Fisherman's Bastion
| Fisherman's Bastion (Hungarian: Halászbástya) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General information | |
| Type | Fortification |
| Architectural style | Romanesque Revival |
| Location | Budapest, Hungary |
| Coordinates | 47°30′10″N 19°02′04″E / 47.5027°N 19.0344°E |
| Construction started | 1844 |
| Completed | 1851 |
| Design and construction | |
| Architect(s) | Frigyes Schulek |
| Website | |
| www | |
| Official name | Budapest, including the Banks of the Danube, the Buda Castle Quarter and Andrássy Avenue |
| Criteria | Cultural: ii, iv |
| Reference | 400 |
| Inscription | 1987 (11th Session) |
| Extensions | 2002 |
| Area | 473.3 ha |
The Halászbástya (Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈhɒlaːzbaːʃcɒ]) or Fisherman's Bastion is one of the best known historical monuments in Budapest, located near the Buda Castle, in the Várkerület (Buda Castle District). Since 1987, it has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site as part of the Várkerület District (Buda Castle District).
It offers a unique panorama of Budapest from its Neo-Romanesque lookout terraces. The Fisherman's Bastion's main façade, parallel to the Danube, is approximately 140 metres long, of which the southern aisle is about 40 metres long, the north is 65 metres long, and the ornate central parapet is 35 metres long. Its seven high-pitched stone towers symbolise the seven chieftains of the Hungarians who founded Hungary in 895.[1]
The original walls were built in the 1700s, forming part of the walls of a castle. A consensus among historians is that in the Middle Ages this part of the castle wall was protected by the guild of fishermen (halász), who lived under the walls in the so-called Fishtown or Watertown.[2][3] The current structure was built between 1895 and 1902,[1] in Neo-Romanesque style, on the base of a stretch of the Buda Castle walls, by architect Frigyes Schulek,[2] who was also responsible for the restoration.
Origin of the name
[edit]The building was formerly known as the 'Fishermen's Bastion', presumably from the section of the Buda City Wall entrusted to the guild of fishermen, but more likely to the Danube side settlement, Fishtown (Halászváros) also called Watertown.[4][2] The fishermen found their merchandise already in the Middle Ages. Near the Matthias Church it was brought to the fish market. The guild of fishermen not only cared for selling fish, but in wars, its members defiantly defended the city walls.[2]
History
[edit]Origin of the Bastion
[edit]
The Castle Hill served as a lodging and fortification for the surrounding settlements at the time of the kings of Árpád dynasty. The development of the settlement on the Castle Hill for King Béla IV of Hungary became more prominent as a result of urban development, but as the administrative centre of the country, it became dominant in the era of King Matthias Corvinus. Its defences and bastions were fortified in the Middle Ages and during the Turkish occupation, but were repeatedly damaged. The Buda Castle Quarter itself has undergone a major transformation over time. From Matthias' bright, was prosperous the Buda Castle but following the Mohács Disaster during the Turkish rule destroyed, abolished and transformed many things and in the Castle as well. The Austrian forces retook the city from the Turks ruling from Vienna.[2]


It is based on the basement walls of today's Fisherman's Bastion, from the tower of the former Híradás (Telegraph) to the Jezsuita lépcső (Jesuit stairs), following the folded layout of the former bastion. This folded castle wall protection system breaks the bastion line so that each section can protect each other with a side fire. This section was built after the defeat of the Rákóczi's War of Independence by Austrian Command, according to what was then a modern military principle. The northern lobby tower of today's Fisherman's Bastion, was erected on the site of the circular tower.
The Fisherman's Bastion gradually deteriorated despite the renovation of some of its defences and the rebuilding of Austrians, which was recognised by the Austrian military leadership as a military fortress. The Fisherman's Bastion was spared neither by nature nor by the wars. Rain from the mountain loosened, washing away some of the foundations of the castle wall and the Bastion on the hillside. At the same time, in memory of recent wars, many of them had traces of good or bad restoration of the rocks of ball-dart gaps. At the same time, the area rises far above the city and was of decisive importance for the cityscape. However, the Austrian military leadership refused to spend more money on settling the area than would be required for a more prominent fortification, so they only performed the fortification. The fortress character of the Buda Castle was abolished in 1874 when the Ministry of War declared that the Castle as a fortress did not meet the requirements considered modern at that time. From now on, these repairs were also cancelled. While handling the matter in the capital, he had already dealt with the reassuring settlement of the area. Already in 1871 the Pest Committee on Beauty has launched a call for the development of regulatory plans for the newly merged capital. All three winners of the competition dealt with the issue of the settlement of the Castle Hill, and within this the Fisherman's Bastion was given special emphasis.
Renovation
[edit]
The Fisherman's Bastion is due to its architectural and urban planning tasks related to the restoration of Matthias Church.[2] In his summary of the architect Frigyes Schulek, which has done so much to protect and renew the Medieval temples, he has already recognised that the church was once lacking in money and with its peculiar and slightly depressed proportions from a military point of view (it was not possible for its tall, towering tower to be a reference), the lower soil level achieved by the excavation and the environment should be maintained. After the completion of the renewal of the Matthias Church, the question of restoring the environment and making it worthy of the temple became urgent. According to the original ideas, this area should have been organised for the millenary anniversary of the Hungarian state, when the first Hungarian King was crowned,[2] and although it was drafted in Schulek's time and submitted to the Public Works Council of the Capital, in 1894 it was consulted, the construction was eventually limited to 1899 and started in several instalments. In 1901 and 1902, the southern and northern stairs were completed, but the entire Fisherman's Bastion was completed after the construction was completed, 1905. On the 9th of October it was handed over to the capital.
Construction costs
[edit]The implementation of the Fisherman's Bastion and its original appropriation differed, mainly because of a change in the basic concept of the millennium celebration. The first budget appropriation for the construction of the Fisherman's Bastion was of 800,000 forints at that time,[5] of which 100,000 for the stairs, 200,000; for the corridors, 200,000; for the planned St Stephen's Hall. and 300,000 forints for the Seven chieftains halls. The latter idea was highlighted in the plan and elsewhere, on the Pest side of the City Park, at the end of what was then Sugár Road, in today's Heroes Square was realised according to the ideas of Millenium Monument not of Schulek, but of Albert Schickedanz and sculptor György Zala. In the meantime, the cost of another statue of St Stephen and the Millennium Monument has been deducted. In the end, total construction cost was of 1,165,000 forints;[5] of which the stairs and associated landscaping costs, 200,000 forints; were covered by the Metropolitan Public Works Council, and the rest were shared between the capital (685 and 1,000 forints) (280,000).
In WWII and onwards
[edit]
The Fisherman's Bastion was severely damaged during the sieges of World War II, but since it was one of the important landmarks of Budapest, it occupied a prominent place in the restoration priorities after the war. The restoration work was led by László Bors,[5] a state-appointed architect. The restoration was made more difficult by the fact that firefighters had to thoroughly inspect the area from almost a centimetre to an inch before the damage assessment and restoration plans could be completed. The first spectacular part of the process took over the years, the restoration of the Fisherman's Bastion after the World War, was completed in 1953.[5] The Buda Castle was separated from its other parts by a high wood block, which was not inspected, especially on today's Hilton Hotel. There was a constant patrol station to avoid accidents in the Rákosi era, but even after 1957 there were several places that had a real danger but also a political dimension, especially with regard to the control of incoming foreigners.
The hotel building behind the Fisherman's Bastion with its modern windows has been the subject of much controversy. Many saw the Schulek, a purely unified Matthias Church and Fisherman's Bastion, overturned, finding no reason to build a much larger unit of the hotel. Others saw the principles of the modern and the old coming together in what was then a new one in our country, in a close but new unity between the two buildings.
On 30 May 1995 the Castle District introduced an entry fee for the Fisherman's Bastion.[6] In November 2003, the building complex was handed over to the public.
This staircase leads to the dedicated hall of Hungarian faith and to the memories of Hungarian glory, inspired by the faith and memories of the great past in the artistically crafted stones of the Coronation Main Church of Budavár and the exalted convert of the Fisherman's Bastion. Hungarian, you are on this step remember: Our nation is made strong by the unity of faith and patriotism.[7]
— Text from a Fisherman's Bastion Construction stone

Architecture
[edit]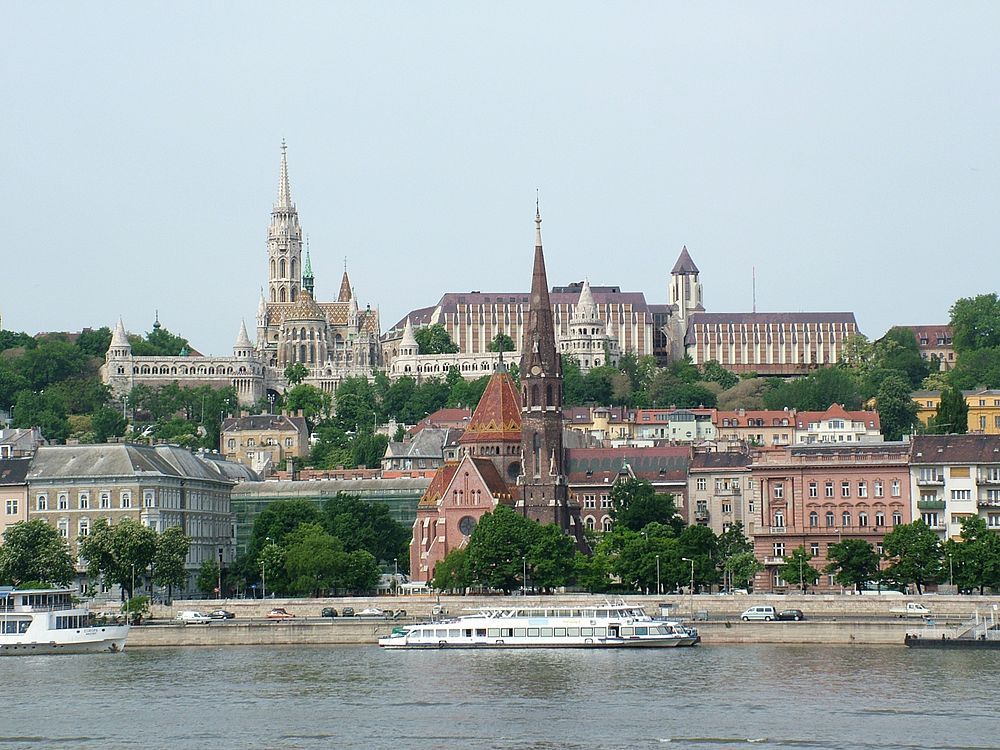
The Fisherman's Bastion, the masterwork of the architect Schulek, is made by three building units and several smaller units, according to Schulek's plans.
The stairs
[edit]
Schulek originally intended to build three-stage staircases reaching the Danube. Until the Fisherman's Bastion was built, in the place was a long stretch of narrow and dark Jesuit stairs, which reached the southern wall of the bastion.[8] It was possible to access the Jesuit stairs from the Fishtown, which was unsuitable for major, larger traffic. Schulek altered the gateway, widening the stairs to 8 metres in some places, and its lower gate was accentuated with a stylish gable, incorporating an original lionic relief from a Romanesque church excavated during the rampart work. Simple stairs made of granite stone are placed on a brick foundation, and only the so-called "stairs" used on the railings were used. It was decorated with truncated, pierced forms with Romanian style features. On the right and left of the staircase, a statues of warriors representing different weaponry of the 10th century Árpád age were placed guarding the gate (at the top of the stairs, under the arch).[2] Four of the seven leading statues on the main stairs were carved by Franz Graf Mikhail (Ferenc Mikula 1861–1926), a sculptor born in Debrecen and educated in Vienna. Also he made the pedestal, the lions and the reliefs of the statue of St. Stephen.
North–South bastions and corridors
[edit]
The north and south bastions, as well as the corridors form the bastion courtyard, are connected below by a staircase connecting the bastions on both sides, above, and on the level of the courtyards by a parapet. One of Schulek's greatest merits is that he transformed this area of the Castle Hill, which was essentially and originally for military purposes, into a peaceful promenade and a lookout object,[2] forming a significant architectural unit of the Castle Hill, with the Matthias Church behind it. Originally, the temple was closed to the battlements for military purposes and could not be built too high, for similar reasons. Schulek, alive to the government decree that unlocked the military objectives, opened the Fisherman's Bastion towards the Danube and Pest by encircling the church trunk and, with the two bastion towers, secured sufficient space for the building complex. He formed covered corridors along the edges of the former battlements, with an arch on an open row of columns, above which he opened an accessible courtyard with ornate buildings (bastions) with conical roofs. Currently, this area serves as a lookout. In the north, a multi-storey, overlapping tower rises, the main tower, below which are the statues of Elder and Álmos leaders, a lion holding a tassel shield, and a mythological creature with an open mouth, a dragon carved[5] in the same style as the two founding leaders. In the narrow area in front of the Matthias Church sanctuary, there is an ornate parapet that connects the two corridors of the Fisherman's Bastion, allowing a view from below. The arcade-like barrier wall is decorated with a balcony in the axis of the middle staircase.
The statue of St. Stephen and the southern yard
[edit]
The third large unit of the monument complex is the southern bastion court and its associated founder, it is initially made by the Stephen I of Hungary, the first king of Hungary.
Schulek's original idea was to have a covered dome around the statue of St. Stephen, but for budgetary reasons a free-standing statue was placed in the middle of the southern courtyard enclosed by corridors on three sides. He asked the sculptor Alajos Stróbl, to make the statue of Szent István; he started the project in 1896 and completed it in 1906.[9] After the statue was placed, its solemn was unveiled on 21 May 1906. On the morning of the inauguration, dr. Antal Nemes, the papal prelate and parish priest of Buda-Pest, then, after the mass, everyone withdrew around the statue and the veil fell under Alajos Stróbl's admonition.

The high priest toured the statue and consecrated it. The shroud was then returned. Three-quarters of government members once appeared: Sándor Wekerle, Count Albert Apponyi, Ignác Darányi, Count János Zichy and Lajos Jekelfalussy. Finally, at one o'clock, the King himself arrived at the bell-ringing and the official ceremony began.[10]
For the statue of Stróbl, Schulek designed the Neo-Romanesque foundation, and around it was an oval-shaped, pierced stone and parapet railing, placed in the geometric centre of the southern bastion court. The foundation structure is decorated with reliefs originally used for murals designed for the walls of the hall, which commemorate a prominent moment of King Stephen's reign: the coronation scene, the introduction of the legislative act, the depiction of Vienna and the Austria-Hungary dualism, while on the back and east we see a series of scenes symbolising the temple construction, where Stróbl depicted the aging Schulek master as the bearded, kneeling, model of King Stephen in the form of a master builder.

Above the relief is a richly decorated ledge, with gold medallions on its sides, agnus dei, evangelist badges and double-cross reliefs. The ledge of the upper member of the foundation is supported by six solid, ornate columns of beams on which the bronze statue of the king is placed.
Originally intended to replace the northern tower group, the Seven Leadership Sculpture Group, which was lifted out of the plan on the fly, was implemented with modifications and major changes to today's Heroes' Square (Hősök tere).
Statue of John Hunyadi
[edit]The John Hunyadi statue erected at the turn of the John Hunyadi road is also an integral part of the Fisherman's Bastion. Tóth István was commissioned to make the statue in 1899,[11] which was ceremoniously inaugurated in 1903. The Neo-Gothic limestone foundation was also built according to Schulek's plans, forming a harmonising unit with the rest of the Fisherman's Bastion. The foundation is closed by leaf-shaped ledges, the façade features the coat of arms of Hunyadi, and the other sides have a marble decoration. The Hero in armor, with a raven-helmet on his head, resting on a pall, heavily on his pallet, with the flags and other military badges of the defeated Turks at his feet, symbolising his victory.
Statue of St. George
[edit]Near the statue of John Hunyadi there is a bronze copy of the statue of St. George the Dragon from 1313 that can be found in the Prague Castle, that original statue was made by medieval Hungarian masters (the Kolozsvari Brothers).[2]
Statue of Julian and Gerhardus
[edit]At the initiative of László Bendefy, a statue of the Friar Julian and Gerhardus belonging to the Monument of the Fisherman's Bastion was erected, to which Bendefy based in the writings of Friar Julian offered their book "Biography and Criticism of the First Asiatic Hungarian Scholar" published in 1936.[12][13] Károly Antal made decades after the handover of the Fisherman's Bastion, in 1937, originally next to the Northwest Tower of the Fisherman's Bastion. A statue depicts friends of Julianus and Gerhardus who, on the orders of Andrew II of Hungary, they set out to search for the remaining of the Hungarians in the Ancient Homeland.

And having passed through the desert without any paths, on the thirty-seventh day they came to the land of the Moslems, called Vedas, in the city of Bundaz. There was no way they could get accommodation here, but had to stay in the fields in the rain and frost. In the daytime, a frater who was healthy, begged for food for himself and his sick companion, and received drinks and more, especially from the city governor, who, knowing that he was a Christian, was happy to give him alms, all the people in that region publicly say they should soon be Christian and belong to the Roman Church. From here they went to another city, where in the house of a Mohammedan who received them in the name of God, said the monk Gerhardus, was resting in the Lord and was buried there.
— About the Report of the First Way of Friar Julian of 1237[14]
A typical example of the style of the Római School and one of the outstanding works of the genre is the two-metre high bronze memorial. It was originally located next to the Northwest Tower of the Fisherman's Bastion, but in 1976, when the Hilton Hotel was being built, it was located in the horseshoe-shaped garden of the apse of the former Dominican church. Its pedestal is a limestone of Haraszti with the following inscription:

Dominican Friar Julian started his quest for Hungarians in his native country in 1235. After many adversities, his two companions returned. The third, Gerhardus, died before the goal was reached. Julian was alone by the Volga River in the Tatras of Baskiria, where he found the Eastern Hungarians. On his second journey in 1237 he could not reach the Eastern Hungarians because the Mongols swept them away. He is the first European traveller to bring serious news of the Mongols.[15]
Overview
[edit]Its seven towers represent the seven Magyar tribes that settled in the Carpathian Basin in 895. From the towers and the terrace there is a panoramic view over the Danube, the Margaret Island, the Gellért Hill and Pest (sometimes even further East).
A bronze statue of Stephen I of Hungary mounted on a horse, erected in 1906, can be seen between the Bastion and the Matthias Church. The pedestal was made by Alajos Stróbl, based on the plans of Frigyes Schulek, in Neo-Romanesque style, with episodes illustrating the King's life.
Near the bastion there is a lookout-terrace with numerous stairs and walking paths.
The building was featured as a Pit Stop on the sixth season of American TV show The Amazing Race.[16]
Gallery
[edit]-
Ruins of the 13th century St Michael Chapel.[2]
-
Stairs of the Fisherman's Bastion. Photo of 1963.
-
Fisherman's Bastion.
-
Bronze statue of Stephen I of Hungary.
-
Fisherman's Bastion at the Castle Hill of old Budapest (Buda). Part of the fortification, city centre in the background.
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Fisherman's Bastion- Home". Fisherman's Bastion Official website.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "History of Fisherman's Bastion". Fisherman's Bastion Official website.
- ^ "A Guide to Fisherman's Bastion, Budapest". Culture Trip. 14 March 2018. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ^ Fónagy Zoltán. "Fisherman's Bastion". Budapest History Museum website.
- ^ a b c d e "Így lett Budapest ékessége a Halászbástya (This is how Fisherman's Bastion became the ornament of Budapest)". Múlt Kor Magazine. 9 October 2015.
- ^ This was initially set at 50 forints.
- ^ "Lengyel Géza: A Halászbástya építője. Schulek Frigyes (Géza Lengyel : Fisherman's Bastion builder. Frigyes Schulek)". Online Newspaper Archive. Hungarian Online Library. MEK (in Hungarian). 1911.
- ^ "Halászbástya Budapest (Fisherman's Bastion Budapest)". Városom.hu (in Hungarian). Archived from the original on 2022-03-27. Retrieved 2019-09-02.
- ^ "Halászbástya (Fisherman's Bastion)". Kirandulastippek.hu (in Hungarian).
- ^ "St Stephen's Statue in the Castle", A Pesti Hirlap Vasárnapja [Pest News Sunday], Budapest, 23 August 1936 – via Antikvárium.hu
- ^ "János Hunyadi (John Hunyadi)". kozterkep.hu.
- ^ Bendefy, László; The Unknown Julian (1936). Biography and Criticism of the First Asiatic Hungarian Scholar (in Hungarian).
{{cite book}}:|website=ignored (help) - ^ "Mérnök elődök. László Bendefy. (Engineers of the Past. László Bendefy)- Biography". Vas County Engineering Chamber official website (in Hungarian). Archived from the original on 2017-07-29. Retrieved 2019-08-22.
- ^ Riccardus frater (c. 1200s). "A JULIANUS ELSŐ ÚTJÁRÓL KÉSZÜLT JELENTÉS 1237-BŐL (Report of the First Way of Julianus of 1237)". MEK-Hungarian Online Library website. Hungarian National Library (in Hungarian).
- ^ "MAGYAR KIRÁLYOK KÖNYVE (The book of the Hungarian Kings)" (in Hungarian).
- ^ ""One of You, I'm Gonna Break in Half - Leg 6 Part 2 " - January 4". Game Show Newsnet. Retrieved December 19, 2019.


![Ruins of the 13th century St Michael Chapel.[2]](/uploads/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d8/Buda_Dominican_Church.jpg/138px-Buda_Dominican_Church.jpg?auto=webp)




