Sea Islands
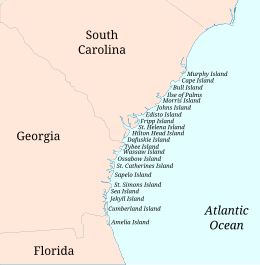 Map of the Sea islands | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Atlantic Ocean |
| Total islands | Over 100 |
| Administration | |
United States | |
The Sea Islands are a chain of over a hundred tidal and barrier islands on the Atlantic Ocean coast of the Southeastern United States, between the mouths of the Santee and St. Johns rivers along South Carolina, Georgia and Florida. The largest is Johns Island, South Carolina. Sapelo Island is home to the Gullah people. All of the islands are acutely threatened by sea level rise due to climate change.[1]
History
[edit]Settled by indigenous cultures thousands of years ago, the islands were selected by Spanish colonists as sites for founding of colonial missions. Historically the Spanish influenced the Guale and Mocama chiefdoms by establishing Christian missions in their major settlements, from St. Catherine's Island south to Fort George Island (at present-day Jacksonville, Florida).[2]
Both chiefdoms extended to the coastal areas on the mainland. The Mocama Province included territory to the St. Johns River in present-day Florida.[3] The mission system ended under pressure of repeated raids by English South Carolina colonists and Indian allies.[4] Spain ceded its territory of Florida to Great Britain in 1763.[5]
After 18th-century European-American settlement of Georgia and Florida, planters purchased and enslaved Africans for labor. Many were used to work the labor-intensive cotton, rice, and indigo plantations on the Sea Islands, which generated much of the wealth of the colony and state. The Sea Islands were known historically for the production of Sea Island cotton.[6] The enslaved workers developed the notable and distinct Gullah culture and language which has survived to contemporary times.[7]
During the American Civil War, the Union Navy and the Union Army soon occupied the islands. The white planter families had fled to other locations on the mainland, sometimes leaving behind their slaves. The slaves largely ran their own lives during this period. They had already created cohesive communities, because planter families often stayed on the mainland to avoid malaria and the isolation of the islands. Large numbers of slaves worked on the rice and indigo plantations, and had limited interaction with whites, which enabled them to develop their own distinct culture. During the war, the Union Army managed the plantations and assigned plots of land to slaves for farming.[8]
After President Abraham Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation became effective on January 1, 1863, more than 5,000 slaves on Union-occupied islands obtained their freedom.[9] After the war, although the freedmen hoped to be given land as compensation for having worked it for so many years in slavery, the federal government generally returned properties to the planters returning from their refuges or exile. Many of the freedmen stayed in the area, working on their former plantations as sharecroppers, tenant farmers or laborers as the system changed to free labor.[8]
The area was home to multiple plantations; in 1863 Fanny Kemble published Journal of a Residence on a Georgian Plantation in 1838–1839 about her experience on her husband's plantations in St. Simon's Island and Butler Island.[10]
After President Abraham Lincoln's Emancipation Proclamation became effective on January 1, 1863, more than 5,000 slaves on Union-occupied islands obtained their freedom.[11]
In 1893, a deadly major hurricane struck the Sea Islands.[6]
List
[edit]South Carolina
[edit]- Bay Point Island
- Cane Island
- Cat Island
- Coosaw Island
- Dataw Island
- Daufuskie Island
- Distant Island
- Fripp Island
- Gibbes Island
- Harbor Island
- Hilton Head Island
- Horse Island
- Hunting Island
- Lady's Island
- Morgan Island
- Parris Island
- Port Royal Island
- Pritchard's Island[12]
- St. Helena Island
- St. Phillips Island
- Spring Island
Georgia
[edit]- Tybee Island
- Little Tybee Island
- Cockspur Island
- Wilmington Island
- Talahi Island
- Whitemarsh Island
- Oatland Island
- Skidaway Island
- Isle of Hope
- Williamson Island
- Dutch Island
- Burnside Island
- Wassaw Island
- Ossabaw Island
- St. Catherine's Island
- Isle of Wight
- Hampton Island
Florida
[edit]- Amelia Island *Little Tiger Island
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Rising seas threaten the Gullah Geechee culture. Here's how they're fighting back". National Geographic Society. 27 July 2022. Archived from the original on 25 October 2022. Retrieved 25 October 2022.
- ^ "Mission Santa Catalina de Guale" Archived 2011-06-06 at the Wayback Machine, New Georgia Encyclopedia, 2008, accessed 13 May 2010
- ^ Charles M. Hudson; Carmen Chaves Tesser (1994). The Forgotten Centuries: Indians and Europeans in the American South, 1521-1704. University of Georgia Press. p. 280. ISBN 978-0-8203-1654-3.
- ^ McEwan, Bonnie G. (1993). The Spanish missions of La Florida. Gainesville : University Press of Florida. p. xx. ISBN 978-0-8130-1231-5.
- ^ Raab, James W. (2007). Spain, Britain and the American Revolution in Florida, 1763-1783. McFarland. pp. 15–16. ISBN 978-0-7864-3213-4.
- ^ a b Stephens, S. G. (1976). "The Origin of Sea Island Cotton". Agricultural History. 50 (2): 391–399. ISSN 0002-1482. JSTOR 3741338.
- ^ Joseph A. Opala (2006). "The Gullah: Rice, Slavery, and the Sierra Leone-American Connection". Yale University. Archived from the original on October 6, 2015.
- ^ a b Inscoe, John C. (2011). The Civil War in Georgia: A New Georgia Encyclopedia Companion. University of Georgia Press. pp. 177–178. ISBN 978-0-8203-4138-5.
- ^ William Klingaman, Abraham Lincoln and the Road to Emancipation, 1861-1865 (NY: Viking Press, 2001), p. 234
- ^ "Journal of a Residence on a Georgian Plantation in 1838–1839". Encyclopedia.com. Archived from the original on 2022-07-05. Retrieved 2022-07-05.
- ^ William Klingaman, Abraham Lincoln and the Road to Emancipation, 1861-1865 (NY: Viking Press, 2001), p. 234
- ^ "University of South Carolina Beaufort - Pritchards Island". www.uscb.edu. Archived from the original on 2 September 2006. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
Further reading
[edit]- Gibson, Count D. (1948). Sea Islands of Georgia—Their Geologic History. Athens, Georgia: University of Georgia Press. ISBN 9780820334943. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
External links
[edit]- Sea Islands
- Barrier islands of the United States
- East Coast islands of the United States
- Islands of Florida
- Islands of Georgia (U.S. state)
- Islands of South Carolina
- Southeastern United States
- South Carolina in the American Civil War
- Lists of islands of the United States
- Cultural regions of the United States


