 June 2013 (UTC)
- I heard Bill Kurtis pronounce it that way, though it sounded like he was pronouncing it /həˈwʌʔiː/. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 13:31, 5 April 2013 (UTC)
Vowels
Shouldn't the open central unrounded vowel be included?50.103.255.130 (talk) 20:18, 1 July 2013 (UTC)
- I don't think enough dictionaries distinguish them to make that practicable. 00:05, 3 July 2013 (UTC)
Nitpick with ɡ consonant row
I though it was weird that this is the only row in the key to give a plaintext variant of the character and then a footnote saying "if these two don't match, you need help with your IPA font rendering". Wouldn't it be better if this plaintext equivalent and footnote was removed and replaced with Template:SpecialChars, like many articles do when using special characters, such as the IPA? Just a thought. (The note after the key, discussing various acceptable fonts, might be removable too if the IPA help pages already discuss it.) Rnddim (talk) 20:54, 19 October 2013 (UTC)
- We do format it as IPA / as in the IPA article. — kwami (talk) 02:17, 20 October 2013 (UTC)
/ɔɪər/
The prior glosses of loir and coir are entirely unhelpful as no one uses either word: where dormice are distinguished from mice, they're called dormice; coconut fiber is (generally) simply called that. The people who say "coir" say it /ˈkɔɪr/, not /ˈkɔɪər/.
I added a word with this pronunciation people actually speak and use (lawyer: OED's IPA /ˈlɔːjə(r)/ & /ˈlɔɪə(r)/; Wikt unhelpfully pretends that the latter is disyllabic but notes that its precisely homophonic with loir), but have ended up getting reverted twice (presumably thrice soon). The user seems not to know the pronunciation of the word (or that there is an alternative to the strong /j/ pronunciation), but we need something better than what we have. — LlywelynII 08:10, 26 November 2013 (UTC)
- Since when do we use Wikt as a source? Follow the OED: Loir has one syllable, lawyer has two. Same diff as hire vs. higher, mare vs. mayor, hour vs. plougher. Yes, loir and coir are uncommon: AFAICT there are no minimal pairs with common words. Perhaps you conflate the pronunciations – many people do – but that doesn't mean they don't exist for other people. — kwami (talk) 08:17, 26 November 2013 (UTC)
- That's fine. The guide explains these pronunciations aren't binding across all dialects. It's still a more helpful example.
- Since there's nothing on the page about the examples needing to be monosyllabic and there's no consensus to the contrary here, I'm restoring the more helpful "lawyer". It remains the correct sound. — LlywelynII 08:03, 29 November 2013 (UTC)
- But it's not the correct sound, so we'll be misinforming our readers. Stop edit warring and reach a consensus. You're confusing your vowels, or at least other people's vowels. If we're going to add disyllables, we'll have an open-ended key. I'm not sure that's something we want, but you at least need consensus for it. — kwami (talk) 08:25, 29 November 2013 (UTC)
- It is the correct sound, albeit in two syllables, so there is no misinformation. Neither is there edit warring, aside from your end: there obviously is not a consensus for completely unhelpful middle English variants of "dormouse" but you keep restoring them.
- But it's not the correct sound, so we'll be misinforming our readers. Stop edit warring and reach a consensus. You're confusing your vowels, or at least other people's vowels. If we're going to add disyllables, we'll have an open-ended key. I'm not sure that's something we want, but you at least need consensus for it. — kwami (talk) 08:25, 29 November 2013 (UTC)
- Still, I'll do a RfC and hopefully get past your WP:OWNERSHIP issues (or at least establish an consensus that supports your view). — LlywelynII 05:08, 17 December 2013 (UTC)
- Like it says in the intro, Help:IPA transcriptions of English are diaphonemic. Because this is a perceptual distinction some people make, loir is analysed as a triphthong, but lawyer as two syllables. Whether you or anybody pronounces them the same isn't actually relevant. — Lfdder (talk) 15:35, 17 December 2013 (UTC)
- Still, I'll do a RfC and hopefully get past your WP:OWNERSHIP issues (or at least establish an consensus that supports your view). — LlywelynII 05:08, 17 December 2013 (UTC)
I don't feel the issue of how the words 'loir' and 'coir' should be transcribed has been fully resolved yet. The fact that these words are obscure or of low frequency doesn't make the argument irrelevant. Unfortunately, it seems to me that in order to answer the question it is necessary to consider some related issues.
- 1. We are talking about vowels and diphthongs here, so we are concerned with the table on the r.h. side of the page, headed "Vowels". It is not clear if the objects in IPA symbols are phonemes of English or some more loosely-defined unit. The two l.h. columns correspond more or less to non-rhotic pronunciation such as the RP/BBC of England. However, the list misses out three diphthongs: the /ɪə/ of NEAR, the /eə/ of SQUARE and the /ʊə/ of POOR.
- 2. Keeping to the "Full vowels" columns, if we want to be able to deal with potential differences between e.g. 'loir' and 'lawyer' the table needs either to list the possible triphthongs /eɪə/ of PLAYER, /aɪə/ of FIRE, /ɔɪə/ of LOYAL, /əʊə/ of LOWER and /aʊə/ of POWER, or to make a statement to the effect that any diphthong ending in /ɪ/ or /ʊ/ may be followed by /ə/, resulting in a triphthong.
- 3. Whichever of the above is preferred, it is also necessary to state that, at least in the RP/BBC accent, many syllables which are usually transcribed as containing triphthongs may be pronounced, or heard, either as a single syllable or as two syllables. Minimal pairs such as 'loir' (with monosyllabic /lɔɪə/) vs. 'lawyer' (with disyllabic /lɔɪ.ə/), or 'byre' (with monosyllabic /baɪə/) vs. 'buyer' (with disyllabic /baɪ.ə/) can be suggested, though I think it would be very hard to find a speaker who systematically distinguished these pairs.
- 3 The next step is to look at the two columns on the right, headed by "...followed by R". I find it very difficult to see what this pair of columns actually represents. At first sight it looks as if it is meant to relate to rhotic accents, and on each line it looks as if the phonemic unit is meant to correspond to the non-rhotic one to its left. In the case of short vowels it is hard to see why there is a separate rhotic list. For example, the transcriptions given for 'moral', 'barrow', 'error', 'mirror', 'courier' and 'borough' are exactly the same as they would be for RP/BBC. Phonemically, this list just contains one of the short vowel phonemes followed by the /r/ phoneme. You could just as well have a column for vowels followed by /l/.
- 4. Now we need to look at those cases where we don't find a straightforward correspondence between non-rhotic V and rhotic V+r, these cases involving mainly diphthongs. If the two r.h. columns are really meant to represent rhotic equivalents of non-rhotic vowels, then we have /aɪər/ apparently corresponding to non-rhotic /aɪ/, /aʊər/ corresponding to non-rhotic /aʊ/ and /ɔɪər/ corresponding to non-rhotic /ɔɪ/. But surely /aɪər/ corresponds to /aɪə/, /aʊər/ corresponds to /aʊə/ and /ɔɪər/ corresponds to /ɔɪə/?
- 5. There are other questionable implied correspondences: on what grounds does the table pair rhotic /ɛər/ (SQUARE) with non-rhotic /eɪ/ (FACE)? /ɪər/ (NEAR) with /iː/ (FLEECE)? /ɔər/ (FORCE) with /oʊ/ (GOAT)? /ʊər/ (BOOR) with /uː/ (GOOSE)? /jʊər/ (CURE) with /juː/ (CUED)? /ɜr/ (NURSE) with /ʌ/ (STRUT)?
- 6. To come back to the 'loir'/'lawyer' question, it seems to me that the fundamental problem is that the table doesn't make clear if all the phonological elements in the boxes are necessarily monosyllabic. Note 8 certainly helps with this, but I think users of the table should be told in the main body of text, above the table, that disyllabic pronunciations of diphthongs and triphthongs should make use of the . syllable-division marker.
Finally, I don't want to open another can of worms, but I can't see why in addition to this article there should be another called "Help: IPA conventions for English" which has a very different table of vowels and no explanation of how it corresponds to the one in "Help: IPA for ENglish". Surely these two could be merged, pruned and rationalized? RoachPeter (talk) 10:34, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- AFAIK, there are no triphthongs ending in schwa except ones that correspond to diphthongs followed by /r/ in rhotic accents. The correspondences are fairly straightforward. The reason we don't give a phonemic transcription is that non-rhotic speakers preferred this partially allophonic one.
- The other help page covers various popular dictionaries, and it is quite explicit as to how it relates to this one. They shouldn't be merged because they serve two different purposes. — kwami (talk) 11:28, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- But "Help: IPA conventions for English" helpfully contains in the WP column /aɪr/, /aɪ.ər/, /aʊr/ and /aʊ.ər/ which don't appear in "Help: IPA for English" except that /aɪr/ and /aʊr/ appear in parentheses as /aɪr./ and /aʊr./. I'm sorry, but I just don't understand the rationale of WP's way of handling English diphthongs and triphthongs across accents. RoachPeter (talk) 14:27, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- /aɪr/ and /aʊr/ are just /aɪ/ and /aʊ/ plus /r/, and so fit the column. If we started adding combinations of V + /ər/, wouldn't we want to add all of them? There would be at least /eɪ.ər/, /oʊ.ər/, /iː.ər/, /(j)uː.ər/, /ɔː.ər/, maybe /ɑː.ər/. I suppose we could double up the way we do for /ʌr/ - /ɜr/. — kwami (talk) 19:29, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- As for the handling: When we set up this convention, RP speakers objected to writing /aɪr/ and /aʊr/ (and others) phonemically, saying they found it confusing. So instead we write /aɪr/ as ⟨aɪər⟩ and /aʊr/ as ⟨aʊər⟩, the way they do in the OED, but unlike e.g. K&K. That is, when we write ⟨ər⟩ in the same syllable as a vowel, what we mean is /r/ for rhotic speakers and /ə/ for non-rhotic speakers. — kwami (talk) 19:34, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- I added those distinctions to the table.[1] Are they worth the extra space? We might be able to take out some if they only occur in derived forms are so are unlikely to be encountered, or misunderstood if they are encountered. — kwami (talk) 19:56, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
- It's hard to predict what any group of speakers would prefer to use for transcribing English, but this seems much better to me. RoachPeter (talk) 22:25, 22 December 2013 (UTC)
Semi-protected edit request on 24 January 2014
This edit request has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
41.41.153.242 (talk) 16:27, 24 January 2014 (UTC)
 Not done: please be more specific about what needs to be changed. -- John of Reading (talk) 16:32, 24 January 2014 (UTC)
Not done: please be more specific about what needs to be changed. -- John of Reading (talk) 16:32, 24 January 2014 (UTC)
Wrong phonetic symbol for the letter "r"
The letter "r" appears with the /r/ symbol (Alveolar trill), while it should really be /ɹ/ (Alveolar approximant).--190.46.2.241 (talk) 02:32, 25 July 2012 (UTC)
- This has been brought up before. using r instead of ɹ is nothing new or unique to transcribing English and is easier for our readers. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 02:57, 25 July 2012 (UTC)
- Please provide evidence that using /r/ instead of /ɹ/ is easier for the readers. (Fletpedia (talk) 12:28, 21 August 2012 (UTC))
- Its a longstanding tradition to use /r/ for English <r> in phonemic transcription. Most learners will always have seen it that way. See for example the OED. −Woodstone (talk) 14:27, 21 August 2012 (UTC)
- It's also a fairly logical assumption that readers will have an easier time with our transcriptions if they have to learn/remember one fewer IPA symbol. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 15:28, 21 August 2012 (UTC)
- OTOH, if a non-native English speaker sees /ˈbɛri/ they might think about a pronunciation that a native speaker would understand as Betty rather than berry, whereas on seeing /ˈbeɹi/, if they don't know what /ɹ/ is, they'd at least realize they have to look it up. (But I don't think this is a good-enough reason to depart from what pretty much all dictionaries do.) — A. di M. 19:26, 21 August 2012 (UTC)
- It's also a fairly logical assumption that readers will have an easier time with our transcriptions if they have to learn/remember one fewer IPA symbol. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 15:28, 21 August 2012 (UTC)
- Its a longstanding tradition to use /r/ for English <r> in phonemic transcription. Most learners will always have seen it that way. See for example the OED. −Woodstone (talk) 14:27, 21 August 2012 (UTC)
- Please provide evidence that using /r/ instead of /ɹ/ is easier for the readers. (Fletpedia (talk) 12:28, 21 August 2012 (UTC))
- I know I'm a little late for the discussion here, but — A. di M. is right; although I knew it couldn't be an [r] (alveolar trill), I thought it was kind of strange and got a bit confused. It is simply incorrect. If you're worried about different accents, don't be. There are many words that can be pronounced in at least 2 or 3 quite different ways, all of them right. You got to choose one, not define your own phonetic alphabet and say "well, 'r' will mean [r], [ɹ] or [ɻ]". I just think it should be changed, and against myself I speak (as my accent sounds kind of american) when I say it should be the [ɹ]. It is better to be right in one way than wrong in all. JMCF125 (discussion • contribs) 17:55, 17 May 2013 (UTC)
- Here is John C. Wells discussing the use of /r/ for the English r-sound. Angr (talk) 21:45, 10 September 2012 (UTC)
- I second this motion. Using the Alveolar trill /r/ symbol incorrectly rather than the correct Alveolar approximant /ɹ/ is laziness. This is valid for the retroflex approximant as well e.g. red [ɻʷɛd]. Based on what I have read above this, the presumption is that /r/ is conventional. There is hardly grounds to consider anything conventional at this point considering that the last IPA convention, which brought us another regular update to the system, was in 2005. Also, dubious symbols make Wikipedia less reliable as a source. The purpose of IPA is to be **international** and not subject to any specific language/cultural conventions. In effect, those in favor of using /r/ where no trill is in opposition to the IPA as a universal system for describing phonemes. Agentxp22 (talk) 11:35, 16 April 2013 (UTC)
- Between slashes, there are a whole host of inaccuracies if phonemes are supposed to be accurate representations of phonetic realizations. But in your very post you've accessed an important point that speaks to using r that doesn't rest on laziness or convention; which is more correct, ɻ or ɹ? Both are English pronunciations, but they're partially dialect-dependent. r, in addition to being the most common symbol used for the English rhotic in linguistic literature, is also neutral to either of these pronunciations. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 14:03, 16 April 2013 (UTC)
- This sentence, *But in your very post you've accessed an important point that speaks to using r that doesn't rest on laziness or convention; which is more correct, ɻ or ɹ?*, does not make sense. By *rhotic* I assume you mean rhetoric? Unless I misunderstood your comment, you have made the same moot point (r is the most common symbol in traditional English textbooks and also is neutral) which I have just criticized. Whether or not to use ɻ or ɹ should indeed be disputed (although there are some standards for where to use them as well). My issue here is that this is a separate argument from [r] versus [ɻ]/[ɹ]. It should not even be an issue. Away with [r] because it is completely inaccurate for American and English speakers and lets move the issue to [ɻ]/[ɹ] in American English. Agentxp22 (talk) 11:55, 23 April 2013 (UTC)
- Rhotic is a catchall term for r-like sounds. I'm not talking about rhetoric (that sentence certainly would not have made sense if I did). It is apparent from your comments above that you are new to phonology, so let me explain something that you are likely unaware of: in phonology (and, of course, phonetics), phonetic transcriptions are placed between [brackets] while phonemic transcriptions are placed between /slashes/. Usually, phonemes are transcribed with the IPA letter that represents one of its allophones. For example, English /t/ has a host of allophones depending on context [tʰ ˀt ʔ ɾ... t]. The IPA letter used may be one of the more common, basic, or neutral allophones, though in the case of ⟨t⟩ it is chosen partly out of convention, partly out of typographic concerns, and partly due to orthography. However, this is not a hard and fast rule of phonemic transcriptions. A linguist could, if she so chose, to use ANY symbol to represent a particular phoneme. Perhaps, instead of /t/, this phoneme is transcribed as /$/ so that cat is transcribed phonemically as /kæ$/ and phonetically as [kʰeəʔt].
- More importantly, and you should know this if you've read the explanatory note, this IPA guide is an attempt to represent the pronunciations of multiple dialects, particularly British and American ones. We have to be careful about biasing the transcription one way or the other. If we choose ɹ, then we're leaning more towards British pronunciations and if we choose ɻ we're leaning more towards American pronunciations. r is more neutral, in addition to the "moot" points that you seem to disagree with. So, the long and the short of it is that transcribing the English rhotic as /r/ is not wrong. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 14:45, 23 April 2013 (UTC)
- No, I am not new to phonetics, although I did not know the term rhotics, because I refer to them as Liquida (or Liquids in English). Anyway, if I were referring to allophones I would NOT have put them in brackets, rather in slashes. For anyone reading this, I specifically chose to use [] in order to provide a phonetic transcription. I wanted to emphasize the differences between languages. Basically the point I am making here is that the differences or worthy of attention and should be noted accordingly with a specific character, not a general character (/r/). I feel like I am repeating myself, so I will stop. Thanks for the tips above, although it came across as patronizing. At least we are definitely on the same wavelength. Your second paragraph is the main issue. In not wanting to favor British or American English, we have chosen to represent the sound with a character that represents a trill, used neither in England, nor in America. That is my gripe. Agentxp22 (talk) 15:31, 1 May 2013 (UTC)
- The thing is, this page is "IPA for English". We're just talking about English, we're not comparing it with other languages. If we were, it would make sense to use /ɹ/ since the other language's rhotic ("liquid" is too general as it includes laterals) might well be a trill. But when our context is English only, there's no reason not to use /r/, which (I must emphasize) does not exclusively mean a trill. It means a trill when you're being very precise; it means "whatever R-sound your language has" when you're not being so precise. Every English dictionary I know of that uses the IPA uses /r/; so do such esteemed phoneticians as Peter Ladefoged, John C. Wells, A.C. Gimson, and Daniel Jones in their work when it's clear from context that only English is under discussion. And dictionaries of other languages where alveolar trills are rare or dialectal, like French and German, also use /r/ to represent their r-sounds. There's nothing incorrect about it. Angr (talk) 18:05, 17 May 2013 (UTC)
- No, I am not new to phonetics, although I did not know the term rhotics, because I refer to them as Liquida (or Liquids in English). Anyway, if I were referring to allophones I would NOT have put them in brackets, rather in slashes. For anyone reading this, I specifically chose to use [] in order to provide a phonetic transcription. I wanted to emphasize the differences between languages. Basically the point I am making here is that the differences or worthy of attention and should be noted accordingly with a specific character, not a general character (/r/). I feel like I am repeating myself, so I will stop. Thanks for the tips above, although it came across as patronizing. At least we are definitely on the same wavelength. Your second paragraph is the main issue. In not wanting to favor British or American English, we have chosen to represent the sound with a character that represents a trill, used neither in England, nor in America. That is my gripe. Agentxp22 (talk) 15:31, 1 May 2013 (UTC)
- This sentence, *But in your very post you've accessed an important point that speaks to using r that doesn't rest on laziness or convention; which is more correct, ɻ or ɹ?*, does not make sense. By *rhotic* I assume you mean rhetoric? Unless I misunderstood your comment, you have made the same moot point (r is the most common symbol in traditional English textbooks and also is neutral) which I have just criticized. Whether or not to use ɻ or ɹ should indeed be disputed (although there are some standards for where to use them as well). My issue here is that this is a separate argument from [r] versus [ɻ]/[ɹ]. It should not even be an issue. Away with [r] because it is completely inaccurate for American and English speakers and lets move the issue to [ɻ]/[ɹ] in American English. Agentxp22 (talk) 11:55, 23 April 2013 (UTC)
- Between slashes, there are a whole host of inaccuracies if phonemes are supposed to be accurate representations of phonetic realizations. But in your very post you've accessed an important point that speaks to using r that doesn't rest on laziness or convention; which is more correct, ɻ or ɹ? Both are English pronunciations, but they're partially dialect-dependent. r, in addition to being the most common symbol used for the English rhotic in linguistic literature, is also neutral to either of these pronunciations. — Ƶ§œš¹ [ãːɱ ˈfɹ̠ˤʷɪ̃ə̃nlɪ] 14:03, 16 April 2013 (UTC)
- There is something incorrect about it. Besides being confusing for people of other languages and not standard IPA, it can be mistaken for the alveolar flap (ɾ), which is a rhotic that does exist in american English. And it's not because some dictionaries of some languages take it as correct, that it is correct. JMCF125 (discussion • contribs) 12:36, 18 May 2013 (UTC)
- Why is the r symbol here used for things that are not alveolar trills? If someone has studied the IPA, they will know that this is the wrong symbol. If they haven't, then they either won't know what many of the symbols represent, or they will learn an incorrect sound. Secondly, where are r-coloured vowels? I read an article and found a bizarre pronunciation for a word which was only clarified by finding out that Wikipedia doesn't actually adhere to the real IPA, but some weird simplified version.
- By the way, someone above mentioned the fact that there isn't a need to use r for a trill in English, well actually there are in fact plenty of dialects of English that have alveolar trills. Why not jut adhere to the real IPA and if someone wonders what the scary upside down r means, they can click on it to find out. 99.236.215.170 (talk) 10:14, 12 January 2014 (UTC)
- My problem with using [r] instead of [ɹ] is that it might make IPA transcriptions in other languages less clear. We English speakers already have a tendency to pronounce ⟨r⟩ in other languages as [ɹ], even though most of us probably know how to say [r]. It was not until I began studying phonetics that I learned that the vast majority of European languages use the trill. I think that using [r] for [ɹ] clouds the issue.
- (suoı̣ʇnqı̣ɹʇuoɔ · ʞlɐʇ) nɯnuı̣ɥԀ 22:20, 24 February 2014 (UTC)
- P.S. I believe that when a more accurate diacritic-free IPA symbol is available, it should be used. I favor using [ɐ] instead of [ʌ].
Hints for pronouncing /ə/
There is a discussion at Template talk:IPAc-en/Archive 1#Mouseover for 'ə' to come up with a better hint for pronouncing /ə/. The current example of "about" isn't ideal because some people may pronounce it with /æ/. Please join the conversation there if you have an opinion. -- Dr Greg talk 15:49, 25 April 2014 (UTC)
Hovertext for (j) hurts my American English brain: where on Earth is the 'yuh' sound in Lucas?
I came here from legume, which I had thought was pronounced leh-zhoom until I heard lae-goom recently (so I'm not sure what the range of pronunciation is at this point). The problem is that the hovertext for the (j) phoneme currently says "optional 'j' in 'Lucas'". Wat. I assume this sounds like an American English consonant y, but without context I don't know what it means by "'j' in 'Lucas'" or if that changes how it is pronounced in context. Do people pronounce it like Lyooh-kus? Looh-kyus? Does it get inserted or transplanted? I am completely stumped on what this is trying to say.
I also don't know where I'm supposed to ask about this b/c I can't find where the hovertext for IPA help comes from, though I'm tripping balls on Lunesta at the moment so for all I know I might be typing on the back of a goat (a goat's back makes for a bad keyboard but the goat does not seem to mind, probably just a friendly monkey massage pushing boundaries a bit too far but what can I do I'm a goat). This is where I ended up, so hopefully it's the right place. Anything that might provide a clue on how the hovertext for (j) is supposed to enlighten me (or else fix the hovertext) would be greatly appreciated. TricksterWolf (talk) 00:04, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- The definitions are found in {{H:IPA}}. I have modified it to show "optional /j/ in Lucas", thereby indicating that the "j" is not the letter 'j', but the IPA symbol /j/. This is not a perfect solution, but is at least less ambiguous. Perhaps "optional /j/ before 'u' in Lucas" would be better? −Woodstone (talk) 08:52, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, the "before 'u' in Lucas" is exactly what I needed. It still seems bizarre, though. I don't understand how to say "lyooh-kuhs" without sounding awkward, or why /(j)/ differs from /j/ such that a strange example is needed for the former. I suspect this is a non-English use searching for a comparable but rare example? Are /(j)/ and /j/ two different sounds, or is this happening because the idea is "to show an optional sound we have to find a comparable sound also in a situation where it is optional"? TricksterWolf (talk) 14:16, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- I must say that 'Lucas' is a very unusual example to pick for syllable-initial /lj/. I have never heard this pronunciation in British English, except possibly in a Welsh accent. I would pick something like 'lewd', 'leukemia' or 'Lurex', where /lj/ is the norm. RoachPeter (talk) 14:31, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- I've never heard "Lyucas", but I've heard trained (American) elocutionists say "Syusan" and "Syuperman", so I believe it occurs. I wonder if Alec Guinness had to be told not to say "Lyuke". (I've also heard an Englishman pronounce music as /muːzɪk/!)
- Perhaps it would be best to have the /j/ in legume represented by a more familiar example, such as stupid or dew, in which many speakers also drop the /j/? Or instead of an "optional /j/" in unsightly parentheses, why not offer two separate alternative pronunciations, /ˈlɛɡjuːm/ and (for barbarians) /lɛɡˈuːm/? (There is, after all, a shift of stress to the second syllable for those who drop the /j/.) J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 14:45, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
Legume is usually "LEG-yoom" (like "leg room" but with a "y" as in "yes") or luh-GYOOM. M-W Collegiate, AHD5, and OxfordDictionaries.com back me on that. By the way, the WP coverage on yod dropping is a good link to provide in this discussion. But the yod in "lute" or "suit" (which general American English drops) is not exactly the same thing as an optional j/y before uː (that is, /uː/ versus /juː/). In American English, phenylketonuria can end in either /-tənʊəriə/ or /-tənjʊəriə/, but the former is not "a yod-dropped version of the latter"—it is, in contrast, /uː/ instread of /juː/. There may be an etic spectrum that I am dichotomizing there, but emically, they are not "the same thing". Quercus solaris (talk) 18:36, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- Quercus solaris seems to be making a distinction without a difference. Why is /-tənʊəriə/ not a "yod-dropped version" of /-tənjʊəriə/? More to the point, is the distinction between /ˈlɛɡjuːm/ and /lɛɡˈuːm/ a case of yod-dropping, and if not, why not? I would expect people who say, /lɛɡˈuːm/ also to say /duː/ for dew and /tuːn/ for tune: i.e. I would expect /lɛɡˈuːm/ as part of a pattern of yod-dropping, not as merely a free-standing alternative to /ˈlɛɡjuːm/. I would be astonished to find that a speaker who says, e.g., /ˈnjuːtʃrəl/ and /tjuːmər/, also said /lɛɡˈuːm/. Is Quercus solaris arguing otherwise? J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 21:29, 19 June 2014 (UTC)
- Oh no, I agree with what you just said ("I would be astonished to find that a speaker who says, e.g., /ˈnjuːtʃrəl/ and /tjuːmər/, also said /lɛɡˈuːm/"), and also with "I would expect people who say, /lɛɡˈuːm/ also to say /duː/ for dew and /tuːn/ for tune". But even as a yod-dropping general-AmE speaker I find /ˈlɛɡuːm/ and /ˌləˈɡuːm/ nonstandard (they feel nonstandard). Although I could be wrong that the yod in "lute" or "suit" (when it exists, that is, for people who pronounce them that way) is different from the /-kiːtənʊəriə/-vs-/-kiːtənjʊəriə/, nevertheless I could swear as a yod-dropping general-AmE speaker that they "feel" different, and I believe I have evidence that they are not always the same, because even though my accent treats lute and loot both as /luːt/ (and similarly with many other examples), it does not treat legume as /ˈlɛɡuːm/ or /ˌləˈɡuːm/. Another example: although I have heard various Indian speakers of Indian English as a second language say /ˈmænuːskrɪpt/, in general American English it's /ˈmænjuːskrɪpt/ (despite that general AmE drops yods in lute and suit). Gen Am-E does not have yod in lute or suit but yet it does have a very deliberate, feels-like-a-consonant-not-a-vowel /j/ before /uː/ in certain words, including cute, puny, menu, volume, vacuum, and legume. My own suspicion about /ˈlɛɡuːm/ and /ˌləˈɡuːm/ (maybe right, maybe wrong) is that they are spelling pronunciations as opposed to dialectal variants. I could imagine someone who has read "legume" but seldom or never heard it not realizing that it belongs to the cute-puny-menu-volume-vacuum class (juː not uː). Quercus solaris (talk) 00:49, 20 June 2014 (UTC)
- Sorry to go on about this (I lack time and probably so do you all), but I just realized that my "not always the same" distinction above has something to with the distinction that the yod dropping coverage makes where it says "... Southern American English preserve the distinction in pairs like loot/lute and do/dew by using a diphthong /ɪu/ in words where RP has /juː/, thus [lut]/[lɪut], [du]/[dɪu], etc" The essence of it is something about a diphthong versus a consonant+vowel. The way I would put it off the top of my head is that there is some underlying reason why yod dropping happens only under certain conditions, and that to a gen AmE speaker, the [ɪ] can evaporate from [dɪu] to yield [du] (pardon the pun), but the [j] cannot evaporate from /ˈlɛɡjuːm/ to yield /ˈlɛɡuːm/ because that [j] is not "the same thing" as that [ɪ]. This is interesting and I wish I could explain it better, but it's got something to do with that. Quercus solaris (talk) 01:09, 20 June 2014 (UTC)
- Here is a very informative set of tables on [uː] vs. [juː]. It says that legume is always /ˈlɛɡjuːm/, but that may reflect RP (I haven't looked into the background of the site). I grew up in Southeastern Virginia and speak a variety of So. Am., so I say /ˈlɛɡjuːm/; but I live in New York City now, where I hear mostly Gen. Am., and I could swear that I most often hear /lɛˈɡuːm/ here.
- The passage Quercus solaris quotes,
- ... Southern American English preserve the distinction in pairs like loot/lute and do/dew by using a diphthong /ɪu/ in words where RP has /juː/, thus [lut]/[lɪut], [du]/[dɪu], etc.
- does not accord with my experience of So. Am. I say [dju:], not [dɪu], for dew, and I have never heard anybody say [dɪu] (except perhaps as a contraction of do you).
- I have never heard any American, Northern or Southern, say [lju:t] (or [lɪu:t]) for lute or [lju:k] (or [lɪu:k]) for Luke. I have heard American announcers and other trained (or affected) elecutionists say such things as [ˈsjuzʌn], [djuːd], and even [njuːn] (which I consider a plain error), but I know of no American accent in which those pronunciations are common and colloquial.
- At any rate, I am at best an informed amateur in this field, and I think any further analysis of the question, if it's to be anything more than an entertaining exchange of subjective anecdotes, will require expert knowledge, so I'm bowing out for now. J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 15:51, 20 June 2014 (UTC)
Accent mark with IPA transcription of words with only one syllable?
I did a quick check of the archives and didn't find anything about this: when writing out an IPA for a word with just one syllable, is the emphasis-mark ' still to be used? It looks like it is used on the WP:IPAE article page for such words, but the OED excludes it (presumably as superfluous and unnecessary, which it would seem it is). Perhaps there is no protocol... Should there be one? If none exists, I'd like to propose that Wikipedia follow the OED and deprecate the use of marks of emphasis with single-syllable words. Thoughts, anyone? KDS4444Talk 03:32, 23 July 2014 (UTC)
- While I am on the subject, the WP:IPAE page suggests that if there are two pronunciations of the same word, they should both be included and be separated by a comma. However, doing so within the IPAc-en template produces a "secondary emphasis" mark, not a genuine comma. So then how should this be done? (this is despite the fact that the Wikipedia IPA character drop down menu for editors contains a definite and distinct symbol for secondary emphasis which is not a comma-- so somewhere, a comma is getting "translated" by the IPA template to be the equivalent of the secondary emphasis symbol). KDS4444Talk 03:42, 23 July 2014 (UTC)
Vowel Length
The template doesn't appear to accommodate /ː/ or /./ to indicate length of vowels. For instance, "|ɑː|" is unsupported, as is "|ɑ|ː|". Shouldn't vowel length be part of our Wikipedia transcriptions? J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 18:42, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- I find that by copying /ɑː/ from the table and pasting it into my text I can put length in the template. Why doesn't typing /ɑː/ work? J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 18:57, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- Can you show us it not working? — Lfdder (talk) 19:01, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- When I try it here, it works: /ˈnɑːˌfʊk/. I don't know why it wouldn't work for me on Norfolk, Virginia. Maybe I was doing something else wrong. At any rate, I got it to work there by pasting, as I said above, so I guess there's no problem. Thanks for responding, and sorry to cause needless concern. J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 19:35, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- Is that how it's pronounced locally? You probably shouldn't use IPAc-en for it 'cause /ɑː/ corresponds to a different diaphoneme. — Lfdder (talk) 19:47, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- That is how it's pronounced, if I'm not getting my IPA wrong. The first vowel sounds more or less like the vowel in General American ball, as if the speaker were saying, "Nollfook", only the /l/ modifies the vowel without actually sounding as /l/ (which is common in Southeastern Am. Eng., even in words that actually are spelt with an /l/, such as Falmouth and Baldwin). The /ɑː/ in father is the closest I know how to come to that in IPA. I'm not knowledgeable about these templates--can you educate me a little? What other template should I use here? Or is there a different IPA symbol that would work in IPAc-en? J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 21:33, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- Is that how it's pronounced locally? You probably shouldn't use IPAc-en for it 'cause /ɑː/ corresponds to a different diaphoneme. — Lfdder (talk) 19:47, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- When I try it here, it works: /ˈnɑːˌfʊk/. I don't know why it wouldn't work for me on Norfolk, Virginia. Maybe I was doing something else wrong. At any rate, I got it to work there by pasting, as I said above, so I guess there's no problem. Thanks for responding, and sorry to cause needless concern. J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 19:35, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
- Can you show us it not working? — Lfdder (talk) 19:01, 12 March 2014 (UTC)
I take it you mean the vowel in doll. That's /ɒ/. Your dialect may not distinguish that from /ɑː/. Do you distinguish cot from caught? If not, the best vowel is probably /ɔː/, since that's the vowel when the ar is pronounced, and the vowel you suggested with "NAW". See what you think of my adjustment.
There's {{IPA-endia}} for rendering English dialects, if you're specifically trying to capture Southern English. We might want to link that to International Phonetic Alphabet chart for English dialects; currently it just links to the generic IPA table. — kwami (talk) 18:18, 25 April 2014 (UTC)
- Thanks for that help. /ɒ/ is indeed the sound I was trying to represent. I saw your adjustment to "Norfolk" before I read your remarks above, but now I've stuck /ɒ/ into the pronunciation of that place name.
- The Tidewater dialect does distinguish between cot and caught. I believe cot is /kat/, but I'm unsure how to write Tidewater caught in IPA, partly because I'm not a native speaker (I grew up there, but my mother tongue is South-Carolinian Piedmontese), and I don't remember how the word is pronounced in the various local accents.
- The {{IPA-endia}} template now redirects to {{IPA-all}}, so I haven't ventured to use it. J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 19:28, 26 April 2014 (UTC)
- Just to verify, they have the same vowel in father, bra, spa as in bother, cot, doll? — kwami (talk) 00:28, 27 April 2014 (UTC)
- I believe I would exclude cot from that list, I think spa has a different vowel from that of father and bra, and I don't think father rhymes with bother; but the harder I try to remember these pronunciations, the less certain I am. I'll have to refresh my memory next time I go home. (Which I realize is prohibited Original Research, but which I hope will be acceptable here on the talk page, at least in the absence of published data.) There is, in any case, quite a variety of accents or sub-dialects within the Tidewater dialect, depending on race, class, age, locality, and perhaps occupation (it's my impression, for example, that watermen speak a distinct sub-dialect). J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 14:51, 28 April 2014 (UTC)
- I say that all the vowels are the same except for doll. --Adeptzare3 (talk) 02:49, 27 July 2014 (UTC)
- We've accepted this kind of OR before. The problem is not so much accepting your honesty as making sure that we're not miscommunicating. — kwami (talk) 21:46, 28 April 2014 (UTC)
Semi-protected edit request on 20 August 2014
This edit request to Help:IPA for English has been answered. Set the |answered= or |ans= parameter to no to reactivate your request. |
103.21.166.13 (talk) 09:28, 20 August 2014 (UTC)
 Not done: as you have not requested a change.
Not done: as you have not requested a change.
If you want to suggest a change, please request this in the form "Please replace XXX with YYY" or "Please add ZZZ between PPP and QQQ". - Arjayay (talk) 09:44, 20 August 2014 (UTC)
Remove "ugh" from x
Could we remove "ugh" from the list of examples for the IPA character x? I have never heard of this word being pronounced this way. — Preceding unsigned comment added by 64.124.61.215 (talk) 19:10, 22 October 2014 (UTC)
- I've heard the sound, but I wouldn't write it as "ugh". The note mentions that it is often pronounced differently. Can you think of a better example? Dbfirs 13:31, 23 October 2014 (UTC)
- If /x/ is the voiceless, guttural sound in Sc. loch or Ger. ach, as I understand it to be, then I agree that ugh is not an example of it in any dialect of English that I'm aware of. Although I think most people reading ugh aloud would be inclined pronounce it like "ug" (because of the deplorable impulse to "speak as you spell"), I believe ugh is properly—that is to say, historically—an attempt to represent a grunt, "uh", with a highly fricative, perhaps voiced, h (which I don't know how to represent in IPA), which may approach, but doesn't equal, /x/—just one of many valiant efforts to represent in writing the inarticulate sounds we sometimes make, such as yuck (or yuch or yecch), tsk-tsk (or tutt-tutt or tch-tch), whew (or phew), and, my favorite, zzzz (to represent snoring). To my way of thinking, none of these is sufficiently standardized in speech (if it even is properly called speech) to be used as a general example of pronunciation. J. D. Crutchfield | Talk 19:09, 23 October 2014 (UTC)
Pronunciation of 'yeah'
I’m a young speaker of RP. I pronounce the word 'yeah' as [jɛː], which I assume would be [jɛə] or similar for an older RP speaker. In any case, it has the SQUARE vowel in a non-rhotic accent.
I’m a bit mystified about how you’re supposed to represent this pronunciation with the Wikipedia IPA system. Since the SQUARE vowel is rhotic, I don’t see a way to represent it for American speakers that wouldn't imply the presence of an ‘r’ where there is none. Is ‘yeah’ an anomaly in this regard? I can’t think of any other words with this property, but it seems impossible that it’s the only one to have this vowel. DavidPKendal (talk) 13:46, 8 May 2014 (UTC)
- Ironic, since it was originally an American expression.
- You're right about the rhoticity problem. Another example is er, which in rhotic American English actually is pronounced with an [r]! (The US equivalent is uh.) And then there are German names with ö/oe, such as Goebbels, which some Americans also pronounce with an [r]. That sounds weird, but anything else sounds weird too. But where would you need this? This key is for unified transcription, but yeah doesn't have a common pronunciation: In the US it has the TRAP vowel. If we want to indicate a regional pronunciation, we can always use the UK, US, or 'local' parameters. And [ɛə] can still be understood as [ɛ] plus [ə]. Interjections are often a bit odd – consider shhh!, when English words normally must have a vowel. Or uh-uh, since we don't normally have a glottal stop. In any case, no system is going to be perfect, and where it isn't, we can revert to a more precise verbal explanation. — kwami (talk) 20:12, 8 May 2014 (UTC)
- User:Dvortygirl has a diphthong of some kind in her pronunciation of it (US), which I’d tentatively transcribe as [jeæ].
- If it is the only word that has this vowel (I’ve asked a few people, we can’t think of any), then perhaps you’re correct that it can just be ignored. But since it’s technically an adverb, not only an interjection, it feels wrong that the transcription system can’t describe it. (Especially since it can describe e.g. ‘loir’, which seems to be about the only word with that vowel, distinct from ‘lawyer’.) DavidPKendal (talk) 10:14, 9 May 2014 (UTC)
- Yeah, definitely [jɛə] in northern England. Wiktionary's rhymes has only the obscure word kolea as a rhyme. Dbfirs 08:39, 27 October 2014 (UTC)
Correction needed
The article states in Dialect Variations section:
For most people from England, and for some New Yorkers, the /r/ in /ˈjɔrk/ is not pronounced and may be ignored; for most people from the United States, including some New Yorkers, the /j/ in /njuː/ is not pronounced and may be ignored.
This should be changed to something like:
For most people from England, and for some New Yorkers, the /r/ in /ˈjɔrk/ is pronounced; for most people from the United States, including some New Yorkers, the /j/ in /njuː/ is not pronounced and may be ignored. 86.174.4.72 (talk) 15:39, 19 March 2013 (UTC)
- But it isn't true that the /r/ in /ˈjɔrk/ is pronounced for most people from England. Angr (talk) 16:38, 19 March 2013 (UTC)
- I think the Scottish IP OP meant "For most people from Scotland ...". Dbfirs 08:48, 27 October 2014 (UTC)
My accent
What about observing the difference between the vowels of fAther [fAŕŕürr] and cAr [kÄr] ( pronunciations given using my own system. sorry!) ==99.190.210.221 (talk) 02:42, 27 July 2014 (UTC) What about ʉ in beautiful being an o sound? --Adeptzare3 (talk) 02:57, 27 July 2014 (UTC)
- Father and car both use
/ä:/[ä:] where I live (northern England), or/a:/[a:] in some areas. The OED has /ˈbjuːtᵻf(ᵿ)l/ for the British pronunciation of "beautiful", but I think my pronunciation is closer to/jʉ:/[jʉ:]. It's difficult to represent every regional variation. Is there a German version of English that we ought to record? Dbfirs 19:36, 23 October 2014 (UTC)- You're mistaking phonemic symbols with phonetic realizations of them. Both [ä:] and [aː] are regional phonetic realizations of the phoneme /ɑː/. The same applies to [jʉː], which is the predominant UK realization of /juː/. Peter238 (v̥ɪˑzɪʔ mɑˑɪ̯ tˢʰoˑk̚ pʰɛˑɪ̯d̥ʒ̊) 17:47, 27 October 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, you are correct. I've corrected my error above. Thanks for the link. I was puzzled by the distinction that Adeptzare3 was trying to make. Dbfirs 01:54, 28 October 2014 (UTC)
- No problem, but which link are you referring to? Peter238 (v̥ɪˑzɪʔ mɑˑɪ̯ tˢʰoˑk̚ pʰɛˑɪ̯d̥ʒ̊) 02:44, 28 October 2014 (UTC)
- Via your talk page.
Do you really talk like that?Dbfirs 07:46, 28 October 2014 (UTC)
- Via your talk page.
- No problem, but which link are you referring to? Peter238 (v̥ɪˑzɪʔ mɑˑɪ̯ tˢʰoˑk̚ pʰɛˑɪ̯d̥ʒ̊) 02:44, 28 October 2014 (UTC)
- Yes, you are correct. I've corrected my error above. Thanks for the link. I was puzzled by the distinction that Adeptzare3 was trying to make. Dbfirs 01:54, 28 October 2014 (UTC)
- You're mistaking phonemic symbols with phonetic realizations of them. Both [ä:] and [aː] are regional phonetic realizations of the phoneme /ɑː/. The same applies to [jʉː], which is the predominant UK realization of /juː/. Peter238 (v̥ɪˑzɪʔ mɑˑɪ̯ tˢʰoˑk̚ pʰɛˑɪ̯d̥ʒ̊) 17:47, 27 October 2014 (UTC)